Pests of Turf Grass 1
|
|
|
- Audrey York
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pests of Turf Grass 1
2 Introduction Managing common insects, weeds, plant diseases and certain animal pests found in the backyard can be a challenge. However, there are a number of ways to approach the problem. Information in this publication will help identify and manage pest problems. Pest management methods will vary among individuals according to their tolerance of the pest, the damage and a basic philosophy about handling pest problems. It may not be necessary to control pests if numbers are low and damage is not significant. At other times, simply spraying a tree with water, pruning a branch or digging up a weed will reduce or eliminate the problem. Natural predators may also control the pest problem. Backyard Pest Management is designed to help focus on the key areas of pest management. The first section provides basic approaches to pest management and looks at ways to prevent problems and handle them as they arise. Further sections focus focus on the insects and the types of plants they damage. There are many ways to deal with backyard pest problems. When using pesticides to control a problem, there is the potential for damage and the possibility of legal issues. Use pesticides with caution and always according to label directions. Approaches to Pest Management Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is an environmentally responsible approach to pest management. IPM focuses on prevention, and if problems occur, the method provides a variety of control strategies. Prevention Prevention is the foundation of an IPM program, and one way to do prevent problems is to choose the right plant for a specific location and provide the best growing conditions. Use a variety of plant material in a landscape to avoid a monoculture (growing only one type of plant), which can create potential problems with one species of insect. Select plant species that are less prone to pest problems. Some plants are consistently plagued by certain insect pests and diseases. Evaluate the planting site for exposure to light, low spots, wind speed and direction. Choosing plants suited to their growing conditions reduces plant stress, which helps prevent insect and disease problems. Be aware of soil conditions including ph, drainage, fertility and organic matter. If possible, improve the soil or choose a plant adapted to the conditions. Provide the best start for the plants, using good planting techniques. This approach includes proper planting, pruning, staking and mowing practices. Provide proper maintenance practices for plants including watering, fertilizing, pruning and weed control. Good maintenance practices will ensure healthy plants that are less likely to be affected by pests and diseases. Identifying the problem The first step in controlling a problem, whether it is an insect, disease or weed, is to identify it correctly. When dealing with insect and disease problems, learning about preferred hosts, the type of damage that occurs and life cycle are important when choosing the best control method. For weeds, having information about their life cycle is important because weeds are usually easier to control at some stages than others. Monitoring Monitoring involves checking plants in a yard regularly for the presence of pests. Frequent monitoring of pests is important so that proper treatment can be started when the outbreak first begins. Monitoring should occur throughout the entire growing season. 1
3 Action decisions Proper pest control action involves two steps: first, identifying the injury threshold second, determining the action threshold The injury threshold is the level at which a pest population causes an unacceptable degree of damage so that treatment is necessary. Knowledge of the pest and the plant it is affecting will help when deciding the treatment. For example, most deciduous trees and shrubs can withstand substantial defoliation by insects, especially later in the growing season. However, coniferous trees cannot tolerate defoliation because the needles are not replaced. Having this knowledge about the types of plants, as well as information about the pest, helps in making a decision about treatment when a problem arises. The action threshold is the time to treat the problem to avoid an unacceptable amount of damage or injury threshold. It is important to know the life cycle of the pest and have an understanding of the time it takes for a control measure to be effective. For example, the biological control agent Bacillus thuringiensis Kurstaki will take longer to control caterpillars than a contact insecticide because the agent must be ingested by the caterpillars to be effective. Treatment Five general types of treatments can be used to control pests. Types of treatment Cultural Provide proper maintenance practices such as regular watering, fertilizing, pruning and sanitation. Good maintenance practices keep plants healthy, so they are less likely to be affected by pest problems. Physical One method of physically controlling pests is to remove and destroy the insects, the infested leaves or the part of the plant that is severely affected. Pests such as caterpillars, beetles, slugs and other large pests can be easily removed by hand when infestations are low. Also, removing forest tent caterpillar egg bands on trees in the fall or early spring will reduce the problem the following year. Another effective way to control insects is with a strong jet of water from a garden hose. Spraying trees and shrubs thoroughly and regularly with water will dislodge and kill small caterpillars, aphids, spider mites, pear slugs and other pests. Physical barriers may also be used to prevent insects from attacking plants, especially in the vegetable garden. Floating row covers may be used to prevent some insects from attacking plants. Tarpaper discs may also be used around the base of cole crops to discourage root maggot flies from laying eggs in the soil. Cutworms can be prevented from attacking the roots of transplants by sinking large tin cans, with both ends removed, into the soil around plants to act as cutworm barriers. For diseases, physical control may involve removing plant parts by pruning. For example, the only way to control black knot on mayday is to prune out the affected branches or portions of the branches with the fungus. Also, if an individual plant is affected by a disease, it may need to be removed completely to prevent the spread of the disease to other plants. Physical control for weeds involves simply hoeing or hand digging the weeds. Mechanical Insect vacuums, heat applicators for weed control and motion-triggered water applicators for wildlife may all be used for mechanical pest control. Biological Biological controls are natural enemies of pests such as predatory and parasitic insects as well as birds. These natural enemies will often come to the garden on their own if there are high populations of a pest insect. For example, an outbreak of aphids will attract the natural predator lady beetles (lady bugs). Beneficial insects can be attracted to a yard by growing plants that are sources of nectar and pollen such as aster, marigold, salvia and monarda. Shallow dishes or bird baths act as a water source for both insects and birds, encouraging them to visit the yard. Also, a bird feeder will help supplement the diets of birds like chickadees and other insect eaters. Protect birds and beneficial insects by avoiding the use of pesticides. If pesticides are used to control the pest, the pesticide is likely to kill the beneficial insects as well. If pesticides have to be used, choose the product with the lowest toxicity and shortest residual period. Spot or target spray to minimize the area covered. Beneficial insects are often sold to control backyard insect pests. The most common beneficial insects are ladybeetles and praying mantids. These insects usually have little benefit, as they frequently leave the yard, especially if their food supply is poor. It is preferable to let the native species of beneficial insects control the outbreak. 2
4 A bacterium called Bacillus thuringiensis Kurstaki is another type of biological control. It can be purchased to control leaf feeding caterpillars including forest tent caterpillars and the larvae of cabbage butterflies. It only affects the larvae of moths and butterflies and does not control any other insects. Chemical When purchasing pesticides, choose the product with the lowest toxicity. There are synthetically produced pesticides as well as naturally derived products. When using any product on food crops, follow the label directions for safety precautions and wait periods between spraying and harvest. Many municipalities are moving to minimum or zero-pesticide tolerance and may have a municipality-wide bio-control program. Be aware of these issues in the community, so an informed decision can be made about pest control. Evaluation The last step in any pest management program is evaluation. Monitoring and record keeping are key factors in determining if the control measure was successful. This Information may help in choosing a method in the future. Many commonly used products for pest control in the home garden are being removed from the market. Many municipalities are creating bylaws to reduce or eliminate the use of pesticides. The principals and practices of integrated pest management will become more important in the future. Integrated pest management takes time, planning and patience for it to be a successful. Ants Ants Damage Ants live in nests in the soil, but over time, the soil gets pushed up to form mounds on the surface of the grass. As the soil is pushed up, the plant roots may be cut. The mounds of soil look unattractive, smother the grass and make the lawn bumpy. Description There are many species of ants in Alberta. All ants have three distinct body parts with a small head and enlarged abdomen. They are usually brown, black or red and vary in size from 2 to 10 mm long. Ants may be winged or wingless. The larvae of ants are oval, white and legless. The pupae are also white, but body parts such as legs and antennae appear compressed close to their bodies. Life cycle Ants are social creatures that live in colonies from a dozen to many thousands. The colony has one or more queen ants, but the majority are worker ants. The workers are wingless, sterile females that help to protect the colony, care for the larvae and find food. They bring food back to the ant hill for the queen, larvae and pupae. The queen lays all the eggs, and winged males and queens are produced in large numbers. These emerge from the nest and mate when flying. After mating, the male dies, and the fertilized queen sheds her wings and either starts a new colony or goes to an already established colony. 3
5 Control Repeated watering with a garden hose may encourage some ant species to move from the colony. Place the hose on the ant hill on a slow trickle for approximately half an hour every second day. A preferred product for ant control is diatomaceous earth. Many baits are available that are easy to use in the garden. The workers take the bait back to the ant hill. Other chemical controls are registered for ant control; consult a garden centre or nursery for a suitable product. Earthworms/dew worms Earthworms/dew worms Photo credit: Joseph Berger, Bugwood.org Damage Earthworms feed on organic matter in the soil and on dead leaves and stems of the grass. As they burrow, they make the lawn bumpy and difficult to mow. Their casts are rich in nutrients, but are hard. Description Earthworms can grow up to 20 cm long. They are normally found in the top 30 to 45 cm of soil and come to the surface at night and after heavy rains. Earthworms need a moist environment. Soils with high worm populations often have high organic matter levels. Saline soils, sandy soils and soils with a ph of 4.5 or lower usually have few worms. Life cycle Earthworms have both male and female reproductive organs. After mating, the clitellum (the girdle-like ring around worm) slides down the worm s body, picking up fertilized eggs. This ring is then deposited in the soil and provides protection for the future worms. Control Encourage birds to the yard with bird feeders and baths. Earthworms are attracted to a lawn with a thick thatch layer. Thatch is the thick spongy layer of dead material between the grass crowns and the soil. Remove the thatch layer so it is less than 1.25 cm thick. Adjust thatching rakes or power rakes so the teeth drag through the earthworm mounds and level them. The teeth of the rake should not be set into the grass crowns, or the rake will damage the grass plants. This raking should be done when the soil is slightly damp, but not wet. Water lawns deeply and infrequently to encourage earthworms to remain further down in the soil. One product is registered for dew worm control in turf. 4
6 Glassy cutworm Glassy cutworm Damage Cutworms eat the stems, leaves and crowns of grass plants. They cut the grass plants off at the roots, causing the sod to be easily lifted. The larvae live in tunnels and feed at night close to the tunnel opening. They usually remain underground, rarely coming to the soil surface. Description The cutworm s body is smooth, thick and segmented. They are greenish-grey to white with a brown head. Mature larvae are 3.5 to 4 cm long, and when disturbed, they curl into a C shape. The adult is a greyish-brown moth with dark markings on its wings. The moths are attracted to lights at nighttime. Pupae are long, narrow and reddish-brown. Life cycle The moths lay most of their eggs on the grass blades in August. Once the eggs hatch, the larvae begin feeding on the grass plants. Larvae are usually half grown by the time they overwinter. They begin feeding again the following spring after the plants begin to grow. Pupation occurs in the soil by the end of June. The moths appear in July and are seen until September. There is one generation a year. Control Encourage birds to the yard with bird feeders and baths. Several natural predators, including spiders, big-eyed bugs and ground beetles, are effective in controlling this insect. Consider spot treatments with a registered insecticide. It is difficult to reach the larvae with insecticides because the pests stay in the soil. Sod webworm Sod webworm Damage Damage begins as irregular brown patches in the turf, which grow larger and can cover entire lawns. This condition is usually seen late in the summer. All grass species are attacked, but bluegrass and newly seeded lawns are more commonly affected. The larvae feed at night by chewing off the grass blades just above the thatch. The pests live in silk-lined tunnels constructed in the turf thatch and may continue into the soil under the turf. They produce webbing that binds bits of soil and leaves together. Sod webworms are often found in turf on south facing, steep slopes and banks, where it is hot and dry. Heavily shaded turf is seldom attacked by the larvae. 5
7 Description The caterpillars are whitish or tan, usually with a row of darker spots on their backs. They have a dark brown head and grow up to 2 cm long. The adults are slender, tan-coloured moths approximately 20 mm long. The moths usually keep their wings close to their body when resting on the grass. The moths have a zigzag pattern when flying and are seen during the evenings in late May and June. Life cycle This insect pupates in the spring. After the moths emerge, they lay eggs on the grass blades, and these hatch in 6 to 10 days. The young larvae mine the leaf surface as they move to the soil to build their tunnels. They stop feeding in late September and overwinter in the soil or thatch. Control Keep lawns healthy by watering and fertilizing regularly because the turf grass will be less susceptible to attack. With proper maintenance, the grass can usually outgrow the damage. Inspect damaged areas by parting the grass blades and look for the greenish droppings of the larvae. An effective way to determine if sod webworm larvae are causing damage is to apply a soap solution to a small area of the lawn. Mix 5 ml of liquid soap to 750 ml of water. After applying the soap solution, the larvae will wriggle to the surface in a few minutes. Ants, predatory mites and big-eyed bugs are major predators of the eggs and larvae of the sod webworm. Birds, ground beetles, parasitic flies and wasps also reduce webworm populations. Frequent use of insecticides will kill beneficial species and limit their effectiveness. Apply registered insecticides as spot treatments about two weeks after moths appear. 6
8 Backyard Pest Management: Pests of Turf Grass Published by Alberta Agriculture and Rural Development Information Management Division Street Edmonton, Alberta Canada T6H 5T6 Authors: Pam North and Shelley Barkley Editor: Chris Kaulbars Graphic Designer: Lee Harper Electronic Page Production: J.A. Serafinchon Image Acknowledgements R. Howard S. Barkley B. Casement J. Jones M. Dolinski T. Pheh V. Sowiak H. Philip J. Emond J. Feddes-Calpas L. Hausher A. Tellier G. Rankin D. Johnson University of Alberta Canadian Forest Service Rick and Libby Avis Bugwood.org City of Red Deer Manitoba Agriculture, Food and Rural Development Saskatchewan Ministry of Agriculture Alberta Agriculture and Rural Development Copyright Her Majesty the Queen in right of Alberta (Alberta Agriculture and Rural Development). All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise without written permission from the Information Management Division, Alberta Agriculture and Rural Development. No Endorsement Given: This publication should not be taken as an endorsement by Her Majesty the Queen in right of Alberta of the products or services mentioned herein. Disclaimer: Responsibility for interpretation or application of the content contained in this publication rests with the user. Information in this publication is provided solely for the user s information and while thought to be accurate, is provided strictly as is and without warranty of any kind, either express or implied. Her Majesty, the publishers and contributors to this publication, and their agents, employees or contractors will not be liable to you for any damages, direct or indirect, or lost profits arising out of your use of this publication. ISBN See the website: for information about other publications, CD-ROMs and DVDs. 7
Pests of Coniferous Trees and Shrubs
 Pests of Coniferous Trees and Shrubs 1 Introduction Managing common insects, weeds, plant diseases and certain animal pests found in the backyard can be a challenge. However, there are a number of ways
Pests of Coniferous Trees and Shrubs 1 Introduction Managing common insects, weeds, plant diseases and certain animal pests found in the backyard can be a challenge. However, there are a number of ways
Health Canada. Santé Canada. Common Lawn Problems
 Health Canada Santé Canada Fact Sheet Fact Sheet Fact Sheet Fact Sheet Fact Sheet Fact Sheet Fact Sheet Fact Sheet Common Lawn Problems 2002 Pest Management Regulatory Agency 2720 Riverside Drive Ottawa
Health Canada Santé Canada Fact Sheet Fact Sheet Fact Sheet Fact Sheet Fact Sheet Fact Sheet Fact Sheet Fact Sheet Common Lawn Problems 2002 Pest Management Regulatory Agency 2720 Riverside Drive Ottawa
Life of a Lawn. Fact Sheet
 Life of a Lawn Fact Sheet Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada, represented by the Minister of Health Canada, 2008 All rights reserved. No part of this information (publication or product) may be reproduced
Life of a Lawn Fact Sheet Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada, represented by the Minister of Health Canada, 2008 All rights reserved. No part of this information (publication or product) may be reproduced
Pests of Small Fruits
 Pests of Small Fruits 1 Introduction Managing common insects, weeds, plant diseases and certain animal pests found in the backyard can be a challenge. However, there are a number of ways to approach the
Pests of Small Fruits 1 Introduction Managing common insects, weeds, plant diseases and certain animal pests found in the backyard can be a challenge. However, there are a number of ways to approach the
Cottonwood. Pest Damage on. Plant Problem. September September 1 10 October September November November November 1 10
 Pest Damage on March 21 31 March 11 20 March 1 10 April 21 30 April 11 20 April 1 10 May 21 31 May 11 20 May 1 10 June 21 30 June 11 20 June 1 10 July 21 31 July 11 20 July 1 10 August 21 31 August 11
Pest Damage on March 21 31 March 11 20 March 1 10 April 21 30 April 11 20 April 1 10 May 21 31 May 11 20 May 1 10 June 21 30 June 11 20 June 1 10 July 21 31 July 11 20 July 1 10 August 21 31 August 11
Integrated Pest Management. University of California Statewide IPM Program
 Integrated Pest Management University of California Statewide IPM Program In this presentation. Define IPM Explain what s in an IPM program How IPM can be applied to your garden and orchard Examples of
Integrated Pest Management University of California Statewide IPM Program In this presentation. Define IPM Explain what s in an IPM program How IPM can be applied to your garden and orchard Examples of
Pests of Landscape Trees. Wizzie Brown Texas A&M Agrilife Extension
 Pests of Landscape Trees Wizzie Brown Texas A&M Agrilife Extension Tips for pest management Always identify the insect Pest vs. beneficial Biological Control Using other organisms to control a pest Conservation
Pests of Landscape Trees Wizzie Brown Texas A&M Agrilife Extension Tips for pest management Always identify the insect Pest vs. beneficial Biological Control Using other organisms to control a pest Conservation
TURF. Recommendations for lawns and recreational areas not grazed by livestock.
 TURF G. Byrtus Last updated: May 2005 Recommendations for lawns and recreational areas not grazed by livestock. Important: Mow the lawn before treatment. Keep off treated lawns until dry. Important regulatory
TURF G. Byrtus Last updated: May 2005 Recommendations for lawns and recreational areas not grazed by livestock. Important: Mow the lawn before treatment. Keep off treated lawns until dry. Important regulatory
IPM and Plant Diagnostics
 9 IPM and Plant Diagnostics Jon Traunfeld David Clement, Ph.D. Chapter 9 IPM and Plant Diagnostics I. Learning Objectives II. III. Introduction IPM IV. IPM Steps Healthy Plants: Fewer Problems Taking Action
9 IPM and Plant Diagnostics Jon Traunfeld David Clement, Ph.D. Chapter 9 IPM and Plant Diagnostics I. Learning Objectives II. III. Introduction IPM IV. IPM Steps Healthy Plants: Fewer Problems Taking Action
Common Vegetable Pests
 Common Vegetable Pests Colorado Potato Beetle Yellow and black striped potato beetle. Overwinter in soil as adults. Female beetles lay batches of about 2 dozen orangeyellow eggs on the underside of the
Common Vegetable Pests Colorado Potato Beetle Yellow and black striped potato beetle. Overwinter in soil as adults. Female beetles lay batches of about 2 dozen orangeyellow eggs on the underside of the
Cloud Mountain Farm 6906 Goodwin Rd., Everson, WA (360) voice, (360) fax,
 Disease and Pest Management in the Home Orchard Fruit trees have been grown in home orchards for centuries. The goal of many gardeners today is to have fresh fruit from their own trees with a minimum of
Disease and Pest Management in the Home Orchard Fruit trees have been grown in home orchards for centuries. The goal of many gardeners today is to have fresh fruit from their own trees with a minimum of
Integrated Pest Management
 Integrated Pest Management Integrated Pest Management is a term used to describe an effective and environmentally sensitive approach to pest management. IPM relies on an intimate knowledge of the life
Integrated Pest Management Integrated Pest Management is a term used to describe an effective and environmentally sensitive approach to pest management. IPM relies on an intimate knowledge of the life
Ash. Pest Damage on. Plant Problem. September September 1 10 October September November November November 1 10
 Pest Damage on Ash March 21 31 March 11 20 March 1 10 April 21 30 April 11 20 April 1 10 May 21 31 May 11 20 May 1 10 June 21 30 June 11 20 June 1 10 July 21 31 July 11 20 July 1 10 August 21 31 August
Pest Damage on Ash March 21 31 March 11 20 March 1 10 April 21 30 April 11 20 April 1 10 May 21 31 May 11 20 May 1 10 June 21 30 June 11 20 June 1 10 July 21 31 July 11 20 July 1 10 August 21 31 August
Insect Pests of Home Lawns
 Bringing information and education into the communities of the Granite State Insect Pests of Home Lawns Pest Fact Sheet Dr. Stanley R. Swier, Extension Specialist Emeritus, Entomology Introduction There
Bringing information and education into the communities of the Granite State Insect Pests of Home Lawns Pest Fact Sheet Dr. Stanley R. Swier, Extension Specialist Emeritus, Entomology Introduction There
Potato Insects. Frank G. Zalom, Department of Entomology, UC Davis
 Potato Insects Frank G. Zalom, Department of Entomology, UC Davis Whiteflies Bemisia spp. Greenhouse whitefly (GWF) Adults- tiny, 1.5 mm long Bemisia spp. hold wings at an angle, rooflike over body, space
Potato Insects Frank G. Zalom, Department of Entomology, UC Davis Whiteflies Bemisia spp. Greenhouse whitefly (GWF) Adults- tiny, 1.5 mm long Bemisia spp. hold wings at an angle, rooflike over body, space
EC Entomology : Lawn Insect Control
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Historical Materials from University of Nebraska- Lincoln Extension Extension 1967 EC67-1599 Entomology : Lawn Insect Control
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Historical Materials from University of Nebraska- Lincoln Extension Extension 1967 EC67-1599 Entomology : Lawn Insect Control
SLUGS. How to Control Slugs. Non-Chemical Controls Clean up garbage, weeds, boards, and other hiding places from your field. Remove slugs from plants.
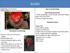 SLUGS Garden slug: Arion hortensis Little gray slug: Deroceras reticulatum How to Control Slugs Non-s Clean up garbage, weeds, boards, and other hiding places from your field. Remove slugs from plants.
SLUGS Garden slug: Arion hortensis Little gray slug: Deroceras reticulatum How to Control Slugs Non-s Clean up garbage, weeds, boards, and other hiding places from your field. Remove slugs from plants.
Common Insect Pests of Cucurbits
 Agnote 805 No. I59 December 2003 Agdex No: 263/622 ISSN No: 0157-8243 Common Insect Pests of Cucurbits H. Brown, Entomology, Darwin INTROD UC TION Cucurbits are a major horticultural crop in the Northern
Agnote 805 No. I59 December 2003 Agdex No: 263/622 ISSN No: 0157-8243 Common Insect Pests of Cucurbits H. Brown, Entomology, Darwin INTROD UC TION Cucurbits are a major horticultural crop in the Northern
Pest Management in Vegetable Gardens. Pam Brown Extension Agent Emeritus, Gardening Coach Pampered Gardeners, LLC
 Pest Management in Vegetable Gardens Pam Brown Extension Agent Emeritus, Gardening Coach Pampered Gardeners, LLC pamperedgardeners@gmail.com Pest Management Involves: Providing proper cultural practices
Pest Management in Vegetable Gardens Pam Brown Extension Agent Emeritus, Gardening Coach Pampered Gardeners, LLC pamperedgardeners@gmail.com Pest Management Involves: Providing proper cultural practices
General Session Papers. REDUCING PESTICIDE INPUTS IN PUBLIC AREAS Frederick Baxendale Department of Entomology University of Nebraska
 REDUCING PESTICIDE INPUTS IN PUBLIC AREAS Frederick Baxendale Department of Entomology University of Nebraska A growing awareness of problems associated with overusing pesticides has prompted many landscape
REDUCING PESTICIDE INPUTS IN PUBLIC AREAS Frederick Baxendale Department of Entomology University of Nebraska A growing awareness of problems associated with overusing pesticides has prompted many landscape
Maple. Pest Damage on. Plant Problem. September September September 1 10 October November November 1 10.
 Pest Damage on March 21 31 March 11 20 March 1 10 April 21 30 April 11 20 April 1 10 May 21 31 May 11 20 May 1 10 June 21 30 June 11 20 June 1 10 July 21 31 July 11 20 July 1 10 August 21 31 August 11
Pest Damage on March 21 31 March 11 20 March 1 10 April 21 30 April 11 20 April 1 10 May 21 31 May 11 20 May 1 10 June 21 30 June 11 20 June 1 10 July 21 31 July 11 20 July 1 10 August 21 31 August 11
Practical Pest Management A workshop provided by Growing Places Volunteers Gaynor Bigelbach and Connie Grabowy
 Practical Pest Management A workshop provided by Growing Places Volunteers Gaynor Bigelbach and Connie Grabowy The first step towards building a healthy vegetable garden is regular maintenance. By keeping
Practical Pest Management A workshop provided by Growing Places Volunteers Gaynor Bigelbach and Connie Grabowy The first step towards building a healthy vegetable garden is regular maintenance. By keeping
Beneficial Insects. Your best buddies for pest control
 Beneficial Insects Your best buddies for pest control Convergent Lady Beetle Adults are generalist predators (especially aphids), also feed on chinch bugs, whiteflies, mites and many other soft-bodied
Beneficial Insects Your best buddies for pest control Convergent Lady Beetle Adults are generalist predators (especially aphids), also feed on chinch bugs, whiteflies, mites and many other soft-bodied
Farmers will increase yield and profit by taking care of the hot pepper from planting the seed to harvesting the fruit.
 INTRODUCTION Farmers will increase yield and profit by taking care of the hot pepper from planting the seed to harvesting the fruit. HEALTHY SEEDLINGS COMPOST in PLANTING HOLES CORRECT FERTILISER and LIME
INTRODUCTION Farmers will increase yield and profit by taking care of the hot pepper from planting the seed to harvesting the fruit. HEALTHY SEEDLINGS COMPOST in PLANTING HOLES CORRECT FERTILISER and LIME
An America Rose Society Presentation 2005
 An America Rose Society Presentation 2005 IPM OF ROSE PESTS Baldo Villegas Entomologist; ARS Master Rosarian Sacramento, CA USDA (Zone 8/9) EMail: sactorose@yahoo.com Home Page: http://www.sactorose.org/
An America Rose Society Presentation 2005 IPM OF ROSE PESTS Baldo Villegas Entomologist; ARS Master Rosarian Sacramento, CA USDA (Zone 8/9) EMail: sactorose@yahoo.com Home Page: http://www.sactorose.org/
Carrots and Parsnips growing problems
 Carrots and Parsnips growing problems Carrots and parsnips grow best in loose, sandy, humus-rich soil. Size does not make for more flavorful carrots and parsnips. For best flavor, lift both crops before
Carrots and Parsnips growing problems Carrots and parsnips grow best in loose, sandy, humus-rich soil. Size does not make for more flavorful carrots and parsnips. For best flavor, lift both crops before
Vegetable Pests. Cutworms. Berry & Vegetable School 2011 Nisku, AB. Range of species
 Vegetable Pests Berry & Vegetable School 2011 Nisku, AB Cutworms CUTWORMS Range of species Affect a wide range of vegetable crop hosts Adults = moths Subterranean caterpillars Feed above ground at night
Vegetable Pests Berry & Vegetable School 2011 Nisku, AB Cutworms CUTWORMS Range of species Affect a wide range of vegetable crop hosts Adults = moths Subterranean caterpillars Feed above ground at night
Science of Life Explorations
 Science of Life Explorations Biological Control and Beneficial Insects IPM uses Biological Control When is something a pest? A pest is what we call living things that are causing problems, such as insects
Science of Life Explorations Biological Control and Beneficial Insects IPM uses Biological Control When is something a pest? A pest is what we call living things that are causing problems, such as insects
Using IPM in your Ag Program- Understanding Texas Laws
 Using IPM in your Ag Program- Understanding Texas Laws What we will cover Basics of School IPM regulations IPM for Greenhouses What are biocontrols Exclusion Cultural controls Sanitation Scouting Identifying
Using IPM in your Ag Program- Understanding Texas Laws What we will cover Basics of School IPM regulations IPM for Greenhouses What are biocontrols Exclusion Cultural controls Sanitation Scouting Identifying
Alternative Pesticide Management for the Lawn and Garden
 Alternative Pesticide Management for the Lawn and Garden XCM-221 A pest-free lawn and garden may sound ideal, but is it really? Maintaining the perfect urban landscape may result in a reliance on pesticides
Alternative Pesticide Management for the Lawn and Garden XCM-221 A pest-free lawn and garden may sound ideal, but is it really? Maintaining the perfect urban landscape may result in a reliance on pesticides
Blueberry fruit fly: Rhagoletis mendax Curran
 Blueberry fruit fly: Rhagoletis mendax Curran Economic importance and damage Regarding Canada, the blueberry fruit fly, or the blueberry maggot, has been reported from the following provinces: Nova Scotia,
Blueberry fruit fly: Rhagoletis mendax Curran Economic importance and damage Regarding Canada, the blueberry fruit fly, or the blueberry maggot, has been reported from the following provinces: Nova Scotia,
Master Gardener Volunteer Program
 Master Gardener Volunteer Program Level 1 Training Plant Presentation-Final Exam 1. Common Name: a. Asparagus 2. Scientific name: a. Asparagus officinalis, genus of the family Asparagaceae 3. Cold hardiness
Master Gardener Volunteer Program Level 1 Training Plant Presentation-Final Exam 1. Common Name: a. Asparagus 2. Scientific name: a. Asparagus officinalis, genus of the family Asparagaceae 3. Cold hardiness
Welcome to the Iowa Certified Nursery Professional Training program Module 9: Managing Plant Diseases and Insects.
 Welcome to the Iowa Certified Nursery Professional Training program Module 9: Managing Plant Diseases and Insects. 1 Upon completing this module you will: 1. Be able to define IPM; 2. Know the basic methods
Welcome to the Iowa Certified Nursery Professional Training program Module 9: Managing Plant Diseases and Insects. 1 Upon completing this module you will: 1. Be able to define IPM; 2. Know the basic methods
EC Sod Webworm
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Historical Materials from University of Nebraska- Lincoln Extension Extension 1971 EC71-1527 Sod Webworm Robert E. Roselle
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Historical Materials from University of Nebraska- Lincoln Extension Extension 1971 EC71-1527 Sod Webworm Robert E. Roselle
Rose. Pest Damage on. Plant Problem. September September September 1 10 October November November 1 10.
 Pest Damage on Rose March 21 31 March 11 20 March 1 10 April 21 30 April 11 20 April 1 10 May 21 31 May 11 20 May 1 10 June 21 30 June 11 20 June 1 10 July 21 31 July 11 20 July 1 10 August 21 31 August
Pest Damage on Rose March 21 31 March 11 20 March 1 10 April 21 30 April 11 20 April 1 10 May 21 31 May 11 20 May 1 10 June 21 30 June 11 20 June 1 10 July 21 31 July 11 20 July 1 10 August 21 31 August
IPM REPORT CARD FOR SCHOOL GROUNDS. Landscape Plantings
 IPM REPORT CARD FOR SCHOOL GROUNDS Landscape Plantings A Self-Assessment Tool for School Administrators and Those Making Pest Control Decisions on School Grounds Compiled by George Hamilton Specialist
IPM REPORT CARD FOR SCHOOL GROUNDS Landscape Plantings A Self-Assessment Tool for School Administrators and Those Making Pest Control Decisions on School Grounds Compiled by George Hamilton Specialist
Raspberry Insect & Mite Biology & Management. Diane Alston Utah State University The 1 st Annual Utah Raspberry Meeting February 23, 2006
 Raspberry Insect & Mite Biology & Management Diane Alston Utah State University The 1 st Annual Utah Raspberry Meeting February 23, 2006 Raspberry Horntail Most common insect pest of raspberry canes in
Raspberry Insect & Mite Biology & Management Diane Alston Utah State University The 1 st Annual Utah Raspberry Meeting February 23, 2006 Raspberry Horntail Most common insect pest of raspberry canes in
9/25/2013. Soil pests 2: White Grubs. Sclerotized head Chewing mouthparts 3 pr segmented legs No prolegs C shaped soft body
 Soil pests 2: White Grubs Coleoptera Scarabaeidae (scarabs) Leaf feeders, decomposers, dung beetles Larvae are white grubs White Grubs Sclerotized head Chewing mouthparts 3 pr segmented legs No prolegs
Soil pests 2: White Grubs Coleoptera Scarabaeidae (scarabs) Leaf feeders, decomposers, dung beetles Larvae are white grubs White Grubs Sclerotized head Chewing mouthparts 3 pr segmented legs No prolegs
PRODUCT RANGE. eco friendly organic garden products
 PRODUCT RANGE eco friendly organic garden products Pest & Disease Control eco-oil is a registered organic miticide/insecticide spray made from Australian grown plant oils and botanical extracts. eco-oil
PRODUCT RANGE eco friendly organic garden products Pest & Disease Control eco-oil is a registered organic miticide/insecticide spray made from Australian grown plant oils and botanical extracts. eco-oil
Master Gardener Recommended Horticulture Best Management Practices
 Master Gardener Recommended Horticulture Best Management Practices Practices that should always be recommended: Group plants with similar needs (water, fertilizer, sun ) for easier maintenance Fertilize
Master Gardener Recommended Horticulture Best Management Practices Practices that should always be recommended: Group plants with similar needs (water, fertilizer, sun ) for easier maintenance Fertilize
flattened, or in groups, in crevices beneath the bark. The eggs soon hatch, and the larvae bore into the sapwood where they make tortuous
 j ^ju Agriculture Canada Publication 1718 B Major pests of birch and maple trees The birch leafminer The birch leafminer (Fenusa pusilla Lepeletier) attacks the white or paper birch (Betula papyrifera
j ^ju Agriculture Canada Publication 1718 B Major pests of birch and maple trees The birch leafminer The birch leafminer (Fenusa pusilla Lepeletier) attacks the white or paper birch (Betula papyrifera
Vegetables Chapter 10 OSUE MGV Training. Pam Bennett OSUE State MGV Coordinator Horticulture Educator
 Vegetables Chapter 10 OSUE MGV Training Pam Bennett OSUE State MGV Coordinator Horticulture Educator Vegetables Site Planning Cultural Sun 8-10 hours sun Water Site CLOSE TO THE FAUCET! Size Physical site
Vegetables Chapter 10 OSUE MGV Training Pam Bennett OSUE State MGV Coordinator Horticulture Educator Vegetables Site Planning Cultural Sun 8-10 hours sun Water Site CLOSE TO THE FAUCET! Size Physical site
Radish VEGETABLE CROPS PRODUCTION GUIDE FOR THE ATLANTIC PROVINCES. Prepared by the ADVISORY COMMITTEE ON VEGETABLE CROPS
 Radish VEGETABLE CROPS PRODUCTION GUIDE FOR THE ATLANTIC PROVINCES Prepared by the ADVISORY COMMITTEE ON VEGETABLE CROPS Published by authority of the ATLANTIC PROVINCES AGRICULTURE SERVICES CO-ORDINATING
Radish VEGETABLE CROPS PRODUCTION GUIDE FOR THE ATLANTIC PROVINCES Prepared by the ADVISORY COMMITTEE ON VEGETABLE CROPS Published by authority of the ATLANTIC PROVINCES AGRICULTURE SERVICES CO-ORDINATING
Apple Clearwing Moth (Synanthedon myopaeformis)
 Apple Clearwing Moth (Synanthedon myopaeformis) February, 2016 The apple clearwing moth (known as small red-belted clearwing moth in Europe) was confirmed in Cawston in 2005 on apple as the first record
Apple Clearwing Moth (Synanthedon myopaeformis) February, 2016 The apple clearwing moth (known as small red-belted clearwing moth in Europe) was confirmed in Cawston in 2005 on apple as the first record
Tips and information for homeowners on lawn care practices, soil health, and common pests.
 SEASONAL LAWN MAINTENANCE Tips and information for homeowners on lawn care practices, soil health, and common pests. early spring L A T E A P R I L - E A R L Y M A Y TIPS FOR A TRULY HEALTHY, RESILIENT
SEASONAL LAWN MAINTENANCE Tips and information for homeowners on lawn care practices, soil health, and common pests. early spring L A T E A P R I L - E A R L Y M A Y TIPS FOR A TRULY HEALTHY, RESILIENT
Minneapolis College of Art and Design Integrated Pest Management Policy and Plan
 Minneapolis College of Art and Design Integrated Pest Management Policy and Plan 1.1 - Pest Management Policy Statement Structural and landscape pests can pose significant problems in the urban environment.
Minneapolis College of Art and Design Integrated Pest Management Policy and Plan 1.1 - Pest Management Policy Statement Structural and landscape pests can pose significant problems in the urban environment.
Horticulture Newsletter
 Taylor County Horticulture Newsletter October 2018 Cooperative Extension Service Taylor County 1143 South Columbia Avenue Campbellsville, KY 42718 (270) 465-4511 Fax: (270) 789-2455 www.taylor.ca.uky.edu
Taylor County Horticulture Newsletter October 2018 Cooperative Extension Service Taylor County 1143 South Columbia Avenue Campbellsville, KY 42718 (270) 465-4511 Fax: (270) 789-2455 www.taylor.ca.uky.edu
JAPANESE BEETLES Beneficial nematodes (Bt)
 JAPANESE BEETLES In our region most injury usually occurs during the last two weeks of July through the first week in August. Injured Fruit is usually infected during the last two weeks before picking.
JAPANESE BEETLES In our region most injury usually occurs during the last two weeks of July through the first week in August. Injured Fruit is usually infected during the last two weeks before picking.
Diseases of Cool-Season Grasses
 Diseases of Cool-Season Grasses Fescue, Bluegrass, and Ryegrass *** NO IMAGES *** Leon T. Lucas, Extension Plant Pathology Specialist Arthur H. Bruneau, Extension Crop Science Specialist Published by North
Diseases of Cool-Season Grasses Fescue, Bluegrass, and Ryegrass *** NO IMAGES *** Leon T. Lucas, Extension Plant Pathology Specialist Arthur H. Bruneau, Extension Crop Science Specialist Published by North
4. E7 Plant Diseases and Disorders
 4. E7 Plant Diseases and Disorders 1 L. Pink snow mold (winter), R. Fusarium patch early fall Introduction Plant disease or disorder a harmful change in the growth or function of a plant. Abiotic non-living
4. E7 Plant Diseases and Disorders 1 L. Pink snow mold (winter), R. Fusarium patch early fall Introduction Plant disease or disorder a harmful change in the growth or function of a plant. Abiotic non-living
Controlling White Grubs in Turfgrass
 Controlling White Grubs in Turfgrass Michael F. Potter and Daniel A. Potter White grubs are the most destructive insect pests of turfgrasses in Kentucky. Turf is damaged when the grubs (the larval or immature
Controlling White Grubs in Turfgrass Michael F. Potter and Daniel A. Potter White grubs are the most destructive insect pests of turfgrasses in Kentucky. Turf is damaged when the grubs (the larval or immature
1. E8 Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Action Plan
 1. E8 Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Action Plan 1 IPM Action Plan, Introduction Integrated Pest Management (IPM) a sustainable approach to reduce pests to a tolerable level by using the best balance
1. E8 Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Action Plan 1 IPM Action Plan, Introduction Integrated Pest Management (IPM) a sustainable approach to reduce pests to a tolerable level by using the best balance
2/5/2009. Top 10 Garden Pests. Integrated Approach to Pest Management
 Outline Insights into Gardening, 2009 Garden Pests of the Willamette Valley Gail Langellotto, Ph.D. (Entomlogy) OSU Department of Horticulture Top 10 Garden Pests Integrated Approach to Pest Management
Outline Insights into Gardening, 2009 Garden Pests of the Willamette Valley Gail Langellotto, Ph.D. (Entomlogy) OSU Department of Horticulture Top 10 Garden Pests Integrated Approach to Pest Management
INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT
 Chapter 5 INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a prevention based way to manage pests effectively, economically, and safely. This approach helps reduce the need for chemical pesticides
Chapter 5 INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a prevention based way to manage pests effectively, economically, and safely. This approach helps reduce the need for chemical pesticides
Lync Session 3 9/21/15
 Lync Session 3 9/21/15 Life cycles & development White grubs Sawflies Fruit flies Jessica and Linda Life cycles and development White grubs Annual Japanese beetle, masked chafers Green June beetle Multi
Lync Session 3 9/21/15 Life cycles & development White grubs Sawflies Fruit flies Jessica and Linda Life cycles and development White grubs Annual Japanese beetle, masked chafers Green June beetle Multi
Propagation. Pests and Diseases. Aphids
 Hibiscus, Chinese Hibiscus Hibiscus rosa-sinensis Propagation Hibiscus are normally propagated by softwood stem tip cuttings taken in late spring. Intermittent mist with soil temperatures of 70 degrees
Hibiscus, Chinese Hibiscus Hibiscus rosa-sinensis Propagation Hibiscus are normally propagated by softwood stem tip cuttings taken in late spring. Intermittent mist with soil temperatures of 70 degrees
Organic Pest Management
 Organic Pest Management Thank you for purchasing Free Spirit Gardens Organic Pest Management White Paper. This paper gives prevention, treatment, and companion plant suggestions for dealing with 9 of the
Organic Pest Management Thank you for purchasing Free Spirit Gardens Organic Pest Management White Paper. This paper gives prevention, treatment, and companion plant suggestions for dealing with 9 of the
Good Bugs. Hunt for bugs -- Identify beneficial insects from pictures. Goal: Supplies:
 good bugs 1 Good Bugs Activity: Goal: Hunt for bugs -- Identify beneficial insects from pictures To learn what beneficial insects are and how you can attract them and use them in your garden Supplies:
good bugs 1 Good Bugs Activity: Goal: Hunt for bugs -- Identify beneficial insects from pictures To learn what beneficial insects are and how you can attract them and use them in your garden Supplies:
Sustainable, Organic Vegetable Gardening. Presented by: Kent Phillips
 Sustainable, Organic Vegetable Gardening Presented by: Kent Phillips kent.a.phillips@gmail.com College of Agriculture and Natural Resources 2 What is organic gardening? No synthetic pesticides or fertilizers
Sustainable, Organic Vegetable Gardening Presented by: Kent Phillips kent.a.phillips@gmail.com College of Agriculture and Natural Resources 2 What is organic gardening? No synthetic pesticides or fertilizers
Empire Turf Study Guide Maintenance Provider Exam
 Empire Turf Study Guide Maintenance Provider Exam General Information A. Thatch a. Intermingled layer of dead and living shoots, stems, and roots that develops between the zone of green vegetation and
Empire Turf Study Guide Maintenance Provider Exam General Information A. Thatch a. Intermingled layer of dead and living shoots, stems, and roots that develops between the zone of green vegetation and
GOOD BUGS---BAD BUGS
 GOOD BUGS---BAD BUGS A happy garden is when what you think, what you know and what you do in the garden are in harmony. Gandhi As global temperatures rise, many insects are shifting their ranges northward.
GOOD BUGS---BAD BUGS A happy garden is when what you think, what you know and what you do in the garden are in harmony. Gandhi As global temperatures rise, many insects are shifting their ranges northward.
Pine. Pest Damage on. Plant Problem. September September 1 10 October September November November November 1 10
 Pest Damage on Pine March 21 31 March 11 20 March 1 10 April 21 30 April 11 20 April 1 10 May 21 31 May 11 20 May 1 10 June 21 30 June 11 20 June 1 10 July 21 31 July 11 20 July 1 10 August 21 31 August
Pest Damage on Pine March 21 31 March 11 20 March 1 10 April 21 30 April 11 20 April 1 10 May 21 31 May 11 20 May 1 10 June 21 30 June 11 20 June 1 10 July 21 31 July 11 20 July 1 10 August 21 31 August
Greenhouse Pest Management. Greenhouse pests. Fungus gnat -damage by larvae
 Greenhouse Pest Management Greenhouse pests Thrips Whiteflies Fungus gnats Shore flies Mites Bulb mites Aphids Mealybugs Leaf miners (rare in IN) Fungus gnat -damage by larvae Larvae (maggots) feed on
Greenhouse Pest Management Greenhouse pests Thrips Whiteflies Fungus gnats Shore flies Mites Bulb mites Aphids Mealybugs Leaf miners (rare in IN) Fungus gnat -damage by larvae Larvae (maggots) feed on
VEGETABLE INSECTS. rev. 11/04 1
 VEGETABLE INSECTS Flea Beetles Flea beetles are tiny, black, jumping insects that chew small, round holes in the leaves of young tomatoes, eggplant, potatoes and related plants, as well as spinach, beets,
VEGETABLE INSECTS Flea Beetles Flea beetles are tiny, black, jumping insects that chew small, round holes in the leaves of young tomatoes, eggplant, potatoes and related plants, as well as spinach, beets,
ENTOMOLOGY. Learning Objectives The learner will:
 ENTOMOLOGY Learning Objectives The learner will: Gain a basic understanding of the balance of insects on the farm/garden (pests and beneficial insects.) Be able to identify a number of common pests and
ENTOMOLOGY Learning Objectives The learner will: Gain a basic understanding of the balance of insects on the farm/garden (pests and beneficial insects.) Be able to identify a number of common pests and
THE PINK HIBISCUS MEALYBUG MANAGEMENT ADDITIONAL DETAILS WILL BE ADDED AS SOON AS THEY ARE AVAILABLE
 THE PINK HIBISCUS MEALYBUG MANAGEMENT ADDITIONAL DETAILS WILL BE ADDED AS SOON AS THEY ARE AVAILABLE The Pink Hibiscus Mealybug or PHM is a pest that has devastated agriculture in many parts of the world.
THE PINK HIBISCUS MEALYBUG MANAGEMENT ADDITIONAL DETAILS WILL BE ADDED AS SOON AS THEY ARE AVAILABLE The Pink Hibiscus Mealybug or PHM is a pest that has devastated agriculture in many parts of the world.
Basic Chemicals. Following are some terms you will be hearing in connection with plant problems:
 Basic Chemicals Chemicals have become one of the fastest-moving items for retail garden centers. Even though there is almost always a way for nature to correct a problem, it usually takes too long. There
Basic Chemicals Chemicals have become one of the fastest-moving items for retail garden centers. Even though there is almost always a way for nature to correct a problem, it usually takes too long. There
Diseases of Warm-Season Grasses
 Diseases of Warm-Season Grasses Bermudagrass, Centipedegrass, Zoysiagrass, and St. Augustinegrass Leon T. Lucas, Extension Plant Pathology Specialist Arthur H. Bruneau, Extension Crop Science Specialist
Diseases of Warm-Season Grasses Bermudagrass, Centipedegrass, Zoysiagrass, and St. Augustinegrass Leon T. Lucas, Extension Plant Pathology Specialist Arthur H. Bruneau, Extension Crop Science Specialist
Propagation. Pests and Diseases. Black twig borer (Xylosandrus compactus) Magnolia white scale (Pseudaulacaspis cockerelli)
 Magnolia, Southern Magnolia Magnolia grandiflora Propagation Magnolias are usually propagated by semi-hardwood stem tip cuttings taken in the summer. Rooting should occur in 9 weeks with IBA Quick Dip
Magnolia, Southern Magnolia Magnolia grandiflora Propagation Magnolias are usually propagated by semi-hardwood stem tip cuttings taken in the summer. Rooting should occur in 9 weeks with IBA Quick Dip
Compost can be made in many ways, but essentially we do it by two main methods:
 Worms and Compost 1. Activity Looking at Worms 2. Compost Matters Vermiculture and Garden Compost 3. Activity Making Compost 4. Activity Critters in Compost 5. The Sustainable Food and Feed cycle This
Worms and Compost 1. Activity Looking at Worms 2. Compost Matters Vermiculture and Garden Compost 3. Activity Making Compost 4. Activity Critters in Compost 5. The Sustainable Food and Feed cycle This
Diagnosing Insect and Disease Problems in Florida Turfgrass
 Caterpillars Diagnosing Insect and Disease Problems in Florida This key is intended to be a starting point for identifying Florida turfgrass insect pests and diseases. Contact your local county Extension
Caterpillars Diagnosing Insect and Disease Problems in Florida This key is intended to be a starting point for identifying Florida turfgrass insect pests and diseases. Contact your local county Extension
How to Grow Leaf Lettuce
 How to Grow Leaf Lettuce ) 888 246 5233 Planting Lettuce can be started from seed or from plants. Some gardeners like to direct seed their lettuce but many prefer to start transplants and then move them
How to Grow Leaf Lettuce ) 888 246 5233 Planting Lettuce can be started from seed or from plants. Some gardeners like to direct seed their lettuce but many prefer to start transplants and then move them
Horticulture 2016 Newsletter
 Horticulture 2016 Newsletter No. 19 May 10, 2016 2021 Throckmorton Plant Science Cntr. Manhattan, KS 66506 (785) 532-6173 Video of the Week: Cantaloupe - Varieities for Small Spaces Garden Tour in Kansas
Horticulture 2016 Newsletter No. 19 May 10, 2016 2021 Throckmorton Plant Science Cntr. Manhattan, KS 66506 (785) 532-6173 Video of the Week: Cantaloupe - Varieities for Small Spaces Garden Tour in Kansas
Codling Moth Control at Hoch Orchard
 Codling Moth Control at Hoch Orchard April 2011 By Harry Hoch CM control on Hoch Orchard takes a truly integrated approach. There is no single silver bullet that can take care of the problem. We use a
Codling Moth Control at Hoch Orchard April 2011 By Harry Hoch CM control on Hoch Orchard takes a truly integrated approach. There is no single silver bullet that can take care of the problem. We use a
satg WATERMELON CULTIVATION DISEASES PESTS
 satg WATERMELON CULTIVATION DISEASES PESTS Contents Cultivation Climate Requirements...4 a. Temperature...4 b. Exposure...4 Land Preparation...5 A. Soil Requirements...5 B. Propagation...5 Planting...6
satg WATERMELON CULTIVATION DISEASES PESTS Contents Cultivation Climate Requirements...4 a. Temperature...4 b. Exposure...4 Land Preparation...5 A. Soil Requirements...5 B. Propagation...5 Planting...6
Unit G: Pest Management. Lesson 4: Managing Insects
 Unit G: Pest Management Lesson 4: Managing Insects 1 Terms Ametamorphic Antennae Antibiosis control Beneficial insect Biological control Chemical control Chitin Clean culture Complete metamorphosis Cultural
Unit G: Pest Management Lesson 4: Managing Insects 1 Terms Ametamorphic Antennae Antibiosis control Beneficial insect Biological control Chemical control Chitin Clean culture Complete metamorphosis Cultural
TURFGRASS AND LAWNS - CONTROL OF RED IMPORTED FIRE ANTS
 TURFGRASS AND LAWNS - CONTROL OF RED IMPORTED FIRE ANTS General Information RESTRICTIONS Do not apply by air. Do not water the treated area to the point of run-off. Do not make applications during rain.
TURFGRASS AND LAWNS - CONTROL OF RED IMPORTED FIRE ANTS General Information RESTRICTIONS Do not apply by air. Do not water the treated area to the point of run-off. Do not make applications during rain.
HOME VEGETABLE CROPS
 HOME VEGETABLE CROPS R. Spencer and S. Barkley Last Updated: March 2005 This document is only a guide. Always follow labelled rates, instructions for use, appropriate pre-harvest intervals and any listed
HOME VEGETABLE CROPS R. Spencer and S. Barkley Last Updated: March 2005 This document is only a guide. Always follow labelled rates, instructions for use, appropriate pre-harvest intervals and any listed
IPM for Master Gardeners. Mary Louise Flint, Ph.D. Extension Entomologist Emerita Department of Entomology University of California, Davis
 IPM for Master Gardeners Mary Louise Flint, Ph.D. Extension Entomologist Emerita Department of Entomology University of California, Davis What is IPM? Ecosystem-based strategy Focuses on long-term prevention
IPM for Master Gardeners Mary Louise Flint, Ph.D. Extension Entomologist Emerita Department of Entomology University of California, Davis What is IPM? Ecosystem-based strategy Focuses on long-term prevention
MINIBEASTS, HABITATS AND SOIL
 MINIBEASTS, HABITATS AND SOIL Learn more about pollinators and build soil fertility in an orchard. This lesson plan was written by The Orchard Project, a charity that work in partnership with local communities
MINIBEASTS, HABITATS AND SOIL Learn more about pollinators and build soil fertility in an orchard. This lesson plan was written by The Orchard Project, a charity that work in partnership with local communities
Raspberry. Exposure. Soil
 Raspberry The red raspberry is an excellent fruit for the home garden. The fruit has a delightful flavor and is suitable for using fresh, frozen, canned or in jam. Growing red raspberries is a very satisfying
Raspberry The red raspberry is an excellent fruit for the home garden. The fruit has a delightful flavor and is suitable for using fresh, frozen, canned or in jam. Growing red raspberries is a very satisfying
Managing Backyard Apples Organically
 Managing Backyard Apples Organically Deirdre Birmingham The Cider Farm Mineral Point, WI www.theciderfarm.com Note: This presentation is only 50 minutes and cannot cover all aspects of growing apples.
Managing Backyard Apples Organically Deirdre Birmingham The Cider Farm Mineral Point, WI www.theciderfarm.com Note: This presentation is only 50 minutes and cannot cover all aspects of growing apples.
Sanitation Segregate Plants
 Detecting Pests in Systemsbased Pest Management Frank A. Hale Professor Department of Entomology and Plant Pathology Pest Scouting Train and dedicate one person to scout along with one or two backup scouts
Detecting Pests in Systemsbased Pest Management Frank A. Hale Professor Department of Entomology and Plant Pathology Pest Scouting Train and dedicate one person to scout along with one or two backup scouts
Lawn Fungus / Disease
 Lawn Fungus / Disease This guide is a good place to see what affects lawns in our area so you can be a better informed customer. There are many different types of fungus which grow in every lawn and it's
Lawn Fungus / Disease This guide is a good place to see what affects lawns in our area so you can be a better informed customer. There are many different types of fungus which grow in every lawn and it's
XERISCAPE The conservation of water and energy through creative landscape.
 The conservation of water and energy through creative landscape. Almost every summer North Texas has been plagued with drought like conditions. This and a growing population has increased the demand of
The conservation of water and energy through creative landscape. Almost every summer North Texas has been plagued with drought like conditions. This and a growing population has increased the demand of
Biocontrol Demonstrations; An Introduction to Greenhouse Pests and Biocontrols
 Biocontrol Demonstrations; An Introduction to Greenhouse Pests and Biocontrols Dr. Lily Calderwood Commercial Horticulture Cornell Cooperative Extension CAAHP Team Tools used to manage pests while reducing
Biocontrol Demonstrations; An Introduction to Greenhouse Pests and Biocontrols Dr. Lily Calderwood Commercial Horticulture Cornell Cooperative Extension CAAHP Team Tools used to manage pests while reducing
Integrated pest management on vegetables for insect pests and vectors in South Texas
 Integrated pest management on vegetables for insect pests and vectors in South Texas Adrian Silva and Ismael E. Badillo-Vargas Texas A&M AgriLife Research August 2016 Insect pests of vegetables in the
Integrated pest management on vegetables for insect pests and vectors in South Texas Adrian Silva and Ismael E. Badillo-Vargas Texas A&M AgriLife Research August 2016 Insect pests of vegetables in the
Growing Great Tomatoes
 Ten Tips for Terrific Tomatoes Growing Great Tomatoes Mary Roberts Windcrest Farm Monroe, NC www.windcrestorganics.com All photos taken at Windcrest Farm unless otherwise noted Tomatoes and parsley in
Ten Tips for Terrific Tomatoes Growing Great Tomatoes Mary Roberts Windcrest Farm Monroe, NC www.windcrestorganics.com All photos taken at Windcrest Farm unless otherwise noted Tomatoes and parsley in
What Are the Options for Organic Lawn Care?
 What Are the Options for Organic Lawn Care? Dr. Charles H. Peacock NC State University BEST MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Goals of Best Management Practices The ultimate objective of Best Management Practices is
What Are the Options for Organic Lawn Care? Dr. Charles H. Peacock NC State University BEST MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Goals of Best Management Practices The ultimate objective of Best Management Practices is
Green Lawns. Promoting environmental stewardship
 Green Lawns Promoting environmental stewardship Gardening is America s most popular outdoor activity. We enjoy seeing things grow and improving our home environment. Working in the yard is also good exercise
Green Lawns Promoting environmental stewardship Gardening is America s most popular outdoor activity. We enjoy seeing things grow and improving our home environment. Working in the yard is also good exercise
Eggplant Production IDEA-NEW
 Eggplant Production IDEA-NEW Eggplant Introduction Eggplant belongs to the same family (solanaceae) as potatoes, tomatoes, and pepper It has been under cultivation in the Indo-Pakistani subcontinent since
Eggplant Production IDEA-NEW Eggplant Introduction Eggplant belongs to the same family (solanaceae) as potatoes, tomatoes, and pepper It has been under cultivation in the Indo-Pakistani subcontinent since
Growing Tips: Pests and diseases
 Growing Tips: Pests and diseases Troubleshooting Fruit trees make fantastic homes for lots of wildlife, although not all of it will be welcome! Keep your eyes open and check your trees regularly for signs
Growing Tips: Pests and diseases Troubleshooting Fruit trees make fantastic homes for lots of wildlife, although not all of it will be welcome! Keep your eyes open and check your trees regularly for signs
IN AND AROUND YOUR HOME
 A RESPONSIBLE APPROACH TO IN AND AROUND YOUR HOME Pests can come in many forms. Some, like termites, ants, grubs, and invasive weeds, can cause damage to our property. Some threaten our health by triggering
A RESPONSIBLE APPROACH TO IN AND AROUND YOUR HOME Pests can come in many forms. Some, like termites, ants, grubs, and invasive weeds, can cause damage to our property. Some threaten our health by triggering
Shade Tree Insect and Mite Pests Larry Sagers Extension Horticulture Specialist Utah State University Extension Service Thanksgiving Point Office
 Shade Tree Insect and Mite Pests Larry Sagers Extension Horticulture Specialist Utah State University Extension Service Thanksgiving Point Office Shade tree pests cause problems including: Nuisance Defoliation
Shade Tree Insect and Mite Pests Larry Sagers Extension Horticulture Specialist Utah State University Extension Service Thanksgiving Point Office Shade tree pests cause problems including: Nuisance Defoliation
Rhododendron Insect Pests
 Rhododendron Insect Pests The rhododendron is a commonly used landscape plant that has a specific complex of pests. Many of these insects also cause damage to azalea and mountain laurel. The discussion
Rhododendron Insect Pests The rhododendron is a commonly used landscape plant that has a specific complex of pests. Many of these insects also cause damage to azalea and mountain laurel. The discussion
in the garden explore & discover the New Zealand backyard Ned Barraud & Gillian Candler
 in the garden explore & discover the New Zealand backyard Ned Barraud & Gillian Candler To my wife Niamh NB For my parents GC First published in 2013 by Craig Potton Publishing Craig Potton Publishing
in the garden explore & discover the New Zealand backyard Ned Barraud & Gillian Candler To my wife Niamh NB For my parents GC First published in 2013 by Craig Potton Publishing Craig Potton Publishing
Ecology of Insect Pests and Natural Enemies
 Chapter Eight Ecology of Insect Pests and Natural Enemies This chapter was adapted from: FAO Inter-Country Programme for the Development and Application of Integrated Pest Management in Vegetable Growing
Chapter Eight Ecology of Insect Pests and Natural Enemies This chapter was adapted from: FAO Inter-Country Programme for the Development and Application of Integrated Pest Management in Vegetable Growing
Integrated Pest Management Program Department of Plant Science and Landscape Architecture UConn Extension
 Integrated Pest Management Program Department of Plant Science and Landscape Architecture UConn Extension Homegrown Beetles: Backyard Biocontrol Donna Ellis, Senior Extension Educator UConn Department
Integrated Pest Management Program Department of Plant Science and Landscape Architecture UConn Extension Homegrown Beetles: Backyard Biocontrol Donna Ellis, Senior Extension Educator UConn Department
Cucurbit Powdery Mildew is Here by Sally Miller
 VegNet Vol. 13, No. 11. July 14, 2006 Ohio State University Extension Vegetable Crops On the WEB at: http://vegnet.osu.edu If experiencing problems receiving this fax, Call 614-292-3857 In This Issue 1.
VegNet Vol. 13, No. 11. July 14, 2006 Ohio State University Extension Vegetable Crops On the WEB at: http://vegnet.osu.edu If experiencing problems receiving this fax, Call 614-292-3857 In This Issue 1.
Protecting Your Dahlias From Bugs and Other Perils. Kevin Larkin Corralitos Gardens For The Monterey Bay Dahlia Society March 2012
 Protecting Your Dahlias From Bugs and Other Perils Kevin Larkin Corralitos Gardens For The Monterey Bay Dahlia Society March 2012 Integrated Pest Management 1. Identification 2. Impact Assessment 3. Intervention
Protecting Your Dahlias From Bugs and Other Perils Kevin Larkin Corralitos Gardens For The Monterey Bay Dahlia Society March 2012 Integrated Pest Management 1. Identification 2. Impact Assessment 3. Intervention
