High Efficiency Solar Powered Fans
|
|
|
- Melina Parsons
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Solar Powered Fans Danny Parker University of Central Florida Bart Hibbs AeroVironment, Inc. Find similar works at: University of Central Florida Libraries Recommended Citation Parker, Danny and Hibbs, Bart, "High Efficiency Solar Powered Fans" (21). UCF Patents. Paper This Patent is brought to you for free and open access by the Technology Transfer at STARS. It has been accepted for inclusion in UCF Patents by an authorized administrator of STARS. For more information, please contact
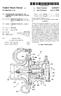
2 I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll US785513B 1 c12) United States Patent Parker et al. (1) Patent No.: US 7,85,513 Bl (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 14, 21 (54) HIGH EFFICIENCY SOLAR POWERED FANS (75) Inventors: Danny Parker, Cocoa Beach, FL (US); Bart Hibbs, Simi Valley, CA (US) (73) Assignee: University of Central Florida Research Foundation, Inc., Orlando, FL (US) ( *) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term ofthis patent is extended or adjusted under 35 U.S.C. 154(b) by 39 days. (21) Appl. No.: 12/183,279 (22) Filed: Jul. 31, 28 OTHER PUBLICATIONS Solar Attic Fan Benefits-SDF-2 The World's Most Powerful Solar Attic Fan, Solar Dynamics Online Publication, 25, 2 pages [Retrieved on Feb. 17, 28], Retrieved from the Internet: <URL : solardynamicsinc.com/page3.html. (Continued) Primary Examiner-Steven B McAllister Assistant Examiner-Patrick F. O'Reilly, III (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Brian S. Steinberger; Law Offices of Brian S. Steinberger, P.A. (57) ABSTRACT (63) (51) (52) (58) (56) AU Related U.S. Application Data Continuation-in-part of application No. 11/433,888, filed on May 12, 26, now Pat. No. 7,57,151. Int. Cl. F24F 717 (26.1) H2N 61 (26.1) U.S. Cl /228; 454/23; 454/9; 416/63; 136/245; D13/12 Field of Classification Search /228, 454/23, 9; 416/63; 136/245; D13/12 See application file for complete search history. References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 1,93,823 A Lougheed (Continued) FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS * 5/1928 (Continued) Highly efficient solar fans used in portable and built in configurations. A ventilation fan can be used for exhausting air out from underneath roofs, and/or for being portable in use and application. The fan can include optimized airflow blades having a twisted configuration that can move at a rotational speed operation of up to approximately 5 rpm. The approximately 15 inch diameter twisted blades can be premolded on a hub that together form a single molded unit of plastic. They can also be fabricated using metal. The unit can be mounted in an exhaust outlet having a conical diffuser on or adjacent to a roof. Another embodiment allows for portable solar powered fans used anywhere there is a need for ventilation and moving of air. The blades can rotate by a solar powered motor, where the blades and motor can generate up to approximately 14 cfm while using no more than approximately 16 Watts. Portable fans can be powered by solar panels. One embodiment has solar panels mounted to a handtruck. Another embodiment has solar panels in a carrying case with a handle having leg(s) which can bend downward to different angled positions. The solar panel carrying case and the fan can each have single handles that allows for the portable fan assembly to carried and transported by both hands of a single user. 14 Claims, 35 Drawing Sheets / 51 /
3 US 7,85,513 Bl Page 2 1,942,688 A 2,283,956 A 2,345,47 A 2,35,939 A 2,43,225 A 2,45,44 A 2,777,382 A 2,83,779 A * 3,173,49 A 3,416,725 A 3,854,845 A D242,616 s 4,15,919 A 4,197,57 A D261,83 s 4,325,675 A 4,411,598 A 4,416,434 A 4,51,194 A 4,633,769 A 4,657,483 A * 4,73,985 A 4,844,698 A 4,974,633 A 5,78,47 A 5,114,313 A 5,131,888 A 5,253,979 A 5,522,943 A * 5,588,99 A 5,62,368 A 5,814,96 A * U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS Davis 5/1942 Smith 3/1944 Houghton Sprouse Hagler 1/1948 Mills Solzman 4/1958 Wentling /662 3/ 1965 Stuart, III 12/1968 Bohanon 12/1974 Van De Water 12/1976 Meyerhoff et al. 4/1979 Matucheski Hayashi Bohanon, Jr Gallot 1/1983 Okada Thibert et al. 2/1985 Brown Milks 4/1987 Bede /222 3/1988 Rothman et al. 7I1989 Gornstein et al. 12/199 Hickey Wimberly Vorus 7/1992 Adkins, II 1/1993 Fradenburgh et al. 6/1996 Spencer et al /245 12/1996 Ferng 4/1997 Bates et al. 9/1998 Spencer et al /15 6,39,533 A 6,39,541 A 6,21,181 Bl* 6,36,3 Bl 6,481,233 Bl 6,589,18 B2 * 6,659,721 Bl 6,695,692 Bl 6,733,241 B2 6,884,34 Bl D51,316 S * D51,998 S 6,971,82 B2 * 7,14,423 B2 23/ Al* 24/12172 Al* Al 25/ Al* Al * 28/ Al * JP JP JP 3/2 McCabe 3/2 Parker et al. 3/21 Azzam et al /244 1/21 Wilson Calvert 7/23 Chen /14 12/23 Parker et al York 5124 Bird 4125 Parker et al. 1/25 Hayakawa... D13/12 1/25 Parker et al. 12/25 Rossabi et al / /26 Parker et al. 6/23 Hsieh /291 6/24 Gautney /338 8/24 Parker et al. 7/25 Boone, Jr / Gillette, II... 32/17 6/28 Patel /121.3 FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS A * 6/ A * 1/ A * OTHER PUBLICATIONS Solar Attic Fan Technical Information, Solar Dynamics Online Publication, 25, 2 pages [Retrieved Feb. 17, 28], Retrieved from the Internet: <URL /web.archive.org/web/ * cited by examiner
4 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 1of35 US 7,85,513 Bl - /
5 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 2 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl i LE 15 2C ROOT TIP 2D 13X (FIG. 3) FIG. 2B
6 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 3 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl i-l..q- '\-1 ' I - N P-4. N - d I - I I I I! - I -I N u I - E-t N. I - - /.,. N ' E-t d i-l..q- I I I I / I
7 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 4 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl FIG. 2E 14LE 1 / 17 16TE 12 14LE (////////Iii TE FIG. 2F
8 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 5 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl - e= E-4 i::a Cl---- u---- a:i E-4 o-- N -
9 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 6 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl 14LE (\ / FIG. 5A 16TE B\ TE FIG. 5B
10 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 7 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl.13 (\ TE FIG. 5C TE FIG. 5D
11 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 8 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl :\ HP 16TE FIG. 5E
12 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 9 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl M N N N o N
13 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 1 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl l.f) l.f) N N N r V') M N M -
14 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 11of35 US 7,85,513 Bl
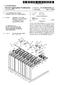
15 rj). = c ('D....i;... N... 1J1 ('D = a... N... (.H Ul d rjl -...l Oo tit = u. w "'"" = "'"" FIG. 9 1 I 15 I Ir r ! lr--;1t; ;;! // 1 11 /;I I/ I/// 1 /;I // I/// L.J-- I I I I/ ---JL I I l( /, 14 -,-;-::..--v I I I I I I II /-1 '" ( l ) l \. // -==---::/ 55
16 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 13 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl FIG. 1 4 \ 488
17 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 14 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl FIG /5 495 /
18 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 15 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl \ l()
19 t-(i ;; fl I 'r' Q \JJ. =!'!)... "' N... rj1!'!) =!'!) O'I... tit Lj "'...:J QO th "' th w = Fig / B 63A
20 61 / 6 (H co ""'"' = Fig sso I I l "'.f;;.. t,,j L-1.-.\ l '\.., ljj I 'IV-596 =- 569_/ -- h.,,,'+_,, d) 568--l M/ 62B - " - - \ / J 63A '--./ \ l..h l'..ll 595 l59 d r.r; 66..., "'"' QO u. 65-Y Q u. ""'"'
21 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 18 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl /...-!.,... < tr), Cll) """" ' \Q V'l
22 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 19 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl
23 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 2 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl
24 U.s. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 21 of JS vs 7,8so,s13 n1
25 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 22 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl
26 \JS 1,sso,s13 Bl \}.S. -patent nee. 14, 21
27 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 24 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl
28 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 25 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl
29 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 26 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl 'r'l 'O
30 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 27 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl N N..,... II")
31 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 28 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl
32 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 29 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl ' l.t') N.,... /"")... ('<.. '-.. '-.. ' '-.. ' '-.. '-.. '-.. '-.. ' '1 V) '-.. '-.. '-.. '-.. N t).f).,... ' ol N I.I') r--- V)
33 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 3 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl lt') $
34 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 31of35 US 7,85,513 Bl t""- N. '""4 ' V) ' V) \ ("- Ir) ' ' V\ \ \
35 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 32 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl \ O'\ \
36 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 33 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl IO
37 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 34 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl In
38 U.S. Patent Dec. 14, 21 Sheet 35 of 35 US 7,85,513 Bl
39 1 HIGH EFFICIENCY SOLAR POWERED FANS This invention is a Continuation-In-Part of U.S. patent application Ser. No. 11/433,888 filed May 12, 26, now issued as U.S. Pat. No. 7,57,151. FIELD OF INVENTION This invention relates to solar powered fans, and in particular to apparatus, devices, systems and methods of using optimized twisted blades as efficient attic exhaust fans and portable fans which are also solar powered and the portable fan modular components which are also easily carriable by users and include carrying cases with handles and fold down legs, and to methods of operating, using, housing and transporting the novel fans. BACKGROUND AND PRIOR ART Fans have been used over the years in semi-permanent mounts for ventilation of buildings, as well as in smaller configurations which allow the fan housings to be moved place to place. These types of fans traditionally require power supplies where power to the fan motors is derived through existing wiring in the buildings and/or through wall mounted power supplies. Additionally, most fans use planar shaped blades to move airflow which limits the amount of airflow that is moved at any given time. US 7,85,513 Bl Ventilation fans for venting hot air from attic areas underneath roofs have been increasing in popularity over the years. 3 Hot air is known to accumulate under rooftops especially in attic areas. This buildup of hot air can lead to poor cooling conditions within the building and increased utility costs to run air conditioning systems and cooling systems, and the like. Thus, it is desirable to improve and maximize air removal rates from under roofs and from attic spaces, and the like. Existing attic ventilation fans have been used but have substantial power requirements from existing building elec- 4 trical supplies. For example, the GRAINGER catalog sells an automatic power attic gable ventilator model number 4YN78 having metal type blades that rotate at 15 RPM (revolutions per minute) generating 132 cfm (cubic feet per minute) and requires 2 Watts of power. Another 45 GRAINGER attic fan model 4YN77 generates a higher level of cfm (162 cfm) but requires 225 Watts of power. Most existing attic ventilation fans use standard stamped generally flat metal fan blades that have only fair air moving performance. Flat type blades are not designed to maximize 5 moving of air. Various attic type ventilation fans have been proposed over the years. See for example, U.S. Patents: Des. 261,83 to Bohanon, Jr.; 4,51,194 to Brown; 5,78,47 to Wimberly; 6,36,3 to Wilson; and 6,695,692 to York. However, none 55 of the cited references, individually or in combination overcome all the problems with the prior art described above. The inventors and assignee of the subject invention have been at the forefront of inventing high efficiency ceiling fans by using novel twisted blade configurations. See for example, U.S. Pat. Nos. 6,884,34 and 6,659,721 and 6,39,541 to Parker et al. However, these fans are designed for maximizing air flow from ceiling fans that have much larger diameters (approximately 42 inches to 64 inches, etc.) and that operate at different speeds (less than approximately 2RPM) than small diameter ventilation fans that are needed to exhaust air from underneath roofs and from attic spaces. 2 Additionally, the inventors and assignee have worked on air conditioner condenser fan blades (see for example, U.S. patents D51,998 to Parker et al. and 7,14,423 to Parker et al. However, the air conditioner condenser fans are not optimized for the ventilation and removal of air from underneath roofs and from attic spaces. Aircraft, marine and automobile engine propeller type blades have been altered over the years to shapes other than flat rectangular. See for example, U.S. Pat. Nos. 1,93,823 to 1 Lougheed; 1,942,688 to Davis; 2,283,956 to Smith; 2,345, 47 to Houghton; 2,45,44 to Mills; 4,197,57 to Hayashi; 4,325,675 to Gallot et al.; 4,411,598 to Okada; 4,416,434 to Thibert; 4,73,985 to Rothman et al. 4,794,633 to Hickey; 4,844,698 to Gornstein; 5,114,313 to Vorus; and 5,253,979 to 15 Fradenburgh et al.; Australian Patent 19,987 to Eather. However, these patents are generally used for high speed water, aircraft, and automobile applications where the propellers are run at high revolutions per minute (rpm) generally in excess of 5 rpm. None of these propellers are designed for opti- 2 mizing airflow to remove undesirable air from attics and from underneath roofs. Portable fans such as handheld battery fans have been used over the years. Similar to the problems presented above, small portable fans do not have blades aerodynamically optimized 25 for airflow. In addition, portable fans have batteries that have limited lifespans since the batteries either need to be constantly recharged from a 12 volt power supply or the batteries need to be constantly replaced. The need for efficient powered portable fans has been growing much more in recent years. Natural disasters such as hurricanes and earthquakes have caused extensive power outages that can last from several hours to weeks or more in the United States. Conventional battery powered fans, cannot be 35 used effectively during these disaster conditions. The prior art listed above does not fix the problems with portable fan use. Thus, the need exists for better performing fans over the prior art. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The first objective of the subject invention is to provide efficient roof/attic exhaust fans, blades, devices, apparatus and methods of operating the fans, that have optimized twisted nonmetal blades for maximizing removal of air from spaces underneath roofs. The second objective of the subject invention is to provide efficient roof/attic exhaust fans, blades, devices, apparatus and methods of operating the fans, that can be solar powered. The third objective of the subject invention is to provide efficient roof/attic exhaust fans, blades, devices, apparatus and methods of operating the fans, that can generate air flow up to at least approximately 3% above existing ventilation fans. The fourth objective of the subject invention is to provide efficient roof/attic exhaust fans, blades, devices, apparatus and methods of operating the fans, that moves more air than existing ventilation fans and requires less power than existing ventilation fans. The invention reduces electrical power con- 6 sumption and is more energy efficient over traditional flat planar ceiling fan blades. The fifth objective of the subject invention is to provide efficient roof/attic exhaust fans, blades, devices, apparatus and methods of operating the fans, having fan blade aerody- 65 namics optimized to maximize airflow in an approximately 15 inch diameter fan operating at up to approximately 5 (revolutions per minute) RPM.
40 US 7,85,513 Bl 3 The sixth objective of the subject invention is to provide efficient roof/attic exhaust fans, blades, devices, apparatus and methods of operating the fans, where the blades and hub are a single molded piece of plastic. The seventh objective of the subject invention is to provide 5 portable fans that can be used anywhere, and blades, devices, apparatus and methods of operating the fans, having optimized twisted nonmetal blades for maximizing air ventilation. The eighth objective of the subject invention is to provide 1 portable fans that can be used anywhere, and blades, devices, apparatus and methods of operating the fans, that can be solar powered. The ninth objective of the subject invention is to provide portable fans that can be used anywhere, and blades, devices, 15 apparatus and methods of operating the fans, that can generate air flow up to at least approximately 3% above existing portable fans. The tenth objective of the subject invention is to provide portable fans that can be used anywhere, and blades, devices, 2 apparatus and methods of operating the fans, that move more air than existing ventilation fans and require less power than existing ventilation fans. The invention reduces electrical power consumption and is more energy efficient over traditional flat planar ceiling fan blades. 25 The eleventh objective of the subject invention is to provide portable fans that can be used anywhere, and blades, devices, apparatus and methods of operating the fans, having fan blade aerodynamics optimized to maximize airflow in an approximately 15 inch diameter fan operating at up to approximately 3 5 (revolutions per minute) RPM. The twelfth objective of the subject invention is to provide portable fans, blades, devices, apparatus and methods of operating the fans, that can be used anywhere such as during and after natural disasters such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and 35 the like, as well as in environments having limited power supplies such as in construction sites, at picnics and other outings, on camping, hiking and fishing trips and at the beach. The thirteenth objective of the invention is to provide methods, systems and devices that allow a single person to easily 4 carry and transport both a fan assembly and a solar powered panel assembly. The fourteenth objective of the invention is to provide methods, systems and devices for allowing for a rechargeable backup power pack to be used with a solar powered fan 45 system when solar power is not available. The fifteenth objective of the invention is to provide methods, systems and devices for allowing for a power pack for rumiing a portable fan to be recharged used using solar power source. The sixteenth objective of the invention is to provide a carrying case similar to a brief case for holding a solar panel ( s) that allows the panel(s) to be easily carried in a single hand when folded, and allows for supporting the panel(s) at selected angles when a leg(s) is deployed. A preferred embodiment can include a plurality of efficient optimized small diameter fan blades with a hub. Diameter sizes of the fans can include but not be limited to less thanand up to approximately 15", and greater. The blades can be made from plastic, and the like, and be pre-molded together with the 6 hub. The blade dimensions and twist angles can be optimized to move air when running at approximately 5 rpm (revolutions per minute). The solar powered fans can be used in attics and under roofs to ventilate and/or exhaust heated air therefrom. Another embodiment has the solar powered fan being portable so that it can be used most anywhere there is a need for moving and circulating air. The fan can be moveable by a wheeled stand, and the solar powered panels can be movable by a hand truck, and the like. A still another embodiment allows for a battery powered fan assembly to be easily carried in one hand while a folded solar panel assembly can be easily carried in another hand, where the fan and solar panel assemblies are portable and easily deployed. The folded solar panel can be mounted in a rectangular type case such as a briefcase where the user can easily transport the panel by a single handle on the case. Further objects and advantages of this invention will be apparent from the following detailed descriptions of the presently preferred embodiments which are illustrated schematically in the accompanying drawings. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FIGURES FIG. la is a perspective view of the novel three twisted blades with hub that can be used with an attic fan. FIG. lb is a bottom view of the blades with hub offig. la. FIG. lc is a side view of the blades and hub of FIG. lb along arrow lcx. FIG. 2A is an upper top perspective view of a single twisted blade of FIGS. la-lc. FIG. 2B is a top view of the single twisted blade of FIG. 2A. FIG. 2C is a root end view of the single twisted blade of FIG. 2B along arrow 2C. FIG. 2D is a tip end view of the single twisted blade of FIG. 2B along arrow 2D. FIG. 2E is a lower bottom perspective view of the twisted blade of FIG. 2A. FIG. 2F is a bottom view of the twisted blade of FIG. 2E. FIG. 3 is a side perspective view of the twisted blade of FIG. 2B along arrow 3x with labeled cross-sections A, B, C, D,E. FIG. 4 is an end view of FIG. 3 showing the different cross-sections A, B, C, D, and E. FIG. SA shows the cross-section A of FIGS FIG. SB shows the cross-section B of FIGS FIG. SC shows the cross-section C of FIGS FIG. SD shows the cross-section D of FIGS FIG. SE shows the cross-section E of FIGS FIG. 6 is a perspective exterior view of a roof alcove exhaust incorporating the fan and blades of the preceding figures with a solar power source. FIG. 7 is a view of the separate components of FIG. 6. FIG. 8 is another perspective exterior view of a roof top exhaust incorporating the fan and blades of the preceding figures with a solar power source. FIG. 9 is a view of the separate components of FIG. 8. FIG.1 is a perspective front view of a portable fan assembly incorporating the fan and blades of the preceding figures with a solar power source. FIG. 11 is a rear view of the portable of FIG. 1. FIG. 12 is a front perspective view of DC powered fan assembly with portable solar panel assembly. FIG. 13 is a rear perspective view of FIG. 12. FIG. 14 is a rear perspective view showing charge cables disconnected. FIG. lsa is a rear perspective view showing remote battery charging. FIG. lsb shows the rechargeable battery pack and AC powered battery charger detached from one another. FIG. lsc shows the rechargeable battery pack and AC 65 powered battery charger of FIG. lsb attached to one another. FIG. 16 shows a left side view of the DC fan of FIG. 12. FIG.17 shows a front view of the DC fan of FIG. 16.
41 US 7,85,513 Bl 5 FIG. 18 shows a right view of the DC fan of FIG. 16. FIG. 19 shows a rear view of the DC fan of FIG. 16. FIG. 2 is a front perspective view of the portable solar panel assembly deployed. FIG. 21 is a rear perspective view of the portable solar 5 panel assembly deployed. FIG. 22 is a front perspective view of the portable solar panel assembly folded for transport. FIG. 23 is a rear perspective view of the portable solar panel assembly folded for transport. FIG. 24 is a left side view of the solar panel assembly folded with ghosted leg and cover function. FIG. 25 is a front view of the folded solar panel assembly. FIG. 26 is a right side view of the folded solar panel assembly. FIG. 27 is a rear view of the folded solar panel assembly. FIG. 28 is another rear view of the folded solar panel assembly. FIG. 29 is a bottom view of the deployed solar panel assembly. FIG. 3 is a side view of the deployed solar panel assembly. FIG. 31 is a front view of the deployed solar panel assembly. DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT Before explaining the disclosed embodiments of the present invention in detail it is to be understood that the invention is not limited in its application to the details of the 3 particular arrangement shown since the invention is capable of other embodiments. Also, the terminology used herein is for the purpose of description and not of limitation. The labeled components will now be described. 1 hub and blade assembly 1 First blade 2 Second blade 3 Third blade 4Hub 5 Motor 55 Power line 12 Root end of blade 18 Tip end of blade 14LE leading edge of blade 16TE trailing edge of blade 15 upper surface of blade 17 lower surface of blade 1 Solar power source 11, 12 PV (photovoltaic panels) 13 Solar panel frame 14 Optional stand 15 Optional Additional panels, frame and stand 2 Roof Alcove Exhaust 21 Roof 215 Opening in roof 22 Gable wall 225 Opening in gable wall 23 Hood 235 Louvers 24 housing 3 Roof Top Exhaust 33 Domed hood cover 335 Lower Opening about overhanging edges of Dome Cover 34 Housing under roof 35 Cylindrical Housing outside of roof 4 Portable Fan 41 Cylinder cover 42 pole 43 triangular base 44 wheels 45 Stand handle 46 fan speed control 47 Solar panels 475 cable/power line 48 handtruck 49 battery power source cable/powerline 5 Portable fan and solar panel case assembly 51 Battery powered fan assembly. 52 Portable solar panel assembly. 53 Rechargeable battery pack downwardly projecting plug 54 DC power supply/battery recharge. 545 power cable 55 DC power switch. 56 Fan handle 565 motor 568 U shaped floor stand with upwardly bent ends 569 rubber footers 57 Solar panel , 578 outer side walls 574 rear support bar 575 rear box 58 Solar panel cover. 582, 588 angled side edges 585 an open end portion 59 Solar panel support stand. 591, 599 hinged tabs 592, 598 inwardly angled ends 594, 596 side legs bottom leg 6 Solar panel carry handle. 61 Fan speed switch. 62A, 62B Wall receptacle charge cable(s). 4 63A, 63B Solar charge cable(s). 64 Solar charge connector. 65 Wall receptacle charge connector. 66 Wall plug/transformer. 67 A.C. powered batter charger (remote) receptacle 68 A.C. wall plug. 69 Solar panel cover hinge pin. FIG. la is a perspective view 1 of the novel three twisted blades 1, 2, 3 with hub 4 that can be used with an attic 5 fan. FIG. lb is a bottom view of the blades 1-3 with hub 4 of FIG. la. FIG. 1 C is a side view of the blades 1-3 and hub 4 of FIG. lb along arrow lcx. FIG. 2A is an upper top perspective view of a single twisted blade 1 of FIGS. la-lc. FIG. 2B is a top view of the single 55 twisted blade 1 of FIG. 2A. FIG. 2C is a root end view of the single twisted blade 1 of FIG. 2B along arrow 2C. FIG. 2D is a tip end view of the single twisted blade 1 of FIG. 2B along arrow 2D. FIG. 2E is a lower bottom perspective view of the twisted blade 1 of FIG. 2A. FIG. 2F is a bottom view 6 of the twisted blade 1 of FIG. 2E. Referring to FIGS. l-2f, the novel fan can have three twisted blades 1, 2, 3 each having a positive twist between their root ends adjacent to the hub 4 and their tip ends. The overall diameter of the fan 1 can be approximately 15 inches 65 across the blade tip ends. The blades 1, 2, 3 and hub 4 can be formed into a single molded unit, such as being formed from injection molded plastic, and the like. 6
42 US 7,85,513 Bl 7 Referring to FIGS. 2B-2D, the single twisted blade 1 can have a length of approximately 5.23 inches between the root end 12 and the tip end 18. The twisted blade 1 can be attached to the hub 4 offigs. la-lc with the leading edge 14LE of the root end 12 having an raised angle of approxi- 5 mately 47.3 degrees above horizontal plane HP with the trailing edge 16TE of the root end 12 being below the horizontal plane HP. The tip end 18 of the blade 1 can have a twist from the root end so that the leading edge 14LE is approximately degrees above the horizontal plane HP 1 with the trailing edge 16TE below the horizontal plane HP. FIG. 3 is a side perspective view of the blade of FIG. 2B along arrow 3X with labeled cross-sections A, B, C, D, E in between the root end 12 and tip end 18. FIG. 4 is an end view of FIG. 3 showing the different cross-sections A, B, C, D, and 15 E, in curved views superimposed over one another showing the varying degrees of twist between the root end and tip end of the blade 1. FIG. SA shows the cross-section A of FIGS. 3-4 having a leading edge 14LE slightly curved down being approximately 41.6 degrees above the horizontal plane HP. Crosssection A has a convex shaped upper surface ls and a lower surface 17 with a concave bend configuration, and trailing edge 16TE below the horizontal plane HP. The leading edge 14 LE having a more blunt rounded edge than the trailing edge 16TE. Cross-section A can have a width of approximately 3.78 inches between the trailing edge 16TE and leading edge 14LE. The thickness of the cross-section A can expand from the trailing edge 16TE to being approximately.9 inches half way to a midpoint of the cross-section which has a 3 thickness of approximately.14 inches, and the thickness hal:!way between the midpoint and the leading edge 14LE being approximately.18 inches. FIG. SB shows the cross-section B of FIGS. 3-4 having a leading edge 14LE slightly curved down being approxi- 35 mately degrees above the horizontal plane HP. Crosssection B has a convex shaped upper surface ls and a lower surface 17 with a concave bend configuration, and trailing edge 16TE below the horizontal plane HP. The leading edge 14 LE having a more blunt rounded edge than the trailing edge 4 16TE. Cross-section B can have a width of approximately 3.81 inches between the trailing edge 16TE and leading edge 14LE. The thickness of the cross-section B can expand from the trailing edge 16TE to being approximately.9 inches half way to a midpoint of the cross-section which has a 45 thickness of approximately.14 inches, and the thickness hal:!way between the midpoint and the leading edge 14LE being approximately.18 inches. FIG. SC shows the cross-section C of FIGS. 3-4 having a leading edge 14LE slightly curved down being approxi- 5 mately degrees above the horizontal plane HP. Crosssection C has a convex shaped upper surface ls and a lower surface 17 with a concave bend configuration, and trailing edge 16TE below the horizontal plane HP. The leading edge 14 LE having a more blunt rounded edge than the trailing edge 55 16TE. Cross-section C can have a width of approximately 3.91 inches between the trailing edge 16TE and leading edge 14LE. The thickness of the cross-section C can expand from the trailing edge 16TE to being approximately.8 inches half way to a midpoint of the cross-section which has a 6 thickness of approximately.13 inches, and the thickness hal:!way between the midpoint and the leading edge 14LE being approximately.18 inches. FIG. SD shows the cross-section D of FIGS. 3-4 having a leading edge 14LE slightly curved down being approxi- 65 mately 3.26 degrees above the horizontal plane HP. Crosssection D has a convex shaped upper surface ls and a lower 8 surface 17 with a concave bend configuration, and trailing edge 16TE below the horizontal plane HP. The leading edge 14LE having a more blunt rounded edge than the trailing edge 161E. Cross-section D can have a width of approximately 4. inches between the trailing edge 16TE and leading edge 14LE. The thickness of the cross-section D can expand from the trailing edge 16TE to being approximately.9 inches half way to a midpoint of the cross-section which has a thickness of approximately.14 inches, and the thickness hal:!way between the midpoint and the leading edge 14LE being approximately.18 inches. FIG. SE shows the cross-section E of FIGS. 3-4 having a leading edge 141E slightly curved down being approximately degrees above the horizontal plane HP. Cross-section E has a convex shaped upper surface ls and a lower surface 17 with a concave bend configuration, and trailing edge 16TE below the horizontal plane HP. The leading edge 14LE having a more blunt rounded edge than the trailing edge 16TE. Cross-section E can have a width of approximately inches between the trailing edge 16TE and leading edge 14LE. The thickness of the cross-section E can expand from the trailing edge 16TE to being approximately.9 inches half way to a midpoint of the cross-section which has a thickness of approximately.14 inches, and the thickness 25 hal:!way between the midpoint and the leading edge 14LE being approximately.19 inches. Roof Alcove Exhaust FIG. 6 is a perspective exterior view of a roof alcove exhaust embodiment 2 incorporating the fan 1 and blades 1, 2, 3 of the preceding figures with a solar power source 1. FIG. 7 is a view of the separate components of FIG. 6. Referring to FIGS. 6-7, the novel fan 1 can be mounted with blades 1-3 facing to exhaust sideways in a housing 24 inside of an opening 22S in a gable side wall 22 below a roof 21. The outer hood 23 with louvers 23S can cover the opening 22S in the gable side wall 22. The fan motor SO can draw power through cable/power line SS from a rooftop mounted solar power source 1, which can include two PV (photovoltaic) panels 11, 12 in a frame 13 that can be directly attached (by screws, and the like) into the roof 21. An optional stand 14 can be used to elevate the solar panels 11, 12 and frame 13 above the roof21. Additional power can be provided by another solar power source lso. Roof Top Exhaust FIG. 8 is another perspective exterior view of a roof top exhaust 3 incorporating the fan 1 and blades 1, 2, 3 of the preceding figures with a solar power source 1. FIG. 9 is a view of the separate components of FIG. 8. Referring to FIGS. 8-9, the novel fan 1 can be mounted with blades 1-3 facing to upward in a housing 34 underneath an opening 21S in roof 21. The domed hood cover 33 can overhang a cylindrical housing 3SO outside roof 21 having side edges which overhang the housing 3SO with an exhaust opening 33S thereunder. Similar to FIGS. 6-7, the fan motor SO can draw power through cable/power line SS from a rooftop mounted solar power source 1, which can include two PV (photovoltaic) panels 11, 12 ina frame 13 that can be directly attached (by screws, and the like) into the roof21. An optional stand 14 can be used to elevate the solar panels 11, 12 and frame 13 above the roof21. Additional power can be provided by another solar source lso. Testing of the solar powered fan will now be described. A single low panel with an open circuit voltage of approximately 14 to approximately 15 vdc (volts direct current) was connected to the fan 1 previously described having twisted blades 1, 2, 3.
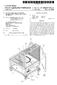
43 US 7,85,513 Bl 9 1 A conventional fan was compared to the novel fan 1 of the invention with the results shown in Table 1. The conventional fan tested was a KING OF FANS Solar Gable Ventilation Fan ( ) using a Brushless DC motor: BOM-ZYW 92/22A-3). The conventional fan used a 15 inch metal blade 5 operating at 7.3 vdc (Volts DC ma (milliamps). The novel improved fan and diffuser used novel twisted blades and a diffuser housing (described more fully below) and used the same DC motor as that of the conventional fan 1 and operated at 7.6 vdc@ 915 ma. The conventional fan got about 6. Watts of useful power (VmA) out of the standard solar powered panel while the novel fan 1 had approximately 7. Watts which would show a better match ofload to IV curve for PV panel. The IV curve is 15 the relationship of the current versus voltage characteristics of a photovoltaic cell, module, or array. The test results simulated those likely seen with two PV (photovoltaic) panels under partly sunny conditions ( approximately 11.2 Volts, approximately 1.4 amps). Tests of the two attic fans were conducted and the results are shown in TABLE 1. One test was with standard metal blades and a cylindrical housing and the second test used the novel twisted blades 1, 2, 3 and a conical diffuser housing for pressure recovery. The inventors tested both models as if they were being run by two PV panels wired parallel: 11.2 Volts DC with approximately 1.4 amp current (approximately 15.7 Watts). A calibrated flow plenum was used for the testing. TABLE 1 ConventionalAttic Novel Fan(KINGOF GRANGER Efficient Fan Type FANS -Fan) Fan Fan TotalCFM Total Watts Total CFM/Watts Table 1 further compared the GRAINGER fan (another fan) as well. Unlike the conventional fan and the novel fan, the GRAINGER fan used a standard AC shaded pole motor instead of being solar powered. The standard conventional fan (KING OF FANS ) and housing was found to move approximately 82 cfm (cubic feet per minute) at approximately. external static pressure. The improved fan 1 with the conical diffuser housing moved approximately 143 cfm at zero static pressure. The novel fan also operated at a lower RPM (revolutions per minute) and was observed to be more quiet than the conventional fan. The test results represented an approximately 3% increase in flow at the same power. Given that shaft power is increasing between the square and the cube of the air mass flow, this presents about an approximately 9% increase in the work being accomplished. The GRAINGER catalogue shows that comparable AC attic vent fans provide about 132 Watts of AC power. The GRAINGER attic vent fan retails for about $5; but that doesn't include the cost for an electrician to wire them up. Assuming that the AC attic fans might be operating 1 hours per day, the solar fans would be saving about $6 a month compared to a conventional AC powered one. The prototype diffuser used with the novel fan had the following dimensions: Narrow point in diffuser throat: 15.5 inches; Fan diameter: approximately 15 inches; Tip clearance: approximately.25 inches; Overall height of diffuser: 2 approximately inches (can shorten to about inches with lip to inlet bell); Exhaust diameter: approximately inches; and Inlet diameter: approximately 16. inches. The region in the diffuser where the fan sweeps (about 4 inches in height as indicated by the hub) should be the narrowest section (approximately 15.5 inches). Above that the diffuser smoothly increases in diameter to inches. The diffuser has an optimal angle of divergence of 7-1 degrees. In summary, the novel fan 1 can generate airflow of at least approximately 9 cfm (cubic feet per minute) from the rotating blades while running the fan with the twisted blades and the motor at an efficiency of at least approximately 6 CFM per watt. The blades can be rotated up to approximately 5 RPM while generating an airflow of at least approximately 1 cfm and up to at least approximately 14 cfm or more. Portable Fans FIG. 1 is a perspective front view of a portable fan 4 incorporating the fan 1 and blades 1, 2, 3 of the preceding figures with a solar power source 47. FIG. 11 is a rear view of the portable fan 4 of FIG. 1. The portable fan embodiment 4 combines a high efficiency fan 1 in a cylindrical housing 41 with a portable stand that can consist of a tele- 25 scopingly height adjustable pole 42 with triangular shaped base 43 having wheels 44. The triangular shaped base 43 can have a rear generally straight edge 432 with wheels 44 mounted at each end, angled sides 434, 436 meeting at a rounded apex 438. The shape of the base 43 allows the fan 4 to be easily tilted back in the direction of arrow B so that 3 a user can move the fan 4 with only two wheels 44 by gripping the handle 45 that is attached to the upper pole 42 of the portable fan A handtruck type stand 48 having an L-shape with wheels 485 on the lower end and hand rails 482 can support solar power panels (PV array) 47, with a battery 49 on the lower ledge 488. The battery power supply 49 can be connected by a power cable 475 to the photovoltaic (PV array) 47 where it becomes a PV powered charger that can be connected by another cable 495 to controls 46 to supply power to the fan 1 on the fan stand42. The fan4 can be moved for portable cooling anywhere outdoors where the cable line 495 can be extended up to approximately 5 feet or more in length from the PV powered charger. Similar to the preceding embodi- 45 ments, the fan 1 and blades 1, 2, 3 can have optimized twist and airfoil as previously described to improve air moving performance. The outdoor portable fan 4 can also use a high-efficiency brush-less DC motor 5 instead of the previously described 5 motor 5 and can be hooked to a 3 Watt PV panel 47 charging two sealed lead acid 17.2 amp-hr gel cells in the battery 49. As previously described, a power cord 495 can allow the fan 4 to be located up to approximately 5 feet or more from the solar powered panels (PV) 47. Although the 55 fan can be used outdoors, the cord 495 allows the fan 4 to be able to be used indoors with the PV panels located outdoors. Fan speed of the DC motor5 or the basic motor5 can be modulated with a knob altered pulse width modulated 6 (PWM) or resistance based control 46 to accordingly adjust speeds. With the invention using the more efficient fan it is possible to move more air than conventional portable fans. It is possible to run the fan longer on a limited battery pack or to use 65 smaller and less expensive PV panels with the invention. The novel portable fan can be operated where no electric power is available, such as in remote locations or with disaster
44 US 7,85,513 Bl 11 relief (post hurricane/post earthquake environments). The portable fan can have use in construction sites, at picnics and other outings, on camping, hiking and fishing trips and at the beach, and can be used both during the day and at night. At full speed, the fan 4 can draw approximately 1.4 amps 5 at approximately 11 volts (approximately 15 Watts). At half speed, the fan 4 can draw approximately 5 Watts. With its 34 amp per hour backup, the fan can operate for approximately 11 hours with an approximate 5% discharge with no sun. The fan 4 can use the plastic molded blades previously 1 described and as a result can be more efficient than metal blades. With an average of approximately 6 hours of sun per day, the portable fan 4 can potentially provide a continuous eight hours of daily operation at full speed, and a continuous 24 hours of operation at half speed. Portable FanAssemblies and Solar Power Panel Case Assemblies FIG. 12 is a front perspective view 5 of DC powered fan 2 assembly 51 with portable solar panel assembly 52. FIG. 13 is a rear perspective view of FIG. 12. FIG. 14 is a rear perspective view showing charge cables 64, 65 disconnected. FIG. 15A is a rear perspective view showing the rechargeable battery pack 53 separated from DC power sup- 25 ply 54. FIG. 15B shows the rechargeable battery pack 53 and AC powered battery charger 67 detached from one another. FIG. 15C shows the rechargeable battery pack 53 and AC powered battery charger 67 offig.15b attached to one another. FIG. 16 shows a left side view of the DC fan 3 assembly 51 of FIG. 12. FIG. 17 shows a front view of the DC fan assembly 51 of FIG. 16. FIG. 18 shows a right view of the DC fan assembly 51 of FIG. 16. FIG. 19 shows a rear view of the DC fan assembly 51 of FIG. 16. Referring to FIGS , the portable embodiment 5 35 can include the combination of a battery powered fan assembly 51 with a portable solar panel assembly 52. The portable solar panel assembly 52 can include a carrying case having a generally rectangular configuration with a handle 6 and having a solar panel 57 that can mounted to an inside 4 of a thin depth rectangular box 575. The bottom edges of the rear box 575 can be attached to a solar panel cover 58 with a cover hinge pin(s) 69. The cover 58 can have angled side edges 582, 588 with an open end portion 585, where the side edges can wrap about the outer side walls 572, 578 of the rear 45 box 575. Across the back of the carrying panel assembly 52 can be horizontal support bar 574, that has a support stand 59 attached thereto. Attached to the support bar 574 can be cylindrical tabs 591, 599, with inwardly angled ends 592, 598 pivotally attached thereto. There are two vertical side legs 594, 596 that extend downward with a horizontal bottom leg 595 attached to the bottoms of the two vertical side legs 594, 596. A handle 6 on top of the base 575 allows for the panel assembly 52 to be easily hand carried. The carrying case configuration allows for the panel(s) to be easily transported in a secure and safe mamier and contains the solar panel( s) in a briefcase type housing. Attached to the back of the panel assembly 52 is a solar charge cable 63A that attaches to another solar charge cable 63B by a plug and socket connector 64. The second charge cable 63B can be attached to a DC power supply 54 that powers fan assembly 51 by another cable 545, where the DC power supply 54 can be powered by a rechargeable battery pack 53. The battery pack 53 can be attached to a wall plug with transformer 66 by a charge cables 62B, 62A that can be attached to one another by another plug and socket con- 12 nectar 65. When the battery pack 53 is charged a switch 55 on the DC power supply 54 can switch on power to the motor 565 to the fan 56. Referring to FIGS. 15A-15C, the rechargeable battery pack 53 can be charged when not being used by having a plug portion 532 that plugs into a receptacle 675 on an AC powered battery charger 67, the latter of which can be plugged into a wall power supply by AC wall plug 68. Referring to FIGS , the rechargeable backup power pack 53 can be used to run the fan assembly 52 when solar power is not available such as during night-time. The fan 56 can be powered by the solar panel 57. Additionally, the rechargeable backup power pack 53 can also be recharged by the solar panel 57. With the backup power pack charged the fan can be also used indoors as well as when wall power supplies are no longer available. Also, with the plug/ transformer 66, the fan assembly 51 can be powered directly by a wall power supply and not need the use of either the rechargeable battery pack or the solar panel. Referring to FIGS , a fan speed switch 61 on the back of the drum fan 56 can control operational speeds of the blades. The blades can be similar in size and dimensions to those previously described, and include twisted blades for enhanced airflow. A carrying handle 562 on top of the cylindrical drum fan housing 56 can allow for the drum fan assembly 51 to be easily carried. AU shaped floor stand 568 having upper bent ends can be pivotally attached to opposite sides of the cylindrical drum fan housing 56. The bottom of the flat U shaped floor stand 568 can be supported off the floor by rubber footers 569. The DC power supply 54 can be fixably mounted to an upper portion of the U shaped floor stand 568, so that the power supply 54 can be carried with the drum fan 56 by the carrying handle 562 on the drum fan assembly 51. FIG. 2 is a front perspective view of the portable solar panel assembly 52 deployed. FIG. 21 is a rear perspective view of the portable solar panel assembly 52 deployed. FIG. 22 is a front perspective view of the portable solar panel assembly 52 folded for transport. FIG. 23 is a rear perspective view of the portable solar panel assembly 52 folded for transport. FIG. 24 is a left side view of the solar panel assembly 52 folded with ghosted leg 59 and cover 58 in closed and deployed positions. FIG. 25 is a front view of the folded solar panel assembly 52. FIG. 26 is a right side view of the folded solar panel assembly 52. FIG. 27 is a rear view of the folded solar panel assembly 52. FIG. 28 is another rear view of the folded solar panel assembly 52. FIG. 29 is a bottom view of the solar panel assembly 52 in a deployed position. FIG. 3 is a side view of the solar panel 5 assembly 52 in a deployed position. FIG. 31 is a front view of the solar panel assembly 52 in a deployed position. Referring to FIGS. 2-31, the solar panel carrying case assembly 52 can include cylindrical tabs 591, 599 attached with a support bar 574 on the back 575 of a rectangular box, 55 with inwardly angled ends 592, 598 pivotally attached thereto. Two vertical side legs 594, 596 that extend downward with a horizontal bottom leg 595 attached to the bottoms of the two vertical side legs 594, 596. The stand components can have a U-shape that can fold substantially flush 6 against the back of the rectangular box 575 when not being used to allow the assembly 52 to be easily carried similar to a brief case by the handle 6. The pivotal hinge portions 591, 599 allow for the stand components to be set at different deployed angles so that the solar panel 57 can be 65 oriented at different selected angles. Referring to FIGS , the novel fan assembly 51 and panel assembly 52 can be carried by a single person using
45 US 7,85,513 Bl 13 the respective handles 562, 6, allowing the invention to be easily transported as a portable fan that can be used wherever needed. While the preferred embodiments describe the fan as having plastic blades and a plastic hub molded into a single unit, 5 the invention can have separate blades attached to a separate hub. While the blades are described as preferably being made from plastic, the blades can be made from composite materials and/or from other materials, such as but not limited to metals, and the like. Metal materials that can be used include 1 but are not limited to aluminum, galvanized metal, steel, and the like. Although the preferred embodiments show the fan with three twisted blades, the invention can apply to fans having two blades, four blades or more. While the invention has been described, disclosed, illustrated and shown in various terms of certain embodiments or modifications which it has presumed in practice, the scope of the invention is not intended to be, nor should it be deemed to be, limited thereby and such other modifications or embodi- 2 ments as may be suggested by the teachings herein are particularly reserved especially as they fall within the breadth and scope of the claims here appended. We claim: 1. A portable fan assembly comprising: a fan housing having fan blades attached to a motor, the fan housing having one carrying handle; and a separate portable rectangular carrying case having a front rigid half wall section hingedly attached to a rear rigid half wall section, the front half wall section having left 3 and right rigid angled side edges and an open end with no angled side edges, the left and right rigid angled side edges wrap about outer side walls of the rear half wall section when the front half wall section and the rear half wall section are in a closed position; the front wall sec- 35 ti on folds downward into an open position; a solar panel being mounted inside of the case and attached to the rear half section; the front half wall section containing no solar panel mounted thereon, the solar panel for providing power to the motor, the solar panel being used when 4 the front wall section is in the open position, and one carrying handle projecting upward from the rigid half wall section of the carrying case between the open end of the front half wall section, and wherein the fan and panel are adapted to be carried by a single user The portable fan assembly of claim 1, wherein the fan blades include: a plurality of twisted blades attached to the motor, each blade having a twist between a root end and a tip end. 3. The portable fan assembly of claim 2, wherein the blades include: a diameter across tip ends of the blades of approximately 15 inches. 4. The portable fan assembly of claim 1, wherein the fan housing is in the form of a cylindrical housing for mounting the blades and motor therein; and wherein the fan further includes a U-shaped stand having upwardly bent ends pivotally attached to opposite sides of the cylindrical housing for supporting the fan over a ground surface. 5. The portable fan assembly of claim 1, wherein the solar panel includes: a leg assembly pivotally attached across a back of the solar panel; the leg assembly having a folded position with the leg assembly substantially flush against the back, and a 65 deployed position with the leg assembly at a bent angle so that the solar panel is oriented at a selected position The portable fan assembly of claim 5, wherein the leg assembly includes: a U-shape having inwardly projecting angled ends pivotally attached to cylindrical tabs located on the back of the solar panel, the U-shape having a lower horizontal leg portion for allowing the leg assembly to be supported over the ground surface. 7. The portable fan assembly of claim 5, wherein the leg assembly includes: a U-shaped configuration having two upper ends; each of the upper ends having inwardly angled edges that pivotally attach to cylindrical tabs that are mounted behind the rear half section of the carrying case. 8. The portable fan assembly of claim 1, further compris- 15 ing: 25 a rechargeable battery power supply for providing power to the motor of the fan when the solar panel is not being used. 9. The portable fan assembly of claim 1, further comprising: a charging adapter having a wall plug for recharging the battery power supply. 1. The portable fan assembly of claim 1, further comprising: a wall plug adapter for directly providing power to the fan and bypassing the solar panel, so that the solar panel is not needed. 11. A portable modular fan system, comprising: a single fan assembly having fan blades attached to a motor, the fan having a carrying handle, and a pivotally attached floor stand for allowing the fan to be oriented at different angles; a separate portable rectangular carrying case having a solar panel, the carrying case having a single carrying handle, and pivotally attached leg assembly, the leg assembly having inwardly protruding upper ends that are rotatable attached to cylindrical tabs that are spaced between side ends of a rear side of the carrying case, the leg assembly having a folded position with the leg assembly substantially flush against the rear side of the carrying case, the leg assembly having a deployed position with the solar panel being pivotal to different angles, the solar panel for providing power to the motor, wherein the fan and panel are adapted to be carried by a single user; and a power supply with a removable battery mounted on the floor stand of the single fan assembly. 12. The portable modular fan system of claim 11, wherein the carrying case includes a front half wall section hingedly attached to a rear half wall section, the front half wall section 5 having left and right rigid angled side edges and an open end with no angled side edges, the left and right rigid angled side edges wrap about outer side walls of the rear half wall section when the front half wall section and the rear half wall section are in a closed position, the front wall section folds downward 55 into an open position, the solar panel being mounted inside of the case and attached to the rear half section, the handle projecting upward from the rear half wail section within the open end of the front half wall section of the carrying case, wherein the front wall section folds downward into an open 6 position when the solar panel is being used. 13. A method of providing a portable fan and solar power supply, comprising the steps of: providing a fan housing having a plurality of blades mounted to a single motor, the blades being held within a grilled cage; mounting a single handle on top of the fan housing; providing a solar panel in a rectangular case;
46 US 7,85,513 Bl 15 providing the case with a front half wall section having left and right angled side edges, and an open end, and a rear half wall section, the rear half wall section having the solar panel mounted thereon, and the front half wall section containing no solar panel mounted thereon; hingedly attaching the front half wall section to a rear half wall section; wrapping the left and right angled side edges about outer side walls of the rear half wall section when the front half wall section and the rear half wall section are in a closed 1 position; mounting another single handle on the rear half wall section of the rectangular case; extending the another single handle up from the open end of the front half wall section when the front half wall 15 section and the rear half wall section of the rectangular case are in the closed position; 16 operating the solar panel when the front half wall section is folded downward from the rear hall wall section when the rectangular case is in an open position; carrying the fan housing by gripping the single fan housing handle; and carrying the rectangular case by gripping the single rectangular case handle. 14. The method of claim 13, further including the steps of: providing a U-shaped leg assembly with inwardly protruding upper ends; pivotally attaching the inwardly protruding upper ends of the leg assembly to cylindrical tabs behind the rear half wall section of the case; and unfolding the leg assembly as a stand for the case when the solar panel is used. * * * * *
High Efficiency solar power Fan.
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency solar power Fan. 3-24-2009 Danny Parker University of Central Florida Bart Hibbs AeroVironment, Inc. Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency solar power Fan. 3-24-2009 Danny Parker University of Central Florida Bart Hibbs AeroVironment, Inc. Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,507,151 B1
 USOO7507151B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,507,151 B1 Parker et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 24, 2009 (54) HIGH EFFICIENCY SOLAR POWERED FAN D261,803 S 1 1/1981 Bohanon, Jr.... D23,163
USOO7507151B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,507,151 B1 Parker et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 24, 2009 (54) HIGH EFFICIENCY SOLAR POWERED FAN D261,803 S 1 1/1981 Bohanon, Jr.... D23,163
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,692,130 B1
 USOO6692130B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Snow (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 17, 2004 (54) SOLAR POWERED HEATING AND 5,433,660 A 7/1995 Ohba VENTILATION SYSTEM FOR VEHICLE 5,588.909 A 12/1996
USOO6692130B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Snow (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 17, 2004 (54) SOLAR POWERED HEATING AND 5,433,660 A 7/1995 Ohba VENTILATION SYSTEM FOR VEHICLE 5,588.909 A 12/1996
Air Distribution Fan and Outside Air Damper Recycling Control
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Air Distribution Fan and Outside Air Damper Recycling Control 3-16-1999 Armin Rudd University of Central Florida Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Air Distribution Fan and Outside Air Damper Recycling Control 3-16-1999 Armin Rudd University of Central Florida Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
United States Patent (19) Olin et al.
 United States Patent (19) Olin et al. 54) VACUUM TOILET UNIT 75 Inventors: Henry Olin, Espoo; Gunner Lindroos, Helsinki; Roland Mattsson, Espoo, all of Finland 73 Assignee: Evac International Oy, Helsinki,
United States Patent (19) Olin et al. 54) VACUUM TOILET UNIT 75 Inventors: Henry Olin, Espoo; Gunner Lindroos, Helsinki; Roland Mattsson, Espoo, all of Finland 73 Assignee: Evac International Oy, Helsinki,
High Efficiency Twisted Leaf Blade Ceiling Fan
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Twisted Leaf Blade Ceiling Fan 7-8-28 Danny Parker University of Central Florida Tyler MacCready AeroVironment, nc. Find similar works at:
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Twisted Leaf Blade Ceiling Fan 7-8-28 Danny Parker University of Central Florida Tyler MacCready AeroVironment, nc. Find similar works at:
United States Patent 19
 United States Patent 19 USOO5853046A 11 Patent Number: 5,853,046 Williams et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 29, 1998 54) HEAT EXCHANGER SEAL APPARATUS 4.914,929 4/1990 Shimazaki. 5,036,931 8/1991 Iritani.
United States Patent 19 USOO5853046A 11 Patent Number: 5,853,046 Williams et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 29, 1998 54) HEAT EXCHANGER SEAL APPARATUS 4.914,929 4/1990 Shimazaki. 5,036,931 8/1991 Iritani.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,654,310 B2. Li (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 2, 2010
 USOO765431 OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Li (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 2, 2010 (54) LOOP HEAT PIPE 6,840,304 B1* 1/2005 Kobayashi et al.... 165,111 7,231,961 B2 * 6/2007 Alex et al....
USOO765431 OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Li (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 2, 2010 (54) LOOP HEAT PIPE 6,840,304 B1* 1/2005 Kobayashi et al.... 165,111 7,231,961 B2 * 6/2007 Alex et al....
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,361,301 B1
 USOO636.1301B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Scaglotti et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 26, 2002 (54) HEATER ASSEMBLY FOR BLOW MOLDING 5,256,341. 10/1993 Denis et al. PLASTIC PREFORMS 5,549,468
USOO636.1301B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Scaglotti et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 26, 2002 (54) HEATER ASSEMBLY FOR BLOW MOLDING 5,256,341. 10/1993 Denis et al. PLASTIC PREFORMS 5,549,468
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Oikawa et al. USOO6778394B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 17, 2004 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE HAVING A HEAT DSSPATION MEMBER (75) Inventors: Hironori Oikawa, Hadano (JP);
(12) United States Patent Oikawa et al. USOO6778394B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 17, 2004 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE HAVING A HEAT DSSPATION MEMBER (75) Inventors: Hironori Oikawa, Hadano (JP);
United States Patent Modine et al.
 United States Patent Modine et al. 54 MODULAR AR COOLED CONDENSER 72) Inventors: Arthur B. Modine; Homer D. Hug gins; Neal A. Cook, all of Racine, Wis. 73) Assignee: Modine Manufacturing Company 22 Filed:
United States Patent Modine et al. 54 MODULAR AR COOLED CONDENSER 72) Inventors: Arthur B. Modine; Homer D. Hug gins; Neal A. Cook, all of Racine, Wis. 73) Assignee: Modine Manufacturing Company 22 Filed:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,920,917 B2
 USOO6920917B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Inoue et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 26, 2005 (54) DOUBLE-PIPE HEAT EXCHANGER 5,950,716 A 9/1999 Appelquist et al.... 165/109.1 6,220,344 B1 *
USOO6920917B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Inoue et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 26, 2005 (54) DOUBLE-PIPE HEAT EXCHANGER 5,950,716 A 9/1999 Appelquist et al.... 165/109.1 6,220,344 B1 *
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,327,816 B1
 USOO6327816B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Walterscheid (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 11, 2001 (54) SIPHON APPARATUS FOR WATERING A 5,779,215 7/1998 DeMasi... 248/523 CHRISTMASTREE 6,145,250
USOO6327816B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Walterscheid (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 11, 2001 (54) SIPHON APPARATUS FOR WATERING A 5,779,215 7/1998 DeMasi... 248/523 CHRISTMASTREE 6,145,250
28, Int. Cl."... H01J 5/32 U.S. Cl /50.54; 220/4.02; 439/76.1; 361/658 Field of Search /52.3, 50.54, 701,906. part.
 United States Patent (19) Bauer et al. USOO5814765A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 29, 1998 54 (75) 56) WATERPROOF HOUSING WITH A PLUG AND-SOCKET CONNECTION FOR PROTECTION ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT
United States Patent (19) Bauer et al. USOO5814765A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 29, 1998 54 (75) 56) WATERPROOF HOUSING WITH A PLUG AND-SOCKET CONNECTION FOR PROTECTION ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT
52 U.S. Cl /95; 362/20, 362/276; of the light Switch or for receiving the electrical plug
 US00601 0228A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,010,228 Blackman et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 4, 2000 54 WIRELESS EMERGENCY SAFETY LIGHT 4,631,649 12/1986 McCue et al.... 362/183 WITH SENSING
US00601 0228A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,010,228 Blackman et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 4, 2000 54 WIRELESS EMERGENCY SAFETY LIGHT 4,631,649 12/1986 McCue et al.... 362/183 WITH SENSING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 200700.44517A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0044517 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2007 (54) DETERGENT SUPPLYING APPARATUS OF CLOTHES WASHING
(19) United States US 200700.44517A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0044517 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2007 (54) DETERGENT SUPPLYING APPARATUS OF CLOTHES WASHING
United States Patent (19) Jackson
 United States Patent (19) Jackson (54) 76 21 22) (51) 52) 58) 56) BUILDING EXTERIOR FIRE PREVENTION SYSTEM Inventor: Willie C. Jackson, 2.4808 Mission Blvd., Hayward, Calif. 94545 Appl. No.:754,792 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Jackson (54) 76 21 22) (51) 52) 58) 56) BUILDING EXTERIOR FIRE PREVENTION SYSTEM Inventor: Willie C. Jackson, 2.4808 Mission Blvd., Hayward, Calif. 94545 Appl. No.:754,792 Filed:
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9655489B2 (12) United States Patent Ha et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,655.489 B2 May 23, 2017 (54) VACUUM CLEANER (71) Applicant: LG ELECTRONICS INC., Seoul (KR) (72) Inventors:
USOO9655489B2 (12) United States Patent Ha et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,655.489 B2 May 23, 2017 (54) VACUUM CLEANER (71) Applicant: LG ELECTRONICS INC., Seoul (KR) (72) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,443,434 B1
 USOO6443434B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Prather (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2002 (54) FORCED-AIR SCENT DISPENSER 5,970,643 A 10/1999 Gawel, Jr.... 43/1 6,050,016 A * 4/2000 Cox... (76)
USOO6443434B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Prather (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2002 (54) FORCED-AIR SCENT DISPENSER 5,970,643 A 10/1999 Gawel, Jr.... 43/1 6,050,016 A * 4/2000 Cox... (76)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,371,246 B1
 USOO8371246B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,371,246 B1 Streng (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 12, 2013 (54) DEVICE FOR DRYING PETS 6,520,120 B1 2/2003 Arnold et al. 6,595,162 B1* 7/2003 Hibbert...
USOO8371246B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,371,246 B1 Streng (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 12, 2013 (54) DEVICE FOR DRYING PETS 6,520,120 B1 2/2003 Arnold et al. 6,595,162 B1* 7/2003 Hibbert...
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US B2
 USOO8432266B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.432.266 B2 Varieur (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 30, 2013 (54) PULL STATION D428,351 S 7, 2000 Hohlfelder 6,380,846 B1 4/2002 Hohlfelder (75) Inventor:
USOO8432266B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.432.266 B2 Varieur (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 30, 2013 (54) PULL STATION D428,351 S 7, 2000 Hohlfelder 6,380,846 B1 4/2002 Hohlfelder (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent
 US007 145105B2 (12) United States Patent Gaullard (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 5, 2006 (54) ELECTRIC KETTLE (75) Inventor: Hervé Gaullard, Courtefontaine (FR) (73) Assignee: SEB SA, Ecully
US007 145105B2 (12) United States Patent Gaullard (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 5, 2006 (54) ELECTRIC KETTLE (75) Inventor: Hervé Gaullard, Courtefontaine (FR) (73) Assignee: SEB SA, Ecully
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0017627 A1 Jeong et al. US 201200 17627A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) APPARATUS FOR PURIFYING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0017627 A1 Jeong et al. US 201200 17627A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) APPARATUS FOR PURIFYING
(21) Appl. No.: 418, Filed: Apr. 7, 1995 (51 Int. CI.'... F28D Ascolillo
 United States Patent (19) Middleton et al. US005605052A 11 Patent umber: 5,605,052 (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 25, 1997 (54) MIST SPRAY SYSTEM FOR REFRIGERATIO CODESERS (76) Inventors: Stephen C. Middleton;
United States Patent (19) Middleton et al. US005605052A 11 Patent umber: 5,605,052 (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 25, 1997 (54) MIST SPRAY SYSTEM FOR REFRIGERATIO CODESERS (76) Inventors: Stephen C. Middleton;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 20100205768A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0205768 A1 Oh (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 19, 2010 (54) BRUSH ASSEMBLY OF VACUUM CLEANER (30) Foreign Application
US 20100205768A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0205768 A1 Oh (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 19, 2010 (54) BRUSH ASSEMBLY OF VACUUM CLEANER (30) Foreign Application
United States Patent (19) DeLeonardis
 United States Patent (19) DeLeonardis 54 76 21 22 60 51 52 58 56 AUTOMATC NASALASPRATORS Inventor: Rocco J. DeLeonardis, P.O. Box 3093, McLean, Va. 22103 Appl. No.: 697,593 Filed: Aug. 27, 1996 Related
United States Patent (19) DeLeonardis 54 76 21 22 60 51 52 58 56 AUTOMATC NASALASPRATORS Inventor: Rocco J. DeLeonardis, P.O. Box 3093, McLean, Va. 22103 Appl. No.: 697,593 Filed: Aug. 27, 1996 Related
US A United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 6,164,575 Karkos, Jr. [45] Date of Patent: Dec. 26, 2000
![US A United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 6,164,575 Karkos, Jr. [45] Date of Patent: Dec. 26, 2000 US A United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 6,164,575 Karkos, Jr. [45] Date of Patent: Dec. 26, 2000](/thumbs/94/122228627.jpg) US006164575A United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 6,164,575 Karkos, Jr. [45] Date of Patent: Dec. 26, 2000 [54] SELF-SEATING COVER ASSEMBLY FOR A Primary Examiner Mark Rosenbaum REMOVABLE FOOD
US006164575A United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 6,164,575 Karkos, Jr. [45] Date of Patent: Dec. 26, 2000 [54] SELF-SEATING COVER ASSEMBLY FOR A Primary Examiner Mark Rosenbaum REMOVABLE FOOD
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,049,615 B1 / /?
 US00704.9615B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,049,615 B1 BrOWne (45) Date of Patent: May 23, 2006 (54) PORTABLE ULTRAVIOLET WATER (56) References Cited PURFER U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (76)
US00704.9615B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,049,615 B1 BrOWne (45) Date of Patent: May 23, 2006 (54) PORTABLE ULTRAVIOLET WATER (56) References Cited PURFER U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (76)
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO8141722B2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,141,722 B2 Heroux (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2012 (54) GARMENT HANGING DEVICE 4.948,019 8, 1990 ROdum 4,953,717 A 9, 1990 ROSch 4,972,961
(12) United States Patent USOO8141722B2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,141,722 B2 Heroux (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2012 (54) GARMENT HANGING DEVICE 4.948,019 8, 1990 ROdum 4,953,717 A 9, 1990 ROSch 4,972,961
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) 11 USOO5826803A Patent Number: 5,826,803 Cooper (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 1998 54) LAWN AND GARDEN SPRINKLER WITH 1989,525 1/1935 Moore... 239/588 X BENDABLE TUBES 2,757,960
United States Patent (19) 11 USOO5826803A Patent Number: 5,826,803 Cooper (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 1998 54) LAWN AND GARDEN SPRINKLER WITH 1989,525 1/1935 Moore... 239/588 X BENDABLE TUBES 2,757,960
US 9,466,551 Bl Oct. 11, 2016
 111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US009466551Bl c12) United States Patent Reist et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,466,551 Bl Oct. 11, 2016 (54) HEAT TRANSFERRING
111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US009466551Bl c12) United States Patent Reist et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,466,551 Bl Oct. 11, 2016 (54) HEAT TRANSFERRING
United States Patent (19) Williams
 United States Patent (19) Williams (11) 45) Sep. 11, 1979 54 PORTABLE SHAMPOO SEAT ADAPTER WITH LIQUID RUN-OFF ATTACHMENT Primary Examiner-Richard E. Aegerter Assistant Examiner-L. Footland Attorney, Agent,
United States Patent (19) Williams (11) 45) Sep. 11, 1979 54 PORTABLE SHAMPOO SEAT ADAPTER WITH LIQUID RUN-OFF ATTACHMENT Primary Examiner-Richard E. Aegerter Assistant Examiner-L. Footland Attorney, Agent,
E=Eal. United States Patent (19) Grooms NN N N E. 11) Patent Number: 4,821, Date of Patent: Apr. 11, 1989
 United States Patent (19) Grooms 54 EAR-MOUNTED ALARM CLOCK 76) Inventor: Reginald M. Grooms, Rte. 6, Box 43, Conway, S.C. 29526 21 Appl. No.: 649,591 22 Filed: Sep. 11, 1984 511 Int. Cl."... G04B 21/08
United States Patent (19) Grooms 54 EAR-MOUNTED ALARM CLOCK 76) Inventor: Reginald M. Grooms, Rte. 6, Box 43, Conway, S.C. 29526 21 Appl. No.: 649,591 22 Filed: Sep. 11, 1984 511 Int. Cl."... G04B 21/08
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,524,394 B2
 USOO6524394B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Okazawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 25, 2003 (54) DRY ICE CLEANING METHOD AND DRY 5,025,597 A 6/1991 Tada et al.... 451/39 ICE CLEANING APPARATUS
USOO6524394B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Okazawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 25, 2003 (54) DRY ICE CLEANING METHOD AND DRY 5,025,597 A 6/1991 Tada et al.... 451/39 ICE CLEANING APPARATUS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,708,183 B2
 USOO7708183B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Dautenhahn (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2010 (54) REFLOW SOLDER OVEN WITH COOLING 5,611,476 A 3, 1997 Soderlund et al. DIFFUSER 5,641,341 A * 6/1997
USOO7708183B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Dautenhahn (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2010 (54) REFLOW SOLDER OVEN WITH COOLING 5,611,476 A 3, 1997 Soderlund et al. DIFFUSER 5,641,341 A * 6/1997
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2
 US007106205B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,106.205 B2 Graef et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 12, 2006 (54) ALARM DEVICE FOR USE WITH FALL 4,846,313 A 7/1989 Sharp PROTECTION EOUIPMENT
US007106205B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,106.205 B2 Graef et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 12, 2006 (54) ALARM DEVICE FOR USE WITH FALL 4,846,313 A 7/1989 Sharp PROTECTION EOUIPMENT
United States Patent (19) Dean
 United States Patent (19) Dean 54 (76) 21) 22 63 51 52 58) 56) ARVENTTLATION CONTROL SYSTEM Inventor: Arthur C. Dean, 13403 Vimy Ridge Rd., Alexander, Ark. 72002 Appl. No.: 63,429 Filed: Jun. 18, 1987
United States Patent (19) Dean 54 (76) 21) 22 63 51 52 58) 56) ARVENTTLATION CONTROL SYSTEM Inventor: Arthur C. Dean, 13403 Vimy Ridge Rd., Alexander, Ark. 72002 Appl. No.: 63,429 Filed: Jun. 18, 1987
4-26. United States Patent (19) Woollenweber et al. R XI N Patent Number: 6,102,672 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 15, (75)
 United States Patent (19) Woollenweber et al. 54 (75) MOTOR-DRIVEN CENTRIFUGAL AIR COMPRESSOR WITH INTERNAL COOLING ARFLOW Inventors: William E. Woollenweber, Carlsbad; Edward M. Halimi, Montecito, both
United States Patent (19) Woollenweber et al. 54 (75) MOTOR-DRIVEN CENTRIFUGAL AIR COMPRESSOR WITH INTERNAL COOLING ARFLOW Inventors: William E. Woollenweber, Carlsbad; Edward M. Halimi, Montecito, both
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2
 US007191560B2 O (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,191.560 B2 Harris (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) FLYING INSECT TRAP 5,928,194 A 7/1999 Maget 5,938,640 A 8/1999 Maget (76) Inventor:
US007191560B2 O (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,191.560 B2 Harris (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) FLYING INSECT TRAP 5,928,194 A 7/1999 Maget 5,938,640 A 8/1999 Maget (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 2008.0005926A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0005926 A1 Goggin (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 10, 2008 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR REDUCING CLOTHES DRYER LINT
US 2008.0005926A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0005926 A1 Goggin (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 10, 2008 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR REDUCING CLOTHES DRYER LINT
219,432,433,436,528,529, 99,483 is ABSTRACT 56) References Cited
 USOO6075229A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,075,229 Vanselow (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2000 54). CUP WARMER HOLDER 4,442,343 4/1984 Genuit et al.... 219/433 4,463,664 8/1984 Peace......
USOO6075229A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,075,229 Vanselow (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2000 54). CUP WARMER HOLDER 4,442,343 4/1984 Genuit et al.... 219/433 4,463,664 8/1984 Peace......
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O136392A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0136392 A1 PULLIAM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 3, 2010 (54) CELL TEMPERATURE SENSING (21) Appl. No.: 12/571,926
(19) United States US 2010O136392A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0136392 A1 PULLIAM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 3, 2010 (54) CELL TEMPERATURE SENSING (21) Appl. No.: 12/571,926
A1(t1) (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1. (19) United States. Jiang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep.
 (19) United States US 2011 O232884A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0232884 A1 Jiang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2011 (54) HEAT EXCHANGER (75) Inventors: Jianlong Jiang,
(19) United States US 2011 O232884A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0232884 A1 Jiang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2011 (54) HEAT EXCHANGER (75) Inventors: Jianlong Jiang,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,397,622 B1
 USOO6397622B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,397,622 B1 Miller et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 4, 2002 (54) WATER FLOW FOR AUGERTYPE POULTRY 4,849.237 A 7/1989 Hurst CHILLER 4,860,554
USOO6397622B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,397,622 B1 Miller et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 4, 2002 (54) WATER FLOW FOR AUGERTYPE POULTRY 4,849.237 A 7/1989 Hurst CHILLER 4,860,554
(12) United States Patent
 () United States Patent Wells et al. USOO6345685B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb., 2002 (54) LOUDSPEAKER SYSTEM (76) Inventors: Leigh D. Wells; Emma-Jane Smith, both of Providence Cottage,
() United States Patent Wells et al. USOO6345685B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb., 2002 (54) LOUDSPEAKER SYSTEM (76) Inventors: Leigh D. Wells; Emma-Jane Smith, both of Providence Cottage,
United States Patent (19) Bratt
 United States Patent (19) Bratt 54) (75) (73) 21 22 63) (51) (52) (58) (56) HOT GAS ENGINE HEATER HEAD Inventor: Jan C. Bratt, Malmö, Sweden Assignee: United Stirling AB, Malmö, Sweden Appl. No.: 852,071
United States Patent (19) Bratt 54) (75) (73) 21 22 63) (51) (52) (58) (56) HOT GAS ENGINE HEATER HEAD Inventor: Jan C. Bratt, Malmö, Sweden Assignee: United Stirling AB, Malmö, Sweden Appl. No.: 852,071
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G08B 17/06 ( ) G08B 17/103 (2006.
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 2 9 A2 (43) Date of publication: 04.01.12 Bulletin 12/01 (1) Int Cl.: G08B 17/06 (06.01) G08B 17/3 (06.01) (21) Application number: 11171928.2 (22) Date
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 2 9 A2 (43) Date of publication: 04.01.12 Bulletin 12/01 (1) Int Cl.: G08B 17/06 (06.01) G08B 17/3 (06.01) (21) Application number: 11171928.2 (22) Date
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060277782A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 14, 2006 (54) NEGATIVE PRESSURE TYPE DRYING MACHINE THAT UTILIZES THE ENERGY OF THE
(19) United States US 20060277782A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 14, 2006 (54) NEGATIVE PRESSURE TYPE DRYING MACHINE THAT UTILIZES THE ENERGY OF THE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080047159A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0047159 A1 Mackay (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 28, 2008 (54) SECONDARY LINT TRAP FOR Publication Classification RESIDENTAL
(19) United States US 20080047159A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0047159 A1 Mackay (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 28, 2008 (54) SECONDARY LINT TRAP FOR Publication Classification RESIDENTAL
III. United States Patent (19) Lin 5,116,182. May 26, 1992
 United States Patent (19) Lin 54 AUTOMATIC CARPARKING SYSTEM 76 Inventor: Bao N. Lin, No. 441, Jen AI Rd., Chu Tung Town, Hsin Chu Hsien, Taiwan (21) Appl. No.: 598,969 22 Filed: Oct. 17, 1990 51 int.
United States Patent (19) Lin 54 AUTOMATIC CARPARKING SYSTEM 76 Inventor: Bao N. Lin, No. 441, Jen AI Rd., Chu Tung Town, Hsin Chu Hsien, Taiwan (21) Appl. No.: 598,969 22 Filed: Oct. 17, 1990 51 int.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kuroki et al. USOO6467288B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 22, 2002 (54) HEAT-PUMP WATER HEATER (75) Inventors: Jyouji Kuroki, Kariya (JP); Hisayoshi Sakakibara, Nishio
(12) United States Patent Kuroki et al. USOO6467288B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 22, 2002 (54) HEAT-PUMP WATER HEATER (75) Inventors: Jyouji Kuroki, Kariya (JP); Hisayoshi Sakakibara, Nishio
IIIHHHHHHHHHHHHH. United States Patent (19) CSi. 11 Patent Number: 5,318,230 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 7, Ferguson et al.
 United States Patent (19) Ferguson et al. 54 GARBAGE DISPOSAL ASSEMBLY WITH DECORATIVE SINK FLANGE MASK 75 Inventors: Lloyd G. Ferguson, Marietta, Ga.; Peter J. Taylor, Bishops Wood, United Kingdom 73)
United States Patent (19) Ferguson et al. 54 GARBAGE DISPOSAL ASSEMBLY WITH DECORATIVE SINK FLANGE MASK 75 Inventors: Lloyd G. Ferguson, Marietta, Ga.; Peter J. Taylor, Bishops Wood, United Kingdom 73)
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7356873B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,356,873 B2 Nielsen (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 2008 (54) HIGHLY EFFICIENT AUTONOMOUS 3,592,566 A 7, 1971 Beardslee VACUUM CLEANER 3,906,585
(12) United States Patent USOO7356873B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,356,873 B2 Nielsen (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 2008 (54) HIGHLY EFFICIENT AUTONOMOUS 3,592,566 A 7, 1971 Beardslee VACUUM CLEANER 3,906,585
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Tominaga 54 (75) (73) 21 22) (51) (52) (58) (56) FLTER FOR USE IN A FSH CULTURING TANK Inventor: Assignee: Kazutoshi Tominaga, Higashiosakashi, Japan Kabushiki Kaisha Tominaga
United States Patent (19) Tominaga 54 (75) (73) 21 22) (51) (52) (58) (56) FLTER FOR USE IN A FSH CULTURING TANK Inventor: Assignee: Kazutoshi Tominaga, Higashiosakashi, Japan Kabushiki Kaisha Tominaga
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,639,797 B2
 USOO66397.97B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Saeki et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 2003 (54) COMPUTER HAVING COOLING DEVICE 6,118,655 A 9/2000 Mecredy et al.... 361/687 6,315,033 B1 *
USOO66397.97B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Saeki et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 2003 (54) COMPUTER HAVING COOLING DEVICE 6,118,655 A 9/2000 Mecredy et al.... 361/687 6,315,033 B1 *
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 2015O164130A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0164130 A1 HARDING et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 18, 2015 (54) COCONUT WATER REMOVAL DEVICE AND Related U.S.
US 2015O164130A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0164130 A1 HARDING et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 18, 2015 (54) COCONUT WATER REMOVAL DEVICE AND Related U.S.
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Fingerett et al. 54) LEASH POUCH FOR ANIMAL WASTE 75 Inventors: Allison Marie Fingerett, Minneapolis, Minn.; Ricki Hope Gale, 5036 Oakland Ave. S., Minneapolis, Minn. 55417; Steven
United States Patent (19) Fingerett et al. 54) LEASH POUCH FOR ANIMAL WASTE 75 Inventors: Allison Marie Fingerett, Minneapolis, Minn.; Ricki Hope Gale, 5036 Oakland Ave. S., Minneapolis, Minn. 55417; Steven
(10) Patent No.: US 6,651,445 B1
 (12) United States Patent Clark et al. USOO6651445B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,651,445 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 25, 2003 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) FOOD CHILLER WITH IDUCTILESS AIR
(12) United States Patent Clark et al. USOO6651445B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,651,445 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 25, 2003 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) FOOD CHILLER WITH IDUCTILESS AIR
(12) United States Patent Okronick et al.
 (12) United States Patent Okronick et al. US006886759B1 (io) Patent No.: US 6,886,759 Bl (45) Date of Patent: May 3,2005 (54) WTER MISTING UMBRELL (76) Inventors: ndrew Okronick, P.O. Box 70305, Reno,
(12) United States Patent Okronick et al. US006886759B1 (io) Patent No.: US 6,886,759 Bl (45) Date of Patent: May 3,2005 (54) WTER MISTING UMBRELL (76) Inventors: ndrew Okronick, P.O. Box 70305, Reno,
(12) United States Patent
 US007997.965B2 (12) United States Patent Veuillet et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.997.965 B2 Aug. 16, 2011 (54) AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Franck Veuillet, Nievroz (FR); Eric
US007997.965B2 (12) United States Patent Veuillet et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.997.965 B2 Aug. 16, 2011 (54) AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Franck Veuillet, Nievroz (FR); Eric
(12) United States Patent
 US008011 196B2 (12) United States Patent Eber et al. (54) REFRIGERANT CONTROL OF A HEATRECOVERY CHILLER (75) Inventors: Alan Hv Eber, La Crosse, WI (US); Steven J. Pitts, LaCrescent, MN (US); Brian T.
US008011 196B2 (12) United States Patent Eber et al. (54) REFRIGERANT CONTROL OF A HEATRECOVERY CHILLER (75) Inventors: Alan Hv Eber, La Crosse, WI (US); Steven J. Pitts, LaCrescent, MN (US); Brian T.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,190,120 B1
 US007190120B1 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: SansOne et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 13, 2007 (54) AIRPORT STROBE LIGHT MONITORING 4,449,073 A * 5/1984 Mongoven et al.... 315/130 SYSTEM (75)
US007190120B1 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: SansOne et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 13, 2007 (54) AIRPORT STROBE LIGHT MONITORING 4,449,073 A * 5/1984 Mongoven et al.... 315/130 SYSTEM (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 20040188059A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0188059 A1 Todd, JR. et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004 (54) HEAT PIPE SYSTEM FOR COOLING FLYWHEEL ENERGY
(19) United States US 20040188059A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0188059 A1 Todd, JR. et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004 (54) HEAT PIPE SYSTEM FOR COOLING FLYWHEEL ENERGY
into "ill (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1 (19) United States 12d Roberts (43) Pub. Date: Feb.
 (19) United States US 2008.0034781A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0034781 A1 Roberts (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 14, 2008 (54) BEVERAGE PITCHER COLD PLATE STATION (76) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2008.0034781A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0034781 A1 Roberts (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 14, 2008 (54) BEVERAGE PITCHER COLD PLATE STATION (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0307237 A1 CHEN US 2013 0307237A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 21, 2013 (54) MEDICAL CART SYSTEM (75) Inventor: (73) Assignee: (21)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0307237 A1 CHEN US 2013 0307237A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 21, 2013 (54) MEDICAL CART SYSTEM (75) Inventor: (73) Assignee: (21)
I I IIII. United States Patent (19) McPhee. 5,537,996 Jul. 23, ) Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent:
 United States Patent (19) McPhee I I IIII US005537996A 11) Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 1996 (54) HEATED RESPIRATORY HUMIDIFIER CONDUT (75) Inventor: Stephen W. McPhee, Auckland, New Zealand
United States Patent (19) McPhee I I IIII US005537996A 11) Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 1996 (54) HEATED RESPIRATORY HUMIDIFIER CONDUT (75) Inventor: Stephen W. McPhee, Auckland, New Zealand
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,182,144 B2
 USOO718214.4B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Baba et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 27, 2007 (54) FIRE-FIGHTING ROBOT 3,768,567 A * 10/1973 Weise... 169,26 4,265,316 A 5/1981 Fee... 169/19
USOO718214.4B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Baba et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 27, 2007 (54) FIRE-FIGHTING ROBOT 3,768,567 A * 10/1973 Weise... 169,26 4,265,316 A 5/1981 Fee... 169/19
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005O183997A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0183997 A1 Happel et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2005 (54) STREET CURB FILTER BASKETSYSTEM Publication Classification
US 2005O183997A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0183997 A1 Happel et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2005 (54) STREET CURB FILTER BASKETSYSTEM Publication Classification
 ( 2 of 52 ) United States Patent 6,557,213 Winn May 6, 2003 Closed loop push/pull system for a cotton gin Abstract A closed loop push/pull system of the present invention employs a hot shelf tower dryer
( 2 of 52 ) United States Patent 6,557,213 Winn May 6, 2003 Closed loop push/pull system for a cotton gin Abstract A closed loop push/pull system of the present invention employs a hot shelf tower dryer
666,667,522, ,566,493 (7. ABSTRACT
 US005.793291A United States Patent 19 11) Patent Number: Thornton 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 11, 1998 54 CHILD ALERT SYSTEM FOR 4,812,819 3/1989 Corsberg... 340/500 AUTOMOBLES 4,831,361 5/1989 Kimura......
US005.793291A United States Patent 19 11) Patent Number: Thornton 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 11, 1998 54 CHILD ALERT SYSTEM FOR 4,812,819 3/1989 Corsberg... 340/500 AUTOMOBLES 4,831,361 5/1989 Kimura......
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004O232165A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 25, 2004 (54) GLUE GUN (52) U.S. Cl.... 222/146.5 (76) Inventor: Kuo-Jium Lee, Taichung (TW)
US 2004O232165A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 25, 2004 (54) GLUE GUN (52) U.S. Cl.... 222/146.5 (76) Inventor: Kuo-Jium Lee, Taichung (TW)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070074369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0074369 A1 Stuthers et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 5, 2007 (54) DUAL PURPOSE FLOOR CLEANING APPARATUS AND METHOD
(19) United States US 20070074369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0074369 A1 Stuthers et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 5, 2007 (54) DUAL PURPOSE FLOOR CLEANING APPARATUS AND METHOD
United States Patent (19) Smith et al.
 United States Patent (19) Smith et al. 54 AUTOMATIC CLOTHES WASHING MACHINES 75 Inventors: Dennis E. Smith; Graeme D. Thomas; Keith D. Ferguson, all of Auckland, New Zealand 73) Assignee: Fisher & Paykel
United States Patent (19) Smith et al. 54 AUTOMATIC CLOTHES WASHING MACHINES 75 Inventors: Dennis E. Smith; Graeme D. Thomas; Keith D. Ferguson, all of Auckland, New Zealand 73) Assignee: Fisher & Paykel
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,588,330 B1
 USOO658833OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,588,330 B1 Importico (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 8, 2003 (54) TRASH COMPACTOR SYSTEM 5,425,458 6/1995 Gilcreest et al. 5,551,576 A 9/1996 Importico
USOO658833OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,588,330 B1 Importico (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 8, 2003 (54) TRASH COMPACTOR SYSTEM 5,425,458 6/1995 Gilcreest et al. 5,551,576 A 9/1996 Importico
United States Patent (19) Mays et al.
 United States Patent (19) Mays et al. 54 DRUM WITH INTERNAL STATIC MDXER 75 Inventors: Harry Mays, Merced; Michael Morrison, Stockton, both of Calif. 73 Assignee: North American Packaging Company, Merced,
United States Patent (19) Mays et al. 54 DRUM WITH INTERNAL STATIC MDXER 75 Inventors: Harry Mays, Merced; Michael Morrison, Stockton, both of Calif. 73 Assignee: North American Packaging Company, Merced,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O140251A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0140251A1 Hsiao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 22, 2004 (54) ULTRAVIOLET CLEANING WATER DEVICE (76) Inventor: Chih-Ling
(19) United States US 2004O140251A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0140251A1 Hsiao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 22, 2004 (54) ULTRAVIOLET CLEANING WATER DEVICE (76) Inventor: Chih-Ling
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7370387 B2 (12) United States Patent Walker et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 13, 2008 (54) HAND-HOLDABLE VACUUM CLEANERS (75) Inventors: Andrew Walker, Newton Hall (GB); Eric Coburn,
USOO7370387 B2 (12) United States Patent Walker et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 13, 2008 (54) HAND-HOLDABLE VACUUM CLEANERS (75) Inventors: Andrew Walker, Newton Hall (GB); Eric Coburn,
United States Patent (19) More
 United States Patent (19) More 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 27, 1984 54 SHREDDING MACHINE FOR RECYCLING TEXT LE FIBERS AND METHOD (75) Inventor: André Morel, La Croix du Mont, France (73)
United States Patent (19) More 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 27, 1984 54 SHREDDING MACHINE FOR RECYCLING TEXT LE FIBERS AND METHOD (75) Inventor: André Morel, La Croix du Mont, France (73)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,647,932 B1
 USOO664.7932B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cui et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 18, 2003 (54) COMPACT BOILER WITH TANKLESS (56) References Cited HEATER FOR PROVIDING HEAT AND DOMESTIC HOT
USOO664.7932B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cui et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 18, 2003 (54) COMPACT BOILER WITH TANKLESS (56) References Cited HEATER FOR PROVIDING HEAT AND DOMESTIC HOT
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US006 173454B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,173,454 B1 Alvarez (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 16, 2001 (54) JONNISAFE 5,191,991 3/1993 Jackson... 220/207 5,347,663 9/1994 Yost... 4/253 (76)
(12) United States Patent US006 173454B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,173,454 B1 Alvarez (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 16, 2001 (54) JONNISAFE 5,191,991 3/1993 Jackson... 220/207 5,347,663 9/1994 Yost... 4/253 (76)
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,794,685 Dean 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1998
 USOO5794685A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Dean 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1998 (54) HEAT SINK DEVICE HAVING RADIAL 5,029.236 7/1991 Yasuda et al.... 455/90 HEAT AND AIRFLOW PATHS 5.191,330
USOO5794685A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Dean 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1998 (54) HEAT SINK DEVICE HAVING RADIAL 5,029.236 7/1991 Yasuda et al.... 455/90 HEAT AND AIRFLOW PATHS 5.191,330
San Francisco, Calif (21) Appl. No.: 810, Filed: Jun. 27, Int. Cl... B01F3/04 52 U.S. C /119 R; 55/244;
 United States Patent (19) Genessi (54) LINT INTERCEPTOR 76 Inventor: Richard J. Genessi, 2434 Rivera St., San Francisco, Calif. 941 16 (21) Appl. No.: 810,387 22 Filed: Jun. 27, 1977 51 Int. Cl... B01F3/04
United States Patent (19) Genessi (54) LINT INTERCEPTOR 76 Inventor: Richard J. Genessi, 2434 Rivera St., San Francisco, Calif. 941 16 (21) Appl. No.: 810,387 22 Filed: Jun. 27, 1977 51 Int. Cl... B01F3/04
High Efficiency Air Conditioner Condenser Fan
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Air Conditioner Condenser Fan 8429 Danny Parker University of Central Florida Bart Hibbs AeroVironment, Inc. John Sherwin University of
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Air Conditioner Condenser Fan 8429 Danny Parker University of Central Florida Bart Hibbs AeroVironment, Inc. John Sherwin University of
United States Patent (19) Moore, Jr. et al.
 United States Patent (19) Moore, Jr. et al. 54 76 AUTOMATIC SEALING SPRINKLER HEAD ADAPTER AND FIRE PROTECTION SPRINKLER SYSTEM Inventors: Fred D. Moore, Jr., 155 Hunt Dr., Horsham, Pa. 19044; Robert L.
United States Patent (19) Moore, Jr. et al. 54 76 AUTOMATIC SEALING SPRINKLER HEAD ADAPTER AND FIRE PROTECTION SPRINKLER SYSTEM Inventors: Fred D. Moore, Jr., 155 Hunt Dr., Horsham, Pa. 19044; Robert L.
Lathim (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014
 (12) United States Patent USOO883.2901 B2 (10) Patent No.: Lathim (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 (54) HAND-OPERABLEVACUUM DEVICE (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: Del Lathim, Pasco, WA (US) U.S.
(12) United States Patent USOO883.2901 B2 (10) Patent No.: Lathim (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 (54) HAND-OPERABLEVACUUM DEVICE (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: Del Lathim, Pasco, WA (US) U.S.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,182,077 B2. DOse (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 10, 2015
 US009 182077B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,182,077 B2 DOse (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 10, 2015 (54) TENTACLE GRIPSUCTION HOLDER FOR (56) References Cited HAND HELD ELECTRONICS U.S. PATENT
US009 182077B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,182,077 B2 DOse (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 10, 2015 (54) TENTACLE GRIPSUCTION HOLDER FOR (56) References Cited HAND HELD ELECTRONICS U.S. PATENT
-10 US 6,964,355 B2. Nov. 15, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: (12) United States Patent (54) (75) (73)
 (12) United States Patent Landau USOO6964355B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 15, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) DRY FOOD DISPENSING SYSTEM Inventor: Ofer Landau, Even
(12) United States Patent Landau USOO6964355B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 15, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) DRY FOOD DISPENSING SYSTEM Inventor: Ofer Landau, Even
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,176,097 B1. Kim (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001
 USOO6176097B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kim (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SIDE BY SIDE TYPE REFRIGERATOR AND 5,477,699 12/1995 Guess et al.... 62/187 METHOD FOR CONTROLLING 5,732,561
USOO6176097B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kim (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SIDE BY SIDE TYPE REFRIGERATOR AND 5,477,699 12/1995 Guess et al.... 62/187 METHOD FOR CONTROLLING 5,732,561
United States Patent (19) Anwunah et al.
 United States Patent (19) Anwunah et al. (54) BATH ROOM SOAP RECYCLING DEVICE 76 Inventors: Vincent Anwunah, John Anwunah, both of 12015 Prest, Detroit, Mich. 48227 (21) Appl. No.: 398,357 (22 Filed: Mar.
United States Patent (19) Anwunah et al. (54) BATH ROOM SOAP RECYCLING DEVICE 76 Inventors: Vincent Anwunah, John Anwunah, both of 12015 Prest, Detroit, Mich. 48227 (21) Appl. No.: 398,357 (22 Filed: Mar.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,014,690 B2
 USOO7014690B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,014,690 B2 Mitsch et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2006 (54) EXPANDABLE DESICCANTELEMENT 5,689,893 A 11/1997 Mitsch 5,715,621. A 2/1998
USOO7014690B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,014,690 B2 Mitsch et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2006 (54) EXPANDABLE DESICCANTELEMENT 5,689,893 A 11/1997 Mitsch 5,715,621. A 2/1998
TEPZZ A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: F25D 25/02 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 7 8 84A T (11) EP 2 728 284 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 07.0.14 Bulletin 14/19 (1) Int Cl.: F2D 2/02 (06.01) (21) Application number: 13191. (22) Date of filing:
(19) TEPZZ 7 8 84A T (11) EP 2 728 284 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 07.0.14 Bulletin 14/19 (1) Int Cl.: F2D 2/02 (06.01) (21) Application number: 13191. (22) Date of filing:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Demers USOO6648198B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 18, 2003 (54) VACUUM BELT CONVEYOR (75) Inventor: Sylvain Demers, St. Louis de France (CA) (73) Assignee: Voith
(12) United States Patent Demers USOO6648198B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 18, 2003 (54) VACUUM BELT CONVEYOR (75) Inventor: Sylvain Demers, St. Louis de France (CA) (73) Assignee: Voith
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004.0099384A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0099384 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: May 27, 2004 (54) ART WALL PAINTING CURTAIN STRUCTURE (76) Inventor: Chieh-Yuan
(19) United States US 2004.0099384A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0099384 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: May 27, 2004 (54) ART WALL PAINTING CURTAIN STRUCTURE (76) Inventor: Chieh-Yuan
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,162,751 B2. Mundt (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 16, 2007
 US007162751B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,162,751 B2 Mundt (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 16, 2007 (54) VENTILATED TOILET SYSTEM 4,232,406 A 11/1980 Beeghly et al.... 4,213 5,029,346 A 7/1991
US007162751B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,162,751 B2 Mundt (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 16, 2007 (54) VENTILATED TOILET SYSTEM 4,232,406 A 11/1980 Beeghly et al.... 4,213 5,029,346 A 7/1991
US 7,588,275 B2. Borg. Sep. 15, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: (56) (12) United States Patent (54) (75) (73)
 US007588275 B2 (12) United States Patent Borg (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,588,275 B2 Sep. 15, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) COMBINATION MULTIPLE-CANISTER CARRIER
US007588275 B2 (12) United States Patent Borg (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,588,275 B2 Sep. 15, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) COMBINATION MULTIPLE-CANISTER CARRIER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014.0137369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0137369 A1 Street (43) Pub. Date: May 22, 2014 (54) SELF-SANITIZING DOOR HANDLE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A47K
(19) United States US 2014.0137369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0137369 A1 Street (43) Pub. Date: May 22, 2014 (54) SELF-SANITIZING DOOR HANDLE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A47K
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8, B2
 USOO8066475B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,066.475 B2 Bulgrin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 29, 2011 (54) LABYRINTH COMPRESSION SEAL AND (56) References Cited TURBINE NCORPORATING
USOO8066475B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,066.475 B2 Bulgrin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 29, 2011 (54) LABYRINTH COMPRESSION SEAL AND (56) References Cited TURBINE NCORPORATING
United States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 5,033,657
 United States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 5,033,657 Whittington 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 1991 54 ADJUSTABLESTROKE PUMP DISPENSER 4,978,036 12/1990 Burd... 222/2O7 75) Inventor: Jimmie L. Whittington,
United States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 5,033,657 Whittington 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 1991 54 ADJUSTABLESTROKE PUMP DISPENSER 4,978,036 12/1990 Burd... 222/2O7 75) Inventor: Jimmie L. Whittington,
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,164,247 Iwasaki et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 26, 2000 LLP
 USOO6164247A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Iwasaki et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 26, 2000 54 INTERMEDIATE FLUID TYPE WAPORIZER, 4,417,951 11/1983 Stanisic et al.... 122/492 AND NATURAL
USOO6164247A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Iwasaki et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 26, 2000 54 INTERMEDIATE FLUID TYPE WAPORIZER, 4,417,951 11/1983 Stanisic et al.... 122/492 AND NATURAL
High Efficiency Air Conditioner Condenser Fan with Performance Enhancements
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Air Conditioner Condenser Fan with Performance Enhancements 7-31-27 Danny Parker University of Central Florida John Sherwin University of
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Air Conditioner Condenser Fan with Performance Enhancements 7-31-27 Danny Parker University of Central Florida John Sherwin University of
