My Soil Won t Drain, Can I Still Use LID? Rob Buchert, John Knutson, Erik Pruneda
|
|
|
- Derrick Wade
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 My Soil Won t Drain, Can I Still Use LID? Rob Buchert, John Knutson, Erik Pruneda
2 Presentation Topics Background information Designing LID for cold and snow prone conditions Applying LID in Pullman s low permeability soils How the soil and BMP type affect the feasibility of retention Options to improve Bioretention in low permeability soils Benefits of using LID even if under-drains are necessary
3 Background Library Site December 5 th 2013, 10 Degrees
4 Background Ecology LID Project Grant Funded, City Match Designed 4 sites - three parking lot retrofits, one new lot 1. Neill Public Library Direct Discharge to SF Palouse River 2. Sims Parking Lot Direct Discharge to Dry Fork Creek 3. Fire Station 1 Direct Discharge to Dry Fork Creek 4. South Street Parking Lot Direct Discharge to SF Palouse River Built two sites Neill Library and South Street
5
6 Background E. WA Climatic Region 4 (NE & Blue Mountains) 21.2 inches of mean annual precipitation 29.1 inches mean annual snow fall
7 Background Geotechnical Investigation Neill Public Library Asphalt (0-2 in.), Silty Gravel Fill (2-9 in.), Silty Clay Fill (9-96 in.) Measured i = 1.3 in/hr (approx. 6.5 ft BGS) Req d subgrade compaction under Permeable Pavers and Asphalt South Street Parking Lot Silty Gravel Fill & Topsoil (0-12 in.), Silt Alluvium ( in.) Measured infiltration rate 0.4 in/hr (approx. 6.5 ft BGS) Did not require subgrade compaction
8 Background BMPs Selected at Each Site Neill Library Permeable Pavers Bioretention Filterra Tree Box Filter Contech CDS South Street Permeable Pavers Porous Asphalt Bioretention Contech CDS - pretreatment for large off-site commercial drainage area. South Street bioretention - enhanced treatment for off-site roadway area.
9 Background Asphalt Filterra Tree Box Bioretention Permeable Pavers Contech CDS Neill Library
10 Background Permeable Pavers Porous Asphalt Bioretention South Street
11 Designing LID for Cold and Snow Prone Conditions South Street Off-Site Roadway to be Treated December 5 th 2013, 10 Degrees
12 Designing LID for Cold and Snow Prone Conditions Response to Pullman Cold and Snow Prone Issues Well drained BMPs to protect from frost depths Consider deicer & traction sand impacts deicer concerns, O&M Adequate sump volume to capture traction grit Avoid edges that catch plow blades, flush curbs must be flush, markers Right pavement section for loading, geotextile separation Bioretention double as snow storage, ID other storage areas Plants selected to handle cold, some deicer, snow storage A little careful thought and collaboration with maintenance staff will save a lot of headaches
13 Applying LID in Pullman s Low Permeability Soils Neill Library Clayey Fill 8/23/16
14 Applying LID in Pullman s Low Permeability Soils Liners and Underdrains Impermeable Liners Considered over clayey subgrade to prevent wetting, but only used under bioretention near steep slope due to stability concerns Geotextile Separation - Used above subgrades to improve strength and prevent subbase migration Underdrains Used to provide positive drainage and avoid prolonged wetting of clayey fill soils at Library site
15 Applying LID in Pullman s Low Permeability Soils Underdrain Elevation (H) Can be selected to foster some stormwater retention if subgrade soils: Are not compacted When under permeable pavements, remain structurally stable when wet H
16 Applying LID in Pullman s Low Permeability Soils Example Underdrain Elevation Calculation Assume infiltration over entire subgrade surface area Assumed constant (or average) infiltration rate = i, in/hr Max allowable draindown time = 72 hrs (E. WA) Storage reservoir gravel porosity = n% Max height to underdrain perforation = H, inches above subgrade soil H = (i x 72)/(n/100) Example: i = 0.05 in/hr, subbase gravel porosity = 30% H = 12 inches Can infiltrate equivalent of 3.6 inches of stored depth in 72 hrs
17 Applying LID in Pullman s Low Permeability Soils For Proper Underdrain Function ALWAYS REMEMBER - water flows downhill, even in LID subbase reservoir layers Keep subgrade level when possible, confine at the edges to build water depth up to underdrains Carefully consider underdrain layout and need for subsurface check dams when working with sloped subgrades
18 How the Soil and Type of BMP Affect the Feasibility of Retaining Stormwater South Street Parking Lot Porous Asphalt and Permeable Pavers 10/28/16
19 How the Soil and Specific BMP Affect the Feasibility of Retaining Stormwater Common Misconceptions Retention/infiltration is impossible or insignificant in fine grained soils with low permeability Receiving water flow control benefit is greatly reduced when using underdrains Let s take a closer look
20 How the Soil and Specific BMP Affect the Feasibility of Retaining Stormwater Two main types of retention BMPs: Type A Infiltration BMPs that concentrate runoff into a small footprint relative to the drainage area (bioretention, infiltration basins, drywells) Type B - BMPs that provide about the same area for infiltration as the overall drainage area (permeable pavements without run-on) The ability of Type A BMPs to retain and infiltrate significant rainfall is more restricted by low permeability soils than Type B BMPs
21 How the Soil and Specific BMP Affect the Feasibility of Retaining Stormwater Consider: Soil with measured i = 0.4 in/hr (South Street Park Site) Permeable pavements over un-compacted subgrade Low plugging concerns, assume long term low head i = 0.2 in/hr Pullman 6 month, 24 hr Type 1A Storm 1.05 in. Pullman 10 yr, 24 hr Type 1A Storm 2.10 in. 6 inch diameter underdrains, perforations three inch above subgrade
22 How the Soil and Specific BMP Affect the Feasibility of Retaining Stormwater Pullman Type 1A Rainfall Intensity Versus Time, 6 Month, 24 hour Needs to be stored in reservoir layer Infiltrates during storm event Permeable Pavement No Run-On, 6 Mo. Storm To infiltrate entire 6 month storm requires storage of: About (0.66 hr)x(0.06 in/hr)/2 = 0.02 in. of rain Accounting for porosity of reservoir gravel, 0.02/0.3 = 0.07 inches of ponding Neglects abstractions, evaporation, etc.
23 How the Soil and Specific BMP Affect the Feasibility of Retaining Stormwater Pullman Type 1A Rainfall Intensity Versus Time, 10 yr, 24 hour Needs to be stored in reservoir layer Infiltrates during storm event Permeable Pavement No Run-On, 10 Yr. Storm To infiltrate entire 10 year storm requires storage of: About (1.2 hr)x(0.3 in/hr)/2 = 0.18 in. of rain Accounting for porosity of reservoir gravel, 0.18/0.3 = 0.6 inches of ponding in storage layer
24 How the Soil and Specific BMP Affect the Feasibility of Retaining Stormwater Clearly Permeable Pavements can retain larger storm events even when used in soils with low infiltration rates Water Quality Benefits Flow Control Benefits Some Key Issues Traffic loading/structural stability Compaction of subgrade Shrink-swell potential Geotextile/geogrid reinforcement Underdrain elevation Run-on
25 How the Soil and Specific BMP Affect the Feasibility of Retaining Stormwater Now Let s Look at South Street Site Bioretention Facility Contributing Drainage Area of 0.29 ac., 100% Impervious 6 month storm: Qp = 0.06 cfs, Vol = 870 cf Active Bioretention Facility Footprint = 500 sf Max Ponding Depth = 3 inches, but underdrain provides free drainage Footprint has approx. available infiltration rate = 0.2 in/hr Approximate infiltration outflow rate = cfs
26 How the Soil and Specific BMP Affect the Feasibility of Retaining Stormwater Bioretention, 6 Mo. Storm Up to 160 cf infiltrates during storm, 710 cf of excess treated runoff Excess treated runoff removed by underdrains Would need to be stored Only minor flow control benefit Options to Improve Flow Control Benefit? Infiltrates
27 Options to Improve Bioretention in Low Permeability Soils
28 Options to Improve Bioretention in Low Permeability Soils Bioretention: Options to Improve Flow Control Benefit Option 1 Keep same geometry and cross-section but remove underdrain and force use of available storage before accessing overflow drainage Option 2 Remove underdrain and add more subsurface storage and infiltration area Option 3 Restrict underdrain outflow to promote more infiltration and provide detention effect for released water We ll look at Options 1 and 2
29 Options to Improve Bioretention in Low Permeability Soils Bioretention Flow Control Improvement Option 1 Same geometry, remove (or raise) underdrain, use available storage Storage Volume = ponding + saturated mulch + saturated media + saturated gravel storage = Approx. 520 cf (accounts for geometry and porosity of granular materials) Volume infiltrated during the storm = 160 cf Est. total volume retained = = 680 cf = 78% of WQ Volume! Max Draindown = (520 cf)/(500 sf x (0.2 in/hr)/(12 in/ft)) = 62.4 hr (ok E WA)
30 Options to Improve Bioretention in Low Permeability Soils Bioretention Flow Control Improvement Option 2 Remove or raise underdrain, add subsurface storage and infiltration area Add 150 ft infiltration trench 18 in. wide, 21 in. tall, 1 ft dia. perf. pipe, gravel n = 30% adds 200 cf storage plus cfs infiltration outflow rate New volume infiltrated during the storm = 160 cf + 79 cf = 239 cf New Storage Volume = 520 cf cf = 720 cf Est. total volume retained = = 959 cf = 110% of WQ Volume! Max draindown = (720 cf)/(725 sf x (0.2 in/hr)/(12 in/ft)) = 59.6 hr (ok E WA)
31 Benefits of Using LID Even if Underdrains are Necessary Permeable pavements in low permeability soils can provide major retention and flow control when: Run-on is minimal Subgrade is not compacted Bioretention in low permeability soils can provide moderate retention and flow control when: The full storage volume is used prior to accessing drainage Extra subsurface storage volume and infiltration area is added Draindown times are acceptable
32 Thank You!
Attachment 2: Permeable Pavement Design Guidelines
 Attachment 2: Permeable Pavement Design Guidelines Design of permeable pavement systems is critical if they are to function properly and efficiently. The area and shape are dependent on the site design,
Attachment 2: Permeable Pavement Design Guidelines Design of permeable pavement systems is critical if they are to function properly and efficiently. The area and shape are dependent on the site design,
5. LOW IMPACT DEVELOPMENT DESIGN STANDARDS
 5. LOW IMPACT DEVELOPMENT DESIGN STANDARDS Low Impact Development (LID) requires a shift in stormwater management away from conveying runoff to a small number of downstream points through hydraulically
5. LOW IMPACT DEVELOPMENT DESIGN STANDARDS Low Impact Development (LID) requires a shift in stormwater management away from conveying runoff to a small number of downstream points through hydraulically
Structural Stormwater Best Management Practices
 Structural Stormwater Best Management Practices for Small Commercial and Residential Applications Timothy Bruno Watershed Manager PA Department of Environmental Protection What are STRUCTURAL BMPs? Physical
Structural Stormwater Best Management Practices for Small Commercial and Residential Applications Timothy Bruno Watershed Manager PA Department of Environmental Protection What are STRUCTURAL BMPs? Physical
WQ-07 INFILTRATION TRENCH
 Greenville County Technical Specification for: WQ-07 INFILTRATION TRENCH 1.0 Infiltration Trench 1.1 Description Infiltration Trenches are excavations filled with stone to create an underground reservoir
Greenville County Technical Specification for: WQ-07 INFILTRATION TRENCH 1.0 Infiltration Trench 1.1 Description Infiltration Trenches are excavations filled with stone to create an underground reservoir
Appendices: Glossary. General Terms. Specific Terms. Low Impact Development Approaches Handbook
 67 67 General Terms Specific Terms 66 Low Impact Development Approaches Handbook The vocabulary of low impact development is evolving, and many terms are used interchangeably and to describe the same or
67 67 General Terms Specific Terms 66 Low Impact Development Approaches Handbook The vocabulary of low impact development is evolving, and many terms are used interchangeably and to describe the same or
4. CONCEPT PLAN DEVELOPMENT
 4. CONCEPT PLAN DEVELOPMENT Concept Plan Step 1: Identify Site Constraints and Opportunities Review the existing site to identify constraints and opportunities for GI Practices to meet the RRv. Constraints
4. CONCEPT PLAN DEVELOPMENT Concept Plan Step 1: Identify Site Constraints and Opportunities Review the existing site to identify constraints and opportunities for GI Practices to meet the RRv. Constraints
Stormwater Control Plan: Small (Tier 1) Land Development Project
 Stormwater Control Plan: Small (Tier 1) Land Development Project Project ID for Tracking (for City Staff only): The California Regional Water Quality Control Board for the Central Coast Region (Water Board)
Stormwater Control Plan: Small (Tier 1) Land Development Project Project ID for Tracking (for City Staff only): The California Regional Water Quality Control Board for the Central Coast Region (Water Board)
Permeable Pavement Systems
 Permeable Pavement Systems EGRA Stone ECO Stone CONSERVATION DESIGN FORUM Permeable Pavement Presentation Outline Case Studies Benefits Hydrologic Design Engineering Design Construction Considerations
Permeable Pavement Systems EGRA Stone ECO Stone CONSERVATION DESIGN FORUM Permeable Pavement Presentation Outline Case Studies Benefits Hydrologic Design Engineering Design Construction Considerations
12/31/2014 County of Mendocino s Low Impact Design Standards Manual v1.0 A P P E N D I X 8. Site Design Measures. 32 P a g e
 12/31/2014 County of Mendocino s Low Impact Design Standards Manual v1.0 A P P E N D I X 8 Site Design Measures 32 P a g e Rooftop and Impervious Area Disconnection (Self-retaining areas) Description Disconnection
12/31/2014 County of Mendocino s Low Impact Design Standards Manual v1.0 A P P E N D I X 8 Site Design Measures 32 P a g e Rooftop and Impervious Area Disconnection (Self-retaining areas) Description Disconnection
ANSWER KEY MGSFlood v WWHM2012 (released 5/15/2015)
 ANSWER KEY MGSFlood v. 4.35 --- WWHM2012 (released 5/15/2015) Name: Date: Module 6.0: Advanced Topics in LID Design: Hydrologic Modeling General instructions: You may model facility dimensions to the nearest
ANSWER KEY MGSFlood v. 4.35 --- WWHM2012 (released 5/15/2015) Name: Date: Module 6.0: Advanced Topics in LID Design: Hydrologic Modeling General instructions: You may model facility dimensions to the nearest
Bioretention cell schematic key
 Bioretention Cells Bioretention cell schematic key 1 3 Hardwood mulch 2 Curb cut 3 18-30 Modified soil 4 Stone aggregate choker layer 5 Stone aggregate base layer 6 Subdrain 7 Undisturbed soil 8 Overflow/Cleanout
Bioretention Cells Bioretention cell schematic key 1 3 Hardwood mulch 2 Curb cut 3 18-30 Modified soil 4 Stone aggregate choker layer 5 Stone aggregate base layer 6 Subdrain 7 Undisturbed soil 8 Overflow/Cleanout
Using Runoff Reduction Practices to Shrink the Water Quality Volume (WQv) September 18, 2018 Jay Dorsey
 Using Runoff Reduction Practices to Shrink the Water Quality Volume (WQv) September 18, 2018 Jay Dorsey This Presentation Ohio EPA Post-Construction Criteria/Guidance Runoff Reduction Accounting Green
Using Runoff Reduction Practices to Shrink the Water Quality Volume (WQv) September 18, 2018 Jay Dorsey This Presentation Ohio EPA Post-Construction Criteria/Guidance Runoff Reduction Accounting Green
INFILTRATION TRENCH - LEAKY PIPE
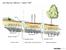 INFILTRATION TRENCH - LEAKY PIPE FLOW PERFORATED CMP OR RCP WITH PULLED JOINTS OVERSIZED PIPE (INLINE DETENTION) PERFORATED CMP OR RCP WITH PULLED JOINTS EXFILTRATE TRENCH VOLUME EXFILTRATE SEDIMENT SUMP
INFILTRATION TRENCH - LEAKY PIPE FLOW PERFORATED CMP OR RCP WITH PULLED JOINTS OVERSIZED PIPE (INLINE DETENTION) PERFORATED CMP OR RCP WITH PULLED JOINTS EXFILTRATE TRENCH VOLUME EXFILTRATE SEDIMENT SUMP
6.1 Bioretention Areas
 SAN MATEO COUNTYWIDE WATER POLLUTION PREVENTION PROGRAM 6.1 Bioretention Areas Figure 6-1. Bioretention Area. Source: City of Brisbane Bioretention areas 1, or rain gardens, are concave landscaped areas
SAN MATEO COUNTYWIDE WATER POLLUTION PREVENTION PROGRAM 6.1 Bioretention Areas Figure 6-1. Bioretention Area. Source: City of Brisbane Bioretention areas 1, or rain gardens, are concave landscaped areas
Preparing a Stormwater Control Plan for a Small Land Development Project
 Preparing a Stormwater Control Plan for a Small Land Development Project Addendum to the Stormwater C.3 Guidebook December 1, 2012 Introduction As of December 1, 2012, development projects that create
Preparing a Stormwater Control Plan for a Small Land Development Project Addendum to the Stormwater C.3 Guidebook December 1, 2012 Introduction As of December 1, 2012, development projects that create
Case Study: Dallas Green Infrastructure for Stormwater
 Case Study: Dallas Green Infrastructure for Stormwater Extension and Research Sandhya Mohan Fouad H. Jaber, PhD Biological and Agricultural Engineering Texas Agrilife, Texas A&M University System Urban
Case Study: Dallas Green Infrastructure for Stormwater Extension and Research Sandhya Mohan Fouad H. Jaber, PhD Biological and Agricultural Engineering Texas Agrilife, Texas A&M University System Urban
Can Urban Redevelopment Restore Aquatic Resources
 Can Urban Redevelopment Restore Aquatic Resources with Standards for Stormwater Retention and Landscape Performance? Rebecca C. Stack District of Columbia Department of the Environment Industry, Agriculture,
Can Urban Redevelopment Restore Aquatic Resources with Standards for Stormwater Retention and Landscape Performance? Rebecca C. Stack District of Columbia Department of the Environment Industry, Agriculture,
Appendix D - Technical Design Criteria for BMPs
 Appendix D - Technical Design Criteria for BMPs City of Wayzata Page 3 On-site infiltration features Definitions and Scope: Infiltration facilities are constructed basins or depressions located in permeable
Appendix D - Technical Design Criteria for BMPs City of Wayzata Page 3 On-site infiltration features Definitions and Scope: Infiltration facilities are constructed basins or depressions located in permeable
Green Infrastructure and Low-Impact Development Technologies
 Green Infrastructure and Low-Impact Development Technologies The guiding principles of these technologies is to manage stormwater at their sources using natural means, and establish conditions so that
Green Infrastructure and Low-Impact Development Technologies The guiding principles of these technologies is to manage stormwater at their sources using natural means, and establish conditions so that
Inspection and Maintenance of Stormwater Best Management Practices
 FAC T S H E E T Inspection and Maintenance of Stormwater Best Management Practices is a general term that refers to vegetated stormwater best management practices (BMPs) that temporarily store rainwater
FAC T S H E E T Inspection and Maintenance of Stormwater Best Management Practices is a general term that refers to vegetated stormwater best management practices (BMPs) that temporarily store rainwater
C.3 STORMWATER TECHNICAL GUIDANCE. Table of Contents. Glossary... viii. Chapter 1 Introduction/How to Use this Handbook
 C.3 STORMWATER TECHNICAL GUIDANCE Table of Contents Glossary... viii Chapter 1 Introduction/How to Use this Handbook... 1-1 1.1 Purpose of this Handbook... 1-1 1.2 What is the Countywide Program?... 1-2
C.3 STORMWATER TECHNICAL GUIDANCE Table of Contents Glossary... viii Chapter 1 Introduction/How to Use this Handbook... 1-1 1.1 Purpose of this Handbook... 1-1 1.2 What is the Countywide Program?... 1-2
Development of LID Design Guide in Edmonton
 Development of LID Design Guide in Edmonton Xiangfei Li and Fayi Zhou, the City of Edmonton Dan Healy, AMEC Earth and Environmental Philadelphia LID Symposium September 26, 2011 Outline Why LID Why develop
Development of LID Design Guide in Edmonton Xiangfei Li and Fayi Zhou, the City of Edmonton Dan Healy, AMEC Earth and Environmental Philadelphia LID Symposium September 26, 2011 Outline Why LID Why develop
Retrofit of the Gwinnett County DWR Facility Using Low Impact Development Practices SESWA 2012 Annual Conference October 19, 2012
 Retrofit of the Gwinnett County DWR Facility Using Low Impact Development Practices SESWA 2012 Annual Conference October 19, 2012 Jeff Herr, P.E., D.WRE National Stormwater Leader jherr@brwncald.com Acknowledgements
Retrofit of the Gwinnett County DWR Facility Using Low Impact Development Practices SESWA 2012 Annual Conference October 19, 2012 Jeff Herr, P.E., D.WRE National Stormwater Leader jherr@brwncald.com Acknowledgements
WQ-23 MOUNTAINOUS AND STEEP SLOPE SITES
 Greenville County Technical Specification for: WQ-23 MOUNTAINOUS AND STEEP SLOPE SITES 1.0 Mountainous and Steep Slope Sites 1.1 Description The geographic locations of portions of Greenville County are
Greenville County Technical Specification for: WQ-23 MOUNTAINOUS AND STEEP SLOPE SITES 1.0 Mountainous and Steep Slope Sites 1.1 Description The geographic locations of portions of Greenville County are
Post Construction BMPs
 Post Construction BMPs Why are Post Construction BMPs important? With increased development brings the increase of impervious cover Parking lots, rooftops, driveways Storm water runoff volume increases
Post Construction BMPs Why are Post Construction BMPs important? With increased development brings the increase of impervious cover Parking lots, rooftops, driveways Storm water runoff volume increases
03/10/2015 PROGRAM OVERVIEW OVERVIEW OF PROGRAM
 1 PROGRAM OVERVIEW 2012: Public and private partners engage state legislature to fund program June 2012: LID Training Steering Committee convened 2012 2013: Washington State LID Training Plan developed:
1 PROGRAM OVERVIEW 2012: Public and private partners engage state legislature to fund program June 2012: LID Training Steering Committee convened 2012 2013: Washington State LID Training Plan developed:
1/31/2017 INSTRUCTORS AGENDA. introduction. hydrologic modeling basics. performance standards. BMP modeling specifics. wrap up
 1 REBECCA DUGOPOLSKI, PE Senior Engineer Key project experience: Stormwater monitoring, design, hydrologic modeling and NPDES Permit compliance INSTRUCTORS MEGHAN FELLER, PE Project Engineer Key project
1 REBECCA DUGOPOLSKI, PE Senior Engineer Key project experience: Stormwater monitoring, design, hydrologic modeling and NPDES Permit compliance INSTRUCTORS MEGHAN FELLER, PE Project Engineer Key project
City of Vallejo. Stormwater Control C.3 Compliance Information. Addendum to C.3 Guidebook by Contra Costa Clean Water Program
 City of Vallejo Stormwater Control C.3 Compliance Information Addendum to C.3 Guidebook by Contra Costa Clean Water Program June 2018 Table of Contents I. PLANNING AHEAD FOR C.3 COMPLIANCE... 1 A. DOES
City of Vallejo Stormwater Control C.3 Compliance Information Addendum to C.3 Guidebook by Contra Costa Clean Water Program June 2018 Table of Contents I. PLANNING AHEAD FOR C.3 COMPLIANCE... 1 A. DOES
NEORSD Green Infrastructure Grant (GIG) Program Opening Remarks
 NEORSD Green Infrastructure Grant (GIG) Program Opening Remarks 2019 NEORSD GIG Eligibility and Technical Requirements Project must be located in the Sewer District s combined sewer area Location Applicant
NEORSD Green Infrastructure Grant (GIG) Program Opening Remarks 2019 NEORSD GIG Eligibility and Technical Requirements Project must be located in the Sewer District s combined sewer area Location Applicant
Appendix G. Detailed Design
 Appendix G Detailed Design G1: Construction details Construction detail drawings usually include important details and specifications for required project design elements. This section provides information
Appendix G Detailed Design G1: Construction details Construction detail drawings usually include important details and specifications for required project design elements. This section provides information
Sustainable Sites. hblanarc.ca. RDN Workshop June 25, David Reid, FCSLA, Landscape Architect, Environmental Designer
 Sustainable Sites RDN Workshop June 25, 2011 David Reid, FCSLA, Landscape Architect, Environmental Designer hblanarc.ca Surrey ESA Networks & linear corridors ESA Network: Develop with Care SITE Hub >10
Sustainable Sites RDN Workshop June 25, 2011 David Reid, FCSLA, Landscape Architect, Environmental Designer hblanarc.ca Surrey ESA Networks & linear corridors ESA Network: Develop with Care SITE Hub >10
Rain Gardens Water Quality the Way Mother Nature Intended
 Rain Gardens Water Quality the Way Mother Nature Intended Maintenance Discussion Design Discussion Susan Morgan, Ph.D, PE Southern Illinois University Edwardsville smorgan@siue.edu (618) 650 5014 Michael
Rain Gardens Water Quality the Way Mother Nature Intended Maintenance Discussion Design Discussion Susan Morgan, Ph.D, PE Southern Illinois University Edwardsville smorgan@siue.edu (618) 650 5014 Michael
SEATTLE PUBLIC UTILITIES Drainage Design Options for street right of ways.
 SEATTLE PUBLIC UTILITIES Drainage Design Options for street right of ways. Numerous ecosystem-based functional stormwater quantity and quality design alternatives are possible within the street ROW. Several
SEATTLE PUBLIC UTILITIES Drainage Design Options for street right of ways. Numerous ecosystem-based functional stormwater quantity and quality design alternatives are possible within the street ROW. Several
Post Construction BMP Inspection. Scott Taylor, P.E. Stormwater
 Post Construction BMP Inspection Scott Taylor, P.E. Learning Objectives To Understand: Types of post construction BMPs Typical construction process of BMPs Construction errors that impact BMP operation
Post Construction BMP Inspection Scott Taylor, P.E. Learning Objectives To Understand: Types of post construction BMPs Typical construction process of BMPs Construction errors that impact BMP operation
Reducing New York City s CSOs Using Green Infrastructure
 Reducing New York City s CSOs Using Green Infrastructure Think Blue Maine Conference November 21-22, 2013 Portland, ME Anne Kitchell, LEED AP, Horsley Witten Group John McLaughlin, NYCDEP Matthew Jones,
Reducing New York City s CSOs Using Green Infrastructure Think Blue Maine Conference November 21-22, 2013 Portland, ME Anne Kitchell, LEED AP, Horsley Witten Group John McLaughlin, NYCDEP Matthew Jones,
Post-Construction Infiltration Practices Table 4b
 Post-Construction Infiltration Practices Table 4b Jay Dorsey, PE, PhD Ohio State University Stormwater Management Program Bowling Green, Ohio September 18, 2018 Table 4b Infiltration Post-Construction
Post-Construction Infiltration Practices Table 4b Jay Dorsey, PE, PhD Ohio State University Stormwater Management Program Bowling Green, Ohio September 18, 2018 Table 4b Infiltration Post-Construction
Stormwater Management Techniques WMPF LAND USE TRAINING INSTITUTE MARCH 14, 2018
 Stormwater Management Techniques WMPF LAND USE TRAINING INSTITUTE MARCH 14, 2018 Potential Impacts of New Development Urban development can significantly increase stormwater runoff Water quality considerations
Stormwater Management Techniques WMPF LAND USE TRAINING INSTITUTE MARCH 14, 2018 Potential Impacts of New Development Urban development can significantly increase stormwater runoff Water quality considerations
Going Green with the NYS Stormwater Design Standards
 Going Green with the NYS Stormwater Design Standards Shohreh Karimipour, P.E. NYSDEC History of Stormwater Management Ancient Greek Cisterns Water Cistern Systems in Greece from Minoan to Hellenistic Period,
Going Green with the NYS Stormwater Design Standards Shohreh Karimipour, P.E. NYSDEC History of Stormwater Management Ancient Greek Cisterns Water Cistern Systems in Greece from Minoan to Hellenistic Period,
Rainwater Management an issue for the 21 st Century. Hydrological Cycle
 Canadian Society of Landscape Architects CONGRESS 2014 Rainwater Management an issue for the 21 st Century Don Crockett, BCSLA, CSLA Principal, Golder Associates Ltd. May 2014 Hydrological Cycle PRE- URBAN
Canadian Society of Landscape Architects CONGRESS 2014 Rainwater Management an issue for the 21 st Century Don Crockett, BCSLA, CSLA Principal, Golder Associates Ltd. May 2014 Hydrological Cycle PRE- URBAN
Example Stormwater Control Plan For a Residential Subdivision Project. Whispering Pines Lane Anytown, USA. February 21, 2018
 Example Stormwater Control Plan For a Residential Subdivision Project Whispering Pines Lane Anytown, USA February 21, 2018 XYZ Corporation Jane Jones, 925-555-1212 This example prepared by Dan Cloak Environmental
Example Stormwater Control Plan For a Residential Subdivision Project Whispering Pines Lane Anytown, USA February 21, 2018 XYZ Corporation Jane Jones, 925-555-1212 This example prepared by Dan Cloak Environmental
Subsurface Infiltration Bed
 Subsurface Infiltration Bed The Subsurface Infiltration Bed BMP consists of a storage bed underlying either a vegetated or hardscaped surface for the purpose of temporary storage and infiltration of stormwater
Subsurface Infiltration Bed The Subsurface Infiltration Bed BMP consists of a storage bed underlying either a vegetated or hardscaped surface for the purpose of temporary storage and infiltration of stormwater
Low Impact Development Practices
 Low Impact Development Practices Michael Dietz, Ph.D. CT Nonpoint Education for Municipal Officials (NEMO) Center for Land Use Education and Research May 8, 2013 Town of Bolton Planning and Zoning Commission
Low Impact Development Practices Michael Dietz, Ph.D. CT Nonpoint Education for Municipal Officials (NEMO) Center for Land Use Education and Research May 8, 2013 Town of Bolton Planning and Zoning Commission
Storm Water Managament at the University of Michigan
 Storm Water Managament at the University of Michigan Standard Operating Procedure Date: 06/23/17 Revision #: 03 The green roof installed on top of the Mott Children s & Von Voigtlander Women s Hospital.
Storm Water Managament at the University of Michigan Standard Operating Procedure Date: 06/23/17 Revision #: 03 The green roof installed on top of the Mott Children s & Von Voigtlander Women s Hospital.
Page 19 L.L.C. (Previously the United Salad Co. Garage) 939 SE Alder St.
 Page 19 L.L.C. (Previously the United Salad Co. Garage) 939 SE Alder St. Project Summary Project Type: Technologies: Major Benefits: Light industrial retrofit (parking lot) - demonstration project Landscape
Page 19 L.L.C. (Previously the United Salad Co. Garage) 939 SE Alder St. Project Summary Project Type: Technologies: Major Benefits: Light industrial retrofit (parking lot) - demonstration project Landscape
Selecting Appropriate Stormwater Control Measures for Your Development Project
 Phase II Post-Construction Stormwater Requirements Workshop - February 10, 2014 Selecting Appropriate Stormwater Control Measures for Your Development Project Jill Bicknell, P.E., EOA, Inc. Outline of
Phase II Post-Construction Stormwater Requirements Workshop - February 10, 2014 Selecting Appropriate Stormwater Control Measures for Your Development Project Jill Bicknell, P.E., EOA, Inc. Outline of
EROSION PREVENTION BMP SUGGESTED USES MATRIX
 EROSION PREVENTION SUGGESTED USES MATRIX Processed Based Tools Software Aids Slope Waterway Surface Concentrated Flows Large Flat Stock Pile Borrow Adjacent Property Impacts Erosion Prevention Measures
EROSION PREVENTION SUGGESTED USES MATRIX Processed Based Tools Software Aids Slope Waterway Surface Concentrated Flows Large Flat Stock Pile Borrow Adjacent Property Impacts Erosion Prevention Measures
Chapter 2 Roof Downspout Controls
 Chapter 2 Roof Downspout Controls 2.1 Description This section presents the criteria for design and implementation of roof downspout controls. Roof downspout controls are simple pre-engineered designs
Chapter 2 Roof Downspout Controls 2.1 Description This section presents the criteria for design and implementation of roof downspout controls. Roof downspout controls are simple pre-engineered designs
Permeable Interlocking Concrete Pavement A Low Impact Development Tool Training for Developers
 Permeable Interlocking Concrete Pavement A Low Impact Development Tool Training for Developers Presented by: Interlocking Concrete Pavement Institute The Low Impact Development Center, Inc. North Carolina
Permeable Interlocking Concrete Pavement A Low Impact Development Tool Training for Developers Presented by: Interlocking Concrete Pavement Institute The Low Impact Development Center, Inc. North Carolina
ACTION PLAN FOR RETROFITTING THE EXISTING MS4 WITH STRUCTURAL BMPS
 ACTION PLAN FOR RETROFITTING THE EXISTING MS4 WITH STRUCTURAL BMPS FEBRUARY 16, 2017 For the City and County of Honolulu MS4 NPDES Permit No. HI S000002 STORMWATER RETROFIT BMP OPPORTUNITIES Permit Requirements
ACTION PLAN FOR RETROFITTING THE EXISTING MS4 WITH STRUCTURAL BMPS FEBRUARY 16, 2017 For the City and County of Honolulu MS4 NPDES Permit No. HI S000002 STORMWATER RETROFIT BMP OPPORTUNITIES Permit Requirements
DRAINAGE CALCULATIONS
 DRAINAGE CALCULATIONS For the Carroll Single Family Residence At Santa Clara County Saratoga, California APN: 517-26-010 December 18, 2015 Prepared For: John and Peggy Carroll Prepared By: RI Engineering,
DRAINAGE CALCULATIONS For the Carroll Single Family Residence At Santa Clara County Saratoga, California APN: 517-26-010 December 18, 2015 Prepared For: John and Peggy Carroll Prepared By: RI Engineering,
What is YOUR biggest challenge in stormwater control measure accounting/planning?
 Introduction Name Affiliation What is YOUR biggest challenge in stormwater control measure accounting/planning? 1 Opti-Tool Outreach Workshop Part 1 Research Based Stormwater System Accounting November,
Introduction Name Affiliation What is YOUR biggest challenge in stormwater control measure accounting/planning? 1 Opti-Tool Outreach Workshop Part 1 Research Based Stormwater System Accounting November,
Map Reading 201: Where Does the Water Go?? Map Reading Map Reading 201. Interconnected Systems
 Map Reading 201: Where Does the Water Go?? Today s Presenters: John Rozum, NEMO Program Paula Stahl, Green Valley Institute A Key Skill for Land Use Commissioners As the map is rolled out at the P&Z meeting...
Map Reading 201: Where Does the Water Go?? Today s Presenters: John Rozum, NEMO Program Paula Stahl, Green Valley Institute A Key Skill for Land Use Commissioners As the map is rolled out at the P&Z meeting...
The following general requirements will be met for all planter box installations:
 Greenville County Technical Specification for: WQ-25 PLANTER BOX 1.0 Planter Box 1.1 Description Planter boxes are designed to capture and temporarily store stormwater runoff. Planter Boxes are intended
Greenville County Technical Specification for: WQ-25 PLANTER BOX 1.0 Planter Box 1.1 Description Planter boxes are designed to capture and temporarily store stormwater runoff. Planter Boxes are intended
Permeable Pavement [STRATEGY] Page 1
![Permeable Pavement [STRATEGY] Page 1 Permeable Pavement [STRATEGY] Page 1](/thumbs/77/75863870.jpg) [STRATEGY] Brief Description Permeable pavement systems, also referred to as pervious or porous paving, allow stormwater runoff to filter through the pavement section and infiltrate into the soil below.
[STRATEGY] Brief Description Permeable pavement systems, also referred to as pervious or porous paving, allow stormwater runoff to filter through the pavement section and infiltrate into the soil below.
Directors Rules for Seattle Municipal Code, Chapters Stormwater Code
 Directors Rules for Seattle Municipal Code, Chapters 22.800 22.808 Stormwater Code Requirements for Green Stormwater Infrastructure to the Maximum Extent Feasible for Single-Family Residential and Parcel-Based
Directors Rules for Seattle Municipal Code, Chapters 22.800 22.808 Stormwater Code Requirements for Green Stormwater Infrastructure to the Maximum Extent Feasible for Single-Family Residential and Parcel-Based
Placement of the soil should be in lifts of mm and loosely compacted (tamped lightly with a backhoe bucket).
 6 Rain Gardens Rain Gardens 6.1 Introduction A rain garden is used to attenuate peak flows and to provide stormwater treatment. Rain gardens use the concept of bioretention, a water quality practice in
6 Rain Gardens Rain Gardens 6.1 Introduction A rain garden is used to attenuate peak flows and to provide stormwater treatment. Rain gardens use the concept of bioretention, a water quality practice in
Post-Construction Stormwater Management Checklist* (5,000 SF or Greater)
 Applicability: Required for projects that create and/or replace 5,000 square feet or greater of impervious surface (i.e. asphalt roads, concrete structures, building area, sidewalks, etc.). Impervious
Applicability: Required for projects that create and/or replace 5,000 square feet or greater of impervious surface (i.e. asphalt roads, concrete structures, building area, sidewalks, etc.). Impervious
Small Town Sustainable Stormwater Solutions
 Small Town Sustainable Stormwater Solutions Kathryn Hamilton, RLA, ASLA Westmoreland Conservation District PA/DE ASLA Annual Meeting April 8-9, 8 2011 Urban, Industrial, Residential, Agricultural Flooding,
Small Town Sustainable Stormwater Solutions Kathryn Hamilton, RLA, ASLA Westmoreland Conservation District PA/DE ASLA Annual Meeting April 8-9, 8 2011 Urban, Industrial, Residential, Agricultural Flooding,
GSI Handbook Details Pervious Pavement
 GSI Handbook Details Workshop April 10, 2018 GSI Handbook Details Pervious Pavement Peter Schultze-Allen, EOA / SCVURPPP Outline of Presentation Pervious pavement basics Types of pervious pavement and
GSI Handbook Details Workshop April 10, 2018 GSI Handbook Details Pervious Pavement Peter Schultze-Allen, EOA / SCVURPPP Outline of Presentation Pervious pavement basics Types of pervious pavement and
Types and Basic Design of Post-Construction BMPs
 Types and Basic Design of Post-Construction BMPs F O R R E S I D E N T I A L L A N D S C A P E R S D A N B O G O E V S K I O H I O E P A N O R T H E A S T D I S T R I C T O F F I C E J U L Y 9, 2 0 1 3
Types and Basic Design of Post-Construction BMPs F O R R E S I D E N T I A L L A N D S C A P E R S D A N B O G O E V S K I O H I O E P A N O R T H E A S T D I S T R I C T O F F I C E J U L Y 9, 2 0 1 3
SITING CONSIDERATIONS
 Bioretention: Siting and Applications Presentation Overview Siting Considerations Native Soil Characterization Lessons Leaned Feasibility & Performance Applications ALICE LANCASTER, PE alancaster@herrerainc.com
Bioretention: Siting and Applications Presentation Overview Siting Considerations Native Soil Characterization Lessons Leaned Feasibility & Performance Applications ALICE LANCASTER, PE alancaster@herrerainc.com
Example Stormwater Control Plan For a Residential Subdivision Project. Whispering Pines Lane Anytown, USA
 Example Stormwater Control Plan For a Residential Subdivision Project Whispering Pines Lane Anytown, USA December 2, 2015 XYZ Corporation Jane Jones, 707-555-1212 This example prepared by Dan Cloak Environmental
Example Stormwater Control Plan For a Residential Subdivision Project Whispering Pines Lane Anytown, USA December 2, 2015 XYZ Corporation Jane Jones, 707-555-1212 This example prepared by Dan Cloak Environmental
Retrofitting Commercial Shopping Centers
 Retrofitting Commercial Shopping Centers Making an impact with LID Overview Commercial Development LID Retrofit Issues Tips and techniques Costs and O&M issues Commercial Development LID Retrofit Issues
Retrofitting Commercial Shopping Centers Making an impact with LID Overview Commercial Development LID Retrofit Issues Tips and techniques Costs and O&M issues Commercial Development LID Retrofit Issues
5/15/2013. Basin Area. Vegetation. Rainfall & Runoff. Soil Type. Topics. Factors Influencing Erosion. Factors Influencing Erosion
 Topics Erosion, TESC and Construction sequencing Procedures and timing Remedies for failing sites Curtis Hinman WSU Extension and Bio Systems Eng. Faculty Low Impact Development Specialist chinman@wsu.edu
Topics Erosion, TESC and Construction sequencing Procedures and timing Remedies for failing sites Curtis Hinman WSU Extension and Bio Systems Eng. Faculty Low Impact Development Specialist chinman@wsu.edu
Example Stormwater Control Plan For a Residential Subdivision Project. Whispering Pines Lane Anytown, USA. February 21, 2018
 Example Stormwater Control Plan For a Residential Subdivision Project Whispering Pines Lane Anytown, USA February 21, 2018 XYZ Corporation Jane Jones, 925-555-1212 This example prepared by Dan Cloak Environmental
Example Stormwater Control Plan For a Residential Subdivision Project Whispering Pines Lane Anytown, USA February 21, 2018 XYZ Corporation Jane Jones, 925-555-1212 This example prepared by Dan Cloak Environmental
ABBREVIATIONS. Dwg LID of 1. Abbreviations
 ABBREVIATIONS DIA DIAMETER EL ELEVATION FT2 SQUARE FOOT GAL/MIN GALLONS PER MINUTE H HORIZONTAL HDPE HIGH DENSITY POLYETHYLENE HMAC HOT MIX ASPHALT CONCRETE IE INVERT ELEVATION MAX MAXIMUM NO. NUMBER ODEQ
ABBREVIATIONS DIA DIAMETER EL ELEVATION FT2 SQUARE FOOT GAL/MIN GALLONS PER MINUTE H HORIZONTAL HDPE HIGH DENSITY POLYETHYLENE HMAC HOT MIX ASPHALT CONCRETE IE INVERT ELEVATION MAX MAXIMUM NO. NUMBER ODEQ
4.6. Low Impact and Retentive Grading
 4.6. Low Impact and Retentive Grading Low Impact Grading techniques focus on utilizing existing topography during Site layout to minimize cost. Proposing structures, roads, and other impervious surfaces
4.6. Low Impact and Retentive Grading Low Impact Grading techniques focus on utilizing existing topography during Site layout to minimize cost. Proposing structures, roads, and other impervious surfaces
WATER QUALITY GUIDANCE MANUAL. Planning and Implementing Stormwater Quality Practices June 2018
 WATER QUALITY GUIDANCE MANUAL Planning and Implementing Stormwater Quality Practices June 2018 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.1 Purpose and Introduction... 1-1 1.2 How to Use This Manual... 1-4 1.3 Water Quality
WATER QUALITY GUIDANCE MANUAL Planning and Implementing Stormwater Quality Practices June 2018 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.1 Purpose and Introduction... 1-1 1.2 How to Use This Manual... 1-4 1.3 Water Quality
Insert Community Name. Homeowner Guide for On-Site Stormwater BMP Maintenance and Care
 Insert Community Name Homeowner Guide for On-Site Stormwater BMP Maintenance and Care Insert Community Name Homeowner Guide for On-Site Stormwater BMP Maintenance and Care Hello! Welcome to the neighborhood.
Insert Community Name Homeowner Guide for On-Site Stormwater BMP Maintenance and Care Insert Community Name Homeowner Guide for On-Site Stormwater BMP Maintenance and Care Hello! Welcome to the neighborhood.
SECTION A-1: DESCRIPTION
 URBAN BIORETENTION Stormwater Planters Expanded Tree Pits Stormwater Curb Extensions VERSION 1.0 SECTION A-1: DESCRIPTION Urban bioretention practices are similar in function to regular bioretention practices
URBAN BIORETENTION Stormwater Planters Expanded Tree Pits Stormwater Curb Extensions VERSION 1.0 SECTION A-1: DESCRIPTION Urban bioretention practices are similar in function to regular bioretention practices
Spokane River Forum: City of Spokane Permeable Pavements
 Spokane River Forum: City of Spokane Permeable Pavements Spokane River Forum March 23, 2016 Mark Papich, PE Senior Engineer City of Spokane Integrated Capital Management It s all about the Spokane River
Spokane River Forum: City of Spokane Permeable Pavements Spokane River Forum March 23, 2016 Mark Papich, PE Senior Engineer City of Spokane Integrated Capital Management It s all about the Spokane River
Retrofitting Low Impact Development (LID) for Stormwater at Sacramento State. City of Sacramento Sacramento State Facilities Management
 Retrofitting Low Impact Development (LID) for Stormwater at Sacramento State City of Sacramento Sacramento State Facilities Management Project Background Campus Storm Drain System Drain Inlet - Campus
Retrofitting Low Impact Development (LID) for Stormwater at Sacramento State City of Sacramento Sacramento State Facilities Management Project Background Campus Storm Drain System Drain Inlet - Campus
HOW TO MODEL IMP FACILITIES USING BAHM. By Douglas Beyerlein, P.E., Clear Creek Solutions, Inc. Introduction
 HOW TO MODEL IMP FACILITIES USING BAHM By Douglas Beyerlein, P.E., Clear Creek Solutions, Inc. Introduction IMP (Integrated Management Practice) facilities are small-scale stormwater control facilities
HOW TO MODEL IMP FACILITIES USING BAHM By Douglas Beyerlein, P.E., Clear Creek Solutions, Inc. Introduction IMP (Integrated Management Practice) facilities are small-scale stormwater control facilities
SITING CONSIDERATIONS
 Bioretention: Siting and Applications Presentation Overview Siting Considerations Native Soil Characterization Lessons Leaned Feasibility & Performance Applications ALICE LANCASTER, PE alancaster@herrerainc.com
Bioretention: Siting and Applications Presentation Overview Siting Considerations Native Soil Characterization Lessons Leaned Feasibility & Performance Applications ALICE LANCASTER, PE alancaster@herrerainc.com
What Are We Inspecting? Stormwater Treatment Measure Type and Design
 What Are We Inspecting? Stormwater Treatment Measure Type and Design Jill Bicknell, P.E., EOA, Inc. Santa Clara Valley Urban Runoff Pollution Prevention Program December 16, 2013 Outline of Presentation
What Are We Inspecting? Stormwater Treatment Measure Type and Design Jill Bicknell, P.E., EOA, Inc. Santa Clara Valley Urban Runoff Pollution Prevention Program December 16, 2013 Outline of Presentation
Technical Guidance for Stormwater Treatment and Site Design Measures
 Chapter 6 Technical Guidance for Stormwater Treatment and Site Design Measures In this Chapter, technical guidance is provided for the stormwater treatment measures allowed by permit requirements as well
Chapter 6 Technical Guidance for Stormwater Treatment and Site Design Measures In this Chapter, technical guidance is provided for the stormwater treatment measures allowed by permit requirements as well
Brian Friedlich, PE. Jeremiah Bergstrom, LLA
 Engineering Concepts for Bioretention Facilities: From Rain Gardens to Basins NJASLA 2011 Annual Meeting & Expo February 1, 2011 Brian Friedlich, PE Senior Engineer Jeremiah Bergstrom, LLA Senior Project
Engineering Concepts for Bioretention Facilities: From Rain Gardens to Basins NJASLA 2011 Annual Meeting & Expo February 1, 2011 Brian Friedlich, PE Senior Engineer Jeremiah Bergstrom, LLA Senior Project
West Virginia Stormwater Management Manual: Methods.
 West Virginia Stormwater Management Manual: Methods Created to deliver targeted training on new tools and practices to improve the quality of stormwater runoff. www.cbstp.org www.chesapeakestormwater.net
West Virginia Stormwater Management Manual: Methods Created to deliver targeted training on new tools and practices to improve the quality of stormwater runoff. www.cbstp.org www.chesapeakestormwater.net
County of Prince Edward. Stormwater Management Plan. Agreement in lieu of a Stormwater Management Plan
 County of Prince Edward Stormwater Management Program Date: E-Permitting Number: This stormwater management plan (Agreement) is hereby submitted by the Owner to specify the methods that will be implemented
County of Prince Edward Stormwater Management Program Date: E-Permitting Number: This stormwater management plan (Agreement) is hereby submitted by the Owner to specify the methods that will be implemented
FACT SHEET: Pervious Pavement with Infiltration
 FACT SHEET: Pervious Pavement with Infiltration DESCRIPTION Pervious pavement is a Green Infrastructure (GI) technique that combines stormwater infiltration, storage, and structural pavement consisting
FACT SHEET: Pervious Pavement with Infiltration DESCRIPTION Pervious pavement is a Green Infrastructure (GI) technique that combines stormwater infiltration, storage, and structural pavement consisting
Incorporating Sustainable Practices and Water Quality into Roadway Design. May 24, 2017
 Incorporating Sustainable Practices and Water Quality into Roadway Design May 24, 2017 Justin Oswald, P.E., CFM Freese and Nichols, Inc. Presenters Todd Buckingham, P.E., ENV SP Freese and Nichols, Inc.
Incorporating Sustainable Practices and Water Quality into Roadway Design May 24, 2017 Justin Oswald, P.E., CFM Freese and Nichols, Inc. Presenters Todd Buckingham, P.E., ENV SP Freese and Nichols, Inc.
Urban Water Management and Soils (ESRM 311 & SEFS 507)
 Urban Water Management and Soils (ESRM 311 & SEFS 507) Cougar Mtn Regional Wildland Park & Lakemont Blvd, Bellevue WA Lecture Today Some Urban Water management terms Examples of water management in urban
Urban Water Management and Soils (ESRM 311 & SEFS 507) Cougar Mtn Regional Wildland Park & Lakemont Blvd, Bellevue WA Lecture Today Some Urban Water management terms Examples of water management in urban
2008 SWMM, 2010 Revision City of Tacoma
 2008 SWMM, 2010 Revision City of Tacoma 2.2.3.1 BMP L630 Rain Gardens Purpose and Definition Bioretention areas are shallow stormwater retention facilities designed to mimic forested systems by controlling
2008 SWMM, 2010 Revision City of Tacoma 2.2.3.1 BMP L630 Rain Gardens Purpose and Definition Bioretention areas are shallow stormwater retention facilities designed to mimic forested systems by controlling
Glencoe Elementary School Parking Lot Retrofit 825 SE 51 st Street
 Glencoe Elementary School Parking Lot Retrofit 825 SE 51 st Street Project Summary Project Type: Technologies: Institutional parking lot retrofit demonstration project Vegetated infiltration swale with
Glencoe Elementary School Parking Lot Retrofit 825 SE 51 st Street Project Summary Project Type: Technologies: Institutional parking lot retrofit demonstration project Vegetated infiltration swale with
Slow it, Spread it, Sink it using Green Stormwater Infrastructure
 Milly Archer Water Resources Coordinator Becky Tharp Green Infrastructure Collaborative Slow it, Spread it, Sink it using Green Stormwater Infrastructure Overview Defining LID and GSI Hydrology and impacts
Milly Archer Water Resources Coordinator Becky Tharp Green Infrastructure Collaborative Slow it, Spread it, Sink it using Green Stormwater Infrastructure Overview Defining LID and GSI Hydrology and impacts
Pollutant Removal Benefits
 Bioswales Bioswales Similar to biocells, but have a slight, but positive grade toward an outlet Designed to convey the WQv event at very low velocities Promote filtration through native vegetation, infiltration
Bioswales Bioswales Similar to biocells, but have a slight, but positive grade toward an outlet Designed to convey the WQv event at very low velocities Promote filtration through native vegetation, infiltration
4.5 City of Indianapolis Stormwater Green Infrastructure Guidance: Bioretention (rain gardens) Bioretention Fact Sheet Bioretention Technical Design
 4.5 City of Indianapolis Stormwater Green Infrastructure Guidance: Bioretention (rain gardens) Bioretention Fact Sheet Bioretention Technical Design Specification Bioretention O & M Manual Draft Green
4.5 City of Indianapolis Stormwater Green Infrastructure Guidance: Bioretention (rain gardens) Bioretention Fact Sheet Bioretention Technical Design Specification Bioretention O & M Manual Draft Green
ROADWAY SECTION PRINCIPAL ARTERIAL 2-01
 ROADWAY SECTION PRINCIPAL ARTERIAL 2-01 ROADWAY SECTION MINOR ARTERIAL COMMERCIAL/MIXED USE 2-02 ROADWAY SECTION MINOR ARTERIAL REDISENTIAL 2-03 ROADWAY SECTION COLLECTOR COMMERCIAL MIXED USE 2-04 ROADWAY
ROADWAY SECTION PRINCIPAL ARTERIAL 2-01 ROADWAY SECTION MINOR ARTERIAL COMMERCIAL/MIXED USE 2-02 ROADWAY SECTION MINOR ARTERIAL REDISENTIAL 2-03 ROADWAY SECTION COLLECTOR COMMERCIAL MIXED USE 2-04 ROADWAY
SUPPORTING DOCUMENT STORMWATER POLLUTION PREVENTION PLAN (SWPPP) NARRATIVE
 SUPPORTING DOCUMENT STORMWATER POLLUTION PREVENTION PLAN (SWPPP) NARRATIVE Please complete this narrative form and submit with your SWPPP drawings. Refer to Kitsap County Stormwater Design Manual Vol.
SUPPORTING DOCUMENT STORMWATER POLLUTION PREVENTION PLAN (SWPPP) NARRATIVE Please complete this narrative form and submit with your SWPPP drawings. Refer to Kitsap County Stormwater Design Manual Vol.
n1. Design 5.4.6a Urban Bioretention 5.4.6a Urban Bioretention Variations: Planter box, Extended tree pits, Stormwater curb extensions.
 5.4.6a Urban Bioretention Variations: Planter box, Extended tree pits, Stormwater curb extensions. Description: Urban bioretention SCM are similar in function to regular bioretention practices except they
5.4.6a Urban Bioretention Variations: Planter box, Extended tree pits, Stormwater curb extensions. Description: Urban bioretention SCM are similar in function to regular bioretention practices except they
SIMPLIFIED APPROACH TO STORMWATER MANAGEMENT FOR SMALL PROJECTS
 SIMPLIFIED APPROACH TO STORMWATER MANAGEMENT FOR SMALL PROJECTS Introduction As required by federal and state law, the Borough of Swarthmore has adopted regulations that affect stormwater runoff and surface
SIMPLIFIED APPROACH TO STORMWATER MANAGEMENT FOR SMALL PROJECTS Introduction As required by federal and state law, the Borough of Swarthmore has adopted regulations that affect stormwater runoff and surface
Local Stormwater Retrofit Case Studies. Westmoreland County Conservation District Updated 11/2011
 Local Stormwater Retrofit Case Studies Westmoreland County Conservation District Updated 11/2011 WCD 2010 Why we do Sustainable Stormwater Management Retrofits To reduce flooding events and combined sewer
Local Stormwater Retrofit Case Studies Westmoreland County Conservation District Updated 11/2011 WCD 2010 Why we do Sustainable Stormwater Management Retrofits To reduce flooding events and combined sewer
Managing Stormwater within the Road Right-of-Way: An Urban NAI Approach
 Turgay Dabak, Joni Calmbacher, Sara DeGroot, Andrea Ryon Managing Stormwater within the Road Right-of-Way: An Urban NAI Approach Presentation Outline Project Background Project Overview BMPs Evaluated
Turgay Dabak, Joni Calmbacher, Sara DeGroot, Andrea Ryon Managing Stormwater within the Road Right-of-Way: An Urban NAI Approach Presentation Outline Project Background Project Overview BMPs Evaluated
Background on LID in Western WA
 Low Impact Development Process (MR #5) Douglas C. Howie, P.E. Department of Ecology Background on LID in Western WA PCHB Requirements from 2007 Permits Two LID Advisory Committees Expanded MR #5 LID Performance
Low Impact Development Process (MR #5) Douglas C. Howie, P.E. Department of Ecology Background on LID in Western WA PCHB Requirements from 2007 Permits Two LID Advisory Committees Expanded MR #5 LID Performance
PERMEABLE PAVEMENTS. Have been around for a long time, but are poised for a resurgence
 PERMEABLE PAVEMENTS Have been around for a long time, but are poised for a resurgence Three Broad Types of Pavers PC: Porous Concrete PA: Porous Asphalt IP: Interlocking Concrete Pavers The depth of the
PERMEABLE PAVEMENTS Have been around for a long time, but are poised for a resurgence Three Broad Types of Pavers PC: Porous Concrete PA: Porous Asphalt IP: Interlocking Concrete Pavers The depth of the
Appendix B DETAILED DESIGN
 Appendix B DETAILED DESIGN Design details for bioretention/bioswale Figures 1 and 2 provide cross-sectional details of standard bioswales and bioretention installations used in design drawings. Table 1
Appendix B DETAILED DESIGN Design details for bioretention/bioswale Figures 1 and 2 provide cross-sectional details of standard bioswales and bioretention installations used in design drawings. Table 1
6.2 Flow-Through Planter
 SAN MATEO COUNTYWIDE WATER POLLUTION PREVENTION PROGRAM 6.2 Flow-Through Planter Figure 6-8: At-grade flow-through planter. Source: City of Emeryville Best uses Treating roof runoff Next to buildings Dense
SAN MATEO COUNTYWIDE WATER POLLUTION PREVENTION PROGRAM 6.2 Flow-Through Planter Figure 6-8: At-grade flow-through planter. Source: City of Emeryville Best uses Treating roof runoff Next to buildings Dense
Low Impact Development for your homes, businesses & streets
 Low Impact Development for your homes, businesses & streets What s the problem anyways? - Development Impacts the Water Cycle In the past, our main pollution concern was Point Source Pollution Our current
Low Impact Development for your homes, businesses & streets What s the problem anyways? - Development Impacts the Water Cycle In the past, our main pollution concern was Point Source Pollution Our current
Key elements : Filter Strips must be designed within parameters required by the Fort Wayne s Development Standards/Criteria Manual.
 4.4. Filter Strips Filter Strips are densely vegetated lands that treat sheet flow storm water from adjacent pervious and impervious areas. They function by slowing runoff, trapping sediment and pollutants,
4.4. Filter Strips Filter Strips are densely vegetated lands that treat sheet flow storm water from adjacent pervious and impervious areas. They function by slowing runoff, trapping sediment and pollutants,
From and
 GREEN INFRASTRUCTURE IN PROVIDENCE, RI The Box Office From http://web.uri.edu/riss/the-box-office/ and http://www.morrisbeacon.com/media/portfolioprojects/implementation/box-office/box%20office.pdf: At
GREEN INFRASTRUCTURE IN PROVIDENCE, RI The Box Office From http://web.uri.edu/riss/the-box-office/ and http://www.morrisbeacon.com/media/portfolioprojects/implementation/box-office/box%20office.pdf: At
