Weather Science To Parents: Read all instruction before provide guidance to your children.
|
|
|
- Veronica Kennedy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Weather Science To Parents: Read all instruction before provide guidance to your children. A. SAFETY MESSAGES 1. Read carefully through all these instructions before you start. Adult supervision is always required. 2. Children can choke on flat or broken balloons. Adult supervision is necessary when using balloons. Flat and broken balloons must be discarded immediately. 3. This kit and its finished product contain small parts which may cause choking if misused. Keep away from children under 3 years old. 4. This kit is intended for children aged over Adult assistance and supervision are recommended when using scissors. 6. Adult supervision is required throughout, and especially where alcohol and desk lamps are used. 7. Always wash your hands after handling soil or compost. B. CONTENTS Also required, but not included in this kit, a glass, some potting soil, some beans, a pencil, 1 plastic bottle, a desk lamp (in case there is no sun shine) and alcoholic drink. Adult supervision is required when getting all there materials from home. 1 x balloon, 1 x cloud-shape cover, 1 x mountain shape, 1 x pimpled stopper, 1 x mountain base, 1 x cloud-making pump, 1 x thermometer arm, 2 x thermometer holders, 1 x pencil stand, 1 x spiral template, 2 x thermometers, 1 x seed tray, ph test paper and detailed instruction.
2 C. LIGHTNING BALLOON A flash of lightning is a giant spark of electricity. Lightning happens when electric charge builds up inside a storm cloud. When the charge becomes large enough, it jumps from the cloud to another cloud, from one part of the cloud to another,or from the cloud to the ground. The electric charge in a cloud is made when ice particles and water drops in the cloud bump into each other. The charge sits on the particles and drops. There are two types of charge: positive and negative. In a thunder cloud, positive charge builds up in the top of the cloud, and negative charge builds up in the bottom. This activity will show you how electric charge is made when you rub a balloon on your hair. This is similar to how a charge is made when particles collide in a stormcloud. Materials required from kit: balloon. STAND UP HAIR 1. Inflate the balloon and tie a knot in its neck (ask anadult to help you with this). Rub your hair lots of timeswith the balloon. 2. Hold the balloon over your head. Your hair will stand on end! Try it on members of your family or friends. They will be amazed. STICKY BALLOON 3. Rub your hair lots of times with the balloon. Carefullyput the balloon on a wall. It will stick to the wall! BENDY WATER 4. Turn on a tap and adjust it so that you have very thin stream of water. Rub your hair lots of times with the balloon. Slowly move the balloon towards the stream of water. The stream of water will bend around the balloon. The sort of electricity you made in the activities is called static electricity because it stays on objects instead of flowing through them. You can make static electricity by rubbing certain combinations of materials together, such as the balloon and your hair. When you rub them together, tiny particles called electrons jump from one material to the other. Electrons carry a negative electric charge. The material that gains the electrons gains a negative charge, and the material that lost them is left with a positive charge. In this case, electrons jump from your hair to the balloon, so the balloon gets a negative charge. Two like charges (two positive or two negative) repel each other, and two opposite charges attract each other. When you put the balloon near an object, its negative charge pushes electrons in the object away, leaving a positive charge on the surface of the object. Then the charge in the balloon and in the surface of the object attract, so the balloon attracts the object. This makes the balloon stick to the wall, or pull up your hair, or attract paper. The particles in water have a positive end and a negative end. When the balloon is close to the stream of water, the balloon attracts the positive ends of the particles, which makes the stream bend. A bolt of lightning contains about 5 billion joules of energy enough to poweran energy-saving light bulb for 20,000 years! Mountaineers caught in thunderstorms sometimes feel the hairs on their heads standing on end because of the electric charge in the thunderclouds. Lightning conductors on buildings are designed to carry the electricity in a lightning bolt safely to the ground. The tiny electric shocks you sometimes get when you touch metal objects indoors are made by static electricity jumping off your body. The electricity is made whenyour shoes rub on nylon carpets.
3 D. CLOUD MAKER Clouds are made up of millions upon millions of tiny water droplets or ice crystals. Water droplets are made when water vapour (the gas form of water) in the air turns to liquid water. This happens when air pressure and temperature fall. Materials required from kit: cloud-making pump. Materials required from home: a drink containingalcohol (such as cooking wine or brandy). Important: you must ask an adult before using alcohol in this activity, and an adult must supervise you when you carry out the experiment. 1. Very carefully pour a little of the alcoholic drink intothe cloud-making pump. You only need enough to coverthe bottom of the pump. Swirl the liquid around insidethe pump. 2. Stand the pump on a table. Put the first two fingers of one hand either side of the pump, halfway down. 3. Press the palm of other other hand firmly onto theneck of the pump. Squash down the bottom section ofthe pump, while keeping your palm firmly on top of theneck. 4. Wait a few seconds. Now very quickly take your palm off the neck of pump. You should see mist suddenly appear in the top of the pump. Cover the opening before the mist disappears. Squash down the bottom section of the pump again, and you will see the mist clear up like magic Some of the alcohol in the drink evaporates into the air in the pump. That means it turns into alcohol vapour. When you squash the pump, the pressure inside the bottle rises, and so does the temperature. When you take your finger off the neck,the pressure drops, and this makes the temperature drop too. The sudden drop in pressure and temperature makes some of the alcohol vapour condense to form tiny droplets that you see as mist. When you press down the pump again, you increasethe pressure and temperature. This makes the alcohol in the tiny droplets evaporate again, so the droplets disappear. This is exactly what happens in the Earth s atmosphere. When air that contains water vapour rises into the atmosphere, its pressure falls and its temperature falls.this makes the water vapour condense into the tiny water droplets that make clouds. You can see the cloud-making effect in a bathroom. Warm air over a bath or from inside a shower contains lots of water vapour. When this air hits a cold mirror, the water vapour condenses, making the mirror misty. The biggest clouds are giant cumulonimbus clouds, which can be more than 10 kilometres tall. Lenticular clouds are flying-saucer-shaped clouds that form when damp air rises over mountains and cools. E. THE GREEN HOUSE EFFECT & GLOBAL WARMING The greenhouse effect is way in which the Earth s atmosphere traps heat from the Sun. This makes the atmosphere warm. Without the greenhouse effect, the Earth would be a much colder place. Certain gases in the atmosphere are better at trapping heat than others. A gas called carbon dioxide is one of the best. Materials required from kit: thermometers, thermometer arm, thermometer holder. Materials required from home: a small, clear plastic drinks bottle, a desk lamp, baking soda, vinegar Important: ask an adult before using a desk lamp, as the lamp could get very hot. 1. Slot a thermometer into each thermometer holder. Push a thermometer holder into each hole at the end of the thermometer arm. Remove the top from a small, clear plastic drinks bottle. Wash out the bottle with water. Write down the temperatureon both thermometers. Carefully put the bottle over the thermometer attached to the screw cap, and screw it into place in the cap. 2. Place the set up outdoors under sunshine or alternatively stand the bottle on a desk. Put a desk lamp (a 60-watt incandescent light bulb) next to the bottle and switch it on. The thermometers should face away from the lamp so that the lamp does not heatthe thermometer bulb, and both should be the same distance about 15 cm (6 inches) from the lamp. 3. Wait for about 20 minutes. Then look at the thermometers again and write down the readings. How much has the temperature risen inside and outside the bottle? The lamp warms the bottle itself, and this warms the air inside the bottle, which makes the temperature of the air trapped inside the bottle rise. The lamp also heats the air around the thermometer outside the bottle, but this time, the warm air can escape and be replaced by cooler air, so the temperature does not rise as high as the temperature inside the bottle. The bottle acts like the Earth atmosphere. It demonstrates how the Earth s atmosphere traps heat.
4 NOW DO THE SECOND PART OF THE EXPERIMENT: 4. Take the thermometer arm off the bottle, with its thermometers, and put it to one side to allows the thermometers to return to room temperature. 5. Put a teaspoon of baking soda and two teaspoons of vinegar into the bottle,and shake the bottle gently. Wait ten seconds and then put the bottle back onto the thermometer arm. 6. Now repeat steps 1 and 2 above. This time, has the temperature in the bottle risen more than it did the first time? The baking soda and the vinegar react together to make a gas called carbon dioxide, and this mixes with the air in the bottle. Carbon dioxide is good at trapping heat. It traps some of the heat that passes through the bottle. So this time the temperature in the bottle rises higher. This shows that adding carbon dioxide to the air in the bottle makes the air trap more heat. This is what is happening in the Earth s atmosphere. We are adding carbon dioxide to the atmosphere, which is causing the phenomenon of global warming. Carbon dioxide is known as a greenhouse gas. Other greenhouse gases include water vapour and methane. Global warming is the slow warming of the atmosphere. It is happening because we are adding carbon dioxide to the atmosphere. The carbon dioxide comes from burning fossil fuels (oil, gas and coal), and from cutting down forests. The average temperature of the atmosphere has risen by about half a degree Celsius since the year Melting glaciers and retreating ice around the North Pole are visible signs of global warming. F. MINI WATER-CYCLE MODEL All the time, water is moving between the oceans, the atmosphere, the land, lakes and rivers and vegetation. Water evaporates from the oceans, condenses in the air to make clouds, water from clouds falls as rain, and runs down rivers into the ocean. This movement of water is called the water cycle. In this activity, you can make a mini model of the water cycle. Materials required from kit: cloud-shaped cover, mountain shape, pimpled stopper, mountain base. Materials required from home: drinking glass, ice, some potting soil, desk lamp. 1. Find the mountain shape, then find the hole in the mountain side. Hold the shape upside down in one hand, keeping a finger over the hole. 2. Pour the soil into the mountain shape. Add a few drops of water to dampen the soil. 3. Put the pimpled stopper on top of the soil, then clip the mountain base intoplace. 4. Put the mountain shape into a glass. Pour water into the base of the glass until the water is about 1 cm (0.5 inches) deep so that it covers the base. Now put the cloud shaped cover on top of the glass. 5. Put a few ice cubes in the top of the cloud cover. 6. Place the model outdoors under sunshine or alternatively put a desk lamp (a 60-watt incandescent light bulb) about 15 cm (6 inches) away from the glass and switch it on. Ask and adult to help you with the desk lamp, as it could get hot. 7. Watch the cloud blister for a couple of 10 minutes. What happens? You will see drops of water condensed underneath of the cover. These are rain The heat from the desk lamp makes the water in the glass warm. This makes some water evaporate into the air in the glass. The warm air rises to the top of the glass, where the ice in the cloud blister cools it down. The water vapour in the air condenses, forming water droplets on the bottom of the cloud. When there s enough water, it drips down onto the mountain, then runs back into the water at the bottom of the glass. This is a mini model of the water cycle. The water in the glass represents the ocean, the cloud blister represents a cloud, and the dripping water represents rain. You will also notice some rain water collects in the small dip in the mountain, which represents a lake. In real life, this would be fresh water because the minerals that make sea water salty are left behind in the sea when the water evaporates. Some water will seep through the soil, and collect in the base of the mountain. This represent underground water. If you want, you can grow a bean on the mountain. Cut open the mountain top with a scissors. Germinate a broad bean. Put the germinating bean into the hole in mountain so it can continue growing. The plant will use water from the water cycle to stay alive. It will also release some water vapour into the atmosphere from its leaves (this is called transpiration).
5 The water in the oceans is salty, but rain is made of fresh water. That s because the minerals in the sea are left behind when the water evaporates. In a hundred years, an average particle of water spends 98 years in the ocean on its way round the water cycle. Only about one hundredth of a thousandth of all the water on Earth is in the atmosphere at one time. The water going round the water cycle today is the same water that was going round the water cycle when the dinosaurs were alive. G. ACID RAIN When we burn some sorts of fossil fuels, such as coal, gases are released into the air. These gases include sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides. When these gases mix with water droplets in clouds, they make materials called acids. When the water falls from the clouds, it is known as acid rain. Acid rain harms plants that it falls on, even large trees. It also harms animals in rivers and lakes. In this activity you can see how acid affects the growth of plants. Materials required from kit: seed tray, ph paper. Materials required from home: vinegar, cotton pads or compost, some beans (such as runner beans or mung beans) 1. Fill each compartment of the seed tray with a cotton pad, or with some compost. Wash your hands after handling compost. Put a bean into each compartment, and water the cotton pad or compost to make it damp. Note the numbers marked on the tray. 2. Put the seed tray somewhere warm. Now you need to wait until the beans germinate (that means a shoot grows upwards and a root grows downwards from the bean). This could take a few days. Keep adding a little water to keep the cotton or compost damp. When thebeans have germinated, put the beans by a window, where they will get some light. 3. Put 250 ml of water into a clean jar. Add two teaspoons (10 ml) of vinegar to the water to make diluted vinegar. Now water plants as follows each day, for five days: Plant 1: 2 teaspoons (10 ml) of plain water only Plant 2: 0.5 teaspoon (2.5 ml) of diluted vinegar from your jar, and 1.5 teaspoons of plain water Plant 3: 1 teaspoon (5 ml) of diluted vinegar, and 1 teaspoon of plain water Plant 4: 1.5 teaspoon (7.5 ml) of diluted vinegar from your jar, and 0.5 teaspoon (2.5 ml) of plain water Please writer down the testing result on the following table. Plant 1 to 4 Water (teaspoon) Diluted Vinegar (teaspoon) ph indicator colour ph value Observation 4. After the five days, test the ph of each pot. To test a pot, press a small piece of ph test paper into the soil. Match the colour of the paper against the ph colour scale (punch out from the box flip) and write down the ph values. Different colours indicate the degree of acidity and alkalinity. For example, red is very acidic, purple is very alkaline, and yellow is neutral. The level of acidity or alkalinity can also be represented with numbers, with 1 = very acidic, 7 = neutral and 14 = very alkaline. Here are the ph values of some household materials e.g. tap water = ph7, tea = ph6, coffee = ph4, vinegar= ph3 tomato= ph8, Olive oil = ph9. 5. After five days, look at your plants. Which plants have grown best? WHAT HAPPENED? You should find that the plant grown in plain water grows best, and the plant grown with most vinegar grows least well. Vinegar contains acid that damages the plants so they can t grow properly. The acid in acid rain is a different sort of acid, but it affects plants in the same way. The ph paper shows the acidity of the soil in each pot. The lower the ph number is, the more acidic the soil is. The pot with the most vinegar added to it will be the most acidic. ph paper contains special chemicals called indicators that change colour when they touch acids (or chemicals called alkalis, which are the opposite of acids). Some acid rain is as strong as the acid in lemon juice. Natural rain is a little bit acidic. That s because it contains carbon dioxide, which turns it into carbonic acid. There is acid snow and acid fog as well as acid rain. Acid rain also damages stone buildings because it slowly eats away some sorts of rock (especially limestone).
6 H. WIND Winds are simply made by air moving from place to place. Air starts moving because it gets warmed by the ground and then rises upwards. This activity shows you how warm air rises. Materials required from kit: pencil stand, spiral template. Materials required from home: a sharpened pencil and a ball-point pen. Carefully punch out the spiral template. Gently push the nib of a ball-point pen into the very centre of the spiral to make a small dent in the paper. Be careful not to make a hole in the paper. Put a sharpened pencil, with its sharp end pointing up, into the pencil holder. Carefully balance the spiral on the pencil, with the central dent of the spiral on the pencil s tip. You need to stand the pencil and spiral on top of a television or computer monitor which emits warmth. Watch what happens to the spiral (you might have to give it a nudge to get it moving). The television or computer heats the air around it, making the air warm. Warm air is lighter than cool air, and it floats up through the cool air around it. So warm air rises from the heater. It pushes against the paper of the spiral, and this makes the spiral spin slowly. The moving air is called a convection current. When the Sun heats the ground, the ground gets warm. The ground heats up the air above it, making the air warm. The air floats upwards. Cool air flows in from side to replace the rising air, making winds. You can see how rising air causes winds when you visit the seaside on a hot day. The Sun heats the land, making it warm. The land heats the air above, making the air warm. The air rises, and is replaced by cool air flowing in from over the sea. This flowing air is called a sea breeze. Glider pilots and birds of prey (such as vultures) use rising air currents to carry them up into the air. The rising currents they use are called thermals. Hot-air balloons use the fact that hot air floats upwards. The hot air makes the balloon lighter than the air around it. I. QUESTION AND COMMENTS We treasure you as a customer and your satisfaction with this product is important to us. In case you have any comments or questions, or you find any parts of this kit missing or defective, please do not hesitate to contact our distributor in your country, whose address is printed on the package. You are also welcome to contact our marketing support team at infodesk@4m-ind.com, Fax (852) , Tel (852) , Web site:
A. SAFETY MESSAGES B. CONTENTS
 Grow-A-Maze A. SAFETY MESSAGES 1. Read these instructions thoroughly before starting the experiments. 2. This kit and its finished product contain small parts which may cause choking if misused. Keep away
Grow-A-Maze A. SAFETY MESSAGES 1. Read these instructions thoroughly before starting the experiments. 2. This kit and its finished product contain small parts which may cause choking if misused. Keep away
In this activity, students will write secret messages that can only be revealed if you know how to read invisible ink!
 Invisible Ink Magic Science 15 20 minutes In this activity, students will write secret messages that can only be revealed if you know how to read invisible ink! Materials Needed Per Student: Half a lemon
Invisible Ink Magic Science 15 20 minutes In this activity, students will write secret messages that can only be revealed if you know how to read invisible ink! Materials Needed Per Student: Half a lemon
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION Water Cycle
 TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION Water Cycle INTRODUCTION: The water cycle transports water from oceans to the atmosphere, the land, and back to the ocean through the physical processes of evaporation, condensation,
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION Water Cycle INTRODUCTION: The water cycle transports water from oceans to the atmosphere, the land, and back to the ocean through the physical processes of evaporation, condensation,
Science Class 6 Chapters 13, 14 and
 Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets Magnetic field of the Earth: Geographical North is Magnetic South and vice versa Two places where the magnetic needle becomes vertical are called the magnetic poles. The magnetic
Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets Magnetic field of the Earth: Geographical North is Magnetic South and vice versa Two places where the magnetic needle becomes vertical are called the magnetic poles. The magnetic
LESSON CLUSTER 9 Explaining Condensation and the Water Cycle
 LESSON CLUSTER 9 Explaining Condensation and the Water Cycle Lesson 9.1: Boiling and Condensation You have been studying changes of state for quite a while now. You have studied melting, freezing or solidifying,
LESSON CLUSTER 9 Explaining Condensation and the Water Cycle Lesson 9.1: Boiling and Condensation You have been studying changes of state for quite a while now. You have studied melting, freezing or solidifying,
13. Fun with Magnets
 13. Fun with Magnets 1. Fill in the blanks in the following (i) Artificial magnets are made in different shapes such as bar magnets, horse-shoe magnet and cylindrical or a ball-ended magnet. (ii) The Materials
13. Fun with Magnets 1. Fill in the blanks in the following (i) Artificial magnets are made in different shapes such as bar magnets, horse-shoe magnet and cylindrical or a ball-ended magnet. (ii) The Materials
Time Sow seeds: 30 min First seedlings: A few days Cress: About 1 week
 Sow seeds: 30 min First seedlings: A few days Cress: About 1 week Cress seeds Small bowls to sow seeds in Soil or cotton wool Plastic We put cress seeds on damp cotton or in moist soil and cover with plastic.
Sow seeds: 30 min First seedlings: A few days Cress: About 1 week Cress seeds Small bowls to sow seeds in Soil or cotton wool Plastic We put cress seeds on damp cotton or in moist soil and cover with plastic.
Changes of State. Lesson 1
 Lesson 1 Changes of State If all the ice in the world melted, the oceans would rise by more than 65 meters (215 feet)! This iceberg is melting in Paraiso Bay, Antarctica. What happens to ice when it melts?
Lesson 1 Changes of State If all the ice in the world melted, the oceans would rise by more than 65 meters (215 feet)! This iceberg is melting in Paraiso Bay, Antarctica. What happens to ice when it melts?
Activity Instructions
 Weather Station Activity Instructions Somewhere Over the Rainbow CD sheet of white bristol board Place the CD label side down on a flat surface in direct sunlight so that light reflects off of it. Hold
Weather Station Activity Instructions Somewhere Over the Rainbow CD sheet of white bristol board Place the CD label side down on a flat surface in direct sunlight so that light reflects off of it. Hold
Danger! Acid Rain. Key Message: Plants are very important, Acid rain can damage plants.
 Key Message: Plants are very important, Acid rain can damage plants. SESE Curriculum Link: Content Strand Environmental Awareness Strand Units Environmental Awareness and Science and the Environment skill
Key Message: Plants are very important, Acid rain can damage plants. SESE Curriculum Link: Content Strand Environmental Awareness Strand Units Environmental Awareness and Science and the Environment skill
Changes of State pg K
 Changes of State pg. 48-53 K Key Terms Melting melting point freezing vaporization Evaporation boiling boiling point condensation Sublimation 48K Picture an ice cream cone on a hot summer day. The ice
Changes of State pg. 48-53 K Key Terms Melting melting point freezing vaporization Evaporation boiling boiling point condensation Sublimation 48K Picture an ice cream cone on a hot summer day. The ice
IGCSE PHYSICS GRADE 11 TERM 1 ASSESSMENT BOOKLET
 PHYSICS IGCSE PHYSICS GRADE 11 TERM 1 ASSESSMENT BOOKLET 2013-2014 STS Page 1 of 44 PHYSICS PHYSI1101 ASSESSMENT TASK COVER PAGE Topic STS Performance Criteria Assessment event Date Time Thermal Physics
PHYSICS IGCSE PHYSICS GRADE 11 TERM 1 ASSESSMENT BOOKLET 2013-2014 STS Page 1 of 44 PHYSICS PHYSI1101 ASSESSMENT TASK COVER PAGE Topic STS Performance Criteria Assessment event Date Time Thermal Physics
2018 Year 11 Physics Week 8. Thermal Energy Transfer
 2018 Year 11 Physics Week 8 Thermal Energy Transfer Thermal energy Thermal or heat energy is the energy that flows from a hot region to a cold region by one or more of the processes of: CONDUCTION CONVECTION
2018 Year 11 Physics Week 8 Thermal Energy Transfer Thermal energy Thermal or heat energy is the energy that flows from a hot region to a cold region by one or more of the processes of: CONDUCTION CONVECTION
Lesson 5. Introduction Water We Talking About? Learning Outcomes & Assessment. Time. Resources. Activities. Handouts. Video.
 Lesson 5 Introduction Water We Talking About? Learning Outcomes & Assessment Time Resources Activities Handouts Video every dr p counts 57 Science Use their senses to interpret observations (Processes
Lesson 5 Introduction Water We Talking About? Learning Outcomes & Assessment Time Resources Activities Handouts Video every dr p counts 57 Science Use their senses to interpret observations (Processes
Natural vs Human-harnessed Electricity
 What is static electricity? Why do you sometimes get shocked when you touch something metal? Why is static electricity more common in the winter? What do you think of when you think of static electricity?
What is static electricity? Why do you sometimes get shocked when you touch something metal? Why is static electricity more common in the winter? What do you think of when you think of static electricity?
Here We Go Again INTRODUCTION TIME NEEDED. Modeling the Water Cycle
 6.06 Here We Go Again Modeling the Water Cycle INTRODUCTION Water is constantly on the move being recycled between the air, the land, and plants and animals. This movement is called the water cycle. Water
6.06 Here We Go Again Modeling the Water Cycle INTRODUCTION Water is constantly on the move being recycled between the air, the land, and plants and animals. This movement is called the water cycle. Water
Heat and temperature. Making a thermometer
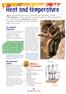 Heat and temperature A bout four hundred years ago, it would have been impossible to tell the temperature of the air, the water or any other substance. That s because there was no such thing as a thermometer
Heat and temperature A bout four hundred years ago, it would have been impossible to tell the temperature of the air, the water or any other substance. That s because there was no such thing as a thermometer
Changes of phase usually involve a transfer of energy Evaporation
 Changes of phase usually involve a transfer of energy. The four possible forms of matter solid, liquid, gas, and plasma are called phases. Matter can change from one phase to another. The phase of matter
Changes of phase usually involve a transfer of energy. The four possible forms of matter solid, liquid, gas, and plasma are called phases. Matter can change from one phase to another. The phase of matter
Unit THE NATURE OF HEAT
 Unit 5.0 - THE NATURE OF HEAT Heat is a form of energy, in the form of infrared radiation. Heat from the sun travels through space at the speed of 300,000,000 m/s. Upon arriving on earth, much of the radiant
Unit 5.0 - THE NATURE OF HEAT Heat is a form of energy, in the form of infrared radiation. Heat from the sun travels through space at the speed of 300,000,000 m/s. Upon arriving on earth, much of the radiant
Homemade Cleaning Products A compilation of found recipes and experiments By April D. Rippel. For Good Health
 Homemade Cleaning Products A compilation of found recipes and experiments By April D. Rippel For Good Health An endeavor to remove toxic chemicals from our homes and environment. 2013 2 tsp. Boric Acid
Homemade Cleaning Products A compilation of found recipes and experiments By April D. Rippel For Good Health An endeavor to remove toxic chemicals from our homes and environment. 2013 2 tsp. Boric Acid
Parents and Educators: use #CuriousCrew #CuriosityGuide to share what your Curious Crew learned!
 Investigation: 01 Can Crusher See the power of air pressure! Soda can Tongs Gloves Container of cold water Hot plate Safety Glasses Adult Supervision 1) Fill a soda can with enough water to cover the bottom
Investigation: 01 Can Crusher See the power of air pressure! Soda can Tongs Gloves Container of cold water Hot plate Safety Glasses Adult Supervision 1) Fill a soda can with enough water to cover the bottom
3B Heat, Light and Sound
 Heat, Light and Sound Heat, light and sound are forms of energy that have many applications in our lives. Heat Heat is a form of energy When petrol burns in a car engine it causes the gases in the cylinders
Heat, Light and Sound Heat, light and sound are forms of energy that have many applications in our lives. Heat Heat is a form of energy When petrol burns in a car engine it causes the gases in the cylinders
I. C O N T E N T S T A N D A R D S
 Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course I. C O N T E N T S T A N D A R D S and radiation between objects or regions that are at different temperatures. 3.1 Explain
Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course I. C O N T E N T S T A N D A R D S and radiation between objects or regions that are at different temperatures. 3.1 Explain
Transfer of Heat. There are three ways in which heat is transferred from one body to another. These are
 Transfer of Heat In the precious chapter you have learnt that heat flows from a body at a higher temperature to a body at a lower temperature, but how does this transfer take place? You will find the answer
Transfer of Heat In the precious chapter you have learnt that heat flows from a body at a higher temperature to a body at a lower temperature, but how does this transfer take place? You will find the answer
AQUAPASS. My guide on water footprint
 AQUAPASS www.aquapath-project.eu My guide on water footprint This project has been funded with support from the European Commission. This publication reflects the views only of the author, and the Commission
AQUAPASS www.aquapath-project.eu My guide on water footprint This project has been funded with support from the European Commission. This publication reflects the views only of the author, and the Commission
Downloaded from
 Do you know, why? ASSIGNMENTS TUTORIAL HEAT 1. The thick glass tumblers break when hot liquid is poured into them Ans: If boiling hot water is poured in a thick glass tumbler, it cracks because glass is
Do you know, why? ASSIGNMENTS TUTORIAL HEAT 1. The thick glass tumblers break when hot liquid is poured into them Ans: If boiling hot water is poured in a thick glass tumbler, it cracks because glass is
Activity Heat Transfer
 Name: Hr: Activity 3.3.6 Heat Transfer Introduction Heat is the transfer of thermal energy. Thermal energy exists when the atoms or molecules in a substance are in motion and vibrate. The atoms possess
Name: Hr: Activity 3.3.6 Heat Transfer Introduction Heat is the transfer of thermal energy. Thermal energy exists when the atoms or molecules in a substance are in motion and vibrate. The atoms possess
Parents and Educators: use #CuriousCrew #CuriosityGuide to share what your Curious Crew learned!
 Investigation: 01 The Unpoppable Water Balloon Why won t this balloon pop? 2 balloons Water Basin Safety glasses Candle Matches Adult supervision 1) Put on safety glasses 2) Place the candle in a shallow
Investigation: 01 The Unpoppable Water Balloon Why won t this balloon pop? 2 balloons Water Basin Safety glasses Candle Matches Adult supervision 1) Put on safety glasses 2) Place the candle in a shallow
Morning Announcements Energy Savings Tips for Students
 Morning Announcements Energy Savings Tips for Students Did you know.? 1. Saving energy means saving money, conserving fossils fuels, and helping to protect our environment. There are lots of ways to save
Morning Announcements Energy Savings Tips for Students Did you know.? 1. Saving energy means saving money, conserving fossils fuels, and helping to protect our environment. There are lots of ways to save
Minutes with Lamp On
 A. Greenhouse Warming Experiment Fill in the tables below with the temperature reading at each time interval. We will stop making measurements when the thermometer has reached a constant value. Table 1.
A. Greenhouse Warming Experiment Fill in the tables below with the temperature reading at each time interval. We will stop making measurements when the thermometer has reached a constant value. Table 1.
Science 7. Unit 3. Heat and. Temperature
 Science 7 Unit 3 Heat and Temperature Name:_ Class:_ TOPIC 1 REINFORMCEMENT Putting Thermal Energy to Work Goal Develop ways to classify natural and manufactured structures. BLM 3-1 When do you use thermal
Science 7 Unit 3 Heat and Temperature Name:_ Class:_ TOPIC 1 REINFORMCEMENT Putting Thermal Energy to Work Goal Develop ways to classify natural and manufactured structures. BLM 3-1 When do you use thermal
Weather: Why do we have weather? Does it serve a purpose?
 Weather: Why do we have weather? Does it serve a purpose? Heat, insulation, the Earth and you: Why people wear different colored clothing in different parts of the world Heat Part I Grandpa, why do people
Weather: Why do we have weather? Does it serve a purpose? Heat, insulation, the Earth and you: Why people wear different colored clothing in different parts of the world Heat Part I Grandpa, why do people
Heat Energy. Heat Energy. A Science A Z Physical Series. Word Count: 1,301. Written by Felicia Brown. Visit
 Heat Energy A Science A Z Physical Series Word Count: 1,301 Heat Energy Written by Felicia Brown Visit www.sciencea-z.com www.sciencea-z.com Heat Energy Key elements Used in This Book The Big Idea: One
Heat Energy A Science A Z Physical Series Word Count: 1,301 Heat Energy Written by Felicia Brown Visit www.sciencea-z.com www.sciencea-z.com Heat Energy Key elements Used in This Book The Big Idea: One
SLUSH PUPPiE MACHINE Instructions For Use
 SLUSH PUPPiE MACHINE Instructions For Use Product Ref: 9041_v7 Voltage: 220-240V 50/60Hz. Power: 20 Watts. Scan me for the instruction video and top tips for the perfect SLUSH PUPPiE! slushpuppie.fizzcreations.com
SLUSH PUPPiE MACHINE Instructions For Use Product Ref: 9041_v7 Voltage: 220-240V 50/60Hz. Power: 20 Watts. Scan me for the instruction video and top tips for the perfect SLUSH PUPPiE! slushpuppie.fizzcreations.com
In Chapter 3 you learnt that woollen
 4 Heat In Chapter 3 you learnt that woollen clothes are made from animal fibres. You also know that cotton clothes are made from plant fibres. We wear woollen clothes during winters when it is cold outside.
4 Heat In Chapter 3 you learnt that woollen clothes are made from animal fibres. You also know that cotton clothes are made from plant fibres. We wear woollen clothes during winters when it is cold outside.
Well Insulated Houses: Helping to Stay Warm in Winter and Cool in Summer
 CON EDISON WEB-BASED MIDDLE SCHOOL ACTIVITY Well Insulated Houses: Helping to Stay Warm in Winter and Cool in Summer Overview In this activity, you and your students will build two house models from discarded
CON EDISON WEB-BASED MIDDLE SCHOOL ACTIVITY Well Insulated Houses: Helping to Stay Warm in Winter and Cool in Summer Overview In this activity, you and your students will build two house models from discarded
Electric and Natural Gas Safety and You Teacher s Guide
 Electric and Natural Gas Safety and You Teacher s Guide Introduction This discussion guide contains background for teachers, followed by questions for each page in the booklet and suggested activities
Electric and Natural Gas Safety and You Teacher s Guide Introduction This discussion guide contains background for teachers, followed by questions for each page in the booklet and suggested activities
Some Demonstration Experiments: Effects of Air Motion, Evaporation, and Pressure Changes on Temperature
 METR 104: Our Dynamic Weather (Lecture w/lab) Some Demonstration Experiments: Effects of Air Motion, Evaporation, and Pressure Changes on Temperature Dr. Dave Dempsey Department of Earth & Climate Sciences
METR 104: Our Dynamic Weather (Lecture w/lab) Some Demonstration Experiments: Effects of Air Motion, Evaporation, and Pressure Changes on Temperature Dr. Dave Dempsey Department of Earth & Climate Sciences
PHYSICS FORM 5 TRANSFER OF THERMAL ENERGY
 Heat energy is transferred from one place to the next by three mechanisms: 1. Conduction 2. Convection 3. Radiation Conduction This is the process of heat transfer from one place to another using the movement/vibration
Heat energy is transferred from one place to the next by three mechanisms: 1. Conduction 2. Convection 3. Radiation Conduction This is the process of heat transfer from one place to another using the movement/vibration
What Makes Up Your Profile?
 What Makes Up Your Profile? Soil Isn t a Dirty Word Objectives Students will be able to determine soil changes in relationship to depth. Students will explain how soils are formed. Materials overhead projector
What Makes Up Your Profile? Soil Isn t a Dirty Word Objectives Students will be able to determine soil changes in relationship to depth. Students will explain how soils are formed. Materials overhead projector
Water: A Never-Ending Story
 Water: A Never-Ending Story A curriculum module intended for grades 3-5. Approximate time frame: 3 class periods I. Teacher Background Water on earth is used over and over. The water cycle, the continuous
Water: A Never-Ending Story A curriculum module intended for grades 3-5. Approximate time frame: 3 class periods I. Teacher Background Water on earth is used over and over. The water cycle, the continuous
Van de Graaff Generator. Spinner Package Demonstration Guide
 Van de Graaff Generator Spinner Package Demonstration Guide Demonstrations for the Science First Van de Graaff generator and its included accessories. Teaching with Van de Graaff The Van de Graaff generator
Van de Graaff Generator Spinner Package Demonstration Guide Demonstrations for the Science First Van de Graaff generator and its included accessories. Teaching with Van de Graaff The Van de Graaff generator
Heat. Energy. Lesson 2. Unit 2: Water! From Waves to Weather
 Unit 2: Water! From Waves to Weather Heat Energy Lesson 2 Unit 2: Water! From Waves to Weather Heat Energy Lesson 2 Heat energy makes molecules move faster. Students learn to explain heat energy observed
Unit 2: Water! From Waves to Weather Heat Energy Lesson 2 Unit 2: Water! From Waves to Weather Heat Energy Lesson 2 Heat energy makes molecules move faster. Students learn to explain heat energy observed
photosynthesis, ventilation & gardening Science Technology Engineering Mathematics
 DISCOVERING BOTANIC LABORATORY photosynthesis, ventilation & gardening Science Technology Engineering Mathematics Learning about: Botanic laboratory What are the differences between monocot and dicot seeds?
DISCOVERING BOTANIC LABORATORY photosynthesis, ventilation & gardening Science Technology Engineering Mathematics Learning about: Botanic laboratory What are the differences between monocot and dicot seeds?
Don't Marry the Mole!
 Don't Marry the Mole! Summary Students will demonstrate the power of solar energy by completing a variety of activities, including the create of a Pizza Box Solar Oven. Main Core Tie Science - 3rd Grade
Don't Marry the Mole! Summary Students will demonstrate the power of solar energy by completing a variety of activities, including the create of a Pizza Box Solar Oven. Main Core Tie Science - 3rd Grade
A Terrarium (Sessions I and II)
 activities 14&15 A Terrarium (Sessions I and II) BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 3 Quarter 2 Activities 14 & 15 SC.D.1.2.3 The student knows that the water cycle is influenced by
activities 14&15 A Terrarium (Sessions I and II) BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 3 Quarter 2 Activities 14 & 15 SC.D.1.2.3 The student knows that the water cycle is influenced by
Thermal Energy. Conduction, Convection, and Radiation. Before You Read. Read to Learn. Conduction. section 2
 chapter 5 Thermal Energy section 2 Conduction, Convection, and What You ll Learn the three ways heat is transferred the difference between insulators and conductors how insulators control the transfer
chapter 5 Thermal Energy section 2 Conduction, Convection, and What You ll Learn the three ways heat is transferred the difference between insulators and conductors how insulators control the transfer
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE. To make the most of your new oven, read the user's instructions carefully and keep them on hand for consultation in the future.
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE INSTALLATION...4 SAFEGUARDING THE ENVIRONMENT... 7 IMPORTANT NOTES... 7 BEFORE USING THE OVEN... 8 OVEN ACCESSORIES... 9 CARE AND MAINTENANCE... 10 TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE... 12 AFTER
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE INSTALLATION...4 SAFEGUARDING THE ENVIRONMENT... 7 IMPORTANT NOTES... 7 BEFORE USING THE OVEN... 8 OVEN ACCESSORIES... 9 CARE AND MAINTENANCE... 10 TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE... 12 AFTER
Week 1 Day 1-2 (combine) Thermal Energy
 Week 1 Day 1-2 (combine) Thermal Energy Heat Transfer Conduction, Convection and Radiation Thermal Energy Transfer Thermal energy transfer is heat moving from a warmer object to a cooler object. This is
Week 1 Day 1-2 (combine) Thermal Energy Heat Transfer Conduction, Convection and Radiation Thermal Energy Transfer Thermal energy transfer is heat moving from a warmer object to a cooler object. This is
Activity Sheet Chapter 2, Lesson 3 Changes of State Condensation
 Activity Sheet Chapter 2, Lesson 3 Changes of State Condensation Name Date DEMONSTRATION 1. Your teacher showed you two cups of water with ice in them. One cup was in a bag with as much air taken out as
Activity Sheet Chapter 2, Lesson 3 Changes of State Condensation Name Date DEMONSTRATION 1. Your teacher showed you two cups of water with ice in them. One cup was in a bag with as much air taken out as
SNC1P Electricity Practice Test
 SNC1P Electricity Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which type of energy comes from the flow of charged particles? a. chemical
SNC1P Electricity Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which type of energy comes from the flow of charged particles? a. chemical
How Seeds Become Plants - Worksheet
 Name: TEACHER S COPY How Seeds Become Plants - Worksheet Think about what part of a plant contains seeds. Where on the plant would you find an apple or tomato seed? In the fruit Are coconuts seeds? How
Name: TEACHER S COPY How Seeds Become Plants - Worksheet Think about what part of a plant contains seeds. Where on the plant would you find an apple or tomato seed? In the fruit Are coconuts seeds? How
Science Test Revision
 John Buchan Middle School Science Test Revision 5D Changing State 52 min 50 marks Name John Buchan Middle School 1 Level 3 1. Changes (a) Kim and Juan change the way some things look. The pictures below
John Buchan Middle School Science Test Revision 5D Changing State 52 min 50 marks Name John Buchan Middle School 1 Level 3 1. Changes (a) Kim and Juan change the way some things look. The pictures below
Melting and Freezing. STEM Activity 1: What melts in the heat of the sun? Background information and Science information
 1 STEM Activity 1: What melts in the heat of the sun? Background information and Science information All solids have a melting point: the temperature when they change from solid to liquid. Most substances
1 STEM Activity 1: What melts in the heat of the sun? Background information and Science information All solids have a melting point: the temperature when they change from solid to liquid. Most substances
Heat Transfer. Heat. Thermal Energy: Heat 1
 Heat Transfer The heat is on! In this lesson, we are going to learn what heat is and how it moves from place to place. You know how they say, If you can t stand the heat, get out of the kitchen.? Well
Heat Transfer The heat is on! In this lesson, we are going to learn what heat is and how it moves from place to place. You know how they say, If you can t stand the heat, get out of the kitchen.? Well
Heat can change into other forms of energy and vice versa. Heat is measured in the unit of energy, the joule (J).
 ExamLearn.ie Heat Heat Heat has the ability to do work or move something. Thus, heat is a form of energy. Heat can change into other forms of energy and vice versa. Heat is measured in the unit of energy,
ExamLearn.ie Heat Heat Heat has the ability to do work or move something. Thus, heat is a form of energy. Heat can change into other forms of energy and vice versa. Heat is measured in the unit of energy,
Earth s climate has been changing rapidly. This change is often referred to as
 Earth s climate has been changing rapidly. This change is often referred to as global warming, and it affects every living thing on the planet plants, animals, people, even you. When certain gases, known
Earth s climate has been changing rapidly. This change is often referred to as global warming, and it affects every living thing on the planet plants, animals, people, even you. When certain gases, known
Rain catcher. GREEN AMBASSADORS 4 Youth. Get informed. Time: You ll need: Who it s for: What to do: WATER. 5 to 10 year olds
 Rain catcher 40 minutes 5 to 10 year olds Plastic bottles Scissors Sand Waterproof craft paint 1. Ask each member to bring a 2 litre plastic bottle to the session with them. 2. Cut the top of the bottle
Rain catcher 40 minutes 5 to 10 year olds Plastic bottles Scissors Sand Waterproof craft paint 1. Ask each member to bring a 2 litre plastic bottle to the session with them. 2. Cut the top of the bottle
Name Science Period 1
 Name Science Period 1 Table of Contents Getting Started 3 Safety Symbols 4 Animal Safety 5 Aprons 5 Breakage 6 Corrosive 7 Disposal 8 Electric 8 Flame 9 Fumes 10 General Safety Awareness 10 Gloves 11 Goggles
Name Science Period 1 Table of Contents Getting Started 3 Safety Symbols 4 Animal Safety 5 Aprons 5 Breakage 6 Corrosive 7 Disposal 8 Electric 8 Flame 9 Fumes 10 General Safety Awareness 10 Gloves 11 Goggles
Seed Growing. Propagation Lecture 2
 Seed Growing Propagation Lecture 2 Vocabulary Seedling Seedling is plant that comes from seed Vocabulary Germination Seed makes root and shoot Picture shows germination Vocabulary Seed Viability Seed Viability-
Seed Growing Propagation Lecture 2 Vocabulary Seedling Seedling is plant that comes from seed Vocabulary Germination Seed makes root and shoot Picture shows germination Vocabulary Seed Viability Seed Viability-
The table gives information about some ways of reducing the energy consumption in a house. Installation cost in. Fit a new hot water boiler
 ## (a) The table gives information about some ways of reducing the energy consumption in a house. Method of reducing energy consumption Installation cost in Annual saving on energy bills in Fit a new hot
## (a) The table gives information about some ways of reducing the energy consumption in a house. Method of reducing energy consumption Installation cost in Annual saving on energy bills in Fit a new hot
More heat energy means more of what type of energy? Does the mass change? So, what must change? What is the same in both containers?
 Quest Chapter 21-23 # Problem Hint 1 When a container of gas is heated, what happens to the average speed of its molecules? 1. Additional information is needed. 2. increases 3. doesn t change 4. decreases
Quest Chapter 21-23 # Problem Hint 1 When a container of gas is heated, what happens to the average speed of its molecules? 1. Additional information is needed. 2. increases 3. doesn t change 4. decreases
LESSON CLUSTER 8 Explaining Evaporation and Boiling
 LESSON CLUSTER 8 Explaining Evaporation and Boiling Lesson 8.1: Where Did the Water Go? You see things drying out around you all the time; puddles dry up; clothes dry on a clothesline or in a dryer; your
LESSON CLUSTER 8 Explaining Evaporation and Boiling Lesson 8.1: Where Did the Water Go? You see things drying out around you all the time; puddles dry up; clothes dry on a clothesline or in a dryer; your
Making a Carousel Lantern. Grade 7 Activity Plan
 Making a Carousel Lantern Grade 7 Activity Plan 1 Reviews and Updates - Carousel Lanterns Activity added by Fola Akpan in July 2017 2 Making a Carousel Lantern Objectives: 1. To compare two methods of
Making a Carousel Lantern Grade 7 Activity Plan 1 Reviews and Updates - Carousel Lanterns Activity added by Fola Akpan in July 2017 2 Making a Carousel Lantern Objectives: 1. To compare two methods of
SCIENCE TOTAL KEY STAGE LEVELS TEST A TEST A. First Name. Last Name. School. Downloaded from Compare4Kids.co.
 SCIENCE KEY STAGE 2 2005 TEST A LEVELS 3 5 PAGE 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 20 TOTAL MARKS TEST A First Name Last Name School INSTRUCTIONS Read this carefully. You have 45 minutes for this test. Answers This
SCIENCE KEY STAGE 2 2005 TEST A LEVELS 3 5 PAGE 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 20 TOTAL MARKS TEST A First Name Last Name School INSTRUCTIONS Read this carefully. You have 45 minutes for this test. Answers This
Cloning Cannabis Marijuana
 Document: Cloning Cannabis Marijuana Source: www.kiwiland.com Pages: 10 Cloning Cannabis Marijuana Introduction Asexual Propagation of marijuana (cloning) is not difficult if the correct procedure is followed.
Document: Cloning Cannabis Marijuana Source: www.kiwiland.com Pages: 10 Cloning Cannabis Marijuana Introduction Asexual Propagation of marijuana (cloning) is not difficult if the correct procedure is followed.
Healthy Soil=Healthy Plants
 Healthy Soil=Healthy Plants At a Glance Grade Level: 3 Learning Environment: Indoor Classroom and the Schoolyard or a garden. Prep Time: 15 minutes Length of Lesson: 1.5 hours Description of Lesson Photo:
Healthy Soil=Healthy Plants At a Glance Grade Level: 3 Learning Environment: Indoor Classroom and the Schoolyard or a garden. Prep Time: 15 minutes Length of Lesson: 1.5 hours Description of Lesson Photo:
HEAT What are some sources of Heat?
 HEAT Activity 1. Rub your hands quickly against each other. 2. Then quickly place them onto your face. 3. Describe what you feel. Your hands feel warm. 4. Why does it feel warm? It feels warm as HEAT has
HEAT Activity 1. Rub your hands quickly against each other. 2. Then quickly place them onto your face. 3. Describe what you feel. Your hands feel warm. 4. Why does it feel warm? It feels warm as HEAT has
Operating Instructions Wine storage refrigerator 12/
 Operating Instructions Wine storage refrigerator 12/98 7080641 1 The wine storage refrigerator you have purchased differs from normal refrigerators in that it is suitable for long-term storage of wine.
Operating Instructions Wine storage refrigerator 12/98 7080641 1 The wine storage refrigerator you have purchased differs from normal refrigerators in that it is suitable for long-term storage of wine.
3 From Bedrock to Soil
 CHAPTER 10 3 From Bedrock to Soil SECTION Weathering and Soil Formation BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is soil? How do the features of soil
CHAPTER 10 3 From Bedrock to Soil SECTION Weathering and Soil Formation BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is soil? How do the features of soil
Contents. For your safety About your product Installing your appliance Using your appliance Care & cleaning...
 USER GUIDE TF5517S Contents For your safety..................................................... 1 About your product.................................................. 3 Installing your appliance...............................................
USER GUIDE TF5517S Contents For your safety..................................................... 1 About your product.................................................. 3 Installing your appliance...............................................
Science Fair Project. Environmental Global Warming Callie Fong Mrs. Mcnees Syracuse Junior High
 Science Fair Project Environmental Global Warming Callie Fong Mrs. Mcnees Syracuse Junior High Problem How does carbon dioxide affect plant growth? (Investing global warming) Research More Carbon Dioxide
Science Fair Project Environmental Global Warming Callie Fong Mrs. Mcnees Syracuse Junior High Problem How does carbon dioxide affect plant growth? (Investing global warming) Research More Carbon Dioxide
AP Air Ion Counter Instructions
 AP Air Ion Counter Instructions Standard 2 million ions/cm 3 version- The 6 m long ground cord should be used to connect the meter to earth ground for most types of measurements - - especially if you are
AP Air Ion Counter Instructions Standard 2 million ions/cm 3 version- The 6 m long ground cord should be used to connect the meter to earth ground for most types of measurements - - especially if you are
There are different types of weathering weathering and weathering. Both types work together to change Earth s surface.
 Weathering effects Classifying Sediment The surface processes that break down rock are called. Weathering breaks rock into smaller and smaller pieces. Tiny moss plants, earthworms, wind, rain, and even
Weathering effects Classifying Sediment The surface processes that break down rock are called. Weathering breaks rock into smaller and smaller pieces. Tiny moss plants, earthworms, wind, rain, and even
STATIC MERRY-GO-ROUND
 Curriculum topics: Static Electricity Experimental Variables Momentum Electrically Charged vs. Uncharged STATIC MERRY-GO-ROUND Make and power a version of the first electric motor! Subject: Physical Science
Curriculum topics: Static Electricity Experimental Variables Momentum Electrically Charged vs. Uncharged STATIC MERRY-GO-ROUND Make and power a version of the first electric motor! Subject: Physical Science
LETTER TO FAMILY. Science News. Cut here and paste onto school letterhead before making copies.
 LETTER TO FAMILY Cut here and paste onto school letterhead before making copies. Dear Family, Water is a unique earth material, the only material on Earth that occurs naturally in all three states of matter:
LETTER TO FAMILY Cut here and paste onto school letterhead before making copies. Dear Family, Water is a unique earth material, the only material on Earth that occurs naturally in all three states of matter:
Lab 12E, 12F, 2E: Acid Rain and Seeds
 12E Describe the flow of matter through the carbon and nitrogen cycles and explain the consequences of disrupting these cycles. 12F Describe how environmental change can impact ecosystem stability. 2E
12E Describe the flow of matter through the carbon and nitrogen cycles and explain the consequences of disrupting these cycles. 12F Describe how environmental change can impact ecosystem stability. 2E
Science Test: Heat Energy
 Science Test: Heat Energy Name: Date: Section 1: Vocabulary Select the word below that makes the statement correct. Then write the word in the blank. freeze conductor heat friction melt evaporate radiation
Science Test: Heat Energy Name: Date: Section 1: Vocabulary Select the word below that makes the statement correct. Then write the word in the blank. freeze conductor heat friction melt evaporate radiation
Static Electricity: Bending and Floating
 Static Electricity: Bending and Floating Week 3A Objectives: In this lesson students will learn: About the force of static electricity How electricity relates to our everyday life Intro to electrons Background:
Static Electricity: Bending and Floating Week 3A Objectives: In this lesson students will learn: About the force of static electricity How electricity relates to our everyday life Intro to electrons Background:
Heat Transfer. Heat Transfer. Thermal Equilibrium. Thermal Inequilibrium
 Heat Transfer, Radiation Convection and Heat Transfer Heat is a form of energy. Heat travels from higher temperature(hotter) region to lower temperature(cooler) region. Two bodies are in thermal equilibrium
Heat Transfer, Radiation Convection and Heat Transfer Heat is a form of energy. Heat travels from higher temperature(hotter) region to lower temperature(cooler) region. Two bodies are in thermal equilibrium
THIRD GRADE SCIENCE (SCIENCE3_4)
 Name: Date: THIRD GRADE SCIENCE (SCIENCE3_4) 1. If you put a metal spoon in hot water, the spoon will A. melt. B. dissolve. C. get cold. D. get hot. 2. When one end of a steel rod is held in a flame, the
Name: Date: THIRD GRADE SCIENCE (SCIENCE3_4) 1. If you put a metal spoon in hot water, the spoon will A. melt. B. dissolve. C. get cold. D. get hot. 2. When one end of a steel rod is held in a flame, the
WEATHERING AND SOIL FORMATION. 8th Grade- Mr. Stelma
 WEATHERING AND SOIL FORMATION 8th Grade- Mr. Stelma WEATHERING EFFECTS The surface processes that break down rock are called weathering. Weathering breaks rock into smaller and smaller pieces. Tiny moss
WEATHERING AND SOIL FORMATION 8th Grade- Mr. Stelma WEATHERING EFFECTS The surface processes that break down rock are called weathering. Weathering breaks rock into smaller and smaller pieces. Tiny moss
Contents. Section 1: The Structure of the Atmosphere. Section 2: Natural Cycles. Section 3: Air Pollution
 Contents Section 1: The Structure of the Atmosphere 1. Gases of the Atmosphere... 3 2. Layers of the Atmosphere.... 6 3. Special Layers of the Atmosphere.... 10 4. Effects of the Atmosphere.... 13 5. Quiz
Contents Section 1: The Structure of the Atmosphere 1. Gases of the Atmosphere... 3 2. Layers of the Atmosphere.... 6 3. Special Layers of the Atmosphere.... 10 4. Effects of the Atmosphere.... 13 5. Quiz
TEMPERATURE ACTIVITY
 SCIENCE: Heat MATHEMATICS: Reading a thermometer AIM: Students understand the relationship between heat and density. BACKGROUND: How does a hot air balloon work? As the air inside the balloon becomes hotter
SCIENCE: Heat MATHEMATICS: Reading a thermometer AIM: Students understand the relationship between heat and density. BACKGROUND: How does a hot air balloon work? As the air inside the balloon becomes hotter
LEC L6014W/S User Manual
 LEC L6014W/S User Manual Safety Information Important Please read these instructions fully before installation Before use The installation of this appliance is best carried out by 2 people. Dispose of
LEC L6014W/S User Manual Safety Information Important Please read these instructions fully before installation Before use The installation of this appliance is best carried out by 2 people. Dispose of
CONTENTS QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE PROGRAMME CHART
 1 CONTENTS Please read instruction for use QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE PREPARING THE LAUNDRY SELECTING A PROGRAMME AND OPTIONS STARTING AND COMPLETING A PROGRAMME CHANGING A PROGRAMME PROGRAMME CHART INTERRUPTING
1 CONTENTS Please read instruction for use QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE PREPARING THE LAUNDRY SELECTING A PROGRAMME AND OPTIONS STARTING AND COMPLETING A PROGRAMME CHANGING A PROGRAMME PROGRAMME CHART INTERRUPTING
Fourth Edition HEAT TRANSFER AND CHANGE OF PHASE
 Hewitt/Suchocki/Hewitt Conceptual Physical Science Fourth Edition Chapter 7: HEAT TRANSFER AND CHANGE OF PHASE This lecture will help you understand: Conduction Convection Radiation Newton s Law of Cooling
Hewitt/Suchocki/Hewitt Conceptual Physical Science Fourth Edition Chapter 7: HEAT TRANSFER AND CHANGE OF PHASE This lecture will help you understand: Conduction Convection Radiation Newton s Law of Cooling
INSTRUCTIONS AND WARRANTY
 INSTRUCTIONS AND WARRANTY MODEL NO. SWC 030 PORTABLE AIRCOOLER AND PURIFIER Thank you for purchasing our SALTON Portable Air-cooler. Please read the instructions carefully before using and keep safe for
INSTRUCTIONS AND WARRANTY MODEL NO. SWC 030 PORTABLE AIRCOOLER AND PURIFIER Thank you for purchasing our SALTON Portable Air-cooler. Please read the instructions carefully before using and keep safe for
Age 7 Coloring Book. World Water Day, 22 March
 Age 7 Coloring Book World Water Day, March NAME: AGE: SCHOOL: Connect the Dots Who found the treasure? Did you know that? Octopuses do not have bones. An octopus has a secret weapon. It has a sack full
Age 7 Coloring Book World Water Day, March NAME: AGE: SCHOOL: Connect the Dots Who found the treasure? Did you know that? Octopuses do not have bones. An octopus has a secret weapon. It has a sack full
Building your terrarium:
 What is a Terrarium? A terrarium is a collection of small plants growing in a transparent, sealed container. A terrarium is a closed environment, and can actually be used to illustrate how an ecosystem
What is a Terrarium? A terrarium is a collection of small plants growing in a transparent, sealed container. A terrarium is a closed environment, and can actually be used to illustrate how an ecosystem
Thermal Energy Study Guide
 Goal 1 Thermal Energy Study Guide Name: Hour Define the following in your own words: 1. Conductor - a material that allows heat to flow through it easily Two examples - metal pot, fork 2. Insulator - a
Goal 1 Thermal Energy Study Guide Name: Hour Define the following in your own words: 1. Conductor - a material that allows heat to flow through it easily Two examples - metal pot, fork 2. Insulator - a
Simple Solutions Science Level 2. Level 2. Science. Help Pages
 Level 2 Science 147 A Glossary air pollution comes from factory and car fumes amphibian an animal group that lives part of its life in the water and part on land; lays eggs; breathes with gills when young
Level 2 Science 147 A Glossary air pollution comes from factory and car fumes amphibian an animal group that lives part of its life in the water and part on land; lays eggs; breathes with gills when young
 ST. FRANCIS SECONDARY SCHOOL HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATION 2016-2017 FORM 1 SCIENCE TIME: 1.5 HOURS Name: Class: Read instructions carefully and answer ALL questions in the spaces provided using Black/Blue ink.
ST. FRANCIS SECONDARY SCHOOL HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATION 2016-2017 FORM 1 SCIENCE TIME: 1.5 HOURS Name: Class: Read instructions carefully and answer ALL questions in the spaces provided using Black/Blue ink.
Humidity An excuse for the 80s
 Humidity An excuse for the 80s What is Humidity? Humidity refers to the amount of moisture (water vapor) in the surrounding air. Relative Humidity RATIO of the amount of moisture in the air compared with
Humidity An excuse for the 80s What is Humidity? Humidity refers to the amount of moisture (water vapor) in the surrounding air. Relative Humidity RATIO of the amount of moisture in the air compared with
Soil 1/18/2012. Soils, Nutrients and Fertilizers Part I. Soil Profile
 Soils, Nutrients and Fertilizers Part I Handouts: Soil Texture Triangle ph Nutrient Availability Soil Diverse combination of weathered rock fragments and minerals, with decaying remains of plants and animals
Soils, Nutrients and Fertilizers Part I Handouts: Soil Texture Triangle ph Nutrient Availability Soil Diverse combination of weathered rock fragments and minerals, with decaying remains of plants and animals
Form 4: Integrated Science Notes TOPIC: TEMPERATURE CONTROL AND VENTILATION TEMPERATURE CONTROL: HEAT TRANSFER
 Form 4: Integrated Science Notes TOPIC: TEMPERATURE CONTROL AND VENTILATION TEMPERATURE CONTROL: HEAT TRANSFER Heat energy can be transferred from a place where it is very hot to a place where it is not
Form 4: Integrated Science Notes TOPIC: TEMPERATURE CONTROL AND VENTILATION TEMPERATURE CONTROL: HEAT TRANSFER Heat energy can be transferred from a place where it is very hot to a place where it is not
Nature Notes. For life to exist there must be Sun, Air, Water and Soil. These are all gifts provided by Nature.
 Nature Notes For life to exist there must be Sun, Air, Water and Soil. These are all gifts provided by Nature. We cannot make any of these gifts, but Nature offers them to us. We can take care of these
Nature Notes For life to exist there must be Sun, Air, Water and Soil. These are all gifts provided by Nature. We cannot make any of these gifts, but Nature offers them to us. We can take care of these
Photosynthesis Pictorial
 Photosynthesis Pictorial Have your pupils design a pictorial representation of photosynthesis. This could be a simple poster, a lift the flap diagram or a 3D model. 1. Instruct children to draw a plant
Photosynthesis Pictorial Have your pupils design a pictorial representation of photosynthesis. This could be a simple poster, a lift the flap diagram or a 3D model. 1. Instruct children to draw a plant
Washing Machine. User manual WW9*K5*****/WW8*K5*****/WW7*K5***** Untitled :17:40
 Washing Machine User manual WW9*K5*****/WW8*K5*****/WW7*K5***** Untitled-6 1 2017-12-12 3:17:40 Contents Contents 4 What you need to know about the safety instructions 4 Important safety symbols 4 Important
Washing Machine User manual WW9*K5*****/WW8*K5*****/WW7*K5***** Untitled-6 1 2017-12-12 3:17:40 Contents Contents 4 What you need to know about the safety instructions 4 Important safety symbols 4 Important
How to Use Water Safely in Your Hotel or Motel During a Boil Water Advisory
 How to Use Water Safely in Your Hotel or Motel During a Boil Water Advisory What do I need to do with my water system prior to reopening? If your business has not been operational for any period of time
How to Use Water Safely in Your Hotel or Motel During a Boil Water Advisory What do I need to do with my water system prior to reopening? If your business has not been operational for any period of time
