Vineyard Soil Management. Sydney Environmental & Soil Laboratory Pty Ltd ABN E: W:
|
|
|
- Edwin Doyle
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vineyard Soil Management Sydney Environmental & Soil Laboratory Pty Ltd ABN PO Box 357 Pennant Hills NSW Chilvers Road Thornleigh NSW 2120 Australia T: F: E: W: ISO 9001 Lic QEC21650 SAI Global
2 Sydney Environmental & Soil Laboratory Vineyard Soil Management A brief introduction to understanding, preparing and maintaining a soil for wine grape production. Simon Leake BScAgr(HonsI) ASSSI ASPAC AIAST Principal Soil Scientist: Sydney Environmental and Soil Laboratory. Introduction: Soil properties Most soils in the prime NSW Vineyard areas are of the duplex or podsolic soil type. This means they have a sandy to loamy A horizon generally around 150mm deep but sometimes to 600 mm deep, overlying a clayey B horizon layer of a red or yellow colour. Sometimes they have a sandy pale A2 horizon below the darker A1 horizon. This layer is often quite hostile being acidic, low in organic matter, very low in nutrients, and prone to periodic waterlogging. Periodic waterlogging or poor drainage is indicated by the presence of black and tan colored roundish nodules (Fe/Mn nodules). In their natural state these soils profiles can suffer the following productivity problems: 1. Low organic matter content. Many Australian soils are naturally low in OM but years of sheep grazing, cropping with inadequate rotation, and excessive ploughing will have further degraded them. 2. Low to very low inherent fertility. While they may have supported adequate fine wool pasture and the occasional low wheat yield, their natural fertility is not adequate to support a high yielding intensive horticultural crop like vines. 3. A strong texture contract from the A to the B horizon. This inhibits downward movement of water, results in a very low oxygen subsoil when wet, and impedes downward extension of root growth. 4. Acidity. The soils of the wine grape growing areas are quite variable, some being highly acidic, others being alkaline (calcic or sodic). Other complications can include the presence of areas of light soil country (sandstone geology) and areas of fluvial and volcanic soils. 5. Sodicity. Usually confined to the subsoil, a high sodium level is common in yellow subsoils and gets worse with depth even in red soil country. High sodium leads to clay dispersion, erosion, poor subsoil structure (and hence root growth), and poor drainage and aeration. An understanding of the chemistry and physical properties of a proposed vineyard is essential before planting occurs or even before purchase of the property. Money Vineyard Soil Management - SW Leake 12/5/1999 page 1 of 4
3 saved on a cheaper property may well be spent in bringing the soils up to standard. The ideal properties of a soil for vineyard use shown in Table 1. Table 1. Ideal Vineyard Soil Properties Soil Property Ideal Range ph Exchangeable Na % < 7.0 Exchangeable Ca % 65-75% Exchangeable K % 3-10% Bray P mg/kg >20 Topsoil Organic Matter 3-6% Total N % Density g/cc < 1.4 in the surface Free rooting soil depth 500 mm Almost no natural soils have these characteristics which means that in nearly all cases soils need to be modified before planting and to be maintained and managed so that these characteristics are enhanced and preserved. Establishment The best horticultural soils do not show extreme variation in texture between the A horizon and the B horizon but only a slow increase in texture with depth (ie a gradational profile form). It will thus be necessary to think about destroying any strict A/B boundary by ripping to 500mm. Before ripping soil tests should be performed in order to gauge the need for basic soil ameliorants like lime and gypsum or combinations of both to bring soil ph and Ca levels to within the desired range for the whole of the surface 500mm. The opportunity can also be taken to add phosphorus before ripping so that it too is mixed thoroughly with the whole surface soil. Trace element additions are also advisable during this initial soil preparation period as they are very immobile and surface applied trace elements will stay close to the surface for many years. All nitrogen, potassium, and sulphur nutrients can be watered in or added to subsequent fertiliser programs. Lime, gypsum, and phosphatic fertilisers are not so soluble and should be mixed thoroughly in the topsoil. Superphosphate levels of over 1 tonne per hectare can be needed on soils with high fixation properties. Vineyard Soil Management - SW Leake 12/5/1999 page 2 of 4
4 Sydney Environmental & Soil Laboratory After ripping it is sometimes necessary to deep plough with discs to invert and destroy the A2 horizon, mix a little subsoil into it, and vice versa, mix some topsoil into the heavy clay B horizon and to lower density for new root extension. Certainly on row we should aim at a free rooting depth with good chemical properties of at least 500mm. Hilling on row can be helpful in deepening topsoil on shallow, impeded, or rocky sites. Green manure cropping is often the only cost effective way to increase soil organic matter levels. Ideally at least one green manure crop should be grown on the newly prepared site before planting. The ideal green manure crop in the first instance is a mixed grass/clover sward. If clover is not included then initial nitrogen applications will be need to ensure a good crop of green manure. Green manure should be worked in about 6 weeks before planting so that roots of the new vines have a rich decomposing humus layer to grow into. Yearly Management Management of soil properties aims at optimising nutrient and water supply within the crop cycle and maintaining or even improving soil properties over time. Soil Nitrogen Supply Nitrogen is the element most important in managing vines. Excess nitrogen results in excessive vegetative vigour at the expense of flowers and fruits, but nitrogen deficiency has been clearly shown to affect fermentation time and wine quality. Bad experiences with excessive nitrogen or inappropriate timing has sometimes resulted in the belief that there is an inverse relationship between quality and quantity. The conclusion a lot of people make is that the vines must be starved to produce good wine. This is not correct. All subsequent comments on nitrogen addition should keep the desired wine style in mind. It is now understood that nitrogen application can be manipulated to gain better control over vigour, fruitfulness, juice N content and storage qualities. The propensity of vines to produce a proliferation of vegetative growth or to produce larger fruit with lower quality is controlled by using regulated deficit irrigation (RDI) to concentrate fruit flavours. The following summary of the calender of events should prove helpful: Budburst to Flowering. Stored N provides only about 20% of the N needed for budburst and extension before flowering. The remaining 80% must be obtained from the soil. Therefore - work in winter green manure 6 weeks before budburst. In a highly fertile soil with clover in the green manure this may provide enough N from the decomposing green manure otherwise additional surface applications should be Vineyard Soil Management - SW Leake 12/5/1999 page 3 of 4
5 judged subject to previous experience, crop appearance and testing if needed. Remember that time must be allowed for N to be washed down into the soil to where roots can obtain it if the N was not added prior to ploughing in green manure. Do not apply N too close to flowering as bunch shatter can result. Any other nutrients required, such as phosphorus, potassium, trace elements, etc determined from winter soil analysis should also be added and worked in at around 4-6 weeks prior to budburst. Flowering to Verasion. Nitrogen supply during this period has the greatest effect on final N status of the bunches. Except in the most N fertile soils additional N application during this period will bring the greatest benefits. Up to three soluble N applications as fertigation have been shown to be of benefit. Addition of N should be based strictly on plant petiole testing as it is very difficult to predict the N supplying ability of soil and the plant is the best indicator. Verasion to Harvest. There is usually little advantage in applying N during this stage. The N applied prior to verasion will have had the major effect. Harvest to Dormancy. This is a period of relocation of canopy N into plant stores for the following season. It is widely accepted now that, provided N additions earlier in the season have been adequate, there is no advantage to wine quality from adding N after harvest despite the fact that an additional burst of root growth occurs. In any event, careful records of N fertiliser additions, juice quality determinants, fermentation characteristics should be kept so that a site specific N management program for that crop variety can be arrived at. With time a tailor made program with your wine style in mind can be developed. Potassium is rarely needed in the heavier soil types but may need attention in the lighter soil types. Excessive potassium upsets wine acid balance basically through the precipitation of insoluble potassium bitartrate in the must. Keep potassium at the lower end of adequate in Red grape varieties as a general rule. Winter. The dormant period is an important time in the annual cycle. Soil tests should be performed prior to sowing green manures. All vineyards should, in our opinion, utilise green manure crops. They: 1. increase and maintain a high soil organic matter content 2. stimulate a living healthy soil full or organisms 3. improve soil structure 4. maintain a natural temperature balance 5. utilise fertiliser nutrients wasted in the growing season 6. help break weed life cycles. 7. where clovers are used they fix atmospheric nitrogen 8. prevent erosion Chemical fallow under vines represents an unsustainable practice leading to soil organic matter and structural decline. Use sidecasting mowers to throw mulched Vineyard Soil Management - SW Leake 12/5/1999 page 4 of 4
6 Sydney Environmental & Soil Laboratory inter-row sod growth onto the on row soil surface. All plants grow much better with mulch. Green manures can be cereal, legume, or grass crops grown in the inter-row space. Avoid perennial species that are likely to result in weed problems during the growing season. The most suitable green manure for long term maintenance is probably a clover/annual rye or cereal mixture. Bias the green manure program towards legumes if additional soil N is needed, and toward pure grasses if organic matter is needed. It has been shown that dense ryegrass stands lead to the quickest increase in soil organic matter content. Summary: Treat soil physically to destroy texture boundaries and create a gradational soil profile 500mm deep at minimum. Correct gross deficiencies before planting using lime, gypsum, phosphate, and trace elements as needed. Include green manure in the preplant conditioning program. Develop a N fertilising program over time suited to your variety and site by taking careful records. Include N from winter green manure in the program but add N as needed. Apply readily available N only between flowering and verasion. Use the winter period for ph and Ca adjustment, phosphorus additions, and green manuring. Use inter-row sod grass sward to mulch rows during the growing season, shading and protecting the soil from drying and heating and stimulating soil organisms. Wherever possible do not use drip irrigation, use mini sprayers in pulsed irrigation methods. Further reading- Goldspink B.H. (Ed) Fertilisers for Wine Grapes. West Australian Dept of Agriculture. Vineyard Soil Management - SW Leake 12/5/1999 page 5 of 4
EARTH SCIENCE CONCEPTS -Geologic time scale
 EARTH SCIENCE CONCEPTS -Geologic time scale -Plate Tectonics -Earthquakes *result of vibrations (often due to plate movement) deep in the Earth that release energy *often occur at transform boundaries
EARTH SCIENCE CONCEPTS -Geologic time scale -Plate Tectonics -Earthquakes *result of vibrations (often due to plate movement) deep in the Earth that release energy *often occur at transform boundaries
THE TENNESSEE VEGETABLE GARDEN
 THE BACKYARD SERIES BACKYARD VEGETABLES W 346-A THE TENNESSEE VEGETABLE GARDEN SITE SELECTION AND SOIL TESTING Natalie Bumgarner, Assistant Professor and UT Extension Residential and Consumer Horticulture
THE BACKYARD SERIES BACKYARD VEGETABLES W 346-A THE TENNESSEE VEGETABLE GARDEN SITE SELECTION AND SOIL TESTING Natalie Bumgarner, Assistant Professor and UT Extension Residential and Consumer Horticulture
Information Note Choosing a Cover Crop. Crimson Clover
 Information Note Choosing a Cover Crop Cover crops are primarily grown to provide ground protection and soil enrichment. With an increase in extreme weather events predicted due to climate change, cover
Information Note Choosing a Cover Crop Cover crops are primarily grown to provide ground protection and soil enrichment. With an increase in extreme weather events predicted due to climate change, cover
Soils and plant nutrients
 Soils and plant nutrients Soils and soil texture Soil texture triangle Plant nutrients Major nutrients Secondary nutrients Minor nutrients Exchange Capacity (CEC) Soil ph Soils Consists of a series of
Soils and plant nutrients Soils and soil texture Soil texture triangle Plant nutrients Major nutrients Secondary nutrients Minor nutrients Exchange Capacity (CEC) Soil ph Soils Consists of a series of
Soils. Nutrients needed by plants 10/21/2013. Consists of a series of layers called. Soils consists of: Topsoil (A horizon) upper most layer
 Soils Consists of a series of layers called Topsoil (A horizon) upper most layer Soils consists of: Mineral particles determine soil texture Organic matter Air and Soil organisms Nutrients needed by plants
Soils Consists of a series of layers called Topsoil (A horizon) upper most layer Soils consists of: Mineral particles determine soil texture Organic matter Air and Soil organisms Nutrients needed by plants
Nutrient Management of Irrigated Alfalfa and Timothy
 Nutrient Management of Irrigated Alfalfa and Timothy Irrigated Crop Production Conf. Lethbridge, AB Jan 19, 2016 Ross H. McKenzie Old Agronomist Lethbridge Introduction Alfalfa and Timothy are excellent
Nutrient Management of Irrigated Alfalfa and Timothy Irrigated Crop Production Conf. Lethbridge, AB Jan 19, 2016 Ross H. McKenzie Old Agronomist Lethbridge Introduction Alfalfa and Timothy are excellent
Understanding Soil Variability to Utilize Variable Rate Fertilizer Technology
 Understanding Soil Variability to Utilize Variable Rate Fertilizer Technology Agronomy Update -2012 Red Deer, AB Jan 17 & 18, 2012 Ross H. McKenzie Research Scientist Agronomy Research & Innovation Div.
Understanding Soil Variability to Utilize Variable Rate Fertilizer Technology Agronomy Update -2012 Red Deer, AB Jan 17 & 18, 2012 Ross H. McKenzie Research Scientist Agronomy Research & Innovation Div.
Getting the Most out of Your Strawberry Soil Test Report. General Information
 gardening.cornell.edu Getting the Most out of Your Strawberry Soil Test Report 1. Be certain your soil ph is in the optimal range. 2. Add a nitrogen (N) source at the recommended rate and time. 3. Add
gardening.cornell.edu Getting the Most out of Your Strawberry Soil Test Report 1. Be certain your soil ph is in the optimal range. 2. Add a nitrogen (N) source at the recommended rate and time. 3. Add
Unit D: ph of Soil. Lesson : Identifying the ph Changes in Soil
 Unit D: ph of Soil Lesson : Identifying the ph Changes in Soil 1 KEY TERMS Soil ph Acid Lime Requirement 2 I. The ph scale measures how acidic or basic a substance is. A. It ranges from 0 to 14. 1. A ph
Unit D: ph of Soil Lesson : Identifying the ph Changes in Soil 1 KEY TERMS Soil ph Acid Lime Requirement 2 I. The ph scale measures how acidic or basic a substance is. A. It ranges from 0 to 14. 1. A ph
Unearthing problem soils in the Lachlan Valley
 Vol 24, No 1, page 32 February-March, 2003 The Australian Cottongrower Unearthing problem soils in the Lachlan Valley By Edward Cay and Stephen Cattle, The University of Sydney and Australian Cotton CRC
Vol 24, No 1, page 32 February-March, 2003 The Australian Cottongrower Unearthing problem soils in the Lachlan Valley By Edward Cay and Stephen Cattle, The University of Sydney and Australian Cotton CRC
Establish plants outdoors
 Establish plants outdoors Note: This section is in two parts Prepare ground for establishing plants CONTENTS Part 1 Page Number Preparing the area...2 Soils and growing media...3-4 Clearing the site...5
Establish plants outdoors Note: This section is in two parts Prepare ground for establishing plants CONTENTS Part 1 Page Number Preparing the area...2 Soils and growing media...3-4 Clearing the site...5
CLAY SPREADING AND DELVING FACT SHEET
 JANUARY 2015 CLAY SPREADING AND DELVING FACT SHEET EYRE PENINSULA CLAY SPREADING AND DELVING IN LIGHT, SANDY SOILS Clay spreading or delving can significantly improve yields of sandy soils but it is vital
JANUARY 2015 CLAY SPREADING AND DELVING FACT SHEET EYRE PENINSULA CLAY SPREADING AND DELVING IN LIGHT, SANDY SOILS Clay spreading or delving can significantly improve yields of sandy soils but it is vital
CLAY SPREADING AND DELVING FACT SHEET
 JANUARY 2015 CLAY SPREADING AND DELVING FACT SHEET EYRE PENINSULA CLAY SPREADING AND DELVING IN LIGHT, SANDY SOILS Clay spreading or delving can significantly improve yields of sandy soils but it is vital
JANUARY 2015 CLAY SPREADING AND DELVING FACT SHEET EYRE PENINSULA CLAY SPREADING AND DELVING IN LIGHT, SANDY SOILS Clay spreading or delving can significantly improve yields of sandy soils but it is vital
Mature basalt volcanic soils
 MANAGING NORTHLAND SOILS Mature basalt volcanic soils 8.1.2 Soil types in this group Kerikeri friable clay (KE) Kerikeri friable clay with large boulders (KEb) Matarau friable clay (MC, MCH*) Matarau friable
MANAGING NORTHLAND SOILS Mature basalt volcanic soils 8.1.2 Soil types in this group Kerikeri friable clay (KE) Kerikeri friable clay with large boulders (KEb) Matarau friable clay (MC, MCH*) Matarau friable
Soil Geography Notes JC-Learn. JC-Learn. Geography Notes Soil. 1 P a g e
 JC-Learn Geography Notes Soil 1 P a g e Soil Soil is the thin covering of loose material that makes up the outermost layer of our planet. It is a living thing and a rich natural resource. Plants need soil
JC-Learn Geography Notes Soil 1 P a g e Soil Soil is the thin covering of loose material that makes up the outermost layer of our planet. It is a living thing and a rich natural resource. Plants need soil
Unit 5: Soil - Stages of Soil formation
 Biology Form 3 Page 68 Ms. R. Buttigieg Unit 5: Soil - Stages of Soil formation Soil is the layer of material covering parts of the land, the home of many organisms and the area from which land plants
Biology Form 3 Page 68 Ms. R. Buttigieg Unit 5: Soil - Stages of Soil formation Soil is the layer of material covering parts of the land, the home of many organisms and the area from which land plants
Vineyard Irrigation with a Limited Supply of Water. Glenn McGourty UCCE Mendocino and Lake Counties
 Vineyard Irrigation with a Limited Supply of Water Glenn McGourty UCCE Mendocino and Lake Counties Thanks in Advance to the Land Down Under Michael McCarthy, PIRSA-SARDI, Barossa Valley, SA Chris Penfold,
Vineyard Irrigation with a Limited Supply of Water Glenn McGourty UCCE Mendocino and Lake Counties Thanks in Advance to the Land Down Under Michael McCarthy, PIRSA-SARDI, Barossa Valley, SA Chris Penfold,
Inherent Factors Affecting Soil ph. Soil ph Management
 Soil ph is a measure of soil acidity or alkalinity. It is an important indicator of soil health. It affects crop yields, crop suitability, plant nutrient availability, and soil micro-organism activity
Soil ph is a measure of soil acidity or alkalinity. It is an important indicator of soil health. It affects crop yields, crop suitability, plant nutrient availability, and soil micro-organism activity
HEALTHY SOILS LANDHOLDER SERIES PROPERTY PLANNING GUIDE CHARACTERISTICS OF A HEALTHY SOIL LANDHOLDER SERIES - PROPERTY PLANNING GUIDE HEALTHY SOILS
 LANDHOLDER SERIES PROPERTY PLANNING GUIDE Soil health refers to the condition of the soil and its potential to sustain biological functioning, maintain environmental quality, and promote plant and animal
LANDHOLDER SERIES PROPERTY PLANNING GUIDE Soil health refers to the condition of the soil and its potential to sustain biological functioning, maintain environmental quality, and promote plant and animal
Topoclimate Southland Soil Technical Data Sheet No. 8. Sobig
 This Technical Data Sheet describes the typical average properties of the specified soil. It is essentially a summary of information obtained from one or more profiles of this soil that were examined and
This Technical Data Sheet describes the typical average properties of the specified soil. It is essentially a summary of information obtained from one or more profiles of this soil that were examined and
PASTURE AND HAY FIELDS: SOIL FUNDAMENTALS. Sanders County April 8, Clain Jones
 PASTURE AND HAY FIELDS: SOIL FUNDAMENTALS Sanders County April 8, 2015 Clain Jones clainj@montana.edu 994-6076 Objectives Present soil properties and how they interact with plant nutrients Illustrate the
PASTURE AND HAY FIELDS: SOIL FUNDAMENTALS Sanders County April 8, 2015 Clain Jones clainj@montana.edu 994-6076 Objectives Present soil properties and how they interact with plant nutrients Illustrate the
Getting Started with Your Vegetable Garden
 The Basics Getting Started with Your Vegetable Garden Nathan Gerber Advanced Master Gardener USU Extension Thanksgiving Point A little About Vegetables Choosing the Right Location Planning your Garden
The Basics Getting Started with Your Vegetable Garden Nathan Gerber Advanced Master Gardener USU Extension Thanksgiving Point A little About Vegetables Choosing the Right Location Planning your Garden
Management of Sodic Soils in Alberta
 June 2010 Agdex 518-20 Management of Sodic Soils in Alberta The two main types of salt-affected soils found in Alberta are soils and sodic soils. Saline soils are soils with a high enough concentration
June 2010 Agdex 518-20 Management of Sodic Soils in Alberta The two main types of salt-affected soils found in Alberta are soils and sodic soils. Saline soils are soils with a high enough concentration
Inherent Factors Affecting Soil ph. Soil ph Management
 Soil ph is a measure of soil acidity or alkalinity. It is an important indicator of soil health. It affects crop yields, crop suitability, plant nutrient availability, and soil micro-organism activity,
Soil ph is a measure of soil acidity or alkalinity. It is an important indicator of soil health. It affects crop yields, crop suitability, plant nutrient availability, and soil micro-organism activity,
THINKING ABOUT GROWING PISTACHIOS? BEN THOMAS Ben Thomas Consulting
 THINKING ABOUT GROWING PISTACHIOS? BEN THOMAS Ben Thomas Consulting CLIMATE CONSIDERATIONS Winter chill Winter chill needed to break tree dormancy and promote good, even and timely bud break. Dynamic chill
THINKING ABOUT GROWING PISTACHIOS? BEN THOMAS Ben Thomas Consulting CLIMATE CONSIDERATIONS Winter chill Winter chill needed to break tree dormancy and promote good, even and timely bud break. Dynamic chill
Land Capability Class
 Guide for Applying Conservation Treatments for Land Evaluation (5/23/2011) LAND TREATMENT After examining and determining the physical features of the soil profile, one can determine the land capability
Guide for Applying Conservation Treatments for Land Evaluation (5/23/2011) LAND TREATMENT After examining and determining the physical features of the soil profile, one can determine the land capability
Soil and Plant Basics 2016 EKS Grazing School September 20, 2016
 Soil and Plant Basics 2016 EKS Grazing School September 20, 2016 David G. Hallauer Meadowlark Extension District Agent, Crops & Soils/Horticulture (785) 863 2212 What Plants Need to Grow Sunlight Air Water
Soil and Plant Basics 2016 EKS Grazing School September 20, 2016 David G. Hallauer Meadowlark Extension District Agent, Crops & Soils/Horticulture (785) 863 2212 What Plants Need to Grow Sunlight Air Water
FERTILISING SPORTING FIELDS
 AGRITOPIC December 2014 FERTILISING SPORTING FIELDS (New South Wales) 1. INTRODUCTION Sporting fields vary considerably in their use and management, from major sporting venues that are used throughout
AGRITOPIC December 2014 FERTILISING SPORTING FIELDS (New South Wales) 1. INTRODUCTION Sporting fields vary considerably in their use and management, from major sporting venues that are used throughout
5.1 Introduction to Soil Systems IB ESS Mrs. Page
 5.1 Introduction to Soil Systems IB ESS Mrs. Page 2015-2016 I Am Soil Thinking Routine: See, Think, Wonder Look at the following images. For each image write down what you see Then write down what you
5.1 Introduction to Soil Systems IB ESS Mrs. Page 2015-2016 I Am Soil Thinking Routine: See, Think, Wonder Look at the following images. For each image write down what you see Then write down what you
Inovace studijních programů AF a ZF MENDELU směřující k vytvoření mezioborové integrace CZ.1.07/2.2.00/
 Inovace studijních programů AF a ZF MENDELU směřující k vytvoření mezioborové integrace CZ.1.07/2.2.00/28.0302 Tato prezentace je spolufinancovaná z Evropského sociálního fondu a státního rozpočtu České
Inovace studijních programů AF a ZF MENDELU směřující k vytvoření mezioborové integrace CZ.1.07/2.2.00/28.0302 Tato prezentace je spolufinancovaná z Evropského sociálního fondu a státního rozpočtu České
Unit D: Fruit and Vegetable Crop Production. Lesson 1: Planning and Preparing a Vegetable Garden Site
 Unit D: Fruit and Vegetable Crop Production Lesson 1: Planning and Preparing a Vegetable Garden Site 1 Terms Adequate sunlight Climate Compost Cool-season vegetables Cover crop Crop rotation Fertile soil
Unit D: Fruit and Vegetable Crop Production Lesson 1: Planning and Preparing a Vegetable Garden Site 1 Terms Adequate sunlight Climate Compost Cool-season vegetables Cover crop Crop rotation Fertile soil
Nutrient Management And Nutrient Cycling Raymond C. Ward, President Ward Laboratories, Inc Kearney, NE
 Nutrient Management And Nutrient Cycling Raymond C. Ward, President Ward Laboratories, Inc Kearney, NE www.rayward@wardlab.com Take Good Soil Samples to Evaluate Soil Fertility Status Take soils samples
Nutrient Management And Nutrient Cycling Raymond C. Ward, President Ward Laboratories, Inc Kearney, NE www.rayward@wardlab.com Take Good Soil Samples to Evaluate Soil Fertility Status Take soils samples
Remediated and Constructed Soils of Sydney Olympic Park. Sydney Environmental & Soil Laboratory Pty Ltd ABN
 Remediated and Constructed Soils of Sydney Olympic Park Pty Ltd ABN 70 106 810 708 PO Box 357 Pennant Hills NSW 1715 16 Chilvers Road Thornleigh NSW 2120 Australia T: 02 9980 6554 F: 02 9484 2427 E: info@sesl.com.au
Remediated and Constructed Soils of Sydney Olympic Park Pty Ltd ABN 70 106 810 708 PO Box 357 Pennant Hills NSW 1715 16 Chilvers Road Thornleigh NSW 2120 Australia T: 02 9980 6554 F: 02 9484 2427 E: info@sesl.com.au
PROUDLY MADE IN AUSTRALIA
 Unlock your soil s potential with K-humate Improves soil moisture and nutrient retention Reduces nutrient lock-up in the soil Helps the development of better soil structures Stimulates plant root growth
Unlock your soil s potential with K-humate Improves soil moisture and nutrient retention Reduces nutrient lock-up in the soil Helps the development of better soil structures Stimulates plant root growth
Introduction to Environmental Science. Soil Characteristics. Chapter 11 Soil
 Chapter 11 Soil Soil Characteristics It s more than dirt Most soils are 100s of years old Weathering breaks down parent rock Soil Separates (particle types) Sand (largest) Silt Clay (smallest) Plants contribute
Chapter 11 Soil Soil Characteristics It s more than dirt Most soils are 100s of years old Weathering breaks down parent rock Soil Separates (particle types) Sand (largest) Silt Clay (smallest) Plants contribute
CLAY, SANDY AND PEAT SOILS, AND SOIL ORGANIC MATTER
 CLAY, SANDY AND PEAT SOILS, AND SOIL ORGANIC MATTER Background Most normal soils ( mineral soils ) consist of tiny particles of rock that have been broken into small pieces by such things as wind, water,
CLAY, SANDY AND PEAT SOILS, AND SOIL ORGANIC MATTER Background Most normal soils ( mineral soils ) consist of tiny particles of rock that have been broken into small pieces by such things as wind, water,
Tilth: Tilth: Soil Structure and its Management. Tilth: Soil Structure and its Management
 Tilth: Soil Structure and its Management Sonoma County Vineyard Technical Group May 18, 2017 Tilth: Soil Structure and its Management Paul R. Anamosa, Ph.D. Viticultural Soil Scientist www.vineyardsoil.com
Tilth: Soil Structure and its Management Sonoma County Vineyard Technical Group May 18, 2017 Tilth: Soil Structure and its Management Paul R. Anamosa, Ph.D. Viticultural Soil Scientist www.vineyardsoil.com
SOIL TEST HANDBOOK FOR GEORGIA
 SOIL TEST HANDBOOK FOR GEORGIA Georgia Cooperative Extension College of Agricultural & Environmental Sciences The University of Georgia Athens, Georgia 30602-9105 EDITORS: David E. Kissel Director, Agricultural
SOIL TEST HANDBOOK FOR GEORGIA Georgia Cooperative Extension College of Agricultural & Environmental Sciences The University of Georgia Athens, Georgia 30602-9105 EDITORS: David E. Kissel Director, Agricultural
Apply approx 50-65g per square metre. Available in pack sizes: 1kg, 2kg and 5kg. Apply 100g per square metre, each spring. Water in well.
 FERTILISERS All Purpose Slow Release This is a balanced all round fertiliser with elements which can be used before, during and after planting, and helps with plant growth. Ideal for all chloride-sensitive
FERTILISERS All Purpose Slow Release This is a balanced all round fertiliser with elements which can be used before, during and after planting, and helps with plant growth. Ideal for all chloride-sensitive
Assessing and Amending Your Garden Soil Craig Cogger, Soil Scientist Emeritus Washington State University Puyallup
 Assessing and Amending Your Garden Soil Craig Cogger, Soil Scientist Emeritus Washington State University Puyallup The soil is the great connector of our lives, the source and destination of all. - Wendell
Assessing and Amending Your Garden Soil Craig Cogger, Soil Scientist Emeritus Washington State University Puyallup The soil is the great connector of our lives, the source and destination of all. - Wendell
Soil Test Report. HOME GARDEN VEGETABLE GARDEN Analysis Results
 Analysis VEGETABLE GARDEN Analysis Results Result Account Number: 54321 Page: 1 of 6 Soil Test Rating Very Low Low Medium High Very High Organic Matter, % 4.6 Phosphorus, ppm P (Bray-1 Equiv.) 12 Potassium,
Analysis VEGETABLE GARDEN Analysis Results Result Account Number: 54321 Page: 1 of 6 Soil Test Rating Very Low Low Medium High Very High Organic Matter, % 4.6 Phosphorus, ppm P (Bray-1 Equiv.) 12 Potassium,
THE FOREST NURSERY AND ITS SOILS
 THE FOREST NURSERY AND ITS SOILS Dr. Jack May, Professor School of Forestry University of Georgia Forest tree nurseries are located on a variety of soils ranging in texture from sand to silt loam in the
THE FOREST NURSERY AND ITS SOILS Dr. Jack May, Professor School of Forestry University of Georgia Forest tree nurseries are located on a variety of soils ranging in texture from sand to silt loam in the
A&L Canada Laboratories Inc.
 A&L Canada Laboratories Inc. 2136 Jetstream Rd, London ON N5V3P5 Tel: (519) 457-2575 Fax: (519) 457-2664 SOIL SAMPLING GUIDE SOIL SAMPLING PROCEDURES The intention of the following information is to aid
A&L Canada Laboratories Inc. 2136 Jetstream Rd, London ON N5V3P5 Tel: (519) 457-2575 Fax: (519) 457-2664 SOIL SAMPLING GUIDE SOIL SAMPLING PROCEDURES The intention of the following information is to aid
Recommended Resources: The following resources may be useful in teaching
 Unit B: Establishing a Fruit Garden Lesson 1: Recognize the Characteristics of Soils and the Soil Requirements for Fruit and Nut Crops Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result
Unit B: Establishing a Fruit Garden Lesson 1: Recognize the Characteristics of Soils and the Soil Requirements for Fruit and Nut Crops Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result
Lesson 1: Recognizing the Characteristics of Soils and the Soil Requirements for Fruit and Nut Crops
 Lesson 1: Recognizing the Characteristics of Soils and the Soil Requirements for Fruit and Nut Crops 1 Mineral matter Organic matter Pore spaces Tilth Hygroscopic water Soil aeration 22 I. Soil is a layer
Lesson 1: Recognizing the Characteristics of Soils and the Soil Requirements for Fruit and Nut Crops 1 Mineral matter Organic matter Pore spaces Tilth Hygroscopic water Soil aeration 22 I. Soil is a layer
Iowa FFA Soil Career Development Event 2008
 Iowa FFA Soil Career Development Event 2008 1. In Iowa, corn suitability ratings for soil mapping units specifies a. natural weather conditions b. surface and subsurface drainage installed where needed
Iowa FFA Soil Career Development Event 2008 1. In Iowa, corn suitability ratings for soil mapping units specifies a. natural weather conditions b. surface and subsurface drainage installed where needed
Managing your soil. Cultivation. Beds. Digging tips GS4
 GS4 Managing your soil A fertile one with both a good structure and a good supply of plant foods. When managing your soil, hold both these objectives in mind. Aim to protect and maintain what you have,
GS4 Managing your soil A fertile one with both a good structure and a good supply of plant foods. When managing your soil, hold both these objectives in mind. Aim to protect and maintain what you have,
G A Gardener's Guide for Soil and Nutrient Management in Growing Vegetables
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Historical Materials from University of Nebraska- Lincoln Extension Extension 1990 G90-945 A Gardener's Guide for Soil and
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Historical Materials from University of Nebraska- Lincoln Extension Extension 1990 G90-945 A Gardener's Guide for Soil and
REVIEW OF AVOCADO FERTILIZER PRACTICES IN SAN DIEGO COUNTY
 California Avocado Society 1979 Yearbook 63: 50-57 REVIEW OF AVOCADO FERTILIZER PRACTICES IN SAN DIEGO COUNTY C. Don Gustafson Farm Advisor, Cooperative Extension Service. University of California. San
California Avocado Society 1979 Yearbook 63: 50-57 REVIEW OF AVOCADO FERTILIZER PRACTICES IN SAN DIEGO COUNTY C. Don Gustafson Farm Advisor, Cooperative Extension Service. University of California. San
Soils and their Relationship with Agriculture
 Soils and their Relationship with Agriculture Presentation created by Thomas Gallagher Modified by Hank Bignell Capital Area Agriculture and Horticulture Program Cornell University Cooperative Extension
Soils and their Relationship with Agriculture Presentation created by Thomas Gallagher Modified by Hank Bignell Capital Area Agriculture and Horticulture Program Cornell University Cooperative Extension
AGRICULTURAL LAND CLASSIFICATION AND SOIL PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS LAND NEAR SHIRE HILL FARM SAFFRON WALDEN ESSEX
 AGRICULTURAL LAND CLASSIFICATION AND SOIL PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS LAND NEAR SHIRE HILL FARM SAFFRON WALDEN ESSEX AGRICULTURAL LAND CLASSIFICATION (ALC) AND SOIL PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS LAND NEAR SHIRE
AGRICULTURAL LAND CLASSIFICATION AND SOIL PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS LAND NEAR SHIRE HILL FARM SAFFRON WALDEN ESSEX AGRICULTURAL LAND CLASSIFICATION (ALC) AND SOIL PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS LAND NEAR SHIRE
Soil Resources. Soil Horizons
 Soil Resources Soil Uppermost layer of earth s crust that supports plants, animals and microbes Soil Forming Factors Parent Material Time Climate Organisms Topography Soil Composition Mineral Particles
Soil Resources Soil Uppermost layer of earth s crust that supports plants, animals and microbes Soil Forming Factors Parent Material Time Climate Organisms Topography Soil Composition Mineral Particles
Do Now: From which materials do you think soil is made? Are all soils the same? Think of some ways that they are different?
 Do Now: From which materials do you think soil is made? Are all soils the same? Think of some ways that they are different? Basics Soil is a major component of the biosphere It contains solids, liquids
Do Now: From which materials do you think soil is made? Are all soils the same? Think of some ways that they are different? Basics Soil is a major component of the biosphere It contains solids, liquids
Crop Management Practices. By Simon Bedasie
 Crop Management Practices Fertigation By Simon Bedasie Observations of a Visiting Consultant Water and fertilizer management looked like bucket chemistry. Very basic techniques for water and fertilizer
Crop Management Practices Fertigation By Simon Bedasie Observations of a Visiting Consultant Water and fertilizer management looked like bucket chemistry. Very basic techniques for water and fertilizer
Loam: About 40% sand, 40% silt, 20% clay. Mixture of pore sizes to balance water retention and aeration. Considered the best soil for growing crops.
 Soil Characteristics Soil is formed from a combination of two Primary sources: Weathering of Parent Rock ( ) = material introduced by plants, animals, and decomposers Minor sources: Nutrients incorporated
Soil Characteristics Soil is formed from a combination of two Primary sources: Weathering of Parent Rock ( ) = material introduced by plants, animals, and decomposers Minor sources: Nutrients incorporated
Sunlight. Chlorophyll
 Plant Nutrition & Soil Fertility Richard Smith Vegetable Crop and Weed Science Farm Advisor University of California Cooperative Extension Monterey, Santa Cruz and San Benito Counties Plant Nutrition 1.
Plant Nutrition & Soil Fertility Richard Smith Vegetable Crop and Weed Science Farm Advisor University of California Cooperative Extension Monterey, Santa Cruz and San Benito Counties Plant Nutrition 1.
Effects of the Bupa retirement complex on the soil resources at 25 & 35 Ulyatt Road, Napier
 Independent Agriculture & Horticulture Consultant Network Effects of the Bupa retirement complex on the soil resources at 25 & 35 Ulyatt Road, Napier Prepared for Napier City Council John Wilton 19 January
Independent Agriculture & Horticulture Consultant Network Effects of the Bupa retirement complex on the soil resources at 25 & 35 Ulyatt Road, Napier Prepared for Napier City Council John Wilton 19 January
EDULABZ. Ans. (b) 7. The soft, porous layer with a good water-retaining capacity forms the
 3 SOIL I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. The process of soil formation is called (a) conservation (b) weathering (c) erosion (d) none Ans. (b) 2. Soil profile consists of (a)
3 SOIL I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. The process of soil formation is called (a) conservation (b) weathering (c) erosion (d) none Ans. (b) 2. Soil profile consists of (a)
Eco new farmers. Module 2 Soil and Nutrient Cycling. Section 1 Soils and soil fertility
 Eco new farmers Module 2 Soil and Nutrient Cycling Section 1 Soils and soil fertility Module 2 Soil and Nutrient Cycling Section 1 - Soils and soil fertility www.econewfarmers.eu 1. Introduction You will
Eco new farmers Module 2 Soil and Nutrient Cycling Section 1 Soils and soil fertility Module 2 Soil and Nutrient Cycling Section 1 - Soils and soil fertility www.econewfarmers.eu 1. Introduction You will
Prepare a good seed bed and after sowing, roll to compact the soil and ensure good soil contact with the seeds.
 Establishment Prepare a good seed bed and after sowing, roll to compact the soil and ensure good soil contact with the seeds. Before sowing, inoculate the seeds with Bradyrhizobium rhizobium to enhance
Establishment Prepare a good seed bed and after sowing, roll to compact the soil and ensure good soil contact with the seeds. Before sowing, inoculate the seeds with Bradyrhizobium rhizobium to enhance
Soil Health Practices in the Landscape
 Soil Health Practices in the Landscape Salvatore Mangiafico Rutgers Cooperative Extension Environmental and Resource Management Agent In this session... Benefits of healthy soils in the landscape Plant
Soil Health Practices in the Landscape Salvatore Mangiafico Rutgers Cooperative Extension Environmental and Resource Management Agent In this session... Benefits of healthy soils in the landscape Plant
7. Nutrition and soil fertility
 7. Nutrition and soil fertility Paul Parker, NSW DPI As with any crop, it is critical for profitability to closely match canola s nutritional requirements with target yields. Canola requires high inputs
7. Nutrition and soil fertility Paul Parker, NSW DPI As with any crop, it is critical for profitability to closely match canola s nutritional requirements with target yields. Canola requires high inputs
Renegade Red Clover. Trifolium pratense. Seed agronomy table
 Renegade Red Clover Trifolium pratense Renegade is an erect, early flowering, double cut red clover with improved resistance to southern anthracnose and downy mildew. Renegade is classified as semi-dormant
Renegade Red Clover Trifolium pratense Renegade is an erect, early flowering, double cut red clover with improved resistance to southern anthracnose and downy mildew. Renegade is classified as semi-dormant
Recommended Resources: The following resources may be useful in teaching this
 Unit D: Fruit and Vegetable Crop Production Lesson 1: Planning and Preparing a Vegetable Garden Site Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following
Unit D: Fruit and Vegetable Crop Production Lesson 1: Planning and Preparing a Vegetable Garden Site Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following
Soil Management: the basis of sustainable agriculture
 Soil Management: the basis of sustainable agriculture FAB-465 Lecture 11 Lecture Outline Soil Formation Soil Structure/Texture Indicators of Soil Health or Fertility Soil Conservation Practices 1 Soil
Soil Management: the basis of sustainable agriculture FAB-465 Lecture 11 Lecture Outline Soil Formation Soil Structure/Texture Indicators of Soil Health or Fertility Soil Conservation Practices 1 Soil
Designing and Managing a Community Garden. Toby Day MSU Extension Horticulture Specialist
 Designing and Managing a Community Garden Toby Day MSU Extension Horticulture Specialist Recap of the Last Webinar: Essentials for Starting a Community Garden Who s in Charge of the Community Garden? What
Designing and Managing a Community Garden Toby Day MSU Extension Horticulture Specialist Recap of the Last Webinar: Essentials for Starting a Community Garden Who s in Charge of the Community Garden? What
A PowerPoint has been provided
 Unit D: ph of Soil Lesson 1: Identifying the ph Changes in Soil Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in the students achieving the following objectives: 1. Identify soil
Unit D: ph of Soil Lesson 1: Identifying the ph Changes in Soil Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in the students achieving the following objectives: 1. Identify soil
FERTILISING PARKS, LAWNS AND HOME GARDENS
 AGRITOPIC December 2014 FERTILISING PARKS, LAWNS AND HOME GARDENS (Queensland) 1. INTRODUCTION Apart from air and water, plants need an adequate supply of nutrients for growth. These nutrients are obtained
AGRITOPIC December 2014 FERTILISING PARKS, LAWNS AND HOME GARDENS (Queensland) 1. INTRODUCTION Apart from air and water, plants need an adequate supply of nutrients for growth. These nutrients are obtained
Vine Nutrition. A g e n d a 4/10/2017. Soil How to sample Sample submission sheet Lab analysis & results Interpretation
 A g e n d a 4/10/2017 Chris Clark, CCA Territory Sales Representative Vine Nutrition a major role in the life of a vineyard! Haily Henderson, CCA NMP/GPS Specialist & Agronomist Soil How to sample Sample
A g e n d a 4/10/2017 Chris Clark, CCA Territory Sales Representative Vine Nutrition a major role in the life of a vineyard! Haily Henderson, CCA NMP/GPS Specialist & Agronomist Soil How to sample Sample
Pistachio Project Planning, Irrigation Systems and Irrigation Management. Trevor Sluggett Irrigation Agronomist AgriExchange Pty Ltd
 Pistachio Project Planning, Irrigation Systems and Irrigation Management Trevor Sluggett Irrigation Agronomist AgriExchange Pty Ltd Excited About Pistachios A nut crop other than Almonds Good demand for
Pistachio Project Planning, Irrigation Systems and Irrigation Management Trevor Sluggett Irrigation Agronomist AgriExchange Pty Ltd Excited About Pistachios A nut crop other than Almonds Good demand for
2016 Iowa FFA Soils Evaluation CDE Exam
 2016 Iowa FFA Soils Evaluation CDE Exam 1. Which of the following is true regarding soil horizons? a. A horizon is darker in color and has more organic matter b. B horizon is darker in color and has more
2016 Iowa FFA Soils Evaluation CDE Exam 1. Which of the following is true regarding soil horizons? a. A horizon is darker in color and has more organic matter b. B horizon is darker in color and has more
agriculture, thus it is critical that you do your homework.
 Establishing a Commercial Vineyard in Nebraska Paul E. Read, Professor of Horticulture/Viticulture and Stephen Gamet, Research Technologist University of Nebraska Viticulture Program Department of Agronomy
Establishing a Commercial Vineyard in Nebraska Paul E. Read, Professor of Horticulture/Viticulture and Stephen Gamet, Research Technologist University of Nebraska Viticulture Program Department of Agronomy
Trikkala Sub Clover. Trifolium yanninicum. Seed agronomy table
 Trikkala Sub Clover Trifolium yanninicum Trikkala is a white seeded mid maturing sub clover variety that displays excellent tolerance of waterlogging. It is suited to medium to heavy acidic soils receiving
Trikkala Sub Clover Trifolium yanninicum Trikkala is a white seeded mid maturing sub clover variety that displays excellent tolerance of waterlogging. It is suited to medium to heavy acidic soils receiving
Unit D: Fruit and Vegetable Crop Production. Lesson 3. Growing and Maintaining Small Fruits
 Unit D: Fruit and Vegetable Crop Production Lesson 3. Growing and Maintaining Small Fruits 1 Terms Arbors Banded fertilizer Bleeding Broadcast fertilizer Crown Everbearing strawberries Four-arm kniffen
Unit D: Fruit and Vegetable Crop Production Lesson 3. Growing and Maintaining Small Fruits 1 Terms Arbors Banded fertilizer Bleeding Broadcast fertilizer Crown Everbearing strawberries Four-arm kniffen
Kansas State Agricultural College SWEET CLOVER.
 Kansas State Agricultural College EXPERIMENT STATION Circular No. 34. DEPARTMENT OF AGRONOMY L. E. Call, Agronomist in Charge SWEET CLOVER. By C. C. CUNNINGHAM. SWEET CLOVER is destined to occupy an important
Kansas State Agricultural College EXPERIMENT STATION Circular No. 34. DEPARTMENT OF AGRONOMY L. E. Call, Agronomist in Charge SWEET CLOVER. By C. C. CUNNINGHAM. SWEET CLOVER is destined to occupy an important
Rajah Red Clover. Trifolium pratense. Seed agronomy table
 Rajah Red Clover Trifolium pratense Rajah is a diploid type red clover Intermediate to late flowering variety True grazing type with excellent growth recovery Productive in spring, summer and early autumn
Rajah Red Clover Trifolium pratense Rajah is a diploid type red clover Intermediate to late flowering variety True grazing type with excellent growth recovery Productive in spring, summer and early autumn
Chapter 37. Plant Nutrition. AP Biology
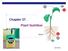 Chapter 37. Plant Nutrition Nutritional needs Autotrophic does not mean autonomous plants need sun as an energy source inorganic compounds as raw materials water (H 2 O) CO 2 minerals Macronutrients Plants
Chapter 37. Plant Nutrition Nutritional needs Autotrophic does not mean autonomous plants need sun as an energy source inorganic compounds as raw materials water (H 2 O) CO 2 minerals Macronutrients Plants
Soils and Fertilizers
 Soils and Fertilizers A Answers to review questions 1. Explain why good soil structure is important to gardeners. Permeability (p. 38-41).. Water-holding capacity (p. 40) Drainage (p. 40) Root penetration
Soils and Fertilizers A Answers to review questions 1. Explain why good soil structure is important to gardeners. Permeability (p. 38-41).. Water-holding capacity (p. 40) Drainage (p. 40) Root penetration
What You Need to Know About Home Lawn Fertilizers
 What You Need to Know About Home Lawn Fertilizers Another Report on Effective Turf Maintenance from the Lawn Institute A well-planned, reasonable fertility program is a basic part of proper lawn maintenance.
What You Need to Know About Home Lawn Fertilizers Another Report on Effective Turf Maintenance from the Lawn Institute A well-planned, reasonable fertility program is a basic part of proper lawn maintenance.
Terminology & Soil Science. Andy Spetch
 Terminology & Soil Science Andy Spetch 1 Presentation Soil Profile Soil Structure Soil Texture Compaction Cation Exchange Capacity Soil ph Nutrients / Organic Matter / EC / PTE s 2 What is Soil: A blend
Terminology & Soil Science Andy Spetch 1 Presentation Soil Profile Soil Structure Soil Texture Compaction Cation Exchange Capacity Soil ph Nutrients / Organic Matter / EC / PTE s 2 What is Soil: A blend
Soil is the Key (Chapter 3)
 Soil is the Key (Chapter 3) Soils 101 Soil profile Soil sources, texture, chemistry, physical properties Soil Amendments Identifying your soil Soil Testing Fertilizers Soil Profile Vertical distribution
Soil is the Key (Chapter 3) Soils 101 Soil profile Soil sources, texture, chemistry, physical properties Soil Amendments Identifying your soil Soil Testing Fertilizers Soil Profile Vertical distribution
Girtridge Monitor Farm Meeting
 Girtridge Monitor Farm Meeting 15 th August 2018 1 Managing Soil Drainage and Compaction in Pasture Key factors for movement of water in the soil Soil Texture Soil Structure Soil Compaction 2 1 Soil Texture
Girtridge Monitor Farm Meeting 15 th August 2018 1 Managing Soil Drainage and Compaction in Pasture Key factors for movement of water in the soil Soil Texture Soil Structure Soil Compaction 2 1 Soil Texture
Management of Solonetzic Soils
 Agdex 518-8 Management of Solonetzic Soils Solonetzic soils, often called burnout or gumbo soils, are characterized by a tough, impermeable hardpan that may vary from 5 to 30 cm (2 to 12 in.) or more below
Agdex 518-8 Management of Solonetzic Soils Solonetzic soils, often called burnout or gumbo soils, are characterized by a tough, impermeable hardpan that may vary from 5 to 30 cm (2 to 12 in.) or more below
Lornshill Academy. Geography Department Higher Revision Physical Environments - Biosphere
 Lornshill Academy Geography Department Higher Revision Physical Environments - Biosphere Physical Environments Biosphere Properties and formation processes of podzol, brown earths and gley soils Natural
Lornshill Academy Geography Department Higher Revision Physical Environments - Biosphere Physical Environments Biosphere Properties and formation processes of podzol, brown earths and gley soils Natural
2018 Iowa FFA Soil Judging CDE Exam 1. Landscape positions characterizes the location of the soil on the landscape and identifies potential risks.
 2018 Iowa FFA Soil Judging CDE Exam 1. Landscape positions characterizes the location of the soil on the landscape and identifies potential risks. Which landscape position is considered the floodplain
2018 Iowa FFA Soil Judging CDE Exam 1. Landscape positions characterizes the location of the soil on the landscape and identifies potential risks. Which landscape position is considered the floodplain
Soils. Living in the Environment, 15 th Edition, Miller
 Soils Living in the Environment, 15 th Edition, Miller Soils: Formation Soil horizons Soil profile Humus O horizon soil A horizon B horizon C horizon Regolith Bedrock soil soil Fig. 10.12, p. 220 Soil
Soils Living in the Environment, 15 th Edition, Miller Soils: Formation Soil horizons Soil profile Humus O horizon soil A horizon B horizon C horizon Regolith Bedrock soil soil Fig. 10.12, p. 220 Soil
27/01/2017. This event is being run by SAC Consulting. What is Soil?
 This event is being run by SAC Consulting What is Soil? 1 Soil Texture It describes the physical composition of the soil % of sand, silt and clay Refers to the mineral fragments of the soil only water
This event is being run by SAC Consulting What is Soil? 1 Soil Texture It describes the physical composition of the soil % of sand, silt and clay Refers to the mineral fragments of the soil only water
Lecture 3: Soil Microclimatology
 Lecture 3: Soil Microclimatology Introduction to Soils Heat Transfer Through Soils Water Transfer Through Soils What is a Soil? Soil is a complex mixture of mineral matter, organic matter and living organisms
Lecture 3: Soil Microclimatology Introduction to Soils Heat Transfer Through Soils Water Transfer Through Soils What is a Soil? Soil is a complex mixture of mineral matter, organic matter and living organisms
Plant Nutrition AP Biology
 Plant Nutrition 2006-2007 Physiological adaptation Dogs pee on trees Why don t trees pee on dogs? NH 3 plant nutrient animal waste Nutritional needs Autotrophic does not mean autonomous plants need sun
Plant Nutrition 2006-2007 Physiological adaptation Dogs pee on trees Why don t trees pee on dogs? NH 3 plant nutrient animal waste Nutritional needs Autotrophic does not mean autonomous plants need sun
REQUIREMENTS FOR SUCCESSFUL ALFALFA ESTABLISHMENT
 REQUIREMENTS FOR SUCCESSFUL ALFALFA ESTABLISHMENT Garry D. Lacefield Extension Forage Specialist University of Kentucky Establishing a good stand of alfalfa is expensive and time consuming, but the success
REQUIREMENTS FOR SUCCESSFUL ALFALFA ESTABLISHMENT Garry D. Lacefield Extension Forage Specialist University of Kentucky Establishing a good stand of alfalfa is expensive and time consuming, but the success
2014 Iowa FFA Soil Judging CDE Exam
 2014 Iowa FFA Soil Judging CDE Exam 1. Landscape position is one aspect of evaluating the surface features of a certain tract of land. Identifying the correct landscape position will indicate: a. If the
2014 Iowa FFA Soil Judging CDE Exam 1. Landscape position is one aspect of evaluating the surface features of a certain tract of land. Identifying the correct landscape position will indicate: a. If the
Topoclimate Southland Soil Technical Data Sheet No Waiau
 This Technical Data Sheet describes the typical average properties of the specified soil. It is essentially a summary of information obtained from one or more profiles of this soil that were examined and
This Technical Data Sheet describes the typical average properties of the specified soil. It is essentially a summary of information obtained from one or more profiles of this soil that were examined and
Soil Testing and Assessing Soil Texture
 Soil Testing and Assessing Soil Texture Assessing the nutrient status and texture of the soil is very important to determine whether the site is suitable for restoration or creation of wildflower grassland.
Soil Testing and Assessing Soil Texture Assessing the nutrient status and texture of the soil is very important to determine whether the site is suitable for restoration or creation of wildflower grassland.
OPTIMISING CROP ESTABLISHIMENT IN PROCESSING CARROTS
 JUNE 2018 OPTIMISING CROP THE IMPORTANCE OF ESTABLISHING A GOOD CROP A key factor in maximising the yield of carrots for processing is promoting the establishment of rapid and uniform early crop. Speedy
JUNE 2018 OPTIMISING CROP THE IMPORTANCE OF ESTABLISHING A GOOD CROP A key factor in maximising the yield of carrots for processing is promoting the establishment of rapid and uniform early crop. Speedy
Maintaining a Healthy Lawn
 Avg. high temperature ( F) Maintaining a Healthy Lawn in Western Oregon A.M. VanDerZanden and T. Cook EC 1521 Reprinted February 2001 $1.50 The typical home lawn is an evolving ecosystem that gets more
Avg. high temperature ( F) Maintaining a Healthy Lawn in Western Oregon A.M. VanDerZanden and T. Cook EC 1521 Reprinted February 2001 $1.50 The typical home lawn is an evolving ecosystem that gets more
Recommended Resources: The following resources may be useful in teaching this
 Unit D: Fruit and Vegetable Crop Production Lesson 3: Growing and Maintaining Small Fruits Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives:
Unit D: Fruit and Vegetable Crop Production Lesson 3: Growing and Maintaining Small Fruits Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives:
Trees, your other Plants: Fertilizer Application
 Trees, your other Plants: Fertilizer Application Bert T. Swanson,Swanson s Nursery Consulting,Inc., Carl Rosen, University of Minnesota and Ed Plaster, Dakota Technical College Trees in urban and suburban
Trees, your other Plants: Fertilizer Application Bert T. Swanson,Swanson s Nursery Consulting,Inc., Carl Rosen, University of Minnesota and Ed Plaster, Dakota Technical College Trees in urban and suburban
Soil Fertility Note 14 Topsoil
 What is Topsoil? Some people have the notion that topsoil is a marvelous, naturally deposited material that contains all the essential chemical, physical and biological components necessary for growing
What is Topsoil? Some people have the notion that topsoil is a marvelous, naturally deposited material that contains all the essential chemical, physical and biological components necessary for growing
Using Fertilizers: Feeding plants. Lydia Clayton UAF Cooperative Extension Service Kenai Peninsula District
 Using Fertilizers: Feeding plants Lydia Clayton UAF Cooperative Extension Service Kenai Peninsula District What to know before you grow? Proper fertilization is essential for: Disease control Weed control
Using Fertilizers: Feeding plants Lydia Clayton UAF Cooperative Extension Service Kenai Peninsula District What to know before you grow? Proper fertilization is essential for: Disease control Weed control
9. The Fossa alterna and the vegetable garden
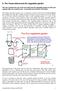 9. The Fossa alterna and the vegetable garden We now combine the use of the eco-toilet and the vegetable garden so they can operate with one common aim to provide more food for the family. This chapter
9. The Fossa alterna and the vegetable garden We now combine the use of the eco-toilet and the vegetable garden so they can operate with one common aim to provide more food for the family. This chapter
