Accepted Manuscript. Heat pipe-based radiator for low grade geothermal energy conversion in domestic
|
|
|
- Berenice Lindsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Accepted Manuscript Heat pipe-based radiator for low grade geothermal energy conversion in domestic space heating K. Kerrigan, H. Jouhara, G.E. O Donnell, A.J. Robinson PII: S-0X(0)00- DOI: 0.0/j.simpat Reference: SIMPAT To appear in: Simulation Modeling Practices and Theory Received Date: October 00 Revised Date: May 00 Accepted Date: May 00 Please cite this article as: K. Kerrigan, H. Jouhara, G.E. O Donnell, A.J. Robinson, Heat pipe-based radiator for low grade geothermal energy conversion in domestic space heating, Simulation Modeling Practices and Theory (00), doi: 0.0/j.simpat This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
2 HEAT PIPE-BASED RADIATOR FOR LOW GRADE GEOTHERMAL ENERGY CONVERSION IN DOMESTIC SPACE HEATING K. Kerrigan, H. Jouhara, G.E. O Donnell, A. J. Robinson * Department of Mechanical & Manufacturing Engineering, Parsons Building, Trinity College Dublin, Ireland; arobins@tcd.ie School of Engineering and Design, Brunel University, Uxbridge, Middlesex, UB PH, UK, Tel: +, Fax: +, hussam.jouhara@brunel.ac.uk ABSTRACT A severe technical drawback of geothermal heat pumps (GHPs) is the fact that the nominal operating temperature available for domestic space heating is typically in the region of 0 C. This is C to 0 C less than conventional boiler settings used in hydronic central heating applications. As a result, GHPs are not generally ideal for direct replacement of conventional hydronic central heating systems because of the low relative distribution temperatures unless extreme measures are taken to improve the thermal insulation of the buildings. A preferable option for GHPs is underfloor heating. In terms of retrofitting existing buildings neither the reinsulating nor the underfloor heating options are attractive due to the large added cost and disruptive nature of the installation. As such, very high performance low temperature radiators that are pluggable into existing hydronic central heating systems are a major enabling technology for this sustainable energy source. In this investigation a Simulation Driven Design technique was utilized to develop a novel low water content and high thermal throughput heat pipe-based radiator. The radiator was subsequently fabricated and tested and showed an exceptionally high power density and very fast response time compared with conventional wet radiators. Keywords: Heat Pipe, Heat Exchanger, Design INTRODUCTION Conventional heat exchangers (HEXs) for hydronic central heating applications have changed very little over the past one hundred years or more. In these types of units, the hot source water flow is channelled within the HEX. In this way, hot fluid comes into contact with a large enough internal surface area within the device to allow the required amount of heat to be dissipated passively into the room by buoyant natural convection and radiation. Newer devices operate on the same principle though may include external fins to decrease the overall size and weight of the units. The main drawbacks of having the hot water flowing within a large internal volume are: that the devices are unnecessarily large and/or must operate with high source water temperatures, typically above 0ºC []; the water cools as it crosses the HEX causing large temperature variations across it (the cooler regions dissipate less heat requiring the HEX to be longer to achieve rated power); due to the very slow moving water within the HEX, the air which is dissolved within the water collects within the device forming air pockets. These air pockets have the effect of making the effective heat dissipating area smaller i.e. operating below design specification, requiring frequent bleeding to dispel the air. Finally, the combination of the fact Corresponding author. Phone: +, arobins@tcd.ie (Anthony Robinson)
3 that the surface area must be large enough to reach a given power dissipation and that the entire unit must have a built strength to withstand over bar operating pressure results in very heavy HEXs that has the negative influence of taking a substantial time to heat to operating temperature/power level. The large mass of material combined with the large volume of water has a major adverse impact on start-up as well as the thermostatic control capability and room comfort. Conventional radiators are not ideal for use in geothermal heat pump (GHP) domestic heating applications because of the low source water temperatures generated. The power densities are typically so low that massively oversized radiators would be required. A preferable option for GHPs is enhanced building insulation or under floor heating systems. In terms of retrofitting existing buildings neither the re-insulating nor the under floor heating options are attractive due to the large added cost and disruptive nature of the installation []. Building legislation and environmental concerns [-] are driving designers of building services and air conditioning systems towards more energy efficient solutions such as heat pipes. Heat pipe technology has proven track records in space technology [, ], thermal storage [, ], harnessing of renewable energy [-0] and in waste heat recovery of various processes [, ]. In domestic air conditioning systems, its advantages and economics are proven [] with an expanding number of applications, which utilise such technology to ensure that energy is transferred in an efficient way [-]. In the current investigation a novel high power density radiator for hydronic central heating applications has been developed that utilizes heat pipes. A heat pipe is a hermetically sealed tube that contains a small amount of fluid, which exists inside the heat pipe shell as vapour and liquid at equilibrium []. When heat is applied at one end of a heat pipe the liquid within it evaporates. The heat transfer rate within the wick structure is extremely high as it is a combination of conduction across a very thin saturated metallic wick and or nucleate boiling []. The vapour which is generated at the heated end spreads to the cooled end of the heat pipe. Here the extraction of energy causes the vapour within the heat pipe to condense back to a liquid phase thus releasing the heat that was absorbed at the heated region albeit at a different location, i.e. at some location remote from the heated end. A porous wick structure wrapped around the inner wall of the heat pipe draws the liquid condensate back to the heated section where it is once again vaporized. In the current investigation, water was chosen as the working fluid and copper as the shell material. As water and copper are chemically compatible, no generation of non condensable gasses (NCGs) will be taking place within the heat pipe [, ]. The generation of NCGs typically has an adverse affect on the performance of a heat pipe as the NCGs accumulate in the condenser section of the heat pipe subsequently reducing the length of heat pipe capable of releasing the latent heat of vaporisation. To achieve the power density required for effective heat dissipation from low grade geothermal heat sources a Simulation Driven Design technique was implemented which utilized commercial computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software to model the convective and radiative heat transport of a single channel of the finned heat pipe tube bundle immersed in otherwise quiescent room temperature air. The purpose of the CFD simulations in this work was therefore to accelerate the design process by allowing multiple geometric configurations to be considered in terms of single phase air side heat transfer capabilities. This meant that while experimental works were later carried out to ensure the validity of the final design, the effectiveness of that final design relative to other pipe configurations and fin spacings could be considered prior to the prototyping/experimental phase of the works.the radiator as well as a test facility was subsequently fabricated and the results compared favourably with simulations. Further, the steady and transient responses were tested against a standard commercially available radiator to illustrate the improved thermal performance.
4 DESIGN CONCEPT The design concept of the heat pipe-based radiator is given in Fig.. As illustrated in the figure, one end of the heat pipes is immersed in the flow of hot source water at the collector end of the HEX called the hot water manifold. Here the heat energy of the hot source water flow is absorbed into the six heat pipes by vaporising the water inside them. Since they are under a partial vacuum the water within them boils at a temperature that is lower than the source hot water temperature. Figure : Schematic of double convector heat pipe-based heat exchanger (top) assembly drawing (bottom) assembled unit. As depicted in Fig. there are dividing plates within the manifold which force the water over the collector ends of the heat pipes within a serpentine channel for improved thermal energy transfer. The steam generated inside the heat pipes at the collector end flows away from the collector region of the heat pipes to the heat ejector end. Here it condenses on the inner wall of the heat pipes releasing the heat at a location which is remote from where it was absorbed. In the heat ejector region the outer surface of the heat pipes are fitted with simple metallic fins (i.e. surface extensions) to achieve the necessary power dissipation for the given operating
5 temperature. In the heat ejector region, referred to as a finned tube bundle, the location of the heat pipes and the spacing between the fins has been designed for optimal heat transfer by buoyant natural convection and thermal radiation. SIMULATION DRIVEN DESIGN Due to the complex nature of the flow and heat transfer within the finned tube bundle, conventional correlations for natural convection are not sufficiently accurate for design purposes. This being the case, a Simulation Driven Design (SDD) technique was implemented whereby the commercial CFD package ANSYS CFX was utilised to simulate the coupled flow and heat transfer within a single channel of the fin bank. The physical domain in this analysis incorporates the assumed isothermal condenser section of the heat pipe(s), the metallic fin attached to the heat pipe and the section of air between the fins and surrounding the heat pipe(s). The isothermal nature of the heat pipes, the repetitive nature of the fin spacing, in combination with the geometric symmetry inherent in the circular tube structures allowed for the use of only one quarter of the overall physical model during analysis (half in the vertical direction and half in the thickness). Such simplifications of the physical model lead to large reductions in computation time. Due to the isothermal nature of heat pipes, the current analysis results were therefore used to determine the power throughput of all channels in the heat dissipating (condenser) region of the HEX. From such results, design aspects such as size and spacing of the fins and tubes were then varied to achieve the desired thermal performance. The CFD code solved the three dimensional equations for continuity, momentum and energy to simulate the thermal and flow fields for the incompressible, steady state natural convection in air model as follows: u v w 0 x y z u u u u v w x y z p x v v v p u v w x y z y w w w p u v w x y z z T T T u v w T x y z u v g In the above set of Navier-Stokes equations, u, v and w represent the x, y and z directional components of air velocity, represents the air density, p is the air pressure, is the dynamic viscosity of the air and g is the gravitational constant. w () () () () ()
6 Figure : Example of the meshed elemental structure for both the [A] air and [B] fin models. The mesh used to generate the domains for the fin and air channel are shown in fig.. Two separate models were meshed using the ANSYS.0 meshing facility and imported into ANSYS CFX as.cdb files. Holes of radius, R p,.mm (representative of where the ¾ inch copper heat pipes would be placed) were positioned at coordinates (L f /,H f /) and (L f /,H f /) in each model. For the air channel model, both the length, L f, and height, H f, of the fin model were increased by 0 percent. This was done to ensure that the analysis included heat transfer effects within the air channel which exceeded the geometry of the fin. Due to large temperature gradients in the region of the heat pipe representative section of the models, grid clustering was implemented in these regions as seen by the dense mesh surrounding the holes of each model in fig.. A separate, diametric mesh boundary region, 0 percent larger than the heat pipe hole diameter, was generated to encompass the area perpendicular to the axis of the heat pipe. The 0 percent larger circumferential lines were divided into 0 segments to facilitate a fine tetrahedral mesh, generating,00 quadrilateral elements in each model. The external edge length for the fin and air were then set to mm and mm respectively and a free quadrilateral mesh resulted in, &, quadrilaterals for the respective models. Two domains were created for this analysis, a fluid (for the air channel) and a solid (for the fin) model. The fluid model incorporated default CFX properties for air at room temperature with the exception of density. The equation for dry air density was used to generate air density as a function of temperature: Where [A] p prescribed () R T is the air density [B] p is atmospheric pressure (.0 x 0 Pa) R is the gas constant for air (.0 J/kgK) T is the temperature (K)
7 The utilization of a temperature dependent density allowed for the full buoyancy model to be incorporated into the analysis, whereby was evaluated directly for each analysis node. The reference density,, was set at.00 kg/m for the air domain. For heat transfer within the fluid domain, the built-in thermal energy model of CFX was used, as described in eq. (). The initial conditions for this domain were: P rel = 0 Pa T = 0 C For the solid domain, the default values in CFX for copper were used. The heat transfer mechanism was also set to thermal for this domain. The initial conditions for the copper fin were: T = 0 C The monte carlo radiation model was used for this analysis. Emissivity values of 0. and were used for the fin (solid domain) and air channel (fluid domain) respectively, while the diffuse fraction value was left as for both domains. Fig. indicates several boundary conditions which were applied. It indicates four axes of symmetry (two in each model view one in the central vertical plane of the side view and one in the central vertical plane of the elevation view). These are denoted by green dashed vertical lines and sym. The air not overlapping or interfacing with the solid domain, i.e. exterior to the fin channel, was also given a symmetry boundary condition, denoted by brown dotted vertical lines and Air Sym.. (L f /) L f / Adiabatic. H f H f Sym Sym Sym R p [A]. (0,0) Front View Elevation View t f t air [B] Opening Adiabatic Opening Interface Heat Adiabatic Front View Opening Heat Air Sym Air Sym Solid/Fluid Interface Elevation View Figure : [A] Side view (left) and elevation (right) of the domains in ANSYS CFX indicating the geometric values used, and [B] Side view (left) and elevation (right) of the domains indicating the various boundary conditions placed on the models prior to running the solver. The outer walls of the Air, denoted by yellow lines were given an opening boundary condition allowing fluid to cross the boundary surface in either direction. A subsonic flow regime was utilised, whereby an assumption was made that air, under natural convection, is incompressible and low-speed. The direction for flow was set normal to the boundary and a relative opening pressure of 0 Pa was used. This value was interpreted as the relative total pressure for the inflow
8 and relative static pressure for outflow at this boundary. The static boundary temperature was set at a standard room temperature of 0 C. The outer walls of the fin were given an adiabatic boundary along the thickness of the wall. In this case the heat flux across the wall boundary is zero, i.e insulated. This assumption was based on the fact that the wall thickness was significantly smaller than the other geometric values. A fixed temperature, i.e. a Heat wall boundary condition, was specified for the surface inside the thickness of both holes in the fin and air models. This was done in order to simulate the relatively isothermal nature of the heat pipes. A domain interface was required for this analysis due to the use of multiple domains (air channel and fin). In this case there was a fluid-solid interface set up. A general connection was used to connect the regions due to the non-matching grids of the two regions. A general grid interface (GGI) tool within CFX was utilised due to potentially non-matching node locations, element types and flow physics across the connection between air and fin. This connection method was selected over direct (one-to-one) connections since in fluid-solid interfaces within ANSYS CFX, the direct connection uses a non-symmetric discretisation of heat flow through the assembly of models, i.e. direct connections use more information from the more conductive side of the interface, while GGI connections sample both regions equally. Up Down Up Down Figure : Simulations for 0 C heat pipe wall temperature. Top: the temperature profile through the centre of the air channel of both up down and up down tube configurations. Bottom: Vector plot of the velocity of the air in the centre of the channel.
9 Heat Transfer (W) ACCEPTED MANUSCRIPT The product of the averaged heat flux values and the surface area of the solid-fluid interface allowed for the heat power throughput to be determined for the finned-tube channel. Multiplying this heat power by a number suitable for the number of symmetries associated with the model (i.e. if planes of symmetry were employed then the multiplier is ) yields the total heat power (W) of a single channel of the HEX. Since the condenser section of the heat pipe is assumed isothermal, this was used to determine the overall performance (in terms of heat power output) of the HEX design. The Simulation Driven Design (SDD) methodology was implemented to determine the ideal channel width and location of the heat pipes for a constrained fin dimension of cm x cm. The fin thickness was confined to 0.mm thick copper sheet in order to ensure both a robust design and to minimise the heat released from the thickness of the fin, thus allowing the adiabatic assumption/boundary condition to be applied. Fig. illustrates an example of the simulated flow and thermal fields along the centreline of the final channel arrangement for the case of a 0 C heat pipe wall temperature for both the up down and up down heat pipe configurations. The SDD process indicated that the staggered arrangement improved the net power output of the channel compared with in-line configurations due to flow blockage by the downstream tubes. Increasing the centre-to-centre distance (pitch) of the tubes tended to improve the heat transfer to a point at which the heat transfer was maximised, since as the tubes approached the outer edge of the fins, the heat spreading within the fins began to deteriorate. The simulated power throughput per channel is given in Fig. for increasing heat pipe wall temperature. It is evident that there is a near linear dependence of the heat transfer rate with wall temperature for the range of temperatures investigated. For a wall temperature of 0 C, roughly that of the source water of a GHP, the channel is predicted to dissipate about.w. Generally, 0% of the total heat transfer was predicted to be due to radiation with the remaining by buoyant natural convection. It is also evident that the up down arrangement tends to outperform the up down arrangement, albeit marginally. 0 0 Up Down Config. Up Down Config Wall Temperature ( C) Figure : Heat transfer rate versus heat pipe wall temperature for a single channel for ambient temperature of 0 C.
10 HEX FABRICATION AND TEST FACILITY Figure : Heat pipe radiator prototype A prototype heat pipe radiator was fabricated in-house and is shown in Fig.. It is the physical embodiment of what is depicted in Fig.. The convector consists of water charged heat pipes of. cm length and. cm diameter. The interior of the heat pipes are lined with wraps of MESH copper screen mesh. The heat collector end is cm long and the heat ejector ends are 0 cm long and each fitted with cm x cm copper fins of 0. mm thickness. The inner part of the pipe consisted of ml of water surrounded completely by a vacuum, with three diametric wraps of MESH copper wick structure gripping the internal surface of the hermetically sealed copper pipe. The overall volume of the HEX is.0 x 0 - m. A thermal performance test facility was constructed to evaluate the overall performance of the radiator. The main features of the test rig are illustrated in Fig.. A circulation pump draws hot water from a storage tank fitted with electrical immersion heaters. The heaters are wired to a control box that regulates the water temperature to a preset value. The volume of flow is controlled by a simple bypass valve and is measured with an inline flow meter. Flexible hoses are then fixed to the inlet and outlet fitting of the radiator being tested. Thermocouples are placed in the hot water flow at the inlet and outlet of the radiator. The power, P, dissipated by the radiator is related to the volumetric flow rate of the water and the net temperature drop across the radiator unit through the equation: where is the water density and V is the water volumetric flow rate. The figure of merit for comparing different radiators of different overall volume, V, is related to the measured power density, given by: for a given water-to-room temperature differential: () () ()
11 Hot water from boiler Radiator Recirculation Line Return Water line Control based on thermocouple at water inlet of radiator Flow Meter Figure : (Top) Schematic of thermal performance characterization test facility. (Bottom) CAD renders of the test facility. Fig. shows a thermal image of the heat pipe prototype for a water inlet temperature of 0 C. It is evident that the heat pipes distribute the heat relatively evenly along the finned tube bank which is ideal. It should be noted that the surface emissivity is non-uniform due to the manufacturing procedure and it was not feasible to paint the entire HEX. Pump Water Filter Mains Electricity PID Insulated Boiler with Heating Elements
12 Heat Transfer (W) ACCEPTED MANUSCRIPT Figure : Thermal image of heat pipe prototype radiator. The net heat transfer rate for increasing inlet water temperature for the prototype heat pipe-based domestic radiator is depicted in Fig. along with the simulation predictions for increasing heat pipe wall temperature. The experimental results include the heat transfer from the collector manifold located at the centre of the unit, which is in the region of 0 W. Taking this into account it is apparent that there is adequate agreement between the experimental results and the CFD simulations. The CFD simulations consistently under predict the heat transfer rate by about % to 0%, which is within the experimental uncertainty of the measured results Simulation Prototype Prototype excl. Manifold Wall Temperature ( C) Figure : Power output versus water inlet temperature / wall temperature comparing experimental prototype with simulations for ambient temperature of 0 C.
13 Maximum Temperature ( C) Power Density (W/m²) ACCEPTED MANUSCRIPT With regard to overall output the prototype can transfer approximately 00W at a water source temperature of 0 C increasing to 00 W for a water source temperature of 0 C. Perhaps a better measure of the performance of the prototype is to compare its power density characteristics versus a popular conventional domestic radiator. This is depicted in Fig. 0 where it is clear that with regard to power output per unit volume, the heat pipe prototype outperforms a conventional radiator by a factor of about two, which is substantial Heat Pipe Prototype Conventional Radiator Water Inlet Temperature ( C) Figure 0 Experimental results: Power density versus temperature for the heat pipe prototype and a popular off the shelf domestic radiator Time (Minutes) Conventional Radiator Heat Pipe Prototype Figure Maximum temperature versus time subsequent to an abrupt stoppage in water flow during experimentation.
14 Another novel aspect of the heat pipe design concept is that there is virtually no water within the heat dissipating region i.e. within the condenser end of the heat pipe. As a result, when the water flow is ceased and the water side thermal resistance becomes so large as to severely reduce the heat transfer capability of the HEX, the heat dissipating end cools very quickly due to the low water content of this region. This is illustrated in Fig.. Here a simple test was performed whereby the inlet valve was closed and the maximum temperature history was recorded with the thermal imaging camera. It is clear from the figure that the heat pipe prototype cools considerably faster than the popular off the shelf unit as the later includes the thermal mass of the water trapped within it which is considerable. To gauge the difference the initial 0 o C drop in temperature takes minutes in the conventional unit and only minutes with the heat pipe radiator which is a notable improvement. CONCLUSIONS AND OUTLOOK The prototype heat pipe based double convector radiator has proven the concept that using heat pipes as heat spreaders for effective heat dissipation in domestic applications has many advantage over conventional wet panel radiators, including a doubling of the power density and significantly reduced thermal mass for improved controllability. The novelty of the overall design is mainly seen in single phase extended surface designs associated with this device and the ability of the heat pipe to efficiently transport heat from the source water to the ambient environment. In the liquid (water) phase, the use of serpentine channels in order to allow a more controlled flow over the heat pipes has not been done in radiator manifold designs previously. In the gas (air) phase, the spacing between fins, fin dimensions and positioning of the pipes within the fin design, as well as the combined influence of these individual characteristics is novel in that this design uses extended surfaces to boost the heat transfer capability of the device whilst reducing the overall volume, ultimately increasing the power density beyond that seen in traditional radiator systems. Due to manufacturing constraints at the time, flat fins were fixed to the heat pipes which limit the effective heat transfer surface area on the air-side of the HEX. Alleviating this limitation by corrugating the fins thus significantly increasing the surface area within the same volume is being explored. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We gratefully acknowledge the support from Enterprise Ireland under the grant CFTD -0 -IT -. REFERENCES []. R. Rawlings, Energy Efficiency Best Practice in Housing Domestic Ground Source Heat Pumps: Design and installation of closed-loop systems March 00. Energy Saving Trust. E&OE. CE. []. ASHRAE. Systems and Equipment Handbook, American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air Conditioning Engineers,. []. CIBSE. 00. Guide A: Environmental design, th Edition London, Chartered Institution of Building Services Engineers. []. Hydronic System Design & Operation, A Guide to Heating & Cooling with Water, Erwin G Hansen, McGraw-Hill Publishing Company. []. C.J. Savage, Heat pipes and vapour chambers for satellite thermal balance. RAE Tech. Report, June.
15 []. T.D. Swanson. G.C. Birur. NASA thermal control technologies for robotic spacecraft. Applied Thermal Engineering,, (00) 0 0. []. A. Caruso, et al. Heat pipe heat storage performance. Heat Recovery Systems CHP, () () 0 0. []. B. Zalba. J.M. Marin. L.F. Cabeza. H. Mehling, Review on thermal energy storage with phase change: materials, heat transfer analysis and applications. Applied Thermal Engineering, (00). []. M.S. Sodha, N.K. Bansal, P. k. Bansal, A. Kumar, M.A.S. Malik, Solar Passive Building: Science and Design. Pergamon, Oxford,. [0]. E. Mathioulakis. V. Belessiotis, A new Heat-pipe Type Solar Domestic Hot Water System, Solar Energy, (), (00) -0. []. Q.P. Sun. X.H. Chen. J. F. Chen, The Development and Application of Solar Energy Heatpipe, Energy Technology, (), (00) 0-. []. L.L. Vasiliev, Heat pipe research and development in the USSR. Heat Recovery Systems. CHP, (), (). []. H. Jouhara, Economic Assessment of the Benefits of Wraparound Heat Pipes in Ventilation Processes for Hot and Humid Climates, International Journal of Low Carbon Technology, (), (00) -0. []. H. Jouhara, R. Meskimmon, Experimental investigation of wraparound loop heat pipe heat exchanger used in energy efficient air handling units, Energy (00), doi:0.0/j.energy []. D. Reay, P. Kew, ( th Ed.), Heat Pipes, USA: Butterworth-Heinemann.; 00 []. A. Faghri, ( st Ed.), Heat Pipe Science and Technology, Taylor & Francis,. []. Kempers, R., Robinson, A.J., Ewing, D., and Ching, C.Y., (00) Characterization of Evaporator and Condenser Thermal Resistances of a Screen Mesh Wicked Heat Pipe, International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, (-), pp []. H. Jouhara. A.J. Robinson, An experimental study of small diameter wickless heat pipes operating in the temperature range 00ºC to 0ºC, Heat Transfer Engineering, (), (00) pp []. H. Jouhara, A.J. Robinson, Experimental investigation of small diameter two-phase closed thermosyphons charged with water, FC-, FC- and FC-, Appl. Therm. Eng. (00), doi:0.0/j.applthermaleng
Compression of Fins pipe and simple Heat pipe Using CFD
 Compression of Fins pipe and simple Heat pipe Using CFD 1. Prof.Bhoodev Mudgal 2. Prof. Gaurav Bhadoriya (e-mail-devmudgal.mudgal@gmail.com) ABSTRACT The aim of this paper is to identify the advantages
Compression of Fins pipe and simple Heat pipe Using CFD 1. Prof.Bhoodev Mudgal 2. Prof. Gaurav Bhadoriya (e-mail-devmudgal.mudgal@gmail.com) ABSTRACT The aim of this paper is to identify the advantages
Numerical Studies On The Performance Of Methanol Based Air To Air Heat Pipe Heat Exchanger
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA) IJCRGG ISSN 0974-4290 Vol.5, No.2, pp 925-934, April-June 2013 ICGSEE-2013[14th 16th March 2013] International Conference on Global Scenario in Environment
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA) IJCRGG ISSN 0974-4290 Vol.5, No.2, pp 925-934, April-June 2013 ICGSEE-2013[14th 16th March 2013] International Conference on Global Scenario in Environment
CFD Analysis of temperature dissipation from a hollow metallic pipe through circular fins using Ansys 14.5
 IJAET International Journal of Application of Engineering and Technology ISSN: 2395-3594 Vol-1 No.-2 CFD Analysis of temperature dissipation from a hollow metallic pipe through circular fins using Ansys
IJAET International Journal of Application of Engineering and Technology ISSN: 2395-3594 Vol-1 No.-2 CFD Analysis of temperature dissipation from a hollow metallic pipe through circular fins using Ansys
Microstructured Heat Exchanger Pipe. for Improving Parameters of Radiator. Based on an Independent Evaporate Circuit
 Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 10, 2017, no. 5, 221-231 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ces.2017.612188 Microstructured Heat Exchanger Pipe for Improving Parameters of Radiator
Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 10, 2017, no. 5, 221-231 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ces.2017.612188 Microstructured Heat Exchanger Pipe for Improving Parameters of Radiator
APPLICATION OF MINI HEAT PIPES FOR THERMAL MANAGEMENT OF OPTO-ELECTRONIC INSTRUMENTS
 16th International Heat Pipe Conference (16th IHPC) Lyon, France, May 20-24, 2012 APPLICATION OF MINI HEAT PIPES FOR THERMAL MANAGEMENT OF OPTO-ELECTRONIC INSTRUMENTS Sandeep Kumar Singh, Sameer Khandekar
16th International Heat Pipe Conference (16th IHPC) Lyon, France, May 20-24, 2012 APPLICATION OF MINI HEAT PIPES FOR THERMAL MANAGEMENT OF OPTO-ELECTRONIC INSTRUMENTS Sandeep Kumar Singh, Sameer Khandekar
CFD Analysis of a 24 Hour Operating Solar Refrigeration Absorption Technology
 IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 11 April 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 CFD Analysis of a 24 Hour Operating Solar Refrigeration Absorption Technology
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 11 April 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 CFD Analysis of a 24 Hour Operating Solar Refrigeration Absorption Technology
Hot Reservoir Stainless-Methanol Variable Conductance Heat Pipes for Constant Evaporator Temperature in Varying Ambient Conditions
 Joint 18th IHPC and 12th IHPS, Jeju, Korea, June 12-16, 2016 Hot Reservoir Stainless-Methanol Variable Conductance Heat Pipes for Constant Evaporator Temperature in Varying Ambient Conditions Jens Weyant
Joint 18th IHPC and 12th IHPS, Jeju, Korea, June 12-16, 2016 Hot Reservoir Stainless-Methanol Variable Conductance Heat Pipes for Constant Evaporator Temperature in Varying Ambient Conditions Jens Weyant
Healthy Buildings 2017 Europe July 2-5, 2017, Lublin, Poland
 Healthy Buildings 2017 Europe July 2-5, 2017, Lublin, Poland Paper ID 0320 ISBN: 978-83-7947-232-1 The Analysis of the Air Velocity Distribution above the Trench Heater with Natural Convection Mariusz
Healthy Buildings 2017 Europe July 2-5, 2017, Lublin, Poland Paper ID 0320 ISBN: 978-83-7947-232-1 The Analysis of the Air Velocity Distribution above the Trench Heater with Natural Convection Mariusz
Heat transfer and heating rate of food stuffs in commercial shop ovens
 Sādhanā Vol. 32, Part 5, October 2007, pp. 535 544. Printed in India Heat transfer and heating rate of food stuffs in commercial shop ovens P NAVANEETHAKRISHNAN,PSSSRINIVASAN and S DHANDAPANI Department
Sādhanā Vol. 32, Part 5, October 2007, pp. 535 544. Printed in India Heat transfer and heating rate of food stuffs in commercial shop ovens P NAVANEETHAKRISHNAN,PSSSRINIVASAN and S DHANDAPANI Department
Shuzo Murakami, Shinsuke Kato, and Taeyeon Kim Institute of Industrial Science, University of Tokyo Tokyo, Japan
 INDOOR CLIMATE DESIGN BASED ON FEEDBACK CONTROL OF HVAC COUPLED SIMULATION OF CONVECTON, RADIATION, AND HVAC CONTROL FOR ATTAINING GIVEN OPERATIVE TEMPERATURE Shuzo Murakami, Shinsuke Kato, and Taeyeon
INDOOR CLIMATE DESIGN BASED ON FEEDBACK CONTROL OF HVAC COUPLED SIMULATION OF CONVECTON, RADIATION, AND HVAC CONTROL FOR ATTAINING GIVEN OPERATIVE TEMPERATURE Shuzo Murakami, Shinsuke Kato, and Taeyeon
Heat Transfer in Evacuated Tubular Solar Collectors
 Heat Transfer in Evacuated Tubular Solar Collectors Graham L. Morrison, Indra Budihardjo and Masud Behnia School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering University of New South Wales Sydney 2052 Australia
Heat Transfer in Evacuated Tubular Solar Collectors Graham L. Morrison, Indra Budihardjo and Masud Behnia School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering University of New South Wales Sydney 2052 Australia
Experimental Study on Waste Heat Recovery from the Pyrolysis Stack using Heat Pipe
 2011 International Conference on Communication Engineering and Networks IPCSIT vol.19 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Experimental Study on Waste Heat Recovery from the Pyrolysis Stack using Heat
2011 International Conference on Communication Engineering and Networks IPCSIT vol.19 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Experimental Study on Waste Heat Recovery from the Pyrolysis Stack using Heat
Simulation on Counter Flow Heat Exchanger for Indirect Evaporative Cooling Applications Avinash Pandey 1 Dr. P.K.Jhinge 2
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 07, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Simulation on Counter Flow Heat Exchanger for Indirect Evaporative Cooling Applications
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 07, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Simulation on Counter Flow Heat Exchanger for Indirect Evaporative Cooling Applications
Numerical study of heat pipe application in heat recovery systems
 Numerical study of heat pipe application in heat recovery systems *Song Lin, John Broadbent, Ryan McGlen Thermacore Europe, 12 Wansbeck Business Park Ashington, Northumberland NE3 QW, UK E-mail: song.lin@thermacore.com
Numerical study of heat pipe application in heat recovery systems *Song Lin, John Broadbent, Ryan McGlen Thermacore Europe, 12 Wansbeck Business Park Ashington, Northumberland NE3 QW, UK E-mail: song.lin@thermacore.com
Modeling and Simulation of Axial Fan Using CFD Hemant Kumawat
 Modeling and Simulation of Axial Fan Using CFD Hemant Kumawat Abstract Axial flow fans, while incapable of developing high pressures, they are well suitable for handling large volumes of air at relatively
Modeling and Simulation of Axial Fan Using CFD Hemant Kumawat Abstract Axial flow fans, while incapable of developing high pressures, they are well suitable for handling large volumes of air at relatively
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
 CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW 2. LITERATURE REVIEW 2.1 Solar dryer history Drying is a simple process of removing excess water or moisture from a product in order to reach the requirement of standard specification
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW 2. LITERATURE REVIEW 2.1 Solar dryer history Drying is a simple process of removing excess water or moisture from a product in order to reach the requirement of standard specification
Performance Comparison of Hydronic Secondary Loop Heat Pump and Conventional Air-Source Heat Pump ABSTRACT 1. INTRODUCTION
 2597, Page 1 Performance Comparison of Hydronic Secondary Loop Heat Pump and Conventional Air-Source Heat Pump Ian H. BELL 1 *, James E. BRAUN 2 1 Bell Thermal Consultants ian.h.bell@gmail.com 2 Purdue
2597, Page 1 Performance Comparison of Hydronic Secondary Loop Heat Pump and Conventional Air-Source Heat Pump Ian H. BELL 1 *, James E. BRAUN 2 1 Bell Thermal Consultants ian.h.bell@gmail.com 2 Purdue
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION. In the modern life, electronic equipments have made their way
 1 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION In the modern life, electronic equipments have made their way in to practically every part, which is from electronic gadgets to high power computers. Electronic components have
1 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION In the modern life, electronic equipments have made their way in to practically every part, which is from electronic gadgets to high power computers. Electronic components have
HOW TO REDUCE ENERGY CONSUMPTION OF BUILT-IN REFRIGERATORS?
 HOW TO REDUCE ENERGY CONSUMPTION OF BUILT-IN REFRIGERATORS? Corresponding author: Jasmin Geppert University of Bonn Household and Appliance Technology Section Nussallee 5 D-53115 Bonn E-Mail: haushaltstechnik@uni-bonn.de
HOW TO REDUCE ENERGY CONSUMPTION OF BUILT-IN REFRIGERATORS? Corresponding author: Jasmin Geppert University of Bonn Household and Appliance Technology Section Nussallee 5 D-53115 Bonn E-Mail: haushaltstechnik@uni-bonn.de
[Eswaran, 3(3): March, 2014] ISSN: Impact Factor: 1.852
![[Eswaran, 3(3): March, 2014] ISSN: Impact Factor: 1.852 [Eswaran, 3(3): March, 2014] ISSN: Impact Factor: 1.852](/thumbs/94/119309146.jpg) IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY Numerical Study on Solar Water Heater using CFD Analysis S.Eswaran *1,M.Chandru 2,M.Vairavel 3, R.Girimurugan 4 *1 Assistant professor,
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY Numerical Study on Solar Water Heater using CFD Analysis S.Eswaran *1,M.Chandru 2,M.Vairavel 3, R.Girimurugan 4 *1 Assistant professor,
Mallikarjun 1, Anandkumar S Malipatil 2
 CFD Analysis of Air Cooled Condenser by Using Copper Tubes and Aluminum Fins Mallikarjun 1, Anandkumar S Malipatil 2 Abstract--In systems involving heat transfer, a condenser is a device or unit used to
CFD Analysis of Air Cooled Condenser by Using Copper Tubes and Aluminum Fins Mallikarjun 1, Anandkumar S Malipatil 2 Abstract--In systems involving heat transfer, a condenser is a device or unit used to
Experimental investigation of Hybrid Nanofluid on wickless heat pipe heat exchanger thermal performance
 Experimental investigation of Hybrid Nanofluid on wickless heat pipe heat exchanger thermal performance #1 Jaydev S. Bade, #2 Dr. Nitin U. Korde 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Savitribai Phule
Experimental investigation of Hybrid Nanofluid on wickless heat pipe heat exchanger thermal performance #1 Jaydev S. Bade, #2 Dr. Nitin U. Korde 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Savitribai Phule
Falling Film Heat Exchangers for Solar Water Heaters
 Y.C., G.L. Morrison and M. Behnia School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering University of New South Wales Sydney 2052 AUSTRALIA E-mail: yens@student.unsw.edu.au Abstract The characteristics of
Y.C., G.L. Morrison and M. Behnia School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering University of New South Wales Sydney 2052 AUSTRALIA E-mail: yens@student.unsw.edu.au Abstract The characteristics of
INFLUENCE OF SOLAR RADIATION AND VENTILATION CONDITIONS ON HEAT BALANCE AND THERMAL COMFORT CONDITIONS IN LIVING-ROOMS
 INFLUENCE OF SOLAR RADIATION AND VENTILATION CONDITIONS ON HEAT BALANCE AND THERMAL COMFORT CONDITIONS IN LIVING-ROOMS Staņislavs GENDELIS, Andris JAKOVIČS Laboratory for mathematical modelling of environmental
INFLUENCE OF SOLAR RADIATION AND VENTILATION CONDITIONS ON HEAT BALANCE AND THERMAL COMFORT CONDITIONS IN LIVING-ROOMS Staņislavs GENDELIS, Andris JAKOVIČS Laboratory for mathematical modelling of environmental
Basic CFD model of heat pipe
 Basic CFD model of heat pipe Peter Hrabovský 1,*, Zuzana Kolková 1, Marián Mokrý 1 and Patrik Nemec 2 1 University of Zilina Reasearch Centre, Univerzitná 8215/1, 010 26 Zilina, Slovakia 2 University of
Basic CFD model of heat pipe Peter Hrabovský 1,*, Zuzana Kolková 1, Marián Mokrý 1 and Patrik Nemec 2 1 University of Zilina Reasearch Centre, Univerzitná 8215/1, 010 26 Zilina, Slovakia 2 University of
Analysis of Evaporative Cooler and Tube in Tube Heat Exchanger in Intercooling of Gas Turbine
 IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 11 April 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Analysis of Evaporative Cooler and Tube in Tube Heat Exchanger in Intercooling
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 11 April 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Analysis of Evaporative Cooler and Tube in Tube Heat Exchanger in Intercooling
FREQUENCY ENHANCEMENT OF DUAL-JUNCTION THERMOCOUPLE PROBES
 XXIII Biannual Symposium on Measuring Techniques in Turbomachinery Transonic and Supersonic Flow in FREQUENCY ENHANCEMENT OF DUAL-JUNCTION THERMOCOUPLE PROBES James Braun Purdue University Indiana, United
XXIII Biannual Symposium on Measuring Techniques in Turbomachinery Transonic and Supersonic Flow in FREQUENCY ENHANCEMENT OF DUAL-JUNCTION THERMOCOUPLE PROBES James Braun Purdue University Indiana, United
Global Journal of Engineering Science and Research Management
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THEORETICAL STUDY OF MINIATURE VAPOR COMPRESSION CYCLE USING MICROCHANNEL CONDENSER Issam M. Ali Aljubury*, Ahmed Q. Mohammed, Marwa S. Neama * Mechanical Eng. Dept. College of Engineering,
EXPERIMENTAL AND THEORETICAL STUDY OF MINIATURE VAPOR COMPRESSION CYCLE USING MICROCHANNEL CONDENSER Issam M. Ali Aljubury*, Ahmed Q. Mohammed, Marwa S. Neama * Mechanical Eng. Dept. College of Engineering,
Analysis of Constant Pressure and Constant Area Mixing Ejector Expansion Refrigeration System using R-1270 as Refrigerant
 Analysis of Constant Pressure and Constant Area Mixing Ejector Expansion Refrigeration System using R-1270 as Refrigerant Ravi Verma 1, Sharad Chaudhary 2 1, 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, IET
Analysis of Constant Pressure and Constant Area Mixing Ejector Expansion Refrigeration System using R-1270 as Refrigerant Ravi Verma 1, Sharad Chaudhary 2 1, 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, IET
Experimental Research and CFD Simulation on Microchannel Evaporator Header to Improve Heat Exchanger Efficiency
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2006 Experimental Research and CFD Simulation on Microchannel Evaporator Header
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2006 Experimental Research and CFD Simulation on Microchannel Evaporator Header
American International Journal of Research in Science, Technology, Engineering & Mathematics
 American International Journal of Research in Science, Technology, Engineering & Mathematics Available online at http://www.iasir.net ISSN (Print): 2328-3491, ISSN (Online): 2328-358, ISSN (CD-ROM): 2328-3629
American International Journal of Research in Science, Technology, Engineering & Mathematics Available online at http://www.iasir.net ISSN (Print): 2328-3491, ISSN (Online): 2328-358, ISSN (CD-ROM): 2328-3629
ENERGY SAVINGS THROUGH LIQUID PRESSURE AMPLIFICATION IN A DAIRY PLANT REFRIGERATION SYSTEM. A. Hadawey, Y. T. Ge, S. A. Tassou
 Condensers ENERGY SAVINGS THROUGH LIQUID PRESSURE AMPLIFICATION IN A DAIRY PLANT REFRIGERATION SYSTEM A. Hadawey, Y. T. Ge, S. A. Tassou 4 7 8 5 3 2 6 1 Produced by: The Centre for Energy and Built Environment
Condensers ENERGY SAVINGS THROUGH LIQUID PRESSURE AMPLIFICATION IN A DAIRY PLANT REFRIGERATION SYSTEM A. Hadawey, Y. T. Ge, S. A. Tassou 4 7 8 5 3 2 6 1 Produced by: The Centre for Energy and Built Environment
NOVEL COMPACT SORPTION GENERATORS FOR HEAT PUMP APPLICATIONS
 - 1 - NOVEL COMPACT SORPTION GENERATORS FOR HEAT PUMP APPLICATIONS S.J. Metcalf, Z. Tamainot-Telto (1) and R.E. Critoph School of Engineering, University of Warwick, Coventry CV4 7AL, UK Abstract: A new
- 1 - NOVEL COMPACT SORPTION GENERATORS FOR HEAT PUMP APPLICATIONS S.J. Metcalf, Z. Tamainot-Telto (1) and R.E. Critoph School of Engineering, University of Warwick, Coventry CV4 7AL, UK Abstract: A new
EXPLORING POSSIBILITIES WITH THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE LOOP HEAT PIPE TECHNOLOGY. Roger R. Riehl
 EXPLORING POSSIBILITIES WITH THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE LOOP HEAT PIPE TECHNOLOGY Roger R. Riehl National Institute for Space Research INPE Space Mechanics and Control Division-DMC Av dos Astronautas 1758,
EXPLORING POSSIBILITIES WITH THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE LOOP HEAT PIPE TECHNOLOGY Roger R. Riehl National Institute for Space Research INPE Space Mechanics and Control Division-DMC Av dos Astronautas 1758,
Experimental study of hybrid loop heat pipe using pump assistance for high heat flux system
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Experimental study of hybrid loop heat pipe using pump assistance for high heat flux system To cite this article: Iwan Setyawan
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Experimental study of hybrid loop heat pipe using pump assistance for high heat flux system To cite this article: Iwan Setyawan
Operation of a Two-Phase Reverse Loop Thermosyphon
 Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, Vol. 18, No. 3, pp. 259 264 (2015) DOI: 10.6180/jase.2015.18.3.06 Operation of a Two-Phase Reverse Loop Thermosyphon Meng-Chang Tsai 1, Shung-Wen Kang 2 *, Heng-Yi
Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, Vol. 18, No. 3, pp. 259 264 (2015) DOI: 10.6180/jase.2015.18.3.06 Operation of a Two-Phase Reverse Loop Thermosyphon Meng-Chang Tsai 1, Shung-Wen Kang 2 *, Heng-Yi
ZONE MODEL VERIFICATION BY ELECTRIC HEATER
 , Volume 6, Number 4, p.284-290, 2004 ZONE MODEL VERIFICATION BY ELECTRIC HEATER Y.T. Chan Department of Building Services Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China ABSTRACT Selecting
, Volume 6, Number 4, p.284-290, 2004 ZONE MODEL VERIFICATION BY ELECTRIC HEATER Y.T. Chan Department of Building Services Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China ABSTRACT Selecting
A Study of Drying Uniformity in a New Design of Tray Dryer
 52, Issue 2 (2018) 129-138 Journal of Advanced Research in Fluid Mechanics and Thermal Sciences Journal homepage: www.akademiabaru.com/arfmts.html ISSN: 2289-7879 A Study of Drying Uniformity in a New
52, Issue 2 (2018) 129-138 Journal of Advanced Research in Fluid Mechanics and Thermal Sciences Journal homepage: www.akademiabaru.com/arfmts.html ISSN: 2289-7879 A Study of Drying Uniformity in a New
STUDY ON TEMPERATURE, RH AND AIR FLOW VELOCITY DISTRIBUTION INSIDE THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT SOLAR DRYER
 STUDY ON TEMPERATURE, RH AND AIR FLOW VELOCITY DISTRIBUTION INSIDE THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT SOLAR DRYER WULANDANI, D., K. ABDULLAH, E. HARTULISTIYOSO Department of Agricultural Engineering, Faculty of Agricultural
STUDY ON TEMPERATURE, RH AND AIR FLOW VELOCITY DISTRIBUTION INSIDE THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT SOLAR DRYER WULANDANI, D., K. ABDULLAH, E. HARTULISTIYOSO Department of Agricultural Engineering, Faculty of Agricultural
CHAPTER 2 EXPERIMENTAL APPARATUS AND PROCEDURES
 CHAPTER 2 EXPERIMENTAL APPARATUS AND PROCEDURES The experimental system established in the present study to investigate the transient flow boiling heat transfer and associated bubble characteristics of
CHAPTER 2 EXPERIMENTAL APPARATUS AND PROCEDURES The experimental system established in the present study to investigate the transient flow boiling heat transfer and associated bubble characteristics of
2. HEAT EXCHANGERS MESA
 1. INTRODUCTION Multiport minichannel and microchannel aluminium tubes are becoming more popular as components in heat exchangers. These heat exchangers are used in various industrial applications and
1. INTRODUCTION Multiport minichannel and microchannel aluminium tubes are becoming more popular as components in heat exchangers. These heat exchangers are used in various industrial applications and
Experimental Investigation of a Hybrid Evacuated Tube Solar Collector
 International Conference on Mechanical, Industrial and Materials Engineering 2015 (ICMIME2015) 11-13 December, 2015, RUET, Rajshahi, Bangladesh Paper ID: ET-46 Experimental Investigation of a Hybrid Evacuated
International Conference on Mechanical, Industrial and Materials Engineering 2015 (ICMIME2015) 11-13 December, 2015, RUET, Rajshahi, Bangladesh Paper ID: ET-46 Experimental Investigation of a Hybrid Evacuated
ENSC 388: Engineering Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer
 ENSC 388: Engineering Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer Experiment 3: Free and Forced Convection Objective Determination of heat transfer coefficient for free and forced convection for different geometries.
ENSC 388: Engineering Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer Experiment 3: Free and Forced Convection Objective Determination of heat transfer coefficient for free and forced convection for different geometries.
Effect of domestic storage and cooking conditions on the risk distribution in ready to cook meat products
 Effect of domestic storage and cooking conditions on the risk distribution in ready to cook meat products Bakalis S.*, Giannakourou M.C. and Taoukis P. School of Chemical Engineering, National Technical
Effect of domestic storage and cooking conditions on the risk distribution in ready to cook meat products Bakalis S.*, Giannakourou M.C. and Taoukis P. School of Chemical Engineering, National Technical
Air Flow Study inside the Supermarket Refrigeration System
 Air Flow Study inside the Supermarket Refrigeration System Sandeep Palaksha Senior CAE Engineer Hussmann Services India LLP #9, Anand s Corner, 2 nd Floor Market Road, Netkallappa Circle Basavanagudi,
Air Flow Study inside the Supermarket Refrigeration System Sandeep Palaksha Senior CAE Engineer Hussmann Services India LLP #9, Anand s Corner, 2 nd Floor Market Road, Netkallappa Circle Basavanagudi,
TWO-PHASE MICRO-CHANNEL HEAT SINK FOR SPACE CRAFT THERMAL CONTROL
 TWO-PHASE MICRO-CHANNEL HEAT SINK FOR SPACE CRAFT THERMAL CONTROL Vance K. Hashimoto Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Hawai i at Mānoa Honolulu, HI 96822 ABSTRACT The increasing requirements
TWO-PHASE MICRO-CHANNEL HEAT SINK FOR SPACE CRAFT THERMAL CONTROL Vance K. Hashimoto Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Hawai i at Mānoa Honolulu, HI 96822 ABSTRACT The increasing requirements
EVALUATING LOOP HEAT PIPE PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENT USING CIRCUMFERENTIAL GROOVES. Nadjara dos Santos, Roger R. Riehl
 Abstract EVALUATING LOOP HEAT PIPE PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENT USING CIRCUMFERENTIAL GROOVES Nadjara dos Santos, Roger R. Riehl National Institute for Space Research INPE - Space Mechanics and Control Division-DMC
Abstract EVALUATING LOOP HEAT PIPE PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENT USING CIRCUMFERENTIAL GROOVES Nadjara dos Santos, Roger R. Riehl National Institute for Space Research INPE - Space Mechanics and Control Division-DMC
Experimental & Analytical Investigation on Modified Solar Dryer with Recirculation of Air
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 4 (2013), pp. 441-448 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Experimental & Analytical
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 4 (2013), pp. 441-448 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Experimental & Analytical
Cooling the Data Center
 Article development led by queue.acm.org doi:10.1145/1721654.1721671 What can be done to make cooling systems in data centers more energy efficient? by Andy Woods Cooling the Data Center Power generation
Article development led by queue.acm.org doi:10.1145/1721654.1721671 What can be done to make cooling systems in data centers more energy efficient? by Andy Woods Cooling the Data Center Power generation
EXPERIMENTAL AND CFD STUDIES ON SURFACE CONDENSATION
 Eighth International IBPSA Conference Eindhoven, Netherlands August 11-14, 2003 EXPERIMENTAL AND CFD STUDIES ON SURFACE CONDENSATION Liu Jing 1, Yoshihiro Aizawa 2, Hiroshi Yoshino 3 1 School of Municipal
Eighth International IBPSA Conference Eindhoven, Netherlands August 11-14, 2003 EXPERIMENTAL AND CFD STUDIES ON SURFACE CONDENSATION Liu Jing 1, Yoshihiro Aizawa 2, Hiroshi Yoshino 3 1 School of Municipal
Pressure drop analysis of evaporator using refrigerants R-22, R-404A and R-407C
 drop analysis of evaporator using refrigerants R-22, R-404A and R-407C #1 Pallavi Sawkar, #2 Dr. Pradeep Patil #12 Department of Mechanical Engineering, JSPM s JSCOE, Savitribai Phule Pune University,
drop analysis of evaporator using refrigerants R-22, R-404A and R-407C #1 Pallavi Sawkar, #2 Dr. Pradeep Patil #12 Department of Mechanical Engineering, JSPM s JSCOE, Savitribai Phule Pune University,
THERMAL PERFORMANCE OF THERMOSYPHON FOR DIFFERENT WORKING FLUIDS
 THERMAL PERFORMANCE OF THERMOSYPHON FOR DIFFERENT WORKING FLUIDS G. M. Russo a, L. Krambeck a, F. B. Nishida a, P. H. D. Santos b, and T. Antonini Alves a Universidade Tecnológica Federal do Paraná Departamento
THERMAL PERFORMANCE OF THERMOSYPHON FOR DIFFERENT WORKING FLUIDS G. M. Russo a, L. Krambeck a, F. B. Nishida a, P. H. D. Santos b, and T. Antonini Alves a Universidade Tecnológica Federal do Paraná Departamento
APPLICATION OF CFD SIMULATIONS FOR LOCATING OUTDOOR UNITS ON HIGH RISE TOWER Basant Kumar Gupta 1, Anand Patil 2
 APPLICATION OF CFD SIMULATIONS FOR LOCATING OUTDOOR UNITS ON HIGH RISE TOWER Basant Kumar Gupta 1, Anand Patil 2 1 Zeus Numerix Private Limited, Pune, India 2 Pankaj Dharkar & Associates, Mumbai, India
APPLICATION OF CFD SIMULATIONS FOR LOCATING OUTDOOR UNITS ON HIGH RISE TOWER Basant Kumar Gupta 1, Anand Patil 2 1 Zeus Numerix Private Limited, Pune, India 2 Pankaj Dharkar & Associates, Mumbai, India
Study of air circulation inside the oven by computational fluid dynamics.
 The 8 th International TIChE Conference (ITIChE 2018) "Designing Tomorrow Towards Sustainable Engineering and Technology" @A-ONE The Royal Cruise Hotel Pattaya, Thailand, November 8-9, 2018 Study of air
The 8 th International TIChE Conference (ITIChE 2018) "Designing Tomorrow Towards Sustainable Engineering and Technology" @A-ONE The Royal Cruise Hotel Pattaya, Thailand, November 8-9, 2018 Study of air
Implementation and testing of a model for the calculation of equilibrium between components of a refrigeration installation
 Implementation and testing of a model for the calculation of equilibrium between components of a refrigeration installation Marco Alexandre Onofre Dias This paper presents a model that was implemented
Implementation and testing of a model for the calculation of equilibrium between components of a refrigeration installation Marco Alexandre Onofre Dias This paper presents a model that was implemented
Analysis of Energy Consumption for Biomass Drying Process
 Environment. Technology. Resources, Rezekne, Latvia Proceedings of the 10 th International Scientific and Practical Conference. Volume II, 317-322 Analysis of Energy Consumption for Biomass Drying Process
Environment. Technology. Resources, Rezekne, Latvia Proceedings of the 10 th International Scientific and Practical Conference. Volume II, 317-322 Analysis of Energy Consumption for Biomass Drying Process
FABRICATING A HEAT PIPE STRUCTURE WITHIN A RADIATING PLATE FOR ELECTRONICS FAN-LESS COOLING
 Journal of Marine Science and Technology, Vol. 18, No. 3, pp. 419-423 (2010) 419 FABRICATING A HEAT PIPE STRUCTURE WITHIN A RADIATING PLATE FOR ELECTRONICS FAN-LESS COOLING Chun-Sheng Yu*, Shung-Wen Kang*,
Journal of Marine Science and Technology, Vol. 18, No. 3, pp. 419-423 (2010) 419 FABRICATING A HEAT PIPE STRUCTURE WITHIN A RADIATING PLATE FOR ELECTRONICS FAN-LESS COOLING Chun-Sheng Yu*, Shung-Wen Kang*,
Experimentation of Heat Pipe Used In Nano-Fluids
 Experimentation of Heat Pipe Used In Nano-Fluids 1 Prashant Shinde, 2 Vinod Shinde, 3 Rajiv Talape, 4 D.N. Korade 1,2,3,4 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sinhgad Institute of Technology & Science,
Experimentation of Heat Pipe Used In Nano-Fluids 1 Prashant Shinde, 2 Vinod Shinde, 3 Rajiv Talape, 4 D.N. Korade 1,2,3,4 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sinhgad Institute of Technology & Science,
Thermal Performance of a Loop Thermosyphon
 Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 13, No. 3, pp. 281 288 (2010) 281 Thermal Performance of a Loop Thermosyphon Shung-Wen Kang*, Meng-Chang Tsai, Chih-Sheng Hsieh and Jian-You Chen Department
Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 13, No. 3, pp. 281 288 (2010) 281 Thermal Performance of a Loop Thermosyphon Shung-Wen Kang*, Meng-Chang Tsai, Chih-Sheng Hsieh and Jian-You Chen Department
Design And Analysis Of Centrifugal Pump
 Design And Analysis Of Centrifugal Pump GUIDED BY: Assistant Professor Jayendra B. Patel PRESENTED BY: Makwana Hardik Modh Hiren Patel Gaurang Patel Dhaval 1 Introduction It Convert the mechanical energy
Design And Analysis Of Centrifugal Pump GUIDED BY: Assistant Professor Jayendra B. Patel PRESENTED BY: Makwana Hardik Modh Hiren Patel Gaurang Patel Dhaval 1 Introduction It Convert the mechanical energy
A Generalized Correlation for Pressure Drop of Refrigerant R-134a through Helical Capillary Tubes
 ISSN 2395-1621 A Generalized Correlation for Pressure Drop of Refrigerant R-134a through Helical Capillary Tubes #1 N. Dhekale, #2 Dr. P. A. Patil 1 amardhekale@gmail.com #12 Research Laboratory, Department
ISSN 2395-1621 A Generalized Correlation for Pressure Drop of Refrigerant R-134a through Helical Capillary Tubes #1 N. Dhekale, #2 Dr. P. A. Patil 1 amardhekale@gmail.com #12 Research Laboratory, Department
Numerical Stability Analysis of a Natural Circulation Steam Generator with a Non-uniform Heating Profile over the tube length
 Numerical Stability Analysis of a Natural Circulation Steam Generator with a Non-uniform Heating Profile over the tube length HEIMO WALTER Institute for Thermodynamics and Energy Conversion Vienna University
Numerical Stability Analysis of a Natural Circulation Steam Generator with a Non-uniform Heating Profile over the tube length HEIMO WALTER Institute for Thermodynamics and Energy Conversion Vienna University
THE GATE COACH All Rights Reserved 28, Jia Sarai N.Delhi-16, ,-9998
 1 P a g e 1 BASIC CONCEPTS IN HEAT TRANSFER Introduction 3 Thermodynamics vs Heat transfer 4 Essential conditions for heat transfer 4 Heat transfer mechanism 4 Thermal conductivity 7 2 CONDUCTION Steady
1 P a g e 1 BASIC CONCEPTS IN HEAT TRANSFER Introduction 3 Thermodynamics vs Heat transfer 4 Essential conditions for heat transfer 4 Heat transfer mechanism 4 Thermal conductivity 7 2 CONDUCTION Steady
Experimental Investigation of a Multi Effect Membrane Based Regenerator for High Concentration Aqueous LiCL Solution as Desiccant
 Proceedings of the World Congress on Momentum, Heat and Mass Transfer (MHMT 16) Prague, Czech Republic April 4 5, 216 Paper No. ENFHT 111 DOI: 1.11159/enfht16.111 Experimental Investigation of a Multi
Proceedings of the World Congress on Momentum, Heat and Mass Transfer (MHMT 16) Prague, Czech Republic April 4 5, 216 Paper No. ENFHT 111 DOI: 1.11159/enfht16.111 Experimental Investigation of a Multi
Influences of temperature of vapour-condenser and pressure in the vacuum chamber on the cooling rate during vacuum cooling
 Influences of temperature of vapour-condenser and pressure in the vacuum chamber on the cooling rate during vacuum cooling Tingxiang JIN,Gailian. LI,Chunxia HU School of Mechanical & Electricity engineering,zhengzhou
Influences of temperature of vapour-condenser and pressure in the vacuum chamber on the cooling rate during vacuum cooling Tingxiang JIN,Gailian. LI,Chunxia HU School of Mechanical & Electricity engineering,zhengzhou
Performance Analysis of Electronic Expansion Valve in 1 TR Window Air Conditioner using Various Refrigerants
 Performance Analysis of Electronic Expansion Valve in 1 TR Window Air Conditioner using Various Refrigerants CHENNUCHETTY CHINNARAJ * Associate Professor in Mechanical Engineering, Government College of
Performance Analysis of Electronic Expansion Valve in 1 TR Window Air Conditioner using Various Refrigerants CHENNUCHETTY CHINNARAJ * Associate Professor in Mechanical Engineering, Government College of
Study of Hot-air Recirculation around Off-road Tier-4 Diesel Engine Unit Using CFD Abbreviations Keywords Abstract Introduction and Background
 Study of Hot-air Recirculation around Off-road Tier-4 Diesel Engine Unit Using CFD Siddharth Jain, Yogesh Deshpande, Atul Bokane, Arun Kumar Santharam, and Deepak Babar, Halliburton Abbreviations: Computational
Study of Hot-air Recirculation around Off-road Tier-4 Diesel Engine Unit Using CFD Siddharth Jain, Yogesh Deshpande, Atul Bokane, Arun Kumar Santharam, and Deepak Babar, Halliburton Abbreviations: Computational
Experimental study on heat transfer characteristics of horizontal concentric tube using twisted wire brush inserts
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 416, P-ISSN 2347 5161 216 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Experimental
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 416, P-ISSN 2347 5161 216 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Experimental
Modeling of Ceiling Fan Based on Velocity Measurement for CFD Simulation of Airflow in Large Room
 Modeling of Ceiling Fan Based on Velocity Measurement for CFD Simulation of Airflow in Large Room Y. Momoi 1, K. Sagara 1, T. Yamanaka 1 and H. Kotani 1 1 Osaka University, Graduate School of Eng., Dept.
Modeling of Ceiling Fan Based on Velocity Measurement for CFD Simulation of Airflow in Large Room Y. Momoi 1, K. Sagara 1, T. Yamanaka 1 and H. Kotani 1 1 Osaka University, Graduate School of Eng., Dept.
Off Design Operation of Hybrid Noncondensable Gas Removal Systems for Flash Steam Cycle Geothermal Power Plants
 GRC Transactions, Vol. 40, 2016 Off Design Operation of Hybrid Noncondensable Gas Removal Systems for Flash Steam Cycle Geothermal Power Plants Jason Project Engineer, Vooner FloGard Corporation, Charlotte
GRC Transactions, Vol. 40, 2016 Off Design Operation of Hybrid Noncondensable Gas Removal Systems for Flash Steam Cycle Geothermal Power Plants Jason Project Engineer, Vooner FloGard Corporation, Charlotte
Improvement on the Efficiency of Condensing Units: Analysis of the AC Precooling machine. Jillian Chodak Suzanne Murphy
 Improvement on the Efficiency of Condensing Units: Analysis of the AC Precooling machine Jillian Chodak Suzanne Murphy Department of Mechanical Engineering, Tulane University, New Orleans, La May 20, 2005
Improvement on the Efficiency of Condensing Units: Analysis of the AC Precooling machine Jillian Chodak Suzanne Murphy Department of Mechanical Engineering, Tulane University, New Orleans, La May 20, 2005
International Journal of Engineering Research (IJOER) [Vol-1, Issue-3, June- 2015]
![International Journal of Engineering Research (IJOER) [Vol-1, Issue-3, June- 2015] International Journal of Engineering Research (IJOER) [Vol-1, Issue-3, June- 2015]](/thumbs/86/93674748.jpg) Experimental Investigation To Develop The Refrigeration System With Two Phases Condensing Ejector Along With Energy Saving Anjani Kumar 1, Kuldip Kumar 2, Ujjwal Kumar Nayak 3 123 Department of mechanical
Experimental Investigation To Develop The Refrigeration System With Two Phases Condensing Ejector Along With Energy Saving Anjani Kumar 1, Kuldip Kumar 2, Ujjwal Kumar Nayak 3 123 Department of mechanical
DFE T ECHNOLOGY. At Conceptronic, the design and management process for reflow soldering systems is called Dynamic Flow Engineering, or DFE.
 DFE T ECHNOLOGY As components become smaller, component mixes become more diverse, and board densities continue to increase, the processes of packaging, interconnection, and assembly are challenging the
DFE T ECHNOLOGY As components become smaller, component mixes become more diverse, and board densities continue to increase, the processes of packaging, interconnection, and assembly are challenging the
Optimization of Various Thermal Management Techniques for High Thermal Loads
 SSC10-VII-4 Optimization of Various Thermal Management Techniques for High Thermal Loads Carl Schwendeman Texas A&M University College Station, Texas;(830)-285-9646 carlsch_005@yahoo.com Rebecca Hay Texas
SSC10-VII-4 Optimization of Various Thermal Management Techniques for High Thermal Loads Carl Schwendeman Texas A&M University College Station, Texas;(830)-285-9646 carlsch_005@yahoo.com Rebecca Hay Texas
MAL-DISTRIBUTION MODEL OF HEAT EXCHANGERS IN MICRO CHANNEL EVAPORATOR
 MAL-DISTRIBUTION MODEL OF HEAT EXCHANGERS IN MICRO CHANNEL EVAPORATOR Santhosh Kumar Student(M.Tech), Mechanical Dept Gokul group of institutions Visakhapatnam, India M Karteek Naidu ASST PROFF, Mechanical
MAL-DISTRIBUTION MODEL OF HEAT EXCHANGERS IN MICRO CHANNEL EVAPORATOR Santhosh Kumar Student(M.Tech), Mechanical Dept Gokul group of institutions Visakhapatnam, India M Karteek Naidu ASST PROFF, Mechanical
Effect of the Use Pattern on Performance of Heat Pump Water Heater
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering July 2018 Effect of the Use Pattern on Performance of Heat Pump Water Heater
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering July 2018 Effect of the Use Pattern on Performance of Heat Pump Water Heater
International Forum on Energy, Environment Science and Materials (IFEESM 2015)
 The Comparison and Analysis of Humidity Environment between Floor and Ceiling Radiant Cooling Systems that Combined with Displacement Ventilation Kai SUN 1 a *, Chuan-hui ZHOU 1 1 College of Urban Construction,
The Comparison and Analysis of Humidity Environment between Floor and Ceiling Radiant Cooling Systems that Combined with Displacement Ventilation Kai SUN 1 a *, Chuan-hui ZHOU 1 1 College of Urban Construction,
Experimental Investigation of Tube Configuration for a Surface Condenser
 Experimental Investigation of Tube Configuration for a Surface Condenser Shrikant Subhash Chaudhari 1, T Mahender 2, Subramanyam Pavuluri 3 PG Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, MLR Institute
Experimental Investigation of Tube Configuration for a Surface Condenser Shrikant Subhash Chaudhari 1, T Mahender 2, Subramanyam Pavuluri 3 PG Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, MLR Institute
Internal flow Patterns of the Horizontal Heat Mode Closed-Loop Oscillating Heat Pipe with Check Valves (HHMCLOHP/CV)
 Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 5(3): 865-869, 2013 ISSN: 2040-7459; E-ISSN: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2013 Submitted: June 13, 2012 Accepted: July 09,
Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 5(3): 865-869, 2013 ISSN: 2040-7459; E-ISSN: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2013 Submitted: June 13, 2012 Accepted: July 09,
Performance of Water-in-Glass Evacuated Tube Solar Water Heaters
 Performance of Water-in-Glass Evacuated Tube Solar Water Heaters I. and G.L.Morrison School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering University of New South Wales Sydney 2052 AUSTRALIA E-mail: g.morrison@unsw.edu.au
Performance of Water-in-Glass Evacuated Tube Solar Water Heaters I. and G.L.Morrison School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering University of New South Wales Sydney 2052 AUSTRALIA E-mail: g.morrison@unsw.edu.au
PERFORMANCE OF A MODEL IN-LINE VORTEX SEPARATOR. Keng-Choon Lee Geothermal Institute, The University of Auckland, Private Bag 92019, Auckland, New
 PERFORMANCE OF A MODEL IN-LINE VORTEX SEPARATOR Keng-Choon Lee Geothermal Institute, The University of Auckland, Private Bag 92019, Auckland, New Key words: Separator, condensate removal, two-phase flow
PERFORMANCE OF A MODEL IN-LINE VORTEX SEPARATOR Keng-Choon Lee Geothermal Institute, The University of Auckland, Private Bag 92019, Auckland, New Key words: Separator, condensate removal, two-phase flow
EFFECT OF PAG OIL CIRCULATION RATE ON THE HEAT TRANSFER PERFORMANCE OF AIR-COOLED HEAT EXCHANGER IN CARBON DIOXIDE HEAT PUMP SYSTEM
 - 1 - EFFECT OF PAG OIL CIRCULATION RATE ON THE HEAT TRANSFER PERFORMANCE OF AIR-COOLED HEAT EXCHANGER IN CARBON DIOXIDE HEAT PUMP SYSTEM Shun YOSHIOKA, Hyunyoung KIM, Kazushige KASAI, Daikin Industries,
- 1 - EFFECT OF PAG OIL CIRCULATION RATE ON THE HEAT TRANSFER PERFORMANCE OF AIR-COOLED HEAT EXCHANGER IN CARBON DIOXIDE HEAT PUMP SYSTEM Shun YOSHIOKA, Hyunyoung KIM, Kazushige KASAI, Daikin Industries,
ijcrr Vol 04 issue 07 Category: Research Received on:06/02/12 Revised on:17/02/12 Accepted on:02/03/12
 EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF THE EFFECT OF FIN GEOMETRY ON HEAT TRANSFER RATE THROUGH THE REFRIGERATOR CONDENSER ijcrr Vol 04 issue 07 Category: Research Received on:06/02/12 Revised on:17/02/12 Accepted on:02/03/12
EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF THE EFFECT OF FIN GEOMETRY ON HEAT TRANSFER RATE THROUGH THE REFRIGERATOR CONDENSER ijcrr Vol 04 issue 07 Category: Research Received on:06/02/12 Revised on:17/02/12 Accepted on:02/03/12
Healthy Buildings 2017 Europe July 2-5, 2017, Lublin, Poland
 Healthy Buildings 2017 Europe July 2-5, 2017, Lublin, Poland Paper ID 0188 ISBN: 978-83-7947-232-1 Dispersion of pollutants released at floor level under three types of heating systems: A CFD study. Laura
Healthy Buildings 2017 Europe July 2-5, 2017, Lublin, Poland Paper ID 0188 ISBN: 978-83-7947-232-1 Dispersion of pollutants released at floor level under three types of heating systems: A CFD study. Laura
Effect of Flow Distortion in Inlet Duct on the Performance of Centrifugal Blower
 Effect of Flow Distortion in Inlet Duct on the Performance of Centrifugal Blower Kalpesh W. Shirsath 1, S.R. Patil 2, Sumit M. Naik 3 PG Student 1,3, Assistant Professor 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering
Effect of Flow Distortion in Inlet Duct on the Performance of Centrifugal Blower Kalpesh W. Shirsath 1, S.R. Patil 2, Sumit M. Naik 3 PG Student 1,3, Assistant Professor 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering
Characterization of a Heat Sink with Embedded Heat Pipe with Variable Heat Dissipating Source Placement for Power Electronics Applications
 Characterization of a Heat Sink with Embedded Heat Pipe with Variable Heat Dissipating Source Placement for Power Electronics Applications Neda Mansouri, Cliff Weasner and Ahmed Zaghlol Mersen Canada Toronto
Characterization of a Heat Sink with Embedded Heat Pipe with Variable Heat Dissipating Source Placement for Power Electronics Applications Neda Mansouri, Cliff Weasner and Ahmed Zaghlol Mersen Canada Toronto
4th International Conference on Sensors, Measurement and Intelligent Materials (ICSMIM 2015)
 4th International Conference on Sensors, Measurement and Intelligent Materials (ICSMIM 2015) Multi-stage Series Heat Pump Drying System with Dehumidification Simulation and Experiment Verification Chao
4th International Conference on Sensors, Measurement and Intelligent Materials (ICSMIM 2015) Multi-stage Series Heat Pump Drying System with Dehumidification Simulation and Experiment Verification Chao
Heat Transfer Enhancement using Herringbone wavy & Smooth Wavy fin Heat Exchanger for Hydraulic Oil Cooling
 Enhancement using Herringbone wavy & Smooth Wavy fin Exchanger for Hydraulic Oil Cooling 1 Mr. Ketan C. Prasadi, 2 Prof. A.M. Patil 1 M.E. Student, P.V.P.I.T.,Budhagaon,Sangli AP-India 2 Associate Professor,
Enhancement using Herringbone wavy & Smooth Wavy fin Exchanger for Hydraulic Oil Cooling 1 Mr. Ketan C. Prasadi, 2 Prof. A.M. Patil 1 M.E. Student, P.V.P.I.T.,Budhagaon,Sangli AP-India 2 Associate Professor,
COMPARING AIR COOLER RATINGS PART 1: Not All Rating Methods are Created Equal
 By Bruce I. Nelson, P.E., President, Colmac Coil Manufacturing, Inc. COMPARING AIR COOLER RATINGS PART 1: Not All Rating Methods are Created Equal Summary Refrigeration air coolers (evaporators) are widely
By Bruce I. Nelson, P.E., President, Colmac Coil Manufacturing, Inc. COMPARING AIR COOLER RATINGS PART 1: Not All Rating Methods are Created Equal Summary Refrigeration air coolers (evaporators) are widely
Experimental Studies on Aero Profile Thermosyphon Solar Water Heating System
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 9, Number 1 (2016), pp. 89-94 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Experimental Studies on
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 9, Number 1 (2016), pp. 89-94 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Experimental Studies on
A Simulation Study on the Energy Efficiency of Gas-Burned Boilers in Heating Systems
 International Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 2015; 4(6): 327-332 Published online December 5, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijepe) doi: 10.11648/j.ijepe.20150406.11 ISSN: 2326-957X
International Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 2015; 4(6): 327-332 Published online December 5, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijepe) doi: 10.11648/j.ijepe.20150406.11 ISSN: 2326-957X
Open and Closed Door Moisture Transport and Corresponding Energy Consumption in Household Refrigerator
 18 R. Saidur et al./journal of Energy & Environment, Vol. 6, May 2007 Open and Closed Door Moisture Transport and Corresponding Energy Consumption in Household Refrigerator R. Saidur, M. A. Sattar, M.
18 R. Saidur et al./journal of Energy & Environment, Vol. 6, May 2007 Open and Closed Door Moisture Transport and Corresponding Energy Consumption in Household Refrigerator R. Saidur, M. A. Sattar, M.
Performance Analysis of a Thin Tube Water Heater for Egerton University Using Comsol
 Performance Analysis of a Thin Tube Water Heater for Egerton University Using Comsol Dr. Owino, George Omollo 1, Isiah Otieno Onditi 2, Lecturer, Department of Industrial and Energy Engineering, Egerton
Performance Analysis of a Thin Tube Water Heater for Egerton University Using Comsol Dr. Owino, George Omollo 1, Isiah Otieno Onditi 2, Lecturer, Department of Industrial and Energy Engineering, Egerton
Performance of an Improved Household Refrigerator/Freezer
 Performance of an Improved Household Refrigerator/Freezer D. O. Ariyo Department of Mechanical Engineering, School of Engineering, Federal Polytechnic, Offa, Nigeria Y. L. Shuaib-Babata Department of Mechanical
Performance of an Improved Household Refrigerator/Freezer D. O. Ariyo Department of Mechanical Engineering, School of Engineering, Federal Polytechnic, Offa, Nigeria Y. L. Shuaib-Babata Department of Mechanical
The Experimental Validation of Numerical Modeling of the Air Distribution in the Indoor Ice Rink Arena
 Proceedings of the World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM 2015) Barcelona, Spain July 20-21, 2015 Paper No. 276 The Experimental Validation of Numerical Modeling of the Air
Proceedings of the World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM 2015) Barcelona, Spain July 20-21, 2015 Paper No. 276 The Experimental Validation of Numerical Modeling of the Air
Performance Analysis of Heat Pipe using Different Screen Mesh Sizes Manikandan.K * 1, Senthilkumar.R 2,
 Performance Analysis of Heat Pipe using Different Screen Mesh Sizes Manikandan.K * 1, Senthilkumar.R 2, 1, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Annamalai University, India, Abstract
Performance Analysis of Heat Pipe using Different Screen Mesh Sizes Manikandan.K * 1, Senthilkumar.R 2, 1, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Annamalai University, India, Abstract
Finned Heat Sinks for Cooling Outdoor Electronics under Natural Convection
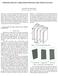 Finned s for Cooling Outdoor Electronics under Natural Convection Lian-Tuu Yeh, Ph D & PE Thermal Consultant, Dallas, TX, 75252 USA Abstract For tower or poled mounted electronics, the heat sink weight
Finned s for Cooling Outdoor Electronics under Natural Convection Lian-Tuu Yeh, Ph D & PE Thermal Consultant, Dallas, TX, 75252 USA Abstract For tower or poled mounted electronics, the heat sink weight
Virtual Household Refrigerators at Steady-State and Transient Conditions. Numerical Model and Experimental Validation.
 Virtual Household Refrigerators at Steady-State and Transient Conditions. Numerical Model and Experimental Validation. Nicolás ABLANQUE, Carles OLIET, Joaquim RIGOLA, Carlos-David PEREZ-SEGARRA Universitat
Virtual Household Refrigerators at Steady-State and Transient Conditions. Numerical Model and Experimental Validation. Nicolás ABLANQUE, Carles OLIET, Joaquim RIGOLA, Carlos-David PEREZ-SEGARRA Universitat
Available online at ScienceDirect. Energy Procedia 78 (2015 ) th International Building Physics Conference, IBPC 2015
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 7 (215 ) 67 72 6th International Building Physics Conference, IBPC 215 Effect of attic insulation thickness and solar gain in a mild
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 7 (215 ) 67 72 6th International Building Physics Conference, IBPC 215 Effect of attic insulation thickness and solar gain in a mild
Design and Optimization of Domestic Solar Dryer
 Science Journal of Energy Engineering 2017; 5(6): 130-135 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/sjee doi: 10.11648/j.sjee.20170506.11 ISSN: 2376-810X (Print); ISSN: 2376-8126 (Online) Review Article
Science Journal of Energy Engineering 2017; 5(6): 130-135 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/sjee doi: 10.11648/j.sjee.20170506.11 ISSN: 2376-810X (Print); ISSN: 2376-8126 (Online) Review Article
