Chilled Beam and Radiant Cooling Basics. Salt Lake City, UT ASHRAE Chapter December 2013 Nick Searle
|
|
|
- Darcy Maxwell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chilled Beam and Radiant Cooling Basics Salt Lake City, UT ASHRAE Chapter December 2013 Nick Searle
2 Contents Radiant Ceilings & Chilled Beam Basics Energy & Space Savings First and Lifecycle Costs Maintenance Application Suitability Design Considerations Application Example # Laboratories Case Study 250 S. Wacker, Chicago
3 Fan Energy Use in Buildings 4.5 Chiller/Compressor 7 Design Load KW/SF Supply & Return Fans Chilled Water Pump Condenser Water Pump Cooling Tower Fan Condenser Fan Energy Use KWh/SF Central VAV Central CAV Packaged CAV 0 Central VAV Central CAV Packaged CAV Energy Consumption Characteristics of Commercial Building HVAC Systems publication prepared for U.S. Department of Energy
4 Water = Efficient Transport 10 1 Ton of Cooling requires 550 CFM of air or ¾ diameter water pipe 4 GPM of water
5 Chilled Ceilings Chilled Ceilings Many buildings heated only PC s appearing on desks Restricted ceiling cavity
6 Chilled Ceilings Radiant Effect CW Supply 5962 F CW Return 6266 F 45% Radiant 55% Convective 76 F Dry Bulb 74 F radiant temperature (black bulb)
7 Chilled Ceilings Advantages Excellent thermal comfort Reduced space requirements Will fit into 6#8 cavity Self regulating Simple controls Low noise Low maintenance Design Issues Low cooling output 20 to 25 BTUH/ft 2 100% coverage 14 to 18 BTUH/ft 2 70% coverage High cost Separate air system required
8 Chilled Sails
9 Chilled Sails
10 Chilled Sails Advantages Good thermal comfort Reduced space requirements Freely suspended Self regulating Simple controls Low noise Low maintenance Design Issues Cooling output 40 to 50 BTUH/ft 2 Separate air system required High cost Cannot heat Need good acoustic treatment to avoid hard spaces Many connections Aesthetics?
11 Passive Chilled Beams Chilled Ceilings Passive Chilled Beams Increased cooling loads Equipment Occupancy Day#lighting Inadequate perimeter cooling
12 Passive Chilled Beams 1 Operation Principle Soffit Suspension rod Water coil Fabric skirt Perforated tile
13 Passive Chilled Beams 1 System Highlights Good thermal comfort Cooling capacity up to 40 BTUH/FT 2 floor space Up to 500 BTUH per LF of beam Reduced ductwork, riser and plant sizes Water transports most of sensible cooling Self regulating simple two position controls Low noise Low maintenance
14 Design Considerations Sensible cooling only Latent gains must be controlled by air system High free area perforated metal ceiling required 28% free area minimum Exposed beams (no ceiling) are an option Beams cannot be installed tight against slab Typically 40% of beam width required above beam Separate heating system must be installed Separate air system must be installed
15 Passive Chilled Beams 1 Airflow Pattern
16 Passive Chilled Beams 1 Recessed Type
17 Passive Chilled Beams 1 Exposed Type
18 Active Chilled Beams Chilled Ceilings Passive Chilled Beams Active Chilled Beams Higher space loads Higher occupant densities Combined ventilation/cooling preferred Integration into fiber tile ceilings required
19 Active Chilled Beam 1 Operation Principle Primary air nozzles Primary air plenum 1 Part Primary Air Suspended ceiling Heat exchanger 4 Parts Room Air
20 Heat Removal Ratio Airflow requirement reduced by 70% 70% of sensible heat removed by chilled beam water coil
21 Active Chilled Beam 1 Airflow Pattern
22 Active Chilled Beams 1 System Highlights Very high cooling capacity Up to 100 BTUH/FT 2 floor space Up to 1500 BTUH per LF Integrated cooling, ventilation and heating All services in the ceiling cavity Suitable for integration into all ceiling types Reduces ceiling costs compared to Passive Beams
23 Active Chilled Beams 1 System Highlights Significant space savings Smaller ductwork saves space in shafts, plant rooms and ceiling Can be installed tight up against the slab Reduced floor to floor heights Reduced construction costs on new buildings Low noise levels Low maintenance No moving or consumable parts
24 Energy Savings 1 Compared to VAV Source Technology Application % Saving* US Dept. of Energy Report (4/2001) Beams/Radiant Ceilings General 25#30 ASHRAE 2010 Technology Awards Passive Chilled Beams Call Center 41 ACEE Emerging Technologies Report (2009) Active Chilled Beams General 20 ASHRAE Journal 2007 Active Chilled Beams Laboratory 57 SmithGroup Active Chilled Beams Offices 24 *Compared to VAV Energy Consumption Characteristics of Commercial Building HVAC Systems publication prepared for U.S. Department of Energy
25 Active Chilled Beams 1 First Costs Office Building, Palo Alto, CA 80,000 ft 2 Thermostat in each office for beam design costs were in line with VAV * *HPAC Engineering Article European Technology Taking Hold in the U.S.: Chilled Beams, Peter Rumsey, PE, CEM, FASHRAE, FRMI
26 Active Chilled Beams 1 First Costs Office Building, Denver, CO 600,000 ft 2 design/build renovation Elimination of two air handlers per floor due to beams the chilledbeam system was equal to the VAV system * *HPAC Engineering Article European Technology Taking Hold in the U.S.: Chilled Beams, Peter Rumsey, PE, CEM, FASHRAE, FRMI, January 1 st 2010
27 Active Chilled Beams 1 Lifecycle Costs 100,000 ft 2 Office Building, Cincinnati, OH 15 year lifecycle study 15% Energy Savings Compared to VAV $0.79 versus $0.93 ft 2 22% reduction in mechanical installation costs $19.50 versus $25.00 per ft 2 Lifecycle costs analysis over 15 years Favored chilled beam system by 20% $32 ft 2 versus $40 ft 2 HIXSON ARCHITECTURAL INTERIORS Spring 2009
28 LEED Certification 1 LEED NC V3.0 Optimize Energy Performance # up to 48% (new) or 44% (existing) more efficient than ASHRAE 90.1 (EA Credit 1) # up to 19 points Increased Ventilation # 30% more outdoor air than ASHRAE 62 (IEQ Credit 2) # 1 point Controllability of Systems # individual temperature control (IEQ Credit 6.2) # 1 point Thermal Comfort # meet ASHRAE 55 (IEQ Credit 7.1) # 1 point (Minimum 40 points needed for certification out of 100 maximum)
29 Maintenance No moving parts No filter No condensate pumps No consumable parts Up to 4 year inspection & clean Easy maintenance access
30 Cleaning Access
31 Active Chilled Beams 1 Typical Installation
32 Active Chilled Beams 1 Typical Installation
33 Active Chilled Beams 1 Typical Installation
34 Concealed Active Beams
35 Bulkhead Active Chilled Beams
36 ACTIVE CHILLED BEAM DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
37 Building Suitability Building Characteristics that favor Active Chilled Beams Zones with moderate#high sensible load densities Where primary airflows would be significantly higher than needed for ventilation Sensible Heat Ratio s (SHR) of 0.8 and above Buildings most affected by space constraints Hi rises, existing buildings with induction systems Zones where the acoustical environment is a key design criterion Laboratories where sensible loads are driving airflows as opposed to air change rates Buildings seeking LEED or Green Globes certification
38 Building Suitability Characteristics that less favor Active Chilled Beams Buildings with operable windows or leaky construction Beams with drain pans could be considered Building pressurization control should be used Zones with relatively low sensible load densities Zones with relatively low sensible heat ratios and low ventilation air requirements Zones with high filtration requirements for the re# circulated room air Zone with high latent loads
39 APPLICATION EXAMPLE: LABORATORIES
40 Laboratory Design Issues Sensible heat gains of up to 70 BTUH/ft 2 Space ventilation requirements of 6 to 8 ACH Laboratories where chemicals and gases are present require 100% outdoor air Air systems require 15 to 20 ACH of outside air to satisfy sensible load
41 Cooling Load and ACH
42 Benefits of Active Beams in Labs Eliminated or reduced reheat Reheat can account for 20% or more HVAC energy costs Water more efficient transport medium Reduces fan energy costs Smaller space requirements System sized for 6 ACH instead of 15 ACH
43 Active Chilled Beam Design Cooling Load = 65 BTU/H ft 2 Ventilation Rate = 6 Air Changes VAV Solution = 15 Air Changes Chilled Beam Solution = 6 Air Changes Active Chilled Beam Solution = 6 x 6 Long, 130 CFM each
44 Reheat Reduction VAV System Minimum Airflow 6 ACH = 760 CFM Cooling Load 65 BTU/H ft 2 41,000 BTU/H Peak Maximum Airflow 1,860 CFM (15 ACH) Minimum Cooling without reheat 6 55 F 16,600 BTU/H Turndown without reheat 16,600/41,000 59% ACB System Minimum Airflow 6 ACH = 760 CFM Cooling Load 65 BTU/H ft 2 41,000 BTU/H Peak Maximum Airflow 760 CFM Minimum Cooling without reheat 6 65 F 8,300 BTU/H Turndown without reheat 8,300/41,000 80%
45 CASE STUDIES
46 250 South Wacker Chicago, IL
47 250 S. Wacker, Chicago 1Case Study 16#story tower 215,000 sq. ft. 1st floor retail 2 16th floor offices Separate HVAC systems for 1st and 16th floors Perimeter induction system with floor#mounted units serving 2 #15th floors Interior constant volume/ variable temperature system serving 2 15th floors
48 250 S. Wacker, Chicago Case Study Building Renovated with 1 100% glazing with E#glass (190 Btuh/Ln.ft. heat loss) Single duct cooling only VAV interior system Evaluated fan#powered VAV or active chilled beam perimeter system Seeking LEED certification
49 250 S. Wacker, Chicago Case Study Perimeter System Type Existing Induction System Proposed Fan#powered VAV System ** Proposed Active Chilled Beam System ** Design Cooling Load 262 tons (382 sq.ft./ton) 156 tons (641 sq.ft./ton) 156 tons (641 sq.ft./ton) Primary Airflow 25,600 cfm (0.5 cfm/sq.ft.) 86,270 cfm (1.7 cfm/sq.ft.) 15,880 cfm (0.3 cfm/sq.ft.) Fan Energy at Design Fan Energy at 70% of Design 64 kw 182 kw 22 kw 64 kw 116 kw 22 kw Pump Energy 28 kw 8 kw 12 kw Combined Fan & Pump Energy 92 kw 190 Design % 34 kw ** Required larger ductwork/risers ** Used existing ductwork/risers
50 250 S. Wacker, Chicago Case Study
51 S. Wacker, Chicago Case Study
52 QUESTIONS?
ENGINEERING BULLETIN. Overview of Chilled Beam Technology. Purpose. Summary. Theory
 Overview of Chilled Beam Technology Purpose Chilled beam technology is new to the United States but has been used in Europe since the 1950 s. Chilled beams can reduce energy costs, improve indoor air quality,
Overview of Chilled Beam Technology Purpose Chilled beam technology is new to the United States but has been used in Europe since the 1950 s. Chilled beams can reduce energy costs, improve indoor air quality,
IDL20e (2 way discharge) IDS60e (4 way discharge) Inffusers. UDI (vertical discharge) Frequently Asked Questions
 IDL20e (2 way discharge) IDS60e ( way discharge) Frequently Asked Questions UDI (vertical discharge) Inffusers INFFUSER FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS The following are frequently asked questions (FAQ s) on
IDL20e (2 way discharge) IDS60e ( way discharge) Frequently Asked Questions UDI (vertical discharge) Inffusers INFFUSER FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS The following are frequently asked questions (FAQ s) on
APPLICATION GUIDE BEAMS
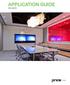 BEAMS There is an increasing need for energy efficient air conditioning systems as energy codes become more stringent. Chilled beam systems are one such alternate to traditional all air conditioning systems.
BEAMS There is an increasing need for energy efficient air conditioning systems as energy codes become more stringent. Chilled beam systems are one such alternate to traditional all air conditioning systems.
UFAD and Displacement Ventilation. Dan Int-Hout, FASHRAE Chief Engineer Krueger Richardson, Texas
 UFAD and Displacement Ventilation Dan Int-Hout, FASHRAE Chief Engineer Krueger Richardson, Texas UFAD and DV Systems, Objectives: Understand Differences between: Well Mixed, Partially Stratified and Fully
UFAD and Displacement Ventilation Dan Int-Hout, FASHRAE Chief Engineer Krueger Richardson, Texas UFAD and DV Systems, Objectives: Understand Differences between: Well Mixed, Partially Stratified and Fully
NOVEMBER 2012 THE EUROPEAN EXPERIENCE
 Radiant-cooling systems have progressed in the last few decades, garnering attention as a comfortable and energy- and material-efficient option. 1 Compared with air radiant-cooling hydronic systems use
Radiant-cooling systems have progressed in the last few decades, garnering attention as a comfortable and energy- and material-efficient option. 1 Compared with air radiant-cooling hydronic systems use
Inffusers. idl20 (2 WAY) ids60 (4 WAY)
 Inffusers idl20 (2 WAY) ids60 (4 WAY) built on innovation what is an inffuser? DADANCO s INFFUSERS are quite simply an induction diffuser that uses special nozzles located in the underside of the air plenum
Inffusers idl20 (2 WAY) ids60 (4 WAY) built on innovation what is an inffuser? DADANCO s INFFUSERS are quite simply an induction diffuser that uses special nozzles located in the underside of the air plenum
Chilled Beams in Labs Eliminating Reheat & Saving Energy on a Budget
 VanceFox.com 2006, American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc. (www.ashrae.org). Published in ASHRAE Journal Vol. 49, Jan. 2006. For personal use only. Additional reproduction,
VanceFox.com 2006, American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc. (www.ashrae.org). Published in ASHRAE Journal Vol. 49, Jan. 2006. For personal use only. Additional reproduction,
Optimizing the use of Chilled Beams for health and comfort GUNNAR SVENSSON
 Optimizing the use of Chilled Beams for health and comfort GUNNAR SVENSSON Lighting Sound Level Air Quality Cleaning Temperature Layout Maintenence Furniture Security How can we reduce the energy consumption?
Optimizing the use of Chilled Beams for health and comfort GUNNAR SVENSSON Lighting Sound Level Air Quality Cleaning Temperature Layout Maintenence Furniture Security How can we reduce the energy consumption?
Modular Active. Chilled. Beams
 Modular Active Chilled Beams How Twa MAC Beams Work Primary air (100% outside air) is dehumidified to between 50-57 F dew point and is used to: control the latent requirements of the space, provide fresh
Modular Active Chilled Beams How Twa MAC Beams Work Primary air (100% outside air) is dehumidified to between 50-57 F dew point and is used to: control the latent requirements of the space, provide fresh
Chilled beams. TRACE 700 incorporates two chilled beam strategies: passive and active.
 TRACE 700 incorporates two chilled beam strategies: passive and active. Passive chilled beams consist of a fin-and-tube cooling coil, contained in a housing (or casing), suspended from the ceiling. Chilled
TRACE 700 incorporates two chilled beam strategies: passive and active. Passive chilled beams consist of a fin-and-tube cooling coil, contained in a housing (or casing), suspended from the ceiling. Chilled
FAST AND ROBUST BUILDING SIMULATION SOFTWARE. Chilled Beam Performance: 1 Shelly Street, Sydney
 FAST AND ROBUST BUILDING SIMULATION SOFTWARE Chilled Beam Performance: 1 Shelly Street, Sydney 3D Model Creation 1 Shelley Street, Sydney 3D Model Creation 1 Shelley Street, Sydney Daylight Analysis 1
FAST AND ROBUST BUILDING SIMULATION SOFTWARE Chilled Beam Performance: 1 Shelly Street, Sydney 3D Model Creation 1 Shelley Street, Sydney 3D Model Creation 1 Shelley Street, Sydney Daylight Analysis 1
State of the art building simulation software... Frenger Radiant chilled beam performance at 1 Shelly St - Sydney
 Frenger Radiant chilled beam performance at 3D Model Creation Daylight Analysis Comparison of the performance of various HVAC systems at 1 Shelly St, Sydney VAV fancoil Active chilled beam Passive chilled
Frenger Radiant chilled beam performance at 3D Model Creation Daylight Analysis Comparison of the performance of various HVAC systems at 1 Shelly St, Sydney VAV fancoil Active chilled beam Passive chilled
Chilled Beams. Getting a Warmer Reception
 Chilled Beams Getting a Warmer Reception Gain an understanding of how chilled-beam technology works, the difference between active/passive chilled beams and potential applications for its use. B y G r
Chilled Beams Getting a Warmer Reception Gain an understanding of how chilled-beam technology works, the difference between active/passive chilled beams and potential applications for its use. B y G r
NEW AR-L AR-C AND HIGH-CAPACITY LINEAR COOLING PANELS. Higher energy efficiency. Increased thermal comfort
 NEW AR-C AND HIGH-CAPACITY LINEAR COOLING PANELS Higher energy efficiency Increased thermal comfort Higher capacity than standard radiant ceilings Significant space savings Reduced new construction costs
NEW AR-C AND HIGH-CAPACITY LINEAR COOLING PANELS Higher energy efficiency Increased thermal comfort Higher capacity than standard radiant ceilings Significant space savings Reduced new construction costs
Active Chilled Beams. Technical Data Bulkhead-Mounted Concealed Model With Horizontal Coil and Auxiliary Drain Pan
 Active Chilled Beams ACB10 Bulkhead-Mounted Concealed (Horizontal discharge) Technical Data Bulkhead-Mounted Concealed Model With Horizontal and Auxiliary Drain Pan APPLICATION CONSIDERATIONS The general
Active Chilled Beams ACB10 Bulkhead-Mounted Concealed (Horizontal discharge) Technical Data Bulkhead-Mounted Concealed Model With Horizontal and Auxiliary Drain Pan APPLICATION CONSIDERATIONS The general
Active & Passive Beams
 Active & Passive Beams www.price-hvac.com Active & Passive Beams Introduction Beam systems are an alternative to traditional all-air conditioning systems. Beams use water to move energy through a building
Active & Passive Beams www.price-hvac.com Active & Passive Beams Introduction Beam systems are an alternative to traditional all-air conditioning systems. Beams use water to move energy through a building
DADANCO Technical Paper
 DADANCO Technical Paper 260 North Elm Street Westfield, MA 01085 Phone: (413) 564-5657 Fax: (413) 568-2969 March 2013 CLASSROOM SOLUTION USING ACTIVE CHILLED BEAMS (Note: This technical paper assumes the
DADANCO Technical Paper 260 North Elm Street Westfield, MA 01085 Phone: (413) 564-5657 Fax: (413) 568-2969 March 2013 CLASSROOM SOLUTION USING ACTIVE CHILLED BEAMS (Note: This technical paper assumes the
7. MECHANICAL SYSTEM DESIGN
 7. MECHANICAL SYSTEM DESIGN The second primary topic of this thesis is to investigate the application of a dedicated outdoor air system (DOAS) to the SLCC. The stated goals for this thesis of improved
7. MECHANICAL SYSTEM DESIGN The second primary topic of this thesis is to investigate the application of a dedicated outdoor air system (DOAS) to the SLCC. The stated goals for this thesis of improved
Displacement Ventilation
 Displacement Ventilation Displacement Ventilation Displacement Ventilation vs. Dilution Ventilation Characteristics Design Considerations Layout and Selection Product Overview Casino Case Study Dilution
Displacement Ventilation Displacement Ventilation Displacement Ventilation vs. Dilution Ventilation Characteristics Design Considerations Layout and Selection Product Overview Casino Case Study Dilution
VH Series B ENVIRO-STAC Vertical Hi-Rise Fan Coil Unit with Enhanced Humidity Control
 VH Series B ENVIRO-STAC Vertical Hi-Rise Fan Unit with Enhanced Humidity Control Motorized Bypass Damper Temperature and Humidity Controller Reheat Control Elastomeric Foam Insulation High Efficiency,
VH Series B ENVIRO-STAC Vertical Hi-Rise Fan Unit with Enhanced Humidity Control Motorized Bypass Damper Temperature and Humidity Controller Reheat Control Elastomeric Foam Insulation High Efficiency,
HVAC 101. H V A C S y s t e m s
 H V A C 1 0 1 S y s t e m s Introduction & Overview Should you care? Mechanical System Types Components & operation Popular Application Key Issues and Design Considerations System Comparisons First Cost
H V A C 1 0 1 S y s t e m s Introduction & Overview Should you care? Mechanical System Types Components & operation Popular Application Key Issues and Design Considerations System Comparisons First Cost
HAP e-help. Modeling Induction Beams in HAP v4.8 QB TIP 001
 This HAP e-help provides a high-level overview of induction beams, how they work and how to model them in HAP 4.8 (and later versions). The first half of the article explains how induction beams work.
This HAP e-help provides a high-level overview of induction beams, how they work and how to model them in HAP 4.8 (and later versions). The first half of the article explains how induction beams work.
1080 Marina Village Parkway, Suite 501 Alameda, CA (510) Fax (510) HVAC DESIGN INTENT
 Taylor Engineering 1080 Marina Village Parkway, Suite 501 Alameda, CA 94501-1142 (510) 749-9135 Fax (510) 749-9136 LLC HVAC DESIGN INTENT PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 Overview A. The project consists of a 3-story
Taylor Engineering 1080 Marina Village Parkway, Suite 501 Alameda, CA 94501-1142 (510) 749-9135 Fax (510) 749-9136 LLC HVAC DESIGN INTENT PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 Overview A. The project consists of a 3-story
Standards and Guidelines. Presented by: Aric Murray December 12, 2014
 TDSHS Ventilation Standards and Guidelines Presented by: Aric Murray December 12, 2014 Agenda 1. What are the TDSHS ventilation 1. What are the TDSHS ventilation requirements? 2. Pressure relationships.
TDSHS Ventilation Standards and Guidelines Presented by: Aric Murray December 12, 2014 Agenda 1. What are the TDSHS ventilation 1. What are the TDSHS ventilation requirements? 2. Pressure relationships.
PRODUCTS TAO TAO PRODUCT: ADVANCING THE SCIENCE OF AIR DISTRIBUTION. temperature ambient optimizer. Redefine your comfort zone.
 A I R D I S T R I B U T I O N PRODUCTS PRODUCT: TAO TAO temperature ambient optimizer F O C U S 04 ADVANCING THE SCIENCE OF AIR DISTRIBUTION Redefine your comfort zone. www.titus-hvac.com Rethink what
A I R D I S T R I B U T I O N PRODUCTS PRODUCT: TAO TAO temperature ambient optimizer F O C U S 04 ADVANCING THE SCIENCE OF AIR DISTRIBUTION Redefine your comfort zone. www.titus-hvac.com Rethink what
HVAC DISTRIBUTION and DELIVERY SYSTEMS
 HVAC DISTRIBUTION and DELIVERY SYSTEMS (Part 1) Ball State Architecture ENVIRONMENTAL SYSTEMS 2 Grondzik 1 REMINDER HVAC = Heating, Ventilating, Air-Conditioning The AC part of HVAC implies a system that
HVAC DISTRIBUTION and DELIVERY SYSTEMS (Part 1) Ball State Architecture ENVIRONMENTAL SYSTEMS 2 Grondzik 1 REMINDER HVAC = Heating, Ventilating, Air-Conditioning The AC part of HVAC implies a system that
Technical Assignment 3
 0 David H. Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research Senior Capstone Mechanical Option Technical Assignment 3 Mechanical Systems and Existing Conditions Report David H. Koch Institute for Integrative
0 David H. Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research Senior Capstone Mechanical Option Technical Assignment 3 Mechanical Systems and Existing Conditions Report David H. Koch Institute for Integrative
Don t Turn Active Beams Into Expensive Diffusers
 This article was published in ASHRAE Journal, April 2012. Copyright 2012 American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc. Posted at www.ashrae.org. This article may not be
This article was published in ASHRAE Journal, April 2012. Copyright 2012 American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc. Posted at www.ashrae.org. This article may not be
CARRIER edesign SUITE NEWS. Modeling 100% OA Constant Volume Air Systems. Volume 6, Issue 1. Page 1 Modeling 100% OA Constant Volume Air Systems
 Volume 6, Issue 1 CARRIER edesign SUITE NEWS Modeling 100% OA Constant Volume Air Systems This article provides an overview of how to model a stand-alone constant air volume (CAV) 100% OA system in HAP.
Volume 6, Issue 1 CARRIER edesign SUITE NEWS Modeling 100% OA Constant Volume Air Systems This article provides an overview of how to model a stand-alone constant air volume (CAV) 100% OA system in HAP.
CARRIER edesign SUITE NEWS. Interpreting High (Low) Peak Design Airflow Sizing Results for HVAC. Equipment Selection.
 Volume 5, Issue 1 CARRIER edesign SUITE NEWS Interpreting High (Low) Peak Design Airflow Sizing Results for HVAC Equipment Selection A design challenge sometimes occurs when computing design loads using
Volume 5, Issue 1 CARRIER edesign SUITE NEWS Interpreting High (Low) Peak Design Airflow Sizing Results for HVAC Equipment Selection A design challenge sometimes occurs when computing design loads using
4-Pipe VAV vs. Active Chilled Beams for Labs
 Steven T. Taylor 4-Pipe VAV vs. Active Chilled Beams for Labs BY STEVEN T. TAYLOR, P.E., FELLOW ASHRAE Variable air volume (VAV) laboratory HVAC systems, including VAV fume hoods, are now standard practice
Steven T. Taylor 4-Pipe VAV vs. Active Chilled Beams for Labs BY STEVEN T. TAYLOR, P.E., FELLOW ASHRAE Variable air volume (VAV) laboratory HVAC systems, including VAV fume hoods, are now standard practice
Introduction to HVAC. American Standard Inc Air Conditioning Clinic TRG-TRC018-EN
 Introduction to HVAC Agenda Psychrometrics Human Comfort Heat Transfer Refrigeration Cycle HVAC Terminology HVAC Systems Introduction to HVAC Psychrometrics 2000 TRG-TRC002-EN Properties of Air Dry-bulb
Introduction to HVAC Agenda Psychrometrics Human Comfort Heat Transfer Refrigeration Cycle HVAC Terminology HVAC Systems Introduction to HVAC Psychrometrics 2000 TRG-TRC002-EN Properties of Air Dry-bulb
KLIMA Active Chilled Beams
 KLIMA 2 600 Active Chilled Beams Index Subject Page Index 1 Introduction 2 General description 3-4 Product features 5-6 Dimensions 7 Performance data 8-11 Section example Guide specifications 13 1 Introduction
KLIMA 2 600 Active Chilled Beams Index Subject Page Index 1 Introduction 2 General description 3-4 Product features 5-6 Dimensions 7 Performance data 8-11 Section example Guide specifications 13 1 Introduction
Selected Laboratory Energy Efficiency Measures
 Selected Laboratory Energy Efficiency Measures These are some of the most effective energy efficiency measures for laboratories 1. Reduce (optimize) air changes per hour in lab space 2. Design to the proper
Selected Laboratory Energy Efficiency Measures These are some of the most effective energy efficiency measures for laboratories 1. Reduce (optimize) air changes per hour in lab space 2. Design to the proper
BALANCING ENERGY EFFICIENCY & INDOOR THERMAL COMFORT
 BALANCING ENERGY EFFICIENCY & INDOOR THERMAL COMFORT Ashak Nathwani AM Adjunct Senior Lecturer ashak.nathwani@sydney.edu.au PRESENTATION THREE SESSIONS This presentation will be in three parts addressing
BALANCING ENERGY EFFICIENCY & INDOOR THERMAL COMFORT Ashak Nathwani AM Adjunct Senior Lecturer ashak.nathwani@sydney.edu.au PRESENTATION THREE SESSIONS This presentation will be in three parts addressing
Dehumidification: Energy Efficiency Comparisons
 Fourth Annual Energy Management Workshop Cocoa, Florida February 10-11, 2003 Dehumidification: Energy Efficiency Comparisons Michael K. West, Ph.D., P.E. Building Systems Scientist Advantek Consulting,
Fourth Annual Energy Management Workshop Cocoa, Florida February 10-11, 2003 Dehumidification: Energy Efficiency Comparisons Michael K. West, Ph.D., P.E. Building Systems Scientist Advantek Consulting,
Energy Savings Potential of Passive Chilled Beam System as a Retrofit Option for Commercial Buildings in Different Climates
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International High Performance Buildings Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2014 Energy Savings Potential of Passive Chilled Beam System as a Retrofit Option for
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International High Performance Buildings Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2014 Energy Savings Potential of Passive Chilled Beam System as a Retrofit Option for
Active Chilled Beams. Technical Data Concealed Ceiling Mounted Model With Vertical Coil and Integral Drain Pan
 ACB35 Concealed Ceiling-Mounted With Vertical and Integral Drain Pan (Vertical down discharge) Technical Data Concealed Ceiling Mounted Model With Vertical and Integral Drain Pan Active Chilled Beams APPLICATION
ACB35 Concealed Ceiling-Mounted With Vertical and Integral Drain Pan (Vertical down discharge) Technical Data Concealed Ceiling Mounted Model With Vertical and Integral Drain Pan Active Chilled Beams APPLICATION
ASHRAE JOURNAL ON REHEAT
 Page: 1 of 7 ASHRAE JOURNAL ON REHEAT Dan Int-Hout Chief Engineer Page: 2 of 7 Overhead Heating: A lost art. March 2007 ASHRAE Journal Article Dan Int-Hout Chief Engineer, Krueger VAV terminals provide
Page: 1 of 7 ASHRAE JOURNAL ON REHEAT Dan Int-Hout Chief Engineer Page: 2 of 7 Overhead Heating: A lost art. March 2007 ASHRAE Journal Article Dan Int-Hout Chief Engineer, Krueger VAV terminals provide
Halton CPT Passive Chilled Beam
 Passive Chilled Beam Ceiling-mounted passive chilled beam Installation above an open grid or perforated ceiling Quiet operation No moving parts Well suited for spaces with high cooling loads, low humidity
Passive Chilled Beam Ceiling-mounted passive chilled beam Installation above an open grid or perforated ceiling Quiet operation No moving parts Well suited for spaces with high cooling loads, low humidity
Product Data. Features/Benefits. 36CBAC,AE,AF,AH,AQ,AN, PB,PD,PS Series Active and Passive Chilled Beams. 11 to 190 cfm
 Product Data 36CBAC,AE,AF,AH,AQ,AN, PB,PD,PS Series Active and Passive Chilled Beams 11 to 190 cfm 36CBAC A36-449.eps Chilled beam units offer: An increase in total airflow Sensible cooling and heating
Product Data 36CBAC,AE,AF,AH,AQ,AN, PB,PD,PS Series Active and Passive Chilled Beams 11 to 190 cfm 36CBAC A36-449.eps Chilled beam units offer: An increase in total airflow Sensible cooling and heating
Single Zone System. One duct system Used mostly in small buildings Forced air system All spaces controlled by a single thermostat Single air return
 Single Zone System One duct system Used mostly in small buildings Forced air system All spaces controlled by a single thermostat Single air return Multi Zone System Used in small to medium sized buildings
Single Zone System One duct system Used mostly in small buildings Forced air system All spaces controlled by a single thermostat Single air return Multi Zone System Used in small to medium sized buildings
The new ASHRAE-REHVA Active and Passive Beam Application Design Guide
 Swegon Air Academy Seminar. Tallinn. 2015 December 3 The new ASHRAE-REHVA Active and Passive Beam Application Design Guide Carlos Lisboa carlos.lisboa@blcnavitas.pt Office +351 214 415 546 Cell +351 919
Swegon Air Academy Seminar. Tallinn. 2015 December 3 The new ASHRAE-REHVA Active and Passive Beam Application Design Guide Carlos Lisboa carlos.lisboa@blcnavitas.pt Office +351 214 415 546 Cell +351 919
Design Considerations For Dedicated OA Systems BY HUGH CROWTHER, P.ENG, MEMBER ASHRAE; YI TENG MA, ASSOCIATE MEMBER ASHRAE
 ASHRAE www.ashrae.org. Used with permission from ASHRAE Journal. This article may not be copied nor distributed in either paper or digital form without ASHRAE s permission. For more information about ASHRAE,
ASHRAE www.ashrae.org. Used with permission from ASHRAE Journal. This article may not be copied nor distributed in either paper or digital form without ASHRAE s permission. For more information about ASHRAE,
Chilled Ceilings / Beams Working Principles & Applications
 5 th International Conference on Energy Sustainable Energy Polices and Technologies 15-17 October 2014 Chilled Ceilings / Beams Working Principles & Applications Francis W H Yik ATAL Building Services
5 th International Conference on Energy Sustainable Energy Polices and Technologies 15-17 October 2014 Chilled Ceilings / Beams Working Principles & Applications Francis W H Yik ATAL Building Services
Dehumidifying with Dedicated Outdoor Air
 Dehumidifying with Dedicated Outdoor Air System Configurations Figure 71. Configurations for dedicated outdoor-air systems A dedicated outdoor-air handler separately filters, cools, dehumidifies, heats,
Dehumidifying with Dedicated Outdoor Air System Configurations Figure 71. Configurations for dedicated outdoor-air systems A dedicated outdoor-air handler separately filters, cools, dehumidifies, heats,
97.501B. Prepared by: (415) Sponsored By: Final Report. Author: Presented at: ASHRAE. Meeting SF Me!
 97.501B Prepared by: Proctor Engineering Group, Ltd. San Rafael, CA 94901 (415) 451-24800 Monitored In-Situ Performance of Residential Air-Co onditioning Systems Sponsored By: Arizona Public Service Company
97.501B Prepared by: Proctor Engineering Group, Ltd. San Rafael, CA 94901 (415) 451-24800 Monitored In-Situ Performance of Residential Air-Co onditioning Systems Sponsored By: Arizona Public Service Company
Engineering Guide VAV Diffusers. Please refer to the Price Engineer s HVAC Handbook for more information on VAV Diffusers.
 VAV Diffusers lease refer to the rice Engineer s HVAC Handbook for more information on VAV Diffusers. Diffuser Types Ceiling Diffusers Conventional air distribution systems typically group several rooms
VAV Diffusers lease refer to the rice Engineer s HVAC Handbook for more information on VAV Diffusers. Diffuser Types Ceiling Diffusers Conventional air distribution systems typically group several rooms
Temperature Control and Zoning of UFAD Systems
 Temperature Control and Zoning of UFAD Systems Presented by TROX USA Raised access flooring systems have become a very popular conduit for the delivery of power, voice and data services, as their accessibility
Temperature Control and Zoning of UFAD Systems Presented by TROX USA Raised access flooring systems have become a very popular conduit for the delivery of power, voice and data services, as their accessibility
Case Study: Furman University Charles H. Townes Center for Science. Michael K. Mantai, PE, CCP President System WorCx
 Case Study: Furman University Charles H. Townes Center for Science Michael K. Mantai, PE, CCP President System WorCx AIA Quality Assurance Learning Objectives 1. Case study example of Chilled Beam technology
Case Study: Furman University Charles H. Townes Center for Science Michael K. Mantai, PE, CCP President System WorCx AIA Quality Assurance Learning Objectives 1. Case study example of Chilled Beam technology
4. OVERVIEW OF MECHANICAL SYSTEM
 4. OVERVIEW OF MECHANICAL SYSTEM The 87,000 SF SLCC is served by six (6) Trane M-Series Climate Changer Air Handing Units (AHUs). Each unit serves a distinct zone within the facility that is unique in
4. OVERVIEW OF MECHANICAL SYSTEM The 87,000 SF SLCC is served by six (6) Trane M-Series Climate Changer Air Handing Units (AHUs). Each unit serves a distinct zone within the facility that is unique in
ELECTRICAL Seminar. B A L A Consulting Engineers, Inc. Edward J. Lynch, PE Vice President, Electrical Department Manager.
 B A L A Consulting Engineers, Inc. PECO Line 13.2kV Incoming Service No. 1 Utility/Generator Medium Voltage Switchgear PECO Line 13.2kV Incoming Service No. 2 Unit Substation ELECTRICAL Seminar HVAC Equip.
B A L A Consulting Engineers, Inc. PECO Line 13.2kV Incoming Service No. 1 Utility/Generator Medium Voltage Switchgear PECO Line 13.2kV Incoming Service No. 2 Unit Substation ELECTRICAL Seminar HVAC Equip.
Radiant Exchange in Stratified Environments: Considerations and Challenges for Hourly Energy Simulation of UFAD, DV, and Radiant Cooling Systems
 Radiant Exchange in Stratified Environments: Considerations and Challenges for Hourly Energy Simulation of UFAD, DV, and Radiant Cooling Systems CBE Timothy Moore CENTER FOR THE BUILT ENVIRONMENT SimBuild
Radiant Exchange in Stratified Environments: Considerations and Challenges for Hourly Energy Simulation of UFAD, DV, and Radiant Cooling Systems CBE Timothy Moore CENTER FOR THE BUILT ENVIRONMENT SimBuild
Ball State Architecture ENVIRONMENTAL SYSTEMS 2 Grondzik 1. Contextual Reminder
 HVAC DISTRIBUTION and DELIVERY SYSTEMS (Part 2) Ball State Architecture ENVIRONMENTAL SYSTEMS 2 Grondzik 1 Contextual Reminder All-air systems Single zone Terminal reheat Multi-zone Dual-duct VAV Combinations
HVAC DISTRIBUTION and DELIVERY SYSTEMS (Part 2) Ball State Architecture ENVIRONMENTAL SYSTEMS 2 Grondzik 1 Contextual Reminder All-air systems Single zone Terminal reheat Multi-zone Dual-duct VAV Combinations
Questions??????? Thank you
 Questions??????? Thank you Sustainable Design Products and Systems Dan Hahne/Eric Dowell ASP Sustainable Designs Overview Price and Uponor Hydronic Heating and Cooling Price Displacement Ventilation Price
Questions??????? Thank you Sustainable Design Products and Systems Dan Hahne/Eric Dowell ASP Sustainable Designs Overview Price and Uponor Hydronic Heating and Cooling Price Displacement Ventilation Price
HVAC: The Next. Variable-air-volume systems. Outside-the-box thinking suggests the integration of dedicated
 cse0301doas.qxd 1/31/2003 9:09 AM Page 38 HVAC: The Next Outside-the-box thinking suggests the integration of dedicated By STANLEY A. MUMMA, Ph.D., P.E., ASHRAE Fellow Professor of Architectural Engineering
cse0301doas.qxd 1/31/2003 9:09 AM Page 38 HVAC: The Next Outside-the-box thinking suggests the integration of dedicated By STANLEY A. MUMMA, Ph.D., P.E., ASHRAE Fellow Professor of Architectural Engineering
b.) Technical Information:
 Section VI- Strategies a.) Summary: It is important for new construction designers to consider the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning needs within a building. There are many different systems,
Section VI- Strategies a.) Summary: It is important for new construction designers to consider the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning needs within a building. There are many different systems,
The Creative and Performing Arts High School (CAPA) Pittsburgh, PA 11/11/2002 Andrew Tech Mechanical Option Prof. S. A. Mumma
 Objectives and Requirements For the Creative and Performing Arts High School (CAPA), the main objective of the mechanical design is to provide an energy efficient system that is easily maintainable and
Objectives and Requirements For the Creative and Performing Arts High School (CAPA), the main objective of the mechanical design is to provide an energy efficient system that is easily maintainable and
INTRODUCTION TO: ASHRAE STANDARD 90.1, HVAC System Requirements for Reducing Energy Consumption in Commercial Buildings
 INTRODUCTION TO: ASHRAE STANDARD 90.1, 2013 HVAC System Requirements for Reducing Energy Consumption in Commercial Buildings Rocky Mountain ASHRAE Technical Conference, April 29, 2016 SEAN BEILMAN, P.E.,
INTRODUCTION TO: ASHRAE STANDARD 90.1, 2013 HVAC System Requirements for Reducing Energy Consumption in Commercial Buildings Rocky Mountain ASHRAE Technical Conference, April 29, 2016 SEAN BEILMAN, P.E.,
Ventilation and Humidity Control in Army Barracks Using DOAS for Better Indoor Air Quality and Energy Conservation
 Ventilation and Humidity Control in Army Barracks Using DOAS for Better Indoor Air Quality and Energy Conservation Author:John Vavrin, PE Presenter: Dale Herron US Army Corps of Engineers Engineer Research
Ventilation and Humidity Control in Army Barracks Using DOAS for Better Indoor Air Quality and Energy Conservation Author:John Vavrin, PE Presenter: Dale Herron US Army Corps of Engineers Engineer Research
1. When using the COMcheck software, the compliance report submitted by the permit holder shall indicate that the applicable code is.
 2018 NC Energy Conservation Code Commercial Mechanical Module 7 CHAPTER 5 [CE] WORKSHEET 1. When using the COMcheck software, the compliance report submitted by the permit holder shall indicate that the
2018 NC Energy Conservation Code Commercial Mechanical Module 7 CHAPTER 5 [CE] WORKSHEET 1. When using the COMcheck software, the compliance report submitted by the permit holder shall indicate that the
MECHANICAL SERVICES 101. Ian White
 MECHANICAL SERVICES 101 Ian White Contents 1. Ventilation 2. Heat Gains & Losses 3. Heating Ventilation Air Conditioning (HVAC) Systems What are Building Services Building Services incorporate all aspects
MECHANICAL SERVICES 101 Ian White Contents 1. Ventilation 2. Heat Gains & Losses 3. Heating Ventilation Air Conditioning (HVAC) Systems What are Building Services Building Services incorporate all aspects
HVAC 101. The Basics of Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning
 HVAC 101 The Basics of Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning HVAC Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning Provides comfort for people Allows humans to exist under adverse conditions. Comfort Comfort
HVAC 101 The Basics of Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning HVAC Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning Provides comfort for people Allows humans to exist under adverse conditions. Comfort Comfort
2009 IECC Commercial Mechanical Requirements
 BUILDING ENERGY CODES UNIVERSITY 2009 IECC Commercial Mechanical Requirements Ken Baker PNNL-SA-66171 Learning(Objec-ves(( ( 1. Find(minimum(equipment(efficiency(requirements( and(recite(at(least(3(common(terms(for(measuring(
BUILDING ENERGY CODES UNIVERSITY 2009 IECC Commercial Mechanical Requirements Ken Baker PNNL-SA-66171 Learning(Objec-ves(( ( 1. Find(minimum(equipment(efficiency(requirements( and(recite(at(least(3(common(terms(for(measuring(
HONORABLE MENTION: COMMERCIAL BUILDINGS, EXISTING
 ASHRAE s BEST This article was published in ASHRAE Journal, November 2010. Copyright 2010 American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and -Conditioning Engineers, Inc. Reprinted here by permission from
ASHRAE s BEST This article was published in ASHRAE Journal, November 2010. Copyright 2010 American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and -Conditioning Engineers, Inc. Reprinted here by permission from
Raised Access Floor - (AE Breadth Area)
 Raised Access Floor - (AE Breadth Area) Currently, the Plaza has a raised access flooring system on both the 7 th and 8 th floors. The 8 th floor is designed with an independent HVAC system utilizing an
Raised Access Floor - (AE Breadth Area) Currently, the Plaza has a raised access flooring system on both the 7 th and 8 th floors. The 8 th floor is designed with an independent HVAC system utilizing an
Humidity Control Systems for Civil Buildings in Hot Summer and Cold. Winter Zone in China
 Humidity Control Systems for Civil Buildings in Hot Summer and Cold Winter Zone in China Xiaoping Yu Doctoral Candidate Chongqing University of Science & Technology Chongqing, China, 400042 xiaoyup@163.com
Humidity Control Systems for Civil Buildings in Hot Summer and Cold Winter Zone in China Xiaoping Yu Doctoral Candidate Chongqing University of Science & Technology Chongqing, China, 400042 xiaoyup@163.com
Mold/Moisture Control Case Study
 Mold/Moisture Control Case Study Presented by Boggarm S. Setty, P.E., FASHRAE Setty & Associates, Ltd. www.clima2005.ch Clima 2005 Lausanne Solothurnstrasse 13 CH-3322 Schönbühl Switzerland th 8 REHVA
Mold/Moisture Control Case Study Presented by Boggarm S. Setty, P.E., FASHRAE Setty & Associates, Ltd. www.clima2005.ch Clima 2005 Lausanne Solothurnstrasse 13 CH-3322 Schönbühl Switzerland th 8 REHVA
UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI Heating Ventilating and Air-Conditioning (HVAC) 2016 Q1
 GENERAL: This section provides general standards for overall sizing and design of Heating, Ventilating, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems. Other sections contain specific standards for each system per
GENERAL: This section provides general standards for overall sizing and design of Heating, Ventilating, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems. Other sections contain specific standards for each system per
Mechanical System Redesign. Dedicated Outdoor Air System. Design Criteria
 Mechanical System Redesign Dedicated Outdoor Air System Design Criteria The outdoor air conditions used were for Philadelphia, Pennsylvania IAP at a 0.4% occurrence. The supply air conditions were developed
Mechanical System Redesign Dedicated Outdoor Air System Design Criteria The outdoor air conditions used were for Philadelphia, Pennsylvania IAP at a 0.4% occurrence. The supply air conditions were developed
Summary Comparison of Simulation Program Features
 Summary Comparison of Simulation Program Features FEATURE DOE2.2 equest TRACE 700 HAP Public/Proprietary Public Domain Proprietary Proprietary Proprietary Simulation Method 8760 hours 8760 hours 8760 hours
Summary Comparison of Simulation Program Features FEATURE DOE2.2 equest TRACE 700 HAP Public/Proprietary Public Domain Proprietary Proprietary Proprietary Simulation Method 8760 hours 8760 hours 8760 hours
Madeira City Schools Madeira, Ohio. HVAC Assessment. December 2011 (Revised February 2012)
 Madeira City Schools Madeira, Ohio HVAC Assessment December 2011 (Revised February 2012) Prepared by: CMTA Engineering Consultants, Inc. 10411 Meeting Street Prospect, KY 40059 www.cmtaegrs.com (502) 326-3085
Madeira City Schools Madeira, Ohio HVAC Assessment December 2011 (Revised February 2012) Prepared by: CMTA Engineering Consultants, Inc. 10411 Meeting Street Prospect, KY 40059 www.cmtaegrs.com (502) 326-3085
INTRODUCTION HVAC BASICS AND HVAC SYSTEM EFFICIENCY IMPROVEMENT SECTION O 4/19/2012
 HVAC BASICS AND HVAC SYSTEM EFFICIENCY IMPROVEMENT SECTION O INTRODUCTION HVAC systems or Heating, Ventilating and Air-Conditioning systems control the environment for people and equipment in our facilities.
HVAC BASICS AND HVAC SYSTEM EFFICIENCY IMPROVEMENT SECTION O INTRODUCTION HVAC systems or Heating, Ventilating and Air-Conditioning systems control the environment for people and equipment in our facilities.
IAQ Building Education and Assessment Model (I-BEAM)
 Heating, Ventilation, and Airconditioning (HVAC) Text Modules IBEAM IAQ in L... http://www.epa.gov/iaq/largebldgs/ibeam/text/hvac.html Page 1 of 6 10/21/08 IAQ in Large Buildings http://www.epa.gov/iaq/largebldgs/ibeam/text/hvac.html
Heating, Ventilation, and Airconditioning (HVAC) Text Modules IBEAM IAQ in L... http://www.epa.gov/iaq/largebldgs/ibeam/text/hvac.html Page 1 of 6 10/21/08 IAQ in Large Buildings http://www.epa.gov/iaq/largebldgs/ibeam/text/hvac.html
Technical Report Three
 Technical Report Three Existing Conditions for Mechanical Systems Contents Executive Summary...2 Building Overview...2 Mechanical Systems Overview...2 Mechanical System...3 Outdoor & Indoor Design Conditions...3
Technical Report Three Existing Conditions for Mechanical Systems Contents Executive Summary...2 Building Overview...2 Mechanical Systems Overview...2 Mechanical System...3 Outdoor & Indoor Design Conditions...3
Designing Energy Efficient Outdoor Air Systems
 Designing Energy Efficient Outdoor Air Systems Joseph Thorndal Applied Products Sales Manager Greenheck, Schofield, Wisconsin 1 Joseph Thorndal BS Industrial Engineering North Dakota State University Work
Designing Energy Efficient Outdoor Air Systems Joseph Thorndal Applied Products Sales Manager Greenheck, Schofield, Wisconsin 1 Joseph Thorndal BS Industrial Engineering North Dakota State University Work
Radiant Heating & Cooling for Commercial Buildings
 Radiant Heating & Cooling for Commercial Buildings Kaveesh Padiachy, PEng, PMP, LEED AP Business Development Manager Central Canada kaveesh.padiachy@uponor.com www.uponorpro.com/engineering Radiant Heating
Radiant Heating & Cooling for Commercial Buildings Kaveesh Padiachy, PEng, PMP, LEED AP Business Development Manager Central Canada kaveesh.padiachy@uponor.com www.uponorpro.com/engineering Radiant Heating
EarthWise System Seminar
 EarthWise System Seminar Tim Gasper, P.E. Solutions Engineer Brady-Trane Services, Inc. EarthWise Systems? Energy Efficiency Emissions Buildings use 39% of the Primary Energy Consumed in the United States
EarthWise System Seminar Tim Gasper, P.E. Solutions Engineer Brady-Trane Services, Inc. EarthWise Systems? Energy Efficiency Emissions Buildings use 39% of the Primary Energy Consumed in the United States
nzeb office building
 nzeb office building Ympäristötalo in Helsinki, Finland City of Helsinki has taken the exemplary role of the public sector seriously. The latest proof is the Environment Centre building Ympäristötalo completed
nzeb office building Ympäristötalo in Helsinki, Finland City of Helsinki has taken the exemplary role of the public sector seriously. The latest proof is the Environment Centre building Ympäristötalo completed
ASHRAE/IESNA Standard
 ASHRAE/IESNA Standard 90.1-1999 An inside look at the requirements of Standard 90.1-1999 Energy Standard for Building Except Low-Rise Residential Building Mick Schwedler, PE Sr. Principal Applications
ASHRAE/IESNA Standard 90.1-1999 An inside look at the requirements of Standard 90.1-1999 Energy Standard for Building Except Low-Rise Residential Building Mick Schwedler, PE Sr. Principal Applications
2009 Washington State Non-Residential Energy Code Scott Rushing, PE, LEED AP - Rushing Company Lisa Rosenow, CSBA, LEED AP NEEC
 2009 Washington State Non-Residential Energy Code Scott Rushing, PE, LEED AP - Rushing Company Lisa Rosenow, CSBA, LEED AP NEEC Mechanical Systems Agenda Changes in NREC Chapter 11 Changes in NREC Chapter
2009 Washington State Non-Residential Energy Code Scott Rushing, PE, LEED AP - Rushing Company Lisa Rosenow, CSBA, LEED AP NEEC Mechanical Systems Agenda Changes in NREC Chapter 11 Changes in NREC Chapter
Architectural Engineering Senior Thesis Mechanical System Redesign
 Saint Joseph Medical Center Architectural Engineering Senior Thesis Mechanical System Redesign Chris Nicolais Building Description Existing Mechanical System Proposed Redesign Alternative Option Emergency
Saint Joseph Medical Center Architectural Engineering Senior Thesis Mechanical System Redesign Chris Nicolais Building Description Existing Mechanical System Proposed Redesign Alternative Option Emergency
August 15, 2013 Page 1 of 19
 Section C401 Application Compliance with C402, C403, C404 and C405 AND (either C406.2, C406.3 or C406.4) Compliance with C402, C403, C404 or C405 Section C402 Building Envelope (Climate Zone 5A) Space-Conditioning
Section C401 Application Compliance with C402, C403, C404 and C405 AND (either C406.2, C406.3 or C406.4) Compliance with C402, C403, C404 or C405 Section C402 Building Envelope (Climate Zone 5A) Space-Conditioning
NET ENERGY WATER LOOPS A clear path to net zero energy buildings
 Presents NET ENERGY WATER LOOPS A clear path to net zero energy buildings Alan Niles WaterFurnace International This ASHRAE Distinguished Lecturer is brought to you by the Society Chapter Technology Transfer
Presents NET ENERGY WATER LOOPS A clear path to net zero energy buildings Alan Niles WaterFurnace International This ASHRAE Distinguished Lecturer is brought to you by the Society Chapter Technology Transfer
TDSHS Air Change Requirements and the Basics of Psychrometrics. Presented by: Aric Murray December 06, 2013
 TDSHS Air Change Requirements and the Basics of Psychrometrics Presented by: Aric Murray December 06, 2013 Agenda 1. What are the air change requirements and how do you calculate them? 2. Why are air change
TDSHS Air Change Requirements and the Basics of Psychrometrics Presented by: Aric Murray December 06, 2013 Agenda 1. What are the air change requirements and how do you calculate them? 2. Why are air change
Senior Thesis Centre Community Hospital East Wing Addition - Proposal Keith Beidel Mechanical Option 12/05/02 1
 Table of Contents Page Number(s) Executive Summary 2 Project Background 3 Proposed Depth Alternatives 4 Proposed Depth Redesign 5-7 Justification of Proposed Depth Redesign 8 Proposed Breath Redesign 9
Table of Contents Page Number(s) Executive Summary 2 Project Background 3 Proposed Depth Alternatives 4 Proposed Depth Redesign 5-7 Justification of Proposed Depth Redesign 8 Proposed Breath Redesign 9
Pharmaceutical Facility Design
 PhEn-602 Pharmaceutical Facility Design J. Manfredi Notes 9A PhEn-602 J. Manfredi 1 Primary & Secondary HVAC units Primary Primary air handling unit arrangement: One unit is responsible for all of the
PhEn-602 Pharmaceutical Facility Design J. Manfredi Notes 9A PhEn-602 J. Manfredi 1 Primary & Secondary HVAC units Primary Primary air handling unit arrangement: One unit is responsible for all of the
System Components with ` Emphasis on Packaged Rooftop Application and Installation. Jerry Cohen President Jacco & Assoc.
 System Components with ` Emphasis on Packaged Rooftop Application and Installation Jerry Cohen President Jacco & Assoc. Agenda Define and relate in practical terms the following components: System Effect
System Components with ` Emphasis on Packaged Rooftop Application and Installation Jerry Cohen President Jacco & Assoc. Agenda Define and relate in practical terms the following components: System Effect
SECTION H. Engineering Guide Radiant Products. Please refer to the Price Engineer s HVAC Handbook for more information on Radiant Heating and Cooling
 SECTION H Radiant Products Please refer to the Price Engineer s HVAC Handbook for more information on Radiant Heating and Cooling Introduction To Radiant Heating and Cooling Radiant heating and cooling
SECTION H Radiant Products Please refer to the Price Engineer s HVAC Handbook for more information on Radiant Heating and Cooling Introduction To Radiant Heating and Cooling Radiant heating and cooling
design brief This design brief provides an introduction into the design and application of DV. It addresses the following issues:
 energydesignresources design brief DISPLACEMENT VENTILATION Summary Displacement ventilation (DV) is an alternate air distribution method for commercial and industrial spaces. 1 Used since the late 1970s
energydesignresources design brief DISPLACEMENT VENTILATION Summary Displacement ventilation (DV) is an alternate air distribution method for commercial and industrial spaces. 1 Used since the late 1970s
Chapter 6 ALL-AIR HVAC SYSTEMS 6.1 CONTEXT
 Chapter 6 ALL-AIR HVAC SYSTEMS 6.1 CONTEXT This chapter and the following chapters on air-and-water and all-water systems are based upon a common context. Key to this context is the idea of a thermal zone.
Chapter 6 ALL-AIR HVAC SYSTEMS 6.1 CONTEXT This chapter and the following chapters on air-and-water and all-water systems are based upon a common context. Key to this context is the idea of a thermal zone.
Do All DOAS Configurations Provide the Same Benefits?
 TECHNIL FTURE This article was published in ASHE Journal, July 2014. Copyright 2014 ASHE. Posted at www.ashrae.org. This article may not be copied and/or distributed electronically or in paper form without
TECHNIL FTURE This article was published in ASHE Journal, July 2014. Copyright 2014 ASHE. Posted at www.ashrae.org. This article may not be copied and/or distributed electronically or in paper form without
December 6, 2018 Optimizing Solutions through Superior Dehumidification Technology SM
 Humidity Control and Heating and Cooling Applications December 6, 2018 Optimizing Solutions through Superior Dehumidification Technology SM Today s Discussion Discussion of cooling, heating and dehumidification
Humidity Control and Heating and Cooling Applications December 6, 2018 Optimizing Solutions through Superior Dehumidification Technology SM Today s Discussion Discussion of cooling, heating and dehumidification
Waterborne Climate Systems
 Overview Waterborne Climate Systems Optimal indoor climate with demand-controlled and energy efficient products Flexible, low energy-use + low maintenance with Swegon s climate systems! There are many
Overview Waterborne Climate Systems Optimal indoor climate with demand-controlled and energy efficient products Flexible, low energy-use + low maintenance with Swegon s climate systems! There are many
Chilled beam technology overview John Woollett 1, Jonas Åkesson 2 Swegon AB 1,2
 Chilled beam technology overview John Woollett 1, Jonas Åkesson 2 Swegon AB 1,2 john.woollett@swegon.se, jonas.akesson@swegon.se SUMMARY The main focus of the paper will be on active beam technology regarding
Chilled beam technology overview John Woollett 1, Jonas Åkesson 2 Swegon AB 1,2 john.woollett@swegon.se, jonas.akesson@swegon.se SUMMARY The main focus of the paper will be on active beam technology regarding
SYNOPSIS. Part-Load Control Strategies for Packaged Rooftop Units. In this issue... Bin Hour Profile Charlotte, NC
 VOLUME ONE NUMBER THREE SYNOPSIS A N H V A C N E W S L E T T E R F O R B U I L D I N G O W N E R S A N D M A N A G E R S In this issue... Part-Load Strategies Why they re important.......... 1 What Things
VOLUME ONE NUMBER THREE SYNOPSIS A N H V A C N E W S L E T T E R F O R B U I L D I N G O W N E R S A N D M A N A G E R S In this issue... Part-Load Strategies Why they re important.......... 1 What Things
RADIANT COOLING SYSTEMS OPPORTUNITIES FOR RADIANT COOLING IN NORTH AMERICAN CONSTRUCTION DALE HANSCOMB, REHAU Sales Manager Building Technology
 RADIANT COOLING SYSTEMS OPPORTUNITIES FOR RADIANT COOLING IN NORTH AMERICAN CONSTRUCTION DALE HANSCOMB, REHAU Sales Manager Building Technology www.rehau.com Construction Automotive Industry LEARNING OBJECTIVES
RADIANT COOLING SYSTEMS OPPORTUNITIES FOR RADIANT COOLING IN NORTH AMERICAN CONSTRUCTION DALE HANSCOMB, REHAU Sales Manager Building Technology www.rehau.com Construction Automotive Industry LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Air System Sizing Summary for Lobby System Project Name: Existing Lobby 04/04/2005 Prepared by: psuae
 APPENDIX C Air System Sizing Summary for Lobby System Project Name: Existing Lobby 04/04/2005 12:56PM Air System Information Air System Name Equipment Class Air System Type Lobby System CW AHU SZCAV Number
APPENDIX C Air System Sizing Summary for Lobby System Project Name: Existing Lobby 04/04/2005 12:56PM Air System Information Air System Name Equipment Class Air System Type Lobby System CW AHU SZCAV Number
ADRIATIC VF. Active chilled beam with cooling, heating and ventilation QUICK FACTS
 Active chilled beam with cooling, heating and ventilation QUICK FACTS The ADRIATIC VF is a chilled beam with integrated recirculated air opening in the face plate. Air is discharged into the room along
Active chilled beam with cooling, heating and ventilation QUICK FACTS The ADRIATIC VF is a chilled beam with integrated recirculated air opening in the face plate. Air is discharged into the room along
Using Embedded Tube Radiant Cooling Systems to Maximize LEED Points
 San Joaquin ASHRAE Chapter Using Embedded Tube Radiant Cooling Systems to Maximize LEED Points Devin Abellon, P.E. Business Development Manager Uponor November 4, 2010 LEED v3 new construction LEED Topic
San Joaquin ASHRAE Chapter Using Embedded Tube Radiant Cooling Systems to Maximize LEED Points Devin Abellon, P.E. Business Development Manager Uponor November 4, 2010 LEED v3 new construction LEED Topic
