LIGHTNING AND DECLINE OF CITRUS TREES IN
|
|
|
- Charlotte Ferguson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 8 FLORIDA STATE HORTICULTURAL SOCIETY, 972 sufficient cold temperatures have occurred to induce cold hardiness in citrus. The lack of hardiness-inducing temperatures during this study did not permit adequate comparison of the 2 threshold temperatures. Under conditions of a more typical Florida winter identification of cold-hardiness inducing periods might be better defined by one or the other threshold temperature. In this study the accepted threshold temperature of 55 was found satisfactory. Although 'Temple' orange is considered to be a less cold hardy variety than 'Hamlin' orange by published ob servational data, this and other research with leaf-freezing points indicates that 'Temple' and 'Hamlin' orange can acquire similar degrees of hardiness if adequate pre-conditioning tempera tures are experienced. Citrus cold hardening temperatures of 55 and 5 occurred more fre quently at Gainesville, least frequently at Dun dee, and with intermediate frequency at Leesburg. The LFP values increased in a highly significant manner as hardiness-inducing tem peratures decreased from Gainesville to Dundee. Literature Cited. Cooper, W. C Cold hardiness in citrus as re lated to dormancy. Proc. Pla. State Hort. Soc. 72: Cooper, W. C, B. S. Gordon and S. D. Tayloe. 95. Freezing tests with small trees and detached leaves of grapefruit. Proc. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 63: , Jack Hearn, Gordon K. Rasmussen, and Roger H. Young The Florida freeze. Calif. Citrograph. 8: Gerber, J. F. and F. Hashemi The freezing point of citrus leaves. Proc. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 86: Hearn, C. J., et al Influence of variety and rootstock upon freeze injury to citrus trees in the 962 Florida freeze. Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 76: Hendershott, C. H The responses of orange trees and fruits to freezing temperatures. Proc. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 86: Hutcheson, C. E. 97. Leaf freezing points and cold hardiness of citrus. Master's Thesis. Univ. of Fla., Gaines ville. 8., and W. J. Wiltbank. 97. Cold hardiness of selected citrus varieties as determined by freezing de tached leaves. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 83: , and 972. The freezing point of detached leaves as a measure of cold hardiness of young budded citrus plants. HortScience. 7() : Jackson, L. K. and J. F. Gerber Cold tolerance and freezing point of citrus seedlings. Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 76:7-7.. Lindsey, R. J. 97. Environment and citrus cold hardiness. Master's Thesis. Univ. of Fla., Gainesville. 2. McCown, J. T Field observations of Florida citrus following the freezes. Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 7: Sites, J. W. 96. Preconditioning of plants in rela tion to cold tolerance. Fla. Agr. Exp. Sta. Ann. Rept. 96: 2.. Young, Roger Cold hardening in citrus seed lings as related to artificial hardening conditions. J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 9(6): Young, R. H., and A. Peynado. 96. Effects of artificial freezing on Red Blush grapefruit. J. Rio Grande Valley Hort. Soc. 5: , and A. Peynado Growth and cold hardiness of citrus and related species when exposed to different night temperatures. Proc. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 8: LIGHTNING AND DECLINE OF CITRUS TREES IN E. P. DuCharme FLORIDA IF AS Agricultural Research and Education Center Lake Alfred Abstract. Each year lightning either direct y or indirectly causes considerable tree loss in Florida citrus groves. One to many trees may be affected by one or more lightning strikes in any grove at one time. The number of trees affected by one strike depends on the size of the discharge area and the planting distance of the trees. The largest number of trees known to have been killed by lightning during one storm was,77 trees in 9 acres of a flatwoods grove. Usually, or 2 trees may be killed when the strike occurs and others will be affected to a Florida Agricultural Experiment Station Journal Series No. 65. GROVES lesser degree progressing from the center of the strike to the periphery of the discharge area. Frequently, some of the more severely affected trees near the center of the strike area decline gradually and die from what appears to be root rot, heart rot, or foot rot within to 3 years after the strike. The less affected trees on the periphery of the discharge area generally do not decline or die. The secondary effects of lightning strikes on citrus trees may have the appearance of a disease spreading through the grove. The symptoms of lightning injury differ from those of rough lemon decline and other declines; but when lightning injury is superimposed on some other condition, the causes of the decline and loss of trees may be obscure. Lightning* is a spectacular and frequent phe nomenon in citrus groves of Florida. Some of the effects of lightning on citrus trees were
2 DUCHARME: LIGHTNING INJURY 8 recognized and described by Stevens in 98 (, 2, 3). Later lightning was determined to be the cause of decline and loss of trees in.% of the groves surveyed for spreading decline caused by the burrowing nematode, Radophohis similis (Cobb) Thorne 99 (). Each year, lightning either directly or indirectly continues to be the cause of decline and loss of many trees in Florida citrus groves. Sometimes the effect of lightning on citrus is clear and precise, but frequently its effects are quite subtle and are not immediately apparent. Often the effects of lightning injury are slow to appear and decline develops long after the strike has occurred, and the storm that produced the discharge has been forgotten. Then the most recent disease to plague citrus or perhaps a newly introduced pesticide, herbicide, and even fertilizer materials might be blamed for the condition. It is even commonplace to have light ning damage confused with the decline and loss of trees caused by tristeza, spreading decline, root rots, flood damage, and more recently by Young Trea Decline and Sand Hill Decline fre quently called rough lemon decline. Because this confusion can and does happen, it was deemed appropriate to present information regarding the kinds and extent of damage caused by lightning in Florida citrus groves and compare the characteristics of lightning injury and rough lemon decline. Characteristics of Lightning Injury in Citrus The effects of lightning on citrus are not characterized by physical violence as often hap pens when lightning strikes other kinds of trees. There is no obvious mechanical damage to citrus at the time of the strike and no fires are started. Branches are not wrenched from the tree and bark is not torn from the trunk or branches by the force of the discharge. Sometimes inconspicious narrow slits may be observed in patches of killed bark on large branches, trunk, and crown roots. These slender splits in the bark are not evident for several days after the strike has occurred. Usually, the first symptoms that become evi dent are permanent wilting of the foliage, yellow ing of the midveinis and leaf blades, and de foliation. Wilting of leaves may start within to 6 hr. after the strike. Leaves of affected trees abscise between the petiole and blade. Peti oles usually remain attached for a while but eventually drop. Death of the foliage may be so rapid that it dries, turns brown, and may re main attached for several weeks. Such trees have the superficial appearance of having been damaged by fire or cold. These foliar symptoms may occur on all or only a portion of the tree depending upon the intensity of the discharge and how much of the tree was injured. One of the most characteristic symptoms to appear on trees struck by lightning is the injury to young green shoots and twigs. Small round to large irregularly shaped patches of green bark between the buds are killed and become tannish gray to brown while the bark surround ing the buds is apparently not damaged and remains green. These irregular shaped patches of injured bark may girdle the small stems or twigs, coalesce into larger areas but the buds remain green and isolated by the brown dead bark. The green bud surrounded by dead bark is a transitory symptom and appears only on the small green shoots and twigs where the discharge occurred. This symptom is evident for only a few weeks and the green disappears as the injured twigs and stems die. This "greenbud-island" symptom has not been observed on tress affected by any other disorder and may be considered specific for.lightning injury. Injured terminal twigs most commonly occur at the top of the tree but may be observed at any place on the periphery of the canopy, even on the tips of branches in contact with the soil or with the cover crop. Patches of bark may be killed on the trunk, main scaffold, and small branches in the path way of the lightning discharge. Ocassionally, a continuous strip of bark or all of the bark on the trunk and one of the main branches will be killed from below the soil surface to the top of the tree. Within a few days, the injured bark develops a water-soaked appearance and becomes somewhat darker than the unaffected adjacent bark. Wood and inner bark in the affected areas become somewhat yellow and gum may begin to accumulate between the wood and injured bark. This gum deposit may account for some of the yellow discoloration. The affected bark is softer than the healthy bark and gradually becomes more granular as it dries and blackens. The blackened bark crumbles readily when rubbed, splits longitudinally as the disintegration and drying proceeds, separates from the wood, and often falls from the tree. The size of the dead patches and total amount of bark killed in struck trees varies with the intensity of the discharge. Injured bark and wood on the trunk and
3 82 FLORIDA STATE HORTICULTURAL SOCIETY, 972 branches become points of entry for wood borers such as shot hole borers and flat headed borers. Several species of Scolytids commonly known as "shot hole borers" invade bark and wood killed by the lightning discharge. Shot hole borers usually enter into killed tissues within 8 to days after the strike has occurred; but if pene tration takes place, a few days after the strike, a small drop of gum will accumulate on the surface of the bark over the entrance hole. The areas of bark and wood killed by the discharge are detected frequently by slender cylinders of white to gray wood detritus protruding from the small holes made by shot hole borers as they penetrate. These slender columns of detritus are approximately /6 inch in diameter and up to /2 inch long. A flat headed borer, Chrysobothris chryseola, commonly invades and feeds only on dead inner bark, phloem, and cambium. The roots of trees struck by lightning may be killed, severely damaged, or not affected, depend ing upon the intensity of the discharge. If the damage is severe, death of the roots is immedi ate and bark decay and disintegration take place rapidly. Bark on killed roots soon becomes soft, water-soaked, turns brown and granular, and finally black. If the discharge strike is relatively mild and only weakens the tree, then root rot develops slowly and such trees may either die of root rot to 3 years later or may recover. Another symptom frequently observed on trees struck by lightning is a band of injured bark to 2 inches wide just under the soil surface. This band of dead bark is often present even though no other bark damage can be detected on the tree or trees struck in the discharge area. This narrow band of killed bark may be made up of a series of small areas on one side of the tree or may completely girdle the trunk as a continuous band of dead bark. If the damage is not extensive or too severe, new wood and bark may be regenerated over the injuries and the trees recover. Exposed wood may also become infected by wood invading organisms such as Ganoderma spp. which cause further trunk de struction. Trees in the later stages of lightninginduced trunk decay might be erroneously diag nosed as initially caused by wood rot organisms. Long range effects on lightning struck trees become evident only or more years after the discharge occurred. Trees mildly to moderately injured by the discharge may be weakened and predisposed to secondary infection by bark and wood rot organisms. These trees may decline and die at first in the center of the strike then pro gressively towards the periphery of the dis charge area. When this happens, the decline and loss of these trees could easily be interpreted as a disease spreading in the grove. Not all trees in a strike area are visibly damaged and some may be only slightly injured but suffer little or no permanent damage. For example, a 5-acre block of 35 trees 2 years old was struck and every tree had at least one green shoot with typical symptoms of lightning injury, i.e., green buds and dead bark. No trees were killed at the time and none were reported to have died during the next years. These trees recover from the shock and perhaps may be struck again years later. It is, therefore, possible that lightning could strike the same tree or trees more than once. Lightning can strike in groves at any time during the year when thunder storms occur. Ordinarily most strikes take place during the summer and infrequently during spring and fall. Known strikes affecting many trees in blocks of or more acres occurred during August in flatwoods areas. Five unusually large strikes have been recorded during August during the past 3 years. The number of trees struck by one strike depends on the size of the discharge area and on the tree spacing. The recognized number of trees struck in groves during any one storm has varied from one to more than 3,. Usually, less than 2 trees are affected in discrete dis charge areas with only to 3 trees killed or several damaged. The number of strike areas in a grove during a storm likewise may vary from one to several depending on the frequency and intensity of the lightning discharges. The size of known discharge areas can and does vary from one tree space to as much as acres. The largest lightning strike known up to the present in one grove during one storm in volved 3 acres in 3 contiguous -acre blocks of 9 trees each. Three weeks after the strike,59 trees were dead or severely damaged and G v/eeks later 3,296 were either dead, severely damaged, or had symptoms of lightning injury, Table. According to the groupings of trees injured or killed in these blocks, there were 3 discharge centers, Table. Affected trees were also noted in other blocks immediately adjacent to the blocks where most of the damage was concentrated. The shape of the discharge areas as reflected by the distribution, of killed and injured trees is extremely variable. The common shape of strike
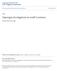
4 DUCHARME: LIGHTNING INJURY 83 Table. Number of trees years old killed or injured by lightning in 3 blocks of acres each in a flatwoods grove during a storm in mid-august, weeks after storm 6 week s after storm Trees dead or in Trees Advanced Twig Total affected Block No. advanced- decline dead decline injury No. Percent Total,59 936,69,25 3, or discharge areas is either an irregular circle of oval or it may be somewhat pear shaped. Occasionally, the area involved may be either lenticular or half moon shaped. A large and very unusual distribution of injured trees in approxi mately acres of grove is illustrated in Fig.. Citrus tree damage due to lightning strikes has been found in all areas of the State where citrus is grown. It is difficult to determine where most of the strikes occur because not all strikes are detected and only relatively few are reported. Groves where the largest strikes have occurred recently are mostly flatwoods groves particularly in the Arcadia, La Belle, and Immokalee areas. Trees along roads, wide middles, and edges of groves next to open areas seem to be hit more frequently than the interior of the groves. Perhaps this is only apparently so because these trees are seen most frequently. Comparison of Lightning Damage and Rough Lemon Decline. Lightning strikes, like rough lemon decline, may occur at any place in a grove. 2. There is no spread from tree to tree of de cline caused by lightning either within or outside the lightning discharge area. Only trees actually struck by lightning decline and die within local ized areas. Rough lemon decline gradually spreads throughout the blocks or groves of susceptible trees until all of the susceptible trees become affected. 3. Lightning strikes trees of all ages from those in nurseries to mature trees more than Fig.. A lightning discharge area in a flatwoods grove of trees 7 years old. The strike or strikes took place during a storm, August 7, 97, and the photograph was taken November 23, 97 after the killed trees had been pulled.
5 8 FLORIDA STATE HORTICULTURAL SOCIETY, years old. Rough lemon decline on the other hand has been observed to affect only trees that are more than 5 years old.. Trees that decline and die from lightning injury commonly develop root rot and perhaps foot rot, whereas rough lemon decline does not. 5. Not all trees struck by lightning die. Sus ceptible trees on rough lemon rootstocks have not been known to permanently recover once they have developed symptoms of rough lemon decline. When lightning and rough lemon decline simultaneously affect trees in a block or grove, the decline and death of trees can be spectacular. When this happens, the cause or causes of the decline may not be readily apparent and may lead to confusion as well as consternation. There seems to be no way to avoid lightning damage in citrus groves other than possibly equipping each tree with lightning rods. It can be expected that lightning will continue to cause considerable tree loss each year; and in some years, there will be more damage than in other years. There seems to be no prospect that these losses will diminish in the future, especially in the flatwoods areas. Literature Cited. Rhoads, Arthur S., and E. F. DeBusk. 93. Diseases of citrus in Florida. Univ. Fla. Agr. Expt. Sta. Bui p Stevens, H. E. 98. Lightning injury to citrus trees in Florida. Phytopathology 8: Florida citrus diseases. Univ. Fla. Agr. Expt. Sta. Bui. 5. p Suit, R. F., and E. P. DuCharme. 97. Citrus de cline. The Citrus Ind. 28(7) :5-8, 3.
USE OF THE ETIOLATION TECHNIQUE IN ROOTING AVOCADO CUTTINGS
 California Avocado Society 1971-72 Yearbook 55: 97-109 USE OF THE ETIOLATION TECHNIQUE IN ROOTING AVOCADO CUTTINGS Edward F. Frolich and Robert G. Platt Technician IV, Department of Agricultural Science.
California Avocado Society 1971-72 Yearbook 55: 97-109 USE OF THE ETIOLATION TECHNIQUE IN ROOTING AVOCADO CUTTINGS Edward F. Frolich and Robert G. Platt Technician IV, Department of Agricultural Science.
The Sun-Blotch Disease of Avocado
 Proceedings of the Rio Grande Valley Horticultural Society 1958 12:69-74 The Sun-Blotch Disease of Avocado J. M. WALLACE University of California, Riverside Unlike most economic plants, the avocado (Persea
Proceedings of the Rio Grande Valley Horticultural Society 1958 12:69-74 The Sun-Blotch Disease of Avocado J. M. WALLACE University of California, Riverside Unlike most economic plants, the avocado (Persea
AL TERNA TE BEARING OF CITRUS IN FLORmA
 AL TERNA TE BEARING OF CITRUS IN FLORmA T. A. WHEATON University of Florida Citrus Research and Education Center 7 Experiment Station Road Lake Alfred, FL 3385 The severity of alternate bearing varies
AL TERNA TE BEARING OF CITRUS IN FLORmA T. A. WHEATON University of Florida Citrus Research and Education Center 7 Experiment Station Road Lake Alfred, FL 3385 The severity of alternate bearing varies
Plant Pathology Fact Sheet
 Plant Pathology Fact Sheet PP-28 Citrus Scab Tom Kucharek and Jack Whiteside, Professor and Extension Plant Pathologist, Department of Plant Pathology; and Professor Emeritus - Plant Pathologist, Citrus
Plant Pathology Fact Sheet PP-28 Citrus Scab Tom Kucharek and Jack Whiteside, Professor and Extension Plant Pathologist, Department of Plant Pathology; and Professor Emeritus - Plant Pathologist, Citrus
air flow) will help keep foliage dry. Spray with maneb or mancozeb on a 7-10 day schedule if the disease
 SNAPDRAGON DISEASES /?. W. Judd, Jr. Extension Horticulturist Snapdragons are susceptible to many diseases. Some attack the stems, leaves and flowers while others attack the root systems. The following
SNAPDRAGON DISEASES /?. W. Judd, Jr. Extension Horticulturist Snapdragons are susceptible to many diseases. Some attack the stems, leaves and flowers while others attack the root systems. The following
Managing Phosphorus Fertilization of Citrus using Soil Testing 1
 SL 186 Managing Phosphorus Fertilization of Citrus using Soil Testing 1 Thomas A. Obreza 2 Introduction The purpose of this publication is to provide a brief review of phosphorus (P) fertilization practices
SL 186 Managing Phosphorus Fertilization of Citrus using Soil Testing 1 Thomas A. Obreza 2 Introduction The purpose of this publication is to provide a brief review of phosphorus (P) fertilization practices
Pests of Ornamentals and Turfgrass
 Kentucky Pesticide Education Program copyright 2016 University of Kentucky Department of Entomology Pests of Ornamentals and Turfgrass Diseases of Turfgrass Accurate identification and diagnosis of plant
Kentucky Pesticide Education Program copyright 2016 University of Kentucky Department of Entomology Pests of Ornamentals and Turfgrass Diseases of Turfgrass Accurate identification and diagnosis of plant
Plant Pathology Fact Sheet
 Plant Pathology Fact Sheet PP-26 Melanose and Phomopsis Stem-End Rot of Citrus Tom Kucharek, Jack Whiteside, and Eldon Brown, Professor and Extension Plant Pathologist, Plant Pathology Department; Professor
Plant Pathology Fact Sheet PP-26 Melanose and Phomopsis Stem-End Rot of Citrus Tom Kucharek, Jack Whiteside, and Eldon Brown, Professor and Extension Plant Pathologist, Plant Pathology Department; Professor
Drought Induced Problems in Our Orchards. Ben Faber
 Drought Induced Problems in Our Orchards Ben Faber Abiotic disorders are plant problems that are non-infective. They are not caused by an organism, but through their damage, they may bring on damage caused
Drought Induced Problems in Our Orchards Ben Faber Abiotic disorders are plant problems that are non-infective. They are not caused by an organism, but through their damage, they may bring on damage caused
Central Florida Youth
 Central Florida Youth Peach Tree Growing Contest UF/IFAS Polk County Extension Service 1702 US Hwy 17-98 South P.O. Box 9005, Drawer HS03 Bartow, FL 33831-9005 Osceola County Extension Service Osceola
Central Florida Youth Peach Tree Growing Contest UF/IFAS Polk County Extension Service 1702 US Hwy 17-98 South P.O. Box 9005, Drawer HS03 Bartow, FL 33831-9005 Osceola County Extension Service Osceola
Your Florida Dooryard Citrus Guide - Introduction 1
 HS 884 Your Florida Dooryard Citrus Guide - Introduction 1 James J. Ferguson 2 Citrus in Florida Our citrus industry developed from 16th-century Spanish introductions of sour orange, sweet orange, lemon,
HS 884 Your Florida Dooryard Citrus Guide - Introduction 1 James J. Ferguson 2 Citrus in Florida Our citrus industry developed from 16th-century Spanish introductions of sour orange, sweet orange, lemon,
Cottonwood. Pest Damage on. Plant Problem. September September 1 10 October September November November November 1 10
 Pest Damage on March 21 31 March 11 20 March 1 10 April 21 30 April 11 20 April 1 10 May 21 31 May 11 20 May 1 10 June 21 30 June 11 20 June 1 10 July 21 31 July 11 20 July 1 10 August 21 31 August 11
Pest Damage on March 21 31 March 11 20 March 1 10 April 21 30 April 11 20 April 1 10 May 21 31 May 11 20 May 1 10 June 21 30 June 11 20 June 1 10 July 21 31 July 11 20 July 1 10 August 21 31 August 11
Training and Pruning Florida Peaches, Nectarines, and Plums 1
 HS1111 Training and Pruning Florida Peaches, Nectarines, and Plums 1 J. Ferguson 2 Fruit from Florida's early maturing peach, nectarine Prunus persica (L.) Batsch), and Japanese plum cultivars (Prunus
HS1111 Training and Pruning Florida Peaches, Nectarines, and Plums 1 J. Ferguson 2 Fruit from Florida's early maturing peach, nectarine Prunus persica (L.) Batsch), and Japanese plum cultivars (Prunus
Training and Pruning Florida Peaches, Nectarines, and Plums 1
 HS1111 Training and Pruning Florida Peaches, Nectarines, and Plums 1 J. Ferguson 2 Fruit from Florida's early maturing peach, nectarine Prunus persica (L.) Batsch), and Japanese plum cultivars (Prunus
HS1111 Training and Pruning Florida Peaches, Nectarines, and Plums 1 J. Ferguson 2 Fruit from Florida's early maturing peach, nectarine Prunus persica (L.) Batsch), and Japanese plum cultivars (Prunus
THE CHINCHONA VENEER-GRAFT METHOD OF PROPAGATING SUBTROPICAL FRUIT TREES
 Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 58:176-180. 1945 THE CHINCHONA VENEER-GRAFT METHOD OF PROPAGATING SUBTROPICAL FRUIT TREES William C. Cooper and J. R. Furr United States Department of Agriculture, Orlando Introduction
Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 58:176-180. 1945 THE CHINCHONA VENEER-GRAFT METHOD OF PROPAGATING SUBTROPICAL FRUIT TREES William C. Cooper and J. R. Furr United States Department of Agriculture, Orlando Introduction
Training and Pruning Florida Peaches, Nectarines, and Plums 1
 HS1111 Training and Pruning Florida Peaches, Nectarines, and Plums 1 J. Ferguson 2 Fruit from Florida s early maturing peach, nectarine Prunus persica (L.) Batsch, and Japanese plum cultivars (Prunus salicina
HS1111 Training and Pruning Florida Peaches, Nectarines, and Plums 1 J. Ferguson 2 Fruit from Florida s early maturing peach, nectarine Prunus persica (L.) Batsch, and Japanese plum cultivars (Prunus salicina
Archival copy: for current recommendations see or your local extension office.
 HS86 Citrus Propagation 1 J. G. Williamson and L. K. Jackson 2 Home fruit growers often want to propagate their own citrus trees, or change varieties by top-working an existing tree with one or more varieties
HS86 Citrus Propagation 1 J. G. Williamson and L. K. Jackson 2 Home fruit growers often want to propagate their own citrus trees, or change varieties by top-working an existing tree with one or more varieties
Propagation by Grafting and Budding
 Propagation by Grafting and Budding Larry A. Sagers Extension Horticulture Specialist Utah State University Thanksgiving Point Office Grafting is a term which covers many propagation techniques. It includes
Propagation by Grafting and Budding Larry A. Sagers Extension Horticulture Specialist Utah State University Thanksgiving Point Office Grafting is a term which covers many propagation techniques. It includes
Fall Juvenile Pistachio Freeze Damage
 Fall Juvenile Pistachio Freeze Damage Craig Kallsen, UCCE Farm Advisor, Kern County cekallsen@ucanr.edu 661-868-6221 Cooperators: Blake Sanden, Soils and Irrigation Farm Advisor, UCCE- Kern County, Mike
Fall Juvenile Pistachio Freeze Damage Craig Kallsen, UCCE Farm Advisor, Kern County cekallsen@ucanr.edu 661-868-6221 Cooperators: Blake Sanden, Soils and Irrigation Farm Advisor, UCCE- Kern County, Mike
CITRUS ROOT GROWTH IN SOILS SUBJECT
 FORD: FLATWOODS CITRUS STUDIES 41 9. Reitz, H. J., C. D. Leonard, Ivan Steward, R. C. J. Koo, D. V. Calvert, C. A. Anderson, P. F. Smith, and G. K. Rasmussen. 1964. Recommended fertilizers and nu tritional
FORD: FLATWOODS CITRUS STUDIES 41 9. Reitz, H. J., C. D. Leonard, Ivan Steward, R. C. J. Koo, D. V. Calvert, C. A. Anderson, P. F. Smith, and G. K. Rasmussen. 1964. Recommended fertilizers and nu tritional
Your Florida Dooryard Citrus Guide - Young Tree Care 1
 HS 887 Your Florida Dooryard Citrus Guide - Young Tree Care 1 James J. Ferguson 2 Weeds and Mulching Since the canopy of a young citrus tree produces very little shade and will be watered and fertilized
HS 887 Your Florida Dooryard Citrus Guide - Young Tree Care 1 James J. Ferguson 2 Weeds and Mulching Since the canopy of a young citrus tree produces very little shade and will be watered and fertilized
Abiotic Diseases of Dry Beans
 Know how. Know now. Abiotic Diseases of Dry Beans Robert M. Harveson, Extension Plant Pathologist, and Carlos A. Urrea, Dry Bean Breeder, University of Nebraska Lincoln Howard F. Schwartz, Extension Plant
Know how. Know now. Abiotic Diseases of Dry Beans Robert M. Harveson, Extension Plant Pathologist, and Carlos A. Urrea, Dry Bean Breeder, University of Nebraska Lincoln Howard F. Schwartz, Extension Plant
FIELD GUIDE TO COMMON PESTS, DISEASES, AND OTHER DISORDERS OF RADIATA PINE IN NEW ZEALAND
 FIELD GUIDE TO COMMON PESTS, DISEASES, AND OTHER DISORDERS OF RADIATA PINE IN NEW ZEALAND Forest Research Bulletin 207 Extract of pages 40 55 OTHER DISORDERS Copyright 2005, New Zealand Forest Research
FIELD GUIDE TO COMMON PESTS, DISEASES, AND OTHER DISORDERS OF RADIATA PINE IN NEW ZEALAND Forest Research Bulletin 207 Extract of pages 40 55 OTHER DISORDERS Copyright 2005, New Zealand Forest Research
1995 RUTGERS Turfgrass Proceedings
 1995 RUTGERS Turfgrass Proceedings Rutgers University THE NEW JERSEY TURFGRASS ASSOCIATION In Cooperation With RUTGERS COOPERATIVE EXTENSION NEW JERSEY AGRICULTURAL EXPERIMENT STATION RUTGERS, THE STATE
1995 RUTGERS Turfgrass Proceedings Rutgers University THE NEW JERSEY TURFGRASS ASSOCIATION In Cooperation With RUTGERS COOPERATIVE EXTENSION NEW JERSEY AGRICULTURAL EXPERIMENT STATION RUTGERS, THE STATE
Diseases of Warm-Season Grasses
 Diseases of Warm-Season Grasses Bermudagrass, Centipedegrass, Zoysiagrass, and St. Augustinegrass Leon T. Lucas, Extension Plant Pathology Specialist Arthur H. Bruneau, Extension Crop Science Specialist
Diseases of Warm-Season Grasses Bermudagrass, Centipedegrass, Zoysiagrass, and St. Augustinegrass Leon T. Lucas, Extension Plant Pathology Specialist Arthur H. Bruneau, Extension Crop Science Specialist
Black Rot of Crucifers
 Plant Pathology Fact Sheet PP-13 Black Rot of Crucifers Tom Kucharek and Jim Strandberg, Professor and Extension Plant Pathologist, Gainesville, FL and, Professor and Research Plant Pathologist, Central
Plant Pathology Fact Sheet PP-13 Black Rot of Crucifers Tom Kucharek and Jim Strandberg, Professor and Extension Plant Pathologist, Gainesville, FL and, Professor and Research Plant Pathologist, Central
Lawn Fungus / Disease
 Lawn Fungus / Disease This guide is a good place to see what affects lawns in our area so you can be a better informed customer. There are many different types of fungus which grow in every lawn and it's
Lawn Fungus / Disease This guide is a good place to see what affects lawns in our area so you can be a better informed customer. There are many different types of fungus which grow in every lawn and it's
Training and Pruning Florida Peaches, Nectarines, and Plums1
 HS1111 Training and Pruning Florida Peaches, Nectarines, and Plums1 Ali Sarkhosh and James Ferguson2 Fruit from Florida s early maturing peach, nectarine, and Japanese plum cultivars mature in April and
HS1111 Training and Pruning Florida Peaches, Nectarines, and Plums1 Ali Sarkhosh and James Ferguson2 Fruit from Florida s early maturing peach, nectarine, and Japanese plum cultivars mature in April and
Effect of Method of Application of Double Superphosphate on the Yield and Phosphorus Uptake by Sugar Beets 1
 Effect of Method of Application of Double Superphosphate on the Yield and Phosphorus Uptake by Sugar Beets 1 W. E. LARSON 2 Optimum phosphate fertilizer placement for sugar beets is probably dependent
Effect of Method of Application of Double Superphosphate on the Yield and Phosphorus Uptake by Sugar Beets 1 W. E. LARSON 2 Optimum phosphate fertilizer placement for sugar beets is probably dependent
VASCULAR STREAK DIEBACK
 IMPORTANCE VASCULAR STREAK DIEBACK The disease is found in most cocoa growing areas in South East Asia. There is strong evidence that the fungus evolved on an indigenous host, as yet unidentified, in South
IMPORTANCE VASCULAR STREAK DIEBACK The disease is found in most cocoa growing areas in South East Asia. There is strong evidence that the fungus evolved on an indigenous host, as yet unidentified, in South
CMG GardenNotes #659 Understanding Tree Roots. Functions of Tree Roots. Support\anchorage
 CMG GardenNotes #659 Understanding Tree Roots Outline: Functions of Tree Roots, page 1 Describing Tree Roots, page 2 Conditions That Can Adversely Affect Roots, page 4 Other Common Root Issues, page 5
CMG GardenNotes #659 Understanding Tree Roots Outline: Functions of Tree Roots, page 1 Describing Tree Roots, page 2 Conditions That Can Adversely Affect Roots, page 4 Other Common Root Issues, page 5
trunks. The main difference between shrubs and trees is size; trees are typically larger than shrubs.
 PRUNE = PUH-ROON Pruning requires more skill and knowledge than most other landscape management practices. When done properly, and at the right time, pruning results in healthy, vigorous trees, improved
PRUNE = PUH-ROON Pruning requires more skill and knowledge than most other landscape management practices. When done properly, and at the right time, pruning results in healthy, vigorous trees, improved
Winter Yellows - A closer look at this physiological disorder and other issues. Sandra Hardy, NSW DPI Pat Barkley, ACG
 Winter Yellows - A closer look at this physiological disorder and other issues Sandra Hardy, NSW DPI Pat Barkley, ACG Outline Winter Yellows: Typical symptoms What we know Previous instances Reasons why?
Winter Yellows - A closer look at this physiological disorder and other issues Sandra Hardy, NSW DPI Pat Barkley, ACG Outline Winter Yellows: Typical symptoms What we know Previous instances Reasons why?
University of California Cooperative Extension Tulare County. Grape Notes. DELAYED GROWTH PREVALENT IN VINEYARDS THIS SPRING Bill Peacock
 University of California Cooperative Extension Tulare County Grape Notes Volume IV, Issue 2 June 2007 DELAYED GROWTH PREVALENT IN VINEYARDS THIS SPRING Bill Peacock Poor bud break and delayed shoot growth
University of California Cooperative Extension Tulare County Grape Notes Volume IV, Issue 2 June 2007 DELAYED GROWTH PREVALENT IN VINEYARDS THIS SPRING Bill Peacock Poor bud break and delayed shoot growth
DISEASES. College of Agricultural Sciences
 I D E N T I F Y I N G DISEASES P O T A T O I N P E N N S Y L V A N I A College of Agricultural Sciences Contents 3 Late Blight 5 Early Blight 6 Verticillium Wilt (Early Dying) 8 Rhizoctonia Canker (Black
I D E N T I F Y I N G DISEASES P O T A T O I N P E N N S Y L V A N I A College of Agricultural Sciences Contents 3 Late Blight 5 Early Blight 6 Verticillium Wilt (Early Dying) 8 Rhizoctonia Canker (Black
FERTILIZER, IRRIGATION STUDIES ON AVOCADOS AND LIMES ON THE ROCKDALE SOILS OF THE HOMESTEAD AREA
 Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 66:228-230. 1953. FERTILIZER, IRRIGATION STUDIES ON AVOCADOS AND LIMES ON THE ROCKDALE SOILS OF THE HOMESTEAD AREA M. H. Gallatin Soil Scientist, U.S.D.A., B.P.I.S.A.E., Soils
Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 66:228-230. 1953. FERTILIZER, IRRIGATION STUDIES ON AVOCADOS AND LIMES ON THE ROCKDALE SOILS OF THE HOMESTEAD AREA M. H. Gallatin Soil Scientist, U.S.D.A., B.P.I.S.A.E., Soils
CMG GardenNotes #613 Structural Training of Young Shade Trees
 CMG GardenNotes #613 Structural Training of Young Shade Trees Outline: Pruning basics, page 1 Time of year, page 2 Size of branches, page 2 Structural pruning steps, page 2 Step 1 Dosage: Maximum amount
CMG GardenNotes #613 Structural Training of Young Shade Trees Outline: Pruning basics, page 1 Time of year, page 2 Size of branches, page 2 Structural pruning steps, page 2 Step 1 Dosage: Maximum amount
VENTURA COUNTY AVOCADO ROOT ROT RESISTANCE PLOT
 California Avocado Society 1967 Yearbook 51: 125-130 VENTURA COUNTY AVOCADO ROOT ROT RESISTANCE PLOT G. A. Zentmyer, W. A. Thorn, C. C, Delphey, R. M. Burns, F. B. Guillemet and E. Johnson The authors
California Avocado Society 1967 Yearbook 51: 125-130 VENTURA COUNTY AVOCADO ROOT ROT RESISTANCE PLOT G. A. Zentmyer, W. A. Thorn, C. C, Delphey, R. M. Burns, F. B. Guillemet and E. Johnson The authors
Acer saccharum Newton Sentry Newton Sentry Sugar Maple 1
 Fact Sheet ST-55 November 1993 Acer saccharum Newton Sentry Newton Sentry Sugar Maple 1 Edward F. Gilman and Dennis G. Watson 2 INTRODUCTION This cultivar of Sugar Maple is very upright and compact (Fig.
Fact Sheet ST-55 November 1993 Acer saccharum Newton Sentry Newton Sentry Sugar Maple 1 Edward F. Gilman and Dennis G. Watson 2 INTRODUCTION This cultivar of Sugar Maple is very upright and compact (Fig.
Impact of Easter Freeze on 1-, 2- and 3-Year Old Muscadines and Recommended Actions Date: 6/7/2007
 Impact of Easter Freeze on 1-, 2- and 3-Year Old Muscadines and Recommended Actions Date: 6/7/2007 Connie Fisk, Muscadine Extension Associate, Dept. of Horticultural Science, NCSU Barclay Poling, Professor,
Impact of Easter Freeze on 1-, 2- and 3-Year Old Muscadines and Recommended Actions Date: 6/7/2007 Connie Fisk, Muscadine Extension Associate, Dept. of Horticultural Science, NCSU Barclay Poling, Professor,
Tomato Leaf Spot Diseases in South Dakota
 South Dakota State University Open PRAIRIE: Open Public Research Access Institutional Repository and Information Exchange Extension Circulars SDSU Extension 5-1944 Tomato Leaf Spot Diseases in South Dakota
South Dakota State University Open PRAIRIE: Open Public Research Access Institutional Repository and Information Exchange Extension Circulars SDSU Extension 5-1944 Tomato Leaf Spot Diseases in South Dakota
Managing Soil Borne Diseases
 Managing Soil Borne Diseases PMA-5205 Spring 2017 Evan Johnson Plant Pathologist UF-IFAS-CREC Citrus Root Health Acquisition of the most important resources applied to the tree is via the root system Most
Managing Soil Borne Diseases PMA-5205 Spring 2017 Evan Johnson Plant Pathologist UF-IFAS-CREC Citrus Root Health Acquisition of the most important resources applied to the tree is via the root system Most
Some Practical Matters Related to Riviera Soil, Depth to Clay, Water Table, Soil Organic Matter, and Swingle Citrumelo Root Systems 1
 HS894 Some Practical Matters Related to Riviera Soil, Depth to Clay, Water Table, Soil Organic Matter, and Swingle Citrumelo Root Systems 1 Bill Castle, Mace Bauer, Brian Boman and Tom Obreza 2 A topographical
HS894 Some Practical Matters Related to Riviera Soil, Depth to Clay, Water Table, Soil Organic Matter, and Swingle Citrumelo Root Systems 1 Bill Castle, Mace Bauer, Brian Boman and Tom Obreza 2 A topographical
California Avocado Society 1960 Yearbook 44: NITROGEN FERTILIZATION OF THE MacARTHUR AVOCADO
 California Avocado Society 1960 Yearbook 44: 93-96 NITROGEN FERTILIZATION OF THE MacARTHUR AVOCADO T. W. Embleton, W. W. Jones, C. K. Labanauskas, C. B. Cree, M. L. Steinacker, S. B. Boswell, C. C. Delphey,
California Avocado Society 1960 Yearbook 44: 93-96 NITROGEN FERTILIZATION OF THE MacARTHUR AVOCADO T. W. Embleton, W. W. Jones, C. K. Labanauskas, C. B. Cree, M. L. Steinacker, S. B. Boswell, C. C. Delphey,
STALK ROTS. When to look for: Mid-August to Early October
 Figure 19. Lodging of corn plants due to stalk rot damage. Photo courtesy of MAFRI. Figure 20. Shredding of internal tissues of a corn stalk by a stalk rot pathogen. Photo courtesy of MAFRI. STALK ROTS
Figure 19. Lodging of corn plants due to stalk rot damage. Photo courtesy of MAFRI. Figure 20. Shredding of internal tissues of a corn stalk by a stalk rot pathogen. Photo courtesy of MAFRI. STALK ROTS
Getting fruit trees off to a good start. Bill Shane Tree Fruit Extension Specialist SW Michigan Research and Extension Center, Benton Harbor, MI
 Getting fruit trees off to a good start Bill Shane Tree Fruit Extension Specialist SW Michigan Research and Extension Center, Benton Harbor, MI Getting fruit trees off to a good start Resources (Handout)
Getting fruit trees off to a good start Bill Shane Tree Fruit Extension Specialist SW Michigan Research and Extension Center, Benton Harbor, MI Getting fruit trees off to a good start Resources (Handout)
Training and Pruning Peach Trees
 January 2018 Horticulture/Fruit/2018-01pr Training and Pruning Peach Trees Sheriden Hansen, Tiffany Maughan and Brent Black Introduction Training and pruning peach trees is critical to the production of
January 2018 Horticulture/Fruit/2018-01pr Training and Pruning Peach Trees Sheriden Hansen, Tiffany Maughan and Brent Black Introduction Training and pruning peach trees is critical to the production of
Propagation. Pests and Diseases. Florida wax scale
 Holly Ilex species Propagation Holly is usually propagated by semi-hardwood stem tip cuttings taken in the summer. Cuttings are rooted in 6-8 weeks with IBA TALC 8000 PPM and intermittent mist with soil
Holly Ilex species Propagation Holly is usually propagated by semi-hardwood stem tip cuttings taken in the summer. Cuttings are rooted in 6-8 weeks with IBA TALC 8000 PPM and intermittent mist with soil
TOMATO WILT DISEASE 1
 TOMATO WILT DISEASE 1 R. P. WHITE DISTRIBUTION OF TOMATO WILT IN KANSAS Wilt, the most serious disease of the tomato in Kansas, is caused by the fungous organism, Fusarium lycopersici Sacc. This disease
TOMATO WILT DISEASE 1 R. P. WHITE DISTRIBUTION OF TOMATO WILT IN KANSAS Wilt, the most serious disease of the tomato in Kansas, is caused by the fungous organism, Fusarium lycopersici Sacc. This disease
LOW VOLUME M8CROSPR1NKLER UNDERTREE IRRIGATION FOR FROST PROTECTION OF YOUNG CITRUS TREES1
 Proc. Ha. State Hort. Soc. 94:55-59. 1981. LOW VOLUME M8CROSPR1NKLER UNDERTREE IRRIGATION FOR FROST PROTECTION OF YOUNG CITRUS TREES1 L. R. Parsons, T. A. Wheaton, and J. D. Whitney University of Florida,
Proc. Ha. State Hort. Soc. 94:55-59. 1981. LOW VOLUME M8CROSPR1NKLER UNDERTREE IRRIGATION FOR FROST PROTECTION OF YOUNG CITRUS TREES1 L. R. Parsons, T. A. Wheaton, and J. D. Whitney University of Florida,
Solutions for Pot-in-Pot Root Escape, Root Circling, and Heat Shock at Harvest by Dr. Carl E. Whitcomb
 Solutions for Pot-in-Pot Root Escape, Root Circling, and Heat Shock at Harvest by Dr. Carl E. Whitcomb Heat, cold and blow-over have been major problems plaguing plant production in the unnatural environment
Solutions for Pot-in-Pot Root Escape, Root Circling, and Heat Shock at Harvest by Dr. Carl E. Whitcomb Heat, cold and blow-over have been major problems plaguing plant production in the unnatural environment
Relationship of Soil Moisture and Drainage Conditions to Tree Decline in Avocado Orchards *
 California Avocado Society 1943 Yearbook 28: 34-37 Relationship of Soil Moisture and Drainage Conditions to Tree Decline in Avocado Orchards * E. R. PARKER and M. B. ROUNDS Citrus Experiment Station, University
California Avocado Society 1943 Yearbook 28: 34-37 Relationship of Soil Moisture and Drainage Conditions to Tree Decline in Avocado Orchards * E. R. PARKER and M. B. ROUNDS Citrus Experiment Station, University
GRAFTING THE MANGO IN HAWAII. William Bembower. Revised by Warren Yee Assistant Specialist in Horticulture
 Agricultural Cooperative Extension Circular No. 59 COOPERATIVE EXTENSION WORK IN AGRICULTURE AND HOME ECONOMICS UNIVERSITY OF HAWAII, HONOLULU 14, HAWAII UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE COOPERATING
Agricultural Cooperative Extension Circular No. 59 COOPERATIVE EXTENSION WORK IN AGRICULTURE AND HOME ECONOMICS UNIVERSITY OF HAWAII, HONOLULU 14, HAWAII UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE COOPERATING
Integration of Tree Spacing, Pruning and Rootstock Selection for Efficient Almond Production
 Integration of Tree Spacing, Pruning and Rootstock Selection for Efficient Almond Production Project No.: Project Leader: Roger Duncan, UC Cooperative Extension, Stanislaus County Project Cooperators:
Integration of Tree Spacing, Pruning and Rootstock Selection for Efficient Almond Production Project No.: Project Leader: Roger Duncan, UC Cooperative Extension, Stanislaus County Project Cooperators:
UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE Agricultural Research Service Washington, D.C
 UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE Agricultural Research Service Washington, D.C. 20250 NOTICE TO FRUIT GROWERS AND 1\u~SERYMENRELATIVE TO THE NAMING ANTI RELEASE OF THE US-897 CITRUS ROOTSTOCK The
UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE Agricultural Research Service Washington, D.C. 20250 NOTICE TO FRUIT GROWERS AND 1\u~SERYMENRELATIVE TO THE NAMING ANTI RELEASE OF THE US-897 CITRUS ROOTSTOCK The
Top Working Fruit Trees Michigan State University Cooperative Extension Service F Folder Series Horticulture Reprinted February pages
 MSU Extension Publication Archive Archive copy of publication, do not use for current recommendations. Up-to-date information about many topics can be obtained from your local Extension office. Top Working
MSU Extension Publication Archive Archive copy of publication, do not use for current recommendations. Up-to-date information about many topics can be obtained from your local Extension office. Top Working
Dogwood Anthracnose. Purdue e-pubs. Purdue University. Paul C. Pecknold Purdue University,
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Historical Documents of the Purdue Cooperative Extension Service Department of Agricultural Communication 1-27-2016 Dogwood Anthracnose Paul C. Pecknold Purdue University,
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Historical Documents of the Purdue Cooperative Extension Service Department of Agricultural Communication 1-27-2016 Dogwood Anthracnose Paul C. Pecknold Purdue University,
Lightning contacts planet Earth about 100 times each
 Plant Disease July 2008 PD-40 Lightning Injury to Plants Scot C. Nelson Department of Plant and Environmental Protection Sciences Lightning contacts planet Earth about 100 times each second, or 8 million
Plant Disease July 2008 PD-40 Lightning Injury to Plants Scot C. Nelson Department of Plant and Environmental Protection Sciences Lightning contacts planet Earth about 100 times each second, or 8 million
Grafting Fruit Trees. Loyd Collett 4/5/2011 1
 Grafting Fruit Trees Loyd Collett 4/5/2011 1 PNW Bulletin 62 4/5/2011 2 4/5/2011 3 Introduction The goal of grafting and budding is to join together two living plant parts so that the combination grows
Grafting Fruit Trees Loyd Collett 4/5/2011 1 PNW Bulletin 62 4/5/2011 2 4/5/2011 3 Introduction The goal of grafting and budding is to join together two living plant parts so that the combination grows
Site Selection Blueberry
 Blueberry Site Selection Blueberry ph 4.0 to 5.5 Full sun and well drained Sandy loam with added organic matter - ideal Avoid frost-prone areas Control weeds bermudagrass wild blackberries ph Requirement
Blueberry Site Selection Blueberry ph 4.0 to 5.5 Full sun and well drained Sandy loam with added organic matter - ideal Avoid frost-prone areas Control weeds bermudagrass wild blackberries ph Requirement
Pruning is one of the oldest
 Pruning and controlled-release fertilizer to rehabilitate HLB trees By Tripti Vashisth and Troy Gainey Pruning is one of the oldest horticultural practices that changes the form and growth of a tree. The
Pruning and controlled-release fertilizer to rehabilitate HLB trees By Tripti Vashisth and Troy Gainey Pruning is one of the oldest horticultural practices that changes the form and growth of a tree. The
DORMANT SEASON TREE CARE. Damage Prevention and Maintenance
 DORMANT SEASON TREE CARE Damage Prevention and Maintenance If you want to ensure your trees survive through winter and thrive come spring and summer, it s important to take some steps now to protect them.
DORMANT SEASON TREE CARE Damage Prevention and Maintenance If you want to ensure your trees survive through winter and thrive come spring and summer, it s important to take some steps now to protect them.
CITRUS PRUNING. Pruning techniques for tree health, pest control, fruit production and size control.
 CITRUS PRUNING Pruning techniques for tree health, pest control, fruit production and size control. Citrus trees generally need to be pruned every two to five years. Primary reasons for pruning citrus
CITRUS PRUNING Pruning techniques for tree health, pest control, fruit production and size control. Citrus trees generally need to be pruned every two to five years. Primary reasons for pruning citrus
report on PLANT DISEASE COLLECTING AND SUBMITTING SOIL SAMPLES FOR NEMATODE ANALYSIS
 report on PLANT DISEASE RPD No. 1100 May 1996 DEPARTMENT OF CROP SCIENCES UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN COLLECTING AND SUBMITTING SOIL SAMPLES The roots of virtually every plant are naturally
report on PLANT DISEASE RPD No. 1100 May 1996 DEPARTMENT OF CROP SCIENCES UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN COLLECTING AND SUBMITTING SOIL SAMPLES The roots of virtually every plant are naturally
B.2. SPECIALIZED USES To change plant size and vigor. To repair damaged parts of established plant. To change plant form. Virus indexing.
 NAME OF THE EXPERIMENT: PRACTICE OF VENEER GRAFTING TECHNIQUE IN MANGO PLANT A. GRAFTING Grafting is a horticultural art of an asexual propagation method in which two different plant parts (rootstock and
NAME OF THE EXPERIMENT: PRACTICE OF VENEER GRAFTING TECHNIQUE IN MANGO PLANT A. GRAFTING Grafting is a horticultural art of an asexual propagation method in which two different plant parts (rootstock and
Fact Sheet Commercial Horticulture Citrus: Care of Freeze Damaged Trees
 10/21/2011 3100 E. New York Ave. DeLand, FL 32724 6410 DeLand: (386) 822 5778 Daytona Beach: (386) 257 6012 New Smyrna Beach: (386) 423 3368 Fax: (386) 822 5767 Email: bjeansonne@ufl.edu bjeansonne@co.volusia.fl.us
10/21/2011 3100 E. New York Ave. DeLand, FL 32724 6410 DeLand: (386) 822 5778 Daytona Beach: (386) 257 6012 New Smyrna Beach: (386) 423 3368 Fax: (386) 822 5767 Email: bjeansonne@ufl.edu bjeansonne@co.volusia.fl.us
Microsprinkler Irrigation for Cold Protection of Florida Citrus 1
 HS931 Microsprinkler Irrigation for Cold Protection of Florida Citrus 1 L. R. Parsons and B. J. Boman 2 Introduction Millions of boxes of fruit and thousands of acres of citrus trees have been lost in
HS931 Microsprinkler Irrigation for Cold Protection of Florida Citrus 1 L. R. Parsons and B. J. Boman 2 Introduction Millions of boxes of fruit and thousands of acres of citrus trees have been lost in
flattened, or in groups, in crevices beneath the bark. The eggs soon hatch, and the larvae bore into the sapwood where they make tortuous
 j ^ju Agriculture Canada Publication 1718 B Major pests of birch and maple trees The birch leafminer The birch leafminer (Fenusa pusilla Lepeletier) attacks the white or paper birch (Betula papyrifera
j ^ju Agriculture Canada Publication 1718 B Major pests of birch and maple trees The birch leafminer The birch leafminer (Fenusa pusilla Lepeletier) attacks the white or paper birch (Betula papyrifera
Growth and nutrient absorption of grapes as affected by soil aeration. I. With non-bearing Delaware grapes A. KOBAYASHI, K. IWASAKI and Y.
 Growth and nutrient absorption of grapes as affected by soil aeration. I. With non-bearing Delaware grapes A. KOBAYASHI, K. IWASAKI and Y. SATO (College of Agriculture, Kyoto University) It is well known
Growth and nutrient absorption of grapes as affected by soil aeration. I. With non-bearing Delaware grapes A. KOBAYASHI, K. IWASAKI and Y. SATO (College of Agriculture, Kyoto University) It is well known
Propagation. Pests and Diseases. Black twig borer (Xylosandrus compactus) Magnolia white scale (Pseudaulacaspis cockerelli)
 Magnolia, Southern Magnolia Magnolia grandiflora Propagation Magnolias are usually propagated by semi-hardwood stem tip cuttings taken in the summer. Rooting should occur in 9 weeks with IBA Quick Dip
Magnolia, Southern Magnolia Magnolia grandiflora Propagation Magnolias are usually propagated by semi-hardwood stem tip cuttings taken in the summer. Rooting should occur in 9 weeks with IBA Quick Dip
Ash. Pest Damage on. Plant Problem. September September 1 10 October September November November November 1 10
 Pest Damage on Ash March 21 31 March 11 20 March 1 10 April 21 30 April 11 20 April 1 10 May 21 31 May 11 20 May 1 10 June 21 30 June 11 20 June 1 10 July 21 31 July 11 20 July 1 10 August 21 31 August
Pest Damage on Ash March 21 31 March 11 20 March 1 10 April 21 30 April 11 20 April 1 10 May 21 31 May 11 20 May 1 10 June 21 30 June 11 20 June 1 10 July 21 31 July 11 20 July 1 10 August 21 31 August
DOWNY MILDEW Fungal disease
 DOWNY MILDEW Fungal disease DOWNY MILDEW Fungal disease Onion downy mildew, caused by the fungus Peronospora destructor, is very common. This fungus can overwinter in plant debris or be brought in on sets
DOWNY MILDEW Fungal disease DOWNY MILDEW Fungal disease Onion downy mildew, caused by the fungus Peronospora destructor, is very common. This fungus can overwinter in plant debris or be brought in on sets
Pruning Landscape Plants
 70 Pruning Landscape Plants Objectives 1. Be able to describe, explain, and defend the reasons for pruning plants and the responses of plants to pruning. 2. Be able to describe, explain, and summarize
70 Pruning Landscape Plants Objectives 1. Be able to describe, explain, and defend the reasons for pruning plants and the responses of plants to pruning. 2. Be able to describe, explain, and summarize
2000 RUTGERS Turfgrass Proceedings
 2000 RUTGERS Turfgrass Proceedings Rutgers University THE NEW JERSEY TURFGRASS ASSOCIATION In Cooperation With RUTGERS COOPERATIVE EXTENSION NEW JERSEY AGRICULTURAL EXPERIMENT STATION RUTGERS, THE STATE
2000 RUTGERS Turfgrass Proceedings Rutgers University THE NEW JERSEY TURFGRASS ASSOCIATION In Cooperation With RUTGERS COOPERATIVE EXTENSION NEW JERSEY AGRICULTURAL EXPERIMENT STATION RUTGERS, THE STATE
Ligustrum, Privet Ligustrum japonicum
 Ligustrum, Privet Ligustrum japonicum Propagation L. japonicum Ligustrum are propagated by softwood cuttings taken in spring, or 5 10 cm semi-hardwood cuttings with a heel taken at the end of the summer.
Ligustrum, Privet Ligustrum japonicum Propagation L. japonicum Ligustrum are propagated by softwood cuttings taken in spring, or 5 10 cm semi-hardwood cuttings with a heel taken at the end of the summer.
MSU Extension Publication Archive. Scroll down to view the publication.
 MSU Extension Publication Archive Archive copy of publication, do not use for current recommendations. Up-to-date information about many topics can be obtained from your local Extension office. Terminal
MSU Extension Publication Archive Archive copy of publication, do not use for current recommendations. Up-to-date information about many topics can be obtained from your local Extension office. Terminal
Research Progress Report Southern Region Small Fruit Consortium
 Research Progress Report Southern Region Small Fruit Consortium Title: Use of phosphite materials for control of Pythium and other root rot species in high-density blueberry production systems Grant Code:
Research Progress Report Southern Region Small Fruit Consortium Title: Use of phosphite materials for control of Pythium and other root rot species in high-density blueberry production systems Grant Code:
Unit E: Fruit and Nut Production. Lesson 3: Growing Apples
 Unit E: Fruit and Nut Production Lesson 3: Growing Apples 1 Terms central leader dwarf rootstocks espaliers open center pomology rootstock scion semi-dwarf rootstocks standard rootstocks 2 I. Apples have
Unit E: Fruit and Nut Production Lesson 3: Growing Apples 1 Terms central leader dwarf rootstocks espaliers open center pomology rootstock scion semi-dwarf rootstocks standard rootstocks 2 I. Apples have
Oxygen Diffusion, Water, and Phytophthora cinnamomi in Root Decay and Nutrition of Avocados 1
 Proceedings of the AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR HORTICULTURAL SCIENCE 1967 90:67-76 Oxygen Diffusion, Water, and Phytophthora cinnamomi in Root Decay and Nutrition of Avocados 1 L. H. STOLZY, G. A. ZENTMYER, L.
Proceedings of the AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR HORTICULTURAL SCIENCE 1967 90:67-76 Oxygen Diffusion, Water, and Phytophthora cinnamomi in Root Decay and Nutrition of Avocados 1 L. H. STOLZY, G. A. ZENTMYER, L.
How to submit a sample to MSU Diagnostic Services
 How to submit a sample to MSU Diagnostic Services Sample Submission Collecting Plant Samples It is best to send entire plants, although we recognize this is not always possible. Plants with root and crown
How to submit a sample to MSU Diagnostic Services Sample Submission Collecting Plant Samples It is best to send entire plants, although we recognize this is not always possible. Plants with root and crown
Tree growth over multiple years
 Tree growth over multiple years All plant growth of originates from meristems or meristematic (capable rapid cell division and differentiation) tissue. Trees are designed to face a problem that annual
Tree growth over multiple years All plant growth of originates from meristems or meristematic (capable rapid cell division and differentiation) tissue. Trees are designed to face a problem that annual
Pruning and Training Deciduous Fruit Trees for the Dooryard 1
 HS82 Pruning and Training Deciduous Fruit Trees for the Dooryard 1 J. G. Williamson 2 Proper pruning and training of fruit trees is necessary to obtain maximum yields of high quality fruit throughout the
HS82 Pruning and Training Deciduous Fruit Trees for the Dooryard 1 J. G. Williamson 2 Proper pruning and training of fruit trees is necessary to obtain maximum yields of high quality fruit throughout the
Evaluation of new low- and moderate-chill peach cultivars in coastal southern California
 Evaluation of new low- and moderate-chill peach cultivars in coastal southern California Daniel A. Hagillih, Center Director, UC South Coast Research and Extension Center, 7601 Irvine Boulevard, Irvine,
Evaluation of new low- and moderate-chill peach cultivars in coastal southern California Daniel A. Hagillih, Center Director, UC South Coast Research and Extension Center, 7601 Irvine Boulevard, Irvine,
Bacterial Ring Rot. of Potatoes L--, J. A. MflbraTh' Circular of Information 491 January Roy A.
 7.3 Bacterial Ring Rot of Potatoes Roy A. J. A. MflbraTh' L--, of Agricultural xperiment Station Oregon State College Corvallis Circular of Information 491 January 1951 G3o.1 O'r3Z CL no4'l C.. 3 DOCU
7.3 Bacterial Ring Rot of Potatoes Roy A. J. A. MflbraTh' L--, of Agricultural xperiment Station Oregon State College Corvallis Circular of Information 491 January 1951 G3o.1 O'r3Z CL no4'l C.. 3 DOCU
Phytophthora Root Rot
 MAJOR DISEASES: Phytophthora Root Rot 17 CHAPTER SIX Phytophthora Root Rot Everett M. Hansen Disease and hosts Phytophthora root rot is caused by any of several Phytophthora species in Northwest nurseries.
MAJOR DISEASES: Phytophthora Root Rot 17 CHAPTER SIX Phytophthora Root Rot Everett M. Hansen Disease and hosts Phytophthora root rot is caused by any of several Phytophthora species in Northwest nurseries.
This is Gardening with Chuck on 1420 KJCK, I m Chuck Otte, Geary County, K-State Research
 Gardening with Chuck for February 19-25, 2018 Fruit Tree Pruning - General and Extension Ag & Natural Resources Agent. Ever since I was probably 12 years old, once the calendar hits mid February, I just
Gardening with Chuck for February 19-25, 2018 Fruit Tree Pruning - General and Extension Ag & Natural Resources Agent. Ever since I was probably 12 years old, once the calendar hits mid February, I just
Diseases in Alfalfa Seed Production. Faye Dokken-Bouchard Provincial Specialist, Plant Disease Crops Branch, Saskatchewan Ministry of Agriculture
 Diseases in Alfalfa Seed Production Faye Dokken-Bouchard Provincial Specialist, Plant Disease Crops Branch, Saskatchewan Ministry of Agriculture Introduction Alfalfa seed production is a well-established
Diseases in Alfalfa Seed Production Faye Dokken-Bouchard Provincial Specialist, Plant Disease Crops Branch, Saskatchewan Ministry of Agriculture Introduction Alfalfa seed production is a well-established
Sprigging Bermudagrass
 www.stma.org Sprigging Bermudagrass Bermudagrass is a warm season turfgrass commonly used for athletic field surfaces in warmer climates and the transition zone. When deciding which cultivar of bermudagrass
www.stma.org Sprigging Bermudagrass Bermudagrass is a warm season turfgrass commonly used for athletic field surfaces in warmer climates and the transition zone. When deciding which cultivar of bermudagrass
Asparagus investigations in south Louisiana
 Louisiana State University LSU Digital Commons LSU Agricultural Experiment Station Reports LSU AgCenter 1936 Asparagus investigations in south Louisiana William Duke Kimbrough Follow this and additional
Louisiana State University LSU Digital Commons LSU Agricultural Experiment Station Reports LSU AgCenter 1936 Asparagus investigations in south Louisiana William Duke Kimbrough Follow this and additional
'UF Multi-flora Peach' and 'UF Multi-flora Pink Frost' Gerberas - University of Florida Cultivars for Landscapes and Large Pots 1
 ENH1043 'UF Multi-flora Peach' and 'UF Multi-flora Pink Frost' Gerberas - University of Florida Cultivars for Landscapes and Large Pots 1 Zhanao Deng and Brent K. Harbaugh 2 Gerbera daisy is an important
ENH1043 'UF Multi-flora Peach' and 'UF Multi-flora Pink Frost' Gerberas - University of Florida Cultivars for Landscapes and Large Pots 1 Zhanao Deng and Brent K. Harbaugh 2 Gerbera daisy is an important
When to Prune? Late Winter-Early Spring
 When to Prune? Late Winter-Early Spring This is the best time to prune most plants because it is before growth begins. Prune a few of the oldest canes from all mature shrubs down to the ground. Trim deciduous
When to Prune? Late Winter-Early Spring This is the best time to prune most plants because it is before growth begins. Prune a few of the oldest canes from all mature shrubs down to the ground. Trim deciduous
Maples. Common name: Japanese maple, Trident maple, Amur maple Botanical name: Acer palmatum, Acer buergerianum, Acer ginnala
 Maples October 2016 V2.1 Vianney Leduc Common name: Japanese maple, Trident maple, Amur maple Botanical name: Acer palmatum, Acer buergerianum, Acer ginnala 1- Esthetic qualities of maples as bonsai a.
Maples October 2016 V2.1 Vianney Leduc Common name: Japanese maple, Trident maple, Amur maple Botanical name: Acer palmatum, Acer buergerianum, Acer ginnala 1- Esthetic qualities of maples as bonsai a.
EXTENSION FOLDER F-122. of the DEPARTMENT OF HORTICULTURE MICHIGAN STATE COLLEGE COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE EAST LANSING
 ~ - b-~r ~ EXTENSION FOLDER F-122 PRUNING By STAFF MEMBERS of the DEPARTMENT OF HORTICULTURE MICHIGAN STATE COLLEGE COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE EAST LANSING Cooperative Extension Work in Agriculture
~ - b-~r ~ EXTENSION FOLDER F-122 PRUNING By STAFF MEMBERS of the DEPARTMENT OF HORTICULTURE MICHIGAN STATE COLLEGE COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE EAST LANSING Cooperative Extension Work in Agriculture
Anthracnose of Strawberry. Production Guideline. In This Issue
 September 2017 Issue No. 14 www.calstrawberry.com Production Guideline The California Strawberry Commission Production Guidelines are produced in cooperation with scientists who conduct research related
September 2017 Issue No. 14 www.calstrawberry.com Production Guideline The California Strawberry Commission Production Guidelines are produced in cooperation with scientists who conduct research related
GRAFTING OF VEGETABLES TO IMPROVE GREENHOUSE PRODUCTION
 GRAFTING OF VEGETABLES TO IMPROVE GREENHOUSE PRODUCTION Masayuki Oda College of Agriculture, Osaka Prefecture University, Sakai Osaka 5998531, Japan ABSTRACT In vegetable production in greenhouses, most
GRAFTING OF VEGETABLES TO IMPROVE GREENHOUSE PRODUCTION Masayuki Oda College of Agriculture, Osaka Prefecture University, Sakai Osaka 5998531, Japan ABSTRACT In vegetable production in greenhouses, most
Effects of Adjusting Night Temperatures on Growth
 Effects of Adjusting Night Temperatures on Growth of Greenhouse Roses* James W. Boodley and John G. Seeley** The practice of reducing night temperatures below those normally maintained as a means of improving
Effects of Adjusting Night Temperatures on Growth of Greenhouse Roses* James W. Boodley and John G. Seeley** The practice of reducing night temperatures below those normally maintained as a means of improving
PARASITIC NEMATODES ON AVOCADOS A PRELIMINARY REPORT
 Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 67:280-284. 1954. PARASITIC NEMATODES ON AVOCADOS A PRELIMINARY REPORT T. W. Young and Geo. D. Ruehle Sub-Tropical Experiment Station, Homestead A decline from unknown cause
Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 67:280-284. 1954. PARASITIC NEMATODES ON AVOCADOS A PRELIMINARY REPORT T. W. Young and Geo. D. Ruehle Sub-Tropical Experiment Station, Homestead A decline from unknown cause
Central Florida Youth
 Central Florida Youth Citrus Tree Growing Contest UF/IFAS Polk County Extension Service 1702 US Hwy 17-98 South P.O. Box 9005, Drawer HS03 Bartow, FL 33831-9005 Osceola County Extension Service Osceola
Central Florida Youth Citrus Tree Growing Contest UF/IFAS Polk County Extension Service 1702 US Hwy 17-98 South P.O. Box 9005, Drawer HS03 Bartow, FL 33831-9005 Osceola County Extension Service Osceola
MANAGING STALK ROTS FACTORS LEADING TO STALK ROTS
 MANAGING STALK ROTS FACTORS LEADING TO STALK ROTS Symptoms of crown rot were observed throughout fields across SE MN in 2014. Many plants were stunted and yellowed even with relatively mild crown decay.
MANAGING STALK ROTS FACTORS LEADING TO STALK ROTS Symptoms of crown rot were observed throughout fields across SE MN in 2014. Many plants were stunted and yellowed even with relatively mild crown decay.
Horticulture Agent Davis County Utah State University
 Top 10 Pathogenic Diseases -Woody OrnamentalsOrnamentalsJayDee Gunnell Horticulture Agent Davis County Utah State University Plant Diseases Disease anything that affects the normal function of the plant.
Top 10 Pathogenic Diseases -Woody OrnamentalsOrnamentalsJayDee Gunnell Horticulture Agent Davis County Utah State University Plant Diseases Disease anything that affects the normal function of the plant.
