S2 Science. Heat. Homework Booklet
|
|
|
- Miles Austin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 S2 Science Heat Homework Booklet 1
2 1. The graph below shows how most substances cool after being taken away from the source of heat. Answer these questions about the graph a. where is the heat loss the greatest: A, B, C or D? b. What is the temperature at point C? c. What is the room temperature? d. What is happening at points A, B, C, and D? e. Draw a simple cooling graph like this graph. Add two more cooling lines with the following characteristics: i. same starting temperature, higher room temperature ii. higher starting temperature, lower room temperature. 2
3 3. These two beakers were both filled with water at 80 o C and left to cool down in a room at 20 o C. a. What temperature will both beakers eventually end up at? b. What beaker will cool down the fastest? c. Draw a temperature / time graph like the one in question 1 above. You will need two lines one for each beaker. 4. Do houses lose heat faster in the winter or summer? a. Explain your answer. b. Explain how this affects the heating bills. 3
4 5. Describe then explain what you see when two metal rods are heated. 6. In terms of particles explain how the heat travels through solids. 7. Copy and complete the table below to show how metals are used in the home because they are good conductors. 4
5 8. Look at these items used in the house Work out what job each article is used for and write your ideas into a table using these headings: Name Table matt What it is made of Conductor or Insulator What is its job To stop heat from hot plates damaging the table. 5
6 9. Choose the most suitable material from the list below for each of these jobs. Explain your answer. copper polystyrene glass aluminium wood air iron fibre glass a. a beaker to keep a drink warm for longest. b. a base for a saucepan c. a handle for a saucepan d. a material for insulating the roof of a house. 10. Use these pieces of apparatus to draw a diagram showing the experiment you did to demonstrate convection currents. Remember to show the convection current as shown up by the dye. 6
7 11. Why do electric kettles have the heating element placed at the bottom? 12. Copy this diagram of a kettle and add arrows to show the convection currents. 13. Why is the outlet pipe at the top of a water tank? 14. Why is the freezing compartment of a fridge at the top of the fridge? 15. Why is it not vital to have the top of a chest freezer closed all the time? 16. What is the main difference between conduction and convection? 7
8 17. Give another name for heat rays. 18. Copy the diagram and draw the direction of heat movement from the Sun to the Earth. 19. If hot water was poured into each flask which flask cools down the fastest? a. How did the flasks lose the heat energy? b. Where did the energy go? 20. What should be made the same to make this a fair comparison? 21. Describe how these flasks could be used to prove that black is a better absorber of heat rays than shiny surfaces. What extra equipment would you need? 8
9 22. On sunny days drivers put a shield up inside the windscreen explain how the shield helps keep the car cool. 23. In sunny countries food can be cooked in a solar cooker. Draw a diagram to show how the solar cooker works. 24. Explain in terms of heat rays why fire fighters wear silver suits. 9
10 25. Explain how the Thermos flask prevents heat loss by: a. convection b. conduction c. radiation. d. Why is a Thermos flask good at keeping drinks cold as well as hot? 26) Design a container that could be used to carry hot fish and chips from a chip shop to your home without them going cold. Draw a diagram of your design and label any special features. Explain why you have put these features into your design. 10
11 27) Look at this diagram of heat loss from a house a) Ask your teacher for a piece or graph paper and draw a bar graph to show how much heat is lost through each part. b) Describe what you could do to reduce each of the heat losses shown. 28) Explain each of the following statements. a) Houses in hot countries are usually painted white. b) Car radiators are painted matt black. c) Anyone standing near a bonfire feels a draught. d) If you stand in front of an open refrigerator you get cold feet. e) Birds fluff up their feathers in winter. 11
12 28) The diagram bellow shows a house designed to save as much heat energy as possible. The labels indicate features of the house that help in this energy saving. a) Explain how each of the six features shown in the diagram helps save heat energy. b) Some of the energy saving features are more expensive to install than others. The table shows roughly how long it takes before they pay for themselves and start to show a profit. c) Which energy saving feature is the most cost effective? 12
13 d) Which energy saving feature is the least cost effective? e) Solar (sunlight) energy is free. Suggest why it takes so long for a house owner living in Scotland to recover the cost of installing solar panels. f) People living in houses close to airports don t just fit double glazing to reduce heat loss. Give one other advantage of fitting double glazing. 29) Explain each of the following statements. a) A saucepan has a copper bottom but a plastic handle. b) Someone feels cold in a string vest, but warm if they wear a tight shirt over it. c) It is safer picking up a hot dish with a dry cloth than a wet one. d) Hot water tanks have a heater fitted at the bottom rather than the top. e) Seeds germinate (start to grow) earlier in soil that is covered with black plastic sheeting. f) Divers stay warm in cold water by wearing a wetsuit water is trapped between the rubber suit and the diver s skin. g) Paper decorations flutter if they are put on a wall above a hot room heater. h) Glider pilots can gain height by flying over large ploughed fields. 13
(a) (i) Through which part of the house is most heat lost? How can the heat loss through the windows be reduced? ...
 Q1. The diagram shows where heat is lost from a house that is not insulated. (a) (i) Through which part of the house is most heat lost? (ii) How can the heat loss through the windows be reduced? (b) A
Q1. The diagram shows where heat is lost from a house that is not insulated. (a) (i) Through which part of the house is most heat lost? (ii) How can the heat loss through the windows be reduced? (b) A
ISLAMAYA ENGLISH SCHOOL
 1 (a) Some water is poured onto a plastic table-top, forming a puddle. The same volume of water is poured into a plastic dish, which is placed alongside the puddle. This is illustrated in Fig. 7.1. water
1 (a) Some water is poured onto a plastic table-top, forming a puddle. The same volume of water is poured into a plastic dish, which is placed alongside the puddle. This is illustrated in Fig. 7.1. water
IGCSE PHYSICS GRADE 11 TERM 1 ASSESSMENT BOOKLET
 PHYSICS IGCSE PHYSICS GRADE 11 TERM 1 ASSESSMENT BOOKLET 2013-2014 STS Page 1 of 44 PHYSICS PHYSI1101 ASSESSMENT TASK COVER PAGE Topic STS Performance Criteria Assessment event Date Time Thermal Physics
PHYSICS IGCSE PHYSICS GRADE 11 TERM 1 ASSESSMENT BOOKLET 2013-2014 STS Page 1 of 44 PHYSICS PHYSI1101 ASSESSMENT TASK COVER PAGE Topic STS Performance Criteria Assessment event Date Time Thermal Physics
Q1. The diagram shows the design of a solar cooker. The cooker heats water using infrared radiation from the Sun.
 Q. The diagram shows the design of a solar cooker. The cooker heats water using infrared radiation from the Sun. (a) Why is the inside of the large curved dish covered with shiny metal foil? () (b) Which
Q. The diagram shows the design of a solar cooker. The cooker heats water using infrared radiation from the Sun. (a) Why is the inside of the large curved dish covered with shiny metal foil? () (b) Which
Infra-Red Radiation. Question Paper. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision. Exam Board. Page 1. Score: /68. Percentage: /100
 Infra-Red Radiation Question Paper Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Physics AQA P1 Infra-Red Radiation Silver Level Question Paper Time Allowed: 68 minutes Score: /68 Percentage:
Infra-Red Radiation Question Paper Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Physics AQA P1 Infra-Red Radiation Silver Level Question Paper Time Allowed: 68 minutes Score: /68 Percentage:
Temperature & Heat Heat is a type of energy. It is measured in joules (J).
 Temperature & Heat Heat is a type of energy. It is measured in joules (J). Temperature is a measure of how hot or cold something is. It is measured in degrees Celsius ( C). Heat energy travels from hot
Temperature & Heat Heat is a type of energy. It is measured in joules (J). Temperature is a measure of how hot or cold something is. It is measured in degrees Celsius ( C). Heat energy travels from hot
When both switches are on, the heater works at the high power setting. What is the power of the heater when it is switched to the high power setting?
 1 (a) The diagram shows two switches on a room heater. The heater has three power settings. The power produced by two of the settings is given in the table. Setting Power in kw Low 0.5 Medium 1.5 High
1 (a) The diagram shows two switches on a room heater. The heater has three power settings. The power produced by two of the settings is given in the table. Setting Power in kw Low 0.5 Medium 1.5 High
St. Anthony's Canossian Secondary School Sec 3E Science (Physics) Chapter 9 Transfer of Thermal Energy. Name: ( ) Class: Sec Date:
 St. Anthony's Canossian Secondary School Sec 3E Science (Physics) Chapter 9 Transfer of Thermal Energy Name: ( ) Class: Sec Date: Candidates should be able to: (a) show understanding that thermal energy
St. Anthony's Canossian Secondary School Sec 3E Science (Physics) Chapter 9 Transfer of Thermal Energy Name: ( ) Class: Sec Date: Candidates should be able to: (a) show understanding that thermal energy
ST. GABRIEL S SECONDARY SCHOOL Lower Secondary Science Chapter 7 Transfer of Thermal Energy
 ST. GRIEL S SEONRY SHOOL Lower Secondary Science hapter 7 Transfer of Thermal Energy Worksheet 7.1 Name : _Suggested nswers ( ) lass : ate : Section : Multiple hoice Questions 1 Two similarly-sized blocks,
ST. GRIEL S SEONRY SHOOL Lower Secondary Science hapter 7 Transfer of Thermal Energy Worksheet 7.1 Name : _Suggested nswers ( ) lass : ate : Section : Multiple hoice Questions 1 Two similarly-sized blocks,
Describe the movement of the particles of helium gas inside the balloon (2)
 The figure below shows a balloon filled with helium gas. (a) Describe the movement of the particles of helium gas inside the balloon............. (2) (b) What name is given to the total kinetic energy
The figure below shows a balloon filled with helium gas. (a) Describe the movement of the particles of helium gas inside the balloon............. (2) (b) What name is given to the total kinetic energy
St. Anthony's Canossian Secondary School Sec 3NA Science (Physics) Chapter 7 Transfer of Thermal Energy. Name: ( ) Class: Sec Date:
 St. Anthony's Canossian Secondary School Sec 3NA Science (Physics) Chapter 7 Transfer of Thermal Energy Name: ( ) Class: Sec Date: Candidates should be able to: (a) show understanding that thermal energy
St. Anthony's Canossian Secondary School Sec 3NA Science (Physics) Chapter 7 Transfer of Thermal Energy Name: ( ) Class: Sec Date: Candidates should be able to: (a) show understanding that thermal energy
Heat and temperature. Making a thermometer
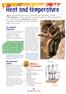 Heat and temperature A bout four hundred years ago, it would have been impossible to tell the temperature of the air, the water or any other substance. That s because there was no such thing as a thermometer
Heat and temperature A bout four hundred years ago, it would have been impossible to tell the temperature of the air, the water or any other substance. That s because there was no such thing as a thermometer
What percentage of infra red is absorbed by the glass? increases. does not change. decreases. Blacksurfaces are poor emitters of infra red radiation.
 Q1. (a) Infra red radiation can be reflected, absorbed and transmitted by glass. (i) What percentage of infra red is absorbed by the glass?... (ii) Complete the following sentence by drawing a ring around
Q1. (a) Infra red radiation can be reflected, absorbed and transmitted by glass. (i) What percentage of infra red is absorbed by the glass?... (ii) Complete the following sentence by drawing a ring around
Transfer of Heat. There are three ways in which heat is transferred from one body to another. These are
 Transfer of Heat In the precious chapter you have learnt that heat flows from a body at a higher temperature to a body at a lower temperature, but how does this transfer take place? You will find the answer
Transfer of Heat In the precious chapter you have learnt that heat flows from a body at a higher temperature to a body at a lower temperature, but how does this transfer take place? You will find the answer
Heat Transfer. Heat Transfer. Thermal Equilibrium. Thermal Inequilibrium
 Heat Transfer, Radiation Convection and Heat Transfer Heat is a form of energy. Heat travels from higher temperature(hotter) region to lower temperature(cooler) region. Two bodies are in thermal equilibrium
Heat Transfer, Radiation Convection and Heat Transfer Heat is a form of energy. Heat travels from higher temperature(hotter) region to lower temperature(cooler) region. Two bodies are in thermal equilibrium
A student investigated how much energy from the Sun was incident on the Earth s surface at her location.
 A student investigated how much energy from the Sun was incident on the Earth s surface at her location. She put an insulated pan of water in direct sunlight and measured the time it took for the temperature
A student investigated how much energy from the Sun was incident on the Earth s surface at her location. She put an insulated pan of water in direct sunlight and measured the time it took for the temperature
Thermal Energy. Conduction, Convection, and Radiation. Before You Read. Read to Learn. Conduction. section 2
 chapter 5 Thermal Energy section 2 Conduction, Convection, and What You ll Learn the three ways heat is transferred the difference between insulators and conductors how insulators control the transfer
chapter 5 Thermal Energy section 2 Conduction, Convection, and What You ll Learn the three ways heat is transferred the difference between insulators and conductors how insulators control the transfer
I. C O N T E N T S T A N D A R D S
 Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course I. C O N T E N T S T A N D A R D S and radiation between objects or regions that are at different temperatures. 3.1 Explain
Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course I. C O N T E N T S T A N D A R D S and radiation between objects or regions that are at different temperatures. 3.1 Explain
Q1. The diagram shows an experiment to find out what happens to infrared waves when they strike different surfaces.
 Q1. The diagram shows an experiment to find out what happens to infrared waves when they strike different surfaces. (a) The water in the black tube gets hotter than the water in the shiny tube. Choose
Q1. The diagram shows an experiment to find out what happens to infrared waves when they strike different surfaces. (a) The water in the black tube gets hotter than the water in the shiny tube. Choose
liquid heating The density of the liquid changes as its temperature increases. This causes energy to be transferred throughout the liquid.
 1 liquid is heated in a beaker. liquid heating The density of the liquid changes as its temperature increases. This causes energy to be transferred throughout the liquid. How does the density change and
1 liquid is heated in a beaker. liquid heating The density of the liquid changes as its temperature increases. This causes energy to be transferred throughout the liquid. How does the density change and
Science 7 Chapter 6 Section 1
 Science 7 Chapter 6 Section 1 Processes of Transferring Heat Processes of Heat Transfer There are 3 processes responsible for heat transfer: 1) Conduction 2) Convection 3) Radiation 1 Conduction Conduction:
Science 7 Chapter 6 Section 1 Processes of Transferring Heat Processes of Heat Transfer There are 3 processes responsible for heat transfer: 1) Conduction 2) Convection 3) Radiation 1 Conduction Conduction:
HEAT TRANSFER. The tips of both brass rods are held in the gas flame. Mark each of the following as True or False.
 HEAT TRANSFER Refer to the following information for the next four questions. The tips of both brass rods are held in the gas flame. Mark each of the following as or. 1. Heat is conducted only along Rod
HEAT TRANSFER Refer to the following information for the next four questions. The tips of both brass rods are held in the gas flame. Mark each of the following as or. 1. Heat is conducted only along Rod
Directions: Read/complete the following sections on the Transfer of Thermal Energy
 Name: _ Period: Date: _ Notes: Thermal Energy Transfers Directions: Read/complete the following sections on the Transfer of Thermal Energy Conduction Heat is transmitted by conduction, convection and radiation.
Name: _ Period: Date: _ Notes: Thermal Energy Transfers Directions: Read/complete the following sections on the Transfer of Thermal Energy Conduction Heat is transmitted by conduction, convection and radiation.
2018 Year 11 Physics Week 8. Thermal Energy Transfer
 2018 Year 11 Physics Week 8 Thermal Energy Transfer Thermal energy Thermal or heat energy is the energy that flows from a hot region to a cold region by one or more of the processes of: CONDUCTION CONVECTION
2018 Year 11 Physics Week 8 Thermal Energy Transfer Thermal energy Thermal or heat energy is the energy that flows from a hot region to a cold region by one or more of the processes of: CONDUCTION CONVECTION
Fundamentals of Heat Transfer
 Fundamentals of Heat Transfer State basic laws of heat transfer Estimate heat transfer rates by different modes Use the concept of thermal resistance to solve steady state heat transfer problems State
Fundamentals of Heat Transfer State basic laws of heat transfer Estimate heat transfer rates by different modes Use the concept of thermal resistance to solve steady state heat transfer problems State
Different energy sources can be used to generate electricity.
 Q1. Electricity is a useful form of energy. (a) Different energy sources can be used to generate electricity. Give one advantage and one disadvantage (other than cost) of using each energy source to generate
Q1. Electricity is a useful form of energy. (a) Different energy sources can be used to generate electricity. Give one advantage and one disadvantage (other than cost) of using each energy source to generate
2 Thermal Physics. Thermal Physics. 1. Simple kinetic molecular model of matter 2. Thermal properties 3. Transfer of thermal energy
 2 Thermal Physics 1. Simple kinetic molecular model of matter 2. Thermal properties 3. Transfer of thermal energy 1. A swimmer climbs out of a swimming pool on a warm, dry day. Almost immediately he begins
2 Thermal Physics 1. Simple kinetic molecular model of matter 2. Thermal properties 3. Transfer of thermal energy 1. A swimmer climbs out of a swimming pool on a warm, dry day. Almost immediately he begins
7 In the process of convection, heat energy is transferred C D E. 9 Boiling water and ice can exist at the same time in a test tube.
 TOPI 9 Transfer of Thermal Energy 1 How may heat be transferred through a vacuum? by convection only by radiation only by conduction only by convection and radiation only E by conduction. convection and
TOPI 9 Transfer of Thermal Energy 1 How may heat be transferred through a vacuum? by convection only by radiation only by conduction only by convection and radiation only E by conduction. convection and
Changes of State. Lesson 1
 Lesson 1 Changes of State If all the ice in the world melted, the oceans would rise by more than 65 meters (215 feet)! This iceberg is melting in Paraiso Bay, Antarctica. What happens to ice when it melts?
Lesson 1 Changes of State If all the ice in the world melted, the oceans would rise by more than 65 meters (215 feet)! This iceberg is melting in Paraiso Bay, Antarctica. What happens to ice when it melts?
energy from hot flame [3] [2]
![energy from hot flame [3] [2] energy from hot flame [3] [2]](/thumbs/79/79286354.jpg) 1 This question is about energy transfer and how it is used in cooking. (a) Steve heats a pan of water on his cooker. Look at the diagram. water aluminium base energy from hot flame (i) Explain how the
1 This question is about energy transfer and how it is used in cooking. (a) Steve heats a pan of water on his cooker. Look at the diagram. water aluminium base energy from hot flame (i) Explain how the
Figure 1 shows a black metal casserole dish that is put inside a hot oven. Food is cooked inside the casserole dish.
 1 Figure 1 shows a black metal casserole dish that is put inside a hot oven. Food is cooked inside the casserole dish. (a) Energy is transferred quickly from the inside of the hot oven, through the metal
1 Figure 1 shows a black metal casserole dish that is put inside a hot oven. Food is cooked inside the casserole dish. (a) Energy is transferred quickly from the inside of the hot oven, through the metal
UNIQUE SCIENCE ACADEMY
 1 (a) UNIQUE SIENE EMY Test (Unit 12) Name :... Paper: Physics ate :... lass: 1 Time llowed: 35Minutes Maximum Marks: 25 Theory Section: [Total 16 Marks] Fig. 1.1 shows a beaker in which coffee is served
1 (a) UNIQUE SIENE EMY Test (Unit 12) Name :... Paper: Physics ate :... lass: 1 Time llowed: 35Minutes Maximum Marks: 25 Theory Section: [Total 16 Marks] Fig. 1.1 shows a beaker in which coffee is served
The table gives information about some ways of reducing the energy consumption in a house. Installation cost in. Fit a new hot water boiler
 ## (a) The table gives information about some ways of reducing the energy consumption in a house. Method of reducing energy consumption Installation cost in Annual saving on energy bills in Fit a new hot
## (a) The table gives information about some ways of reducing the energy consumption in a house. Method of reducing energy consumption Installation cost in Annual saving on energy bills in Fit a new hot
Heat can change into other forms of energy and vice versa. Heat is measured in the unit of energy, the joule (J).
 ExamLearn.ie Heat Heat Heat has the ability to do work or move something. Thus, heat is a form of energy. Heat can change into other forms of energy and vice versa. Heat is measured in the unit of energy,
ExamLearn.ie Heat Heat Heat has the ability to do work or move something. Thus, heat is a form of energy. Heat can change into other forms of energy and vice versa. Heat is measured in the unit of energy,
Thermal Energy Worksheets
 Thermal Energy Worksheets Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit
Thermal Energy Worksheets Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit
HEAT What are some sources of Heat?
 HEAT Activity 1. Rub your hands quickly against each other. 2. Then quickly place them onto your face. 3. Describe what you feel. Your hands feel warm. 4. Why does it feel warm? It feels warm as HEAT has
HEAT Activity 1. Rub your hands quickly against each other. 2. Then quickly place them onto your face. 3. Describe what you feel. Your hands feel warm. 4. Why does it feel warm? It feels warm as HEAT has
Keep It Hot! Handout
 Keep It Hot! Handout Day 1: Introduction Today, you will study heat transfer by conduction and convection! Fill in the rest of these statements: Heat is Heat always flows from to If we heat up a material
Keep It Hot! Handout Day 1: Introduction Today, you will study heat transfer by conduction and convection! Fill in the rest of these statements: Heat is Heat always flows from to If we heat up a material
PHYSICS FORM 5 TRANSFER OF THERMAL ENERGY
 Heat energy is transferred from one place to the next by three mechanisms: 1. Conduction 2. Convection 3. Radiation Conduction This is the process of heat transfer from one place to another using the movement/vibration
Heat energy is transferred from one place to the next by three mechanisms: 1. Conduction 2. Convection 3. Radiation Conduction This is the process of heat transfer from one place to another using the movement/vibration
Four of the appliances, including the fan heater, are designed to transform electrical energy into heat.
 Q1. The pictures show six different household appliances. (a) Four of the appliances, including the fan heater, are designed to transform electrical energy into heat. Name the other three appliances designed
Q1. The pictures show six different household appliances. (a) Four of the appliances, including the fan heater, are designed to transform electrical energy into heat. Name the other three appliances designed
Thermal Energy Study Guide
 Goal 1 Thermal Energy Study Guide Name: Hour Define the following in your own words: 1. Conductor - a material that allows heat to flow through it easily Two examples - metal pot, fork 2. Insulator - a
Goal 1 Thermal Energy Study Guide Name: Hour Define the following in your own words: 1. Conductor - a material that allows heat to flow through it easily Two examples - metal pot, fork 2. Insulator - a
1. What are the scales of temperature? What are the formulas to convert among them? Fahrenheit, Celsius, Kelvin
 -* Name Period 1. What are the scales of temperature? What are the formulas to convert among them? Fahrenheit, Celsius, Kelvin 2. Define Heat and temperature. Heat transfer of thermal energy from hotter
-* Name Period 1. What are the scales of temperature? What are the formulas to convert among them? Fahrenheit, Celsius, Kelvin 2. Define Heat and temperature. Heat transfer of thermal energy from hotter
Page 22a. What heats up faster, sand or water? Which one has a greater specific heat capacity?
 Page 22a Have weather map face-up on table Objective: We will describe the three types of heat transfer and explain their roles in Earth processes. Warm-up: What heats up faster, sand or water? Which one
Page 22a Have weather map face-up on table Objective: We will describe the three types of heat transfer and explain their roles in Earth processes. Warm-up: What heats up faster, sand or water? Which one
5. Transfer of thermal energy
 5. Transfer of thermal energy A bird can reduce the heat loss from its body during cold weather by fluffing up its feathers. What are the processes of heat transfer? Conduction Convection Radiation transfer
5. Transfer of thermal energy A bird can reduce the heat loss from its body during cold weather by fluffing up its feathers. What are the processes of heat transfer? Conduction Convection Radiation transfer
? Radiation. Radiation. How does heat energy get from the Sun to the Earth?
 How does heat energy get from the Sun to the Earth? Radiation There are no particles between the Sun and the Earth so it can not travel by conduction or by convection.? Radiation Radiation Thermal radiation
How does heat energy get from the Sun to the Earth? Radiation There are no particles between the Sun and the Earth so it can not travel by conduction or by convection.? Radiation Radiation Thermal radiation
Downloaded from
 Do you know, why? ASSIGNMENTS TUTORIAL HEAT 1. The thick glass tumblers break when hot liquid is poured into them Ans: If boiling hot water is poured in a thick glass tumbler, it cracks because glass is
Do you know, why? ASSIGNMENTS TUTORIAL HEAT 1. The thick glass tumblers break when hot liquid is poured into them Ans: If boiling hot water is poured in a thick glass tumbler, it cracks because glass is
Fundamentals of Heat Transfer
 Fundamentals of Heat Transfer State basic laws of heat transfer Estimate heat transfer rates by different modes Use the concept of thermal resistance to solve steady state heat transfer problems State
Fundamentals of Heat Transfer State basic laws of heat transfer Estimate heat transfer rates by different modes Use the concept of thermal resistance to solve steady state heat transfer problems State
Within the context of a camping scenario, students are asked to apply their understanding of the principles of heat transfer to various situations.
 Sample assessment task Year level 9 Learning area Subject Title of task Task details of task Type of assessment Suggested time Science Physical Sciences Camping scenario and heat Within the context of
Sample assessment task Year level 9 Learning area Subject Title of task Task details of task Type of assessment Suggested time Science Physical Sciences Camping scenario and heat Within the context of
Transfer of Thermal Energy
 Transfer of Thermal Energy Transfer of Thermal Energy Thermal Energy Transfer Conduction Convection Radiation Transfer of Thermal Energy Thermal Energy Transfer Conduction Convection Radiation Lesson Objectives
Transfer of Thermal Energy Transfer of Thermal Energy Thermal Energy Transfer Conduction Convection Radiation Transfer of Thermal Energy Thermal Energy Transfer Conduction Convection Radiation Lesson Objectives
Activity Heat Transfer
 Name: Hr: Activity 3.3.6 Heat Transfer Introduction Heat is the transfer of thermal energy. Thermal energy exists when the atoms or molecules in a substance are in motion and vibrate. The atoms possess
Name: Hr: Activity 3.3.6 Heat Transfer Introduction Heat is the transfer of thermal energy. Thermal energy exists when the atoms or molecules in a substance are in motion and vibrate. The atoms possess
3B Heat, Light and Sound
 Heat, Light and Sound Heat, light and sound are forms of energy that have many applications in our lives. Heat Heat is a form of energy When petrol burns in a car engine it causes the gases in the cylinders
Heat, Light and Sound Heat, light and sound are forms of energy that have many applications in our lives. Heat Heat is a form of energy When petrol burns in a car engine it causes the gases in the cylinders
Science 7. Unit 3. Heat and. Temperature
 Science 7 Unit 3 Heat and Temperature Name:_ Class:_ TOPIC 1 REINFORMCEMENT Putting Thermal Energy to Work Goal Develop ways to classify natural and manufactured structures. BLM 3-1 When do you use thermal
Science 7 Unit 3 Heat and Temperature Name:_ Class:_ TOPIC 1 REINFORMCEMENT Putting Thermal Energy to Work Goal Develop ways to classify natural and manufactured structures. BLM 3-1 When do you use thermal
Unit THE NATURE OF HEAT
 Unit 5.0 - THE NATURE OF HEAT Heat is a form of energy, in the form of infrared radiation. Heat from the sun travels through space at the speed of 300,000,000 m/s. Upon arriving on earth, much of the radiant
Unit 5.0 - THE NATURE OF HEAT Heat is a form of energy, in the form of infrared radiation. Heat from the sun travels through space at the speed of 300,000,000 m/s. Upon arriving on earth, much of the radiant
Q1. The table gives information about some methods of conserving energy in a house.
 Q1. The table gives information about some methods of conserving energy in a house. Conservation method Installation cost in Annual saving on energy bills in Cavity wall insulation 500 60 Hot water tank
Q1. The table gives information about some methods of conserving energy in a house. Conservation method Installation cost in Annual saving on energy bills in Cavity wall insulation 500 60 Hot water tank
Energy Conservation. Meet Mr.A and Mr.B. They have both received their electricity bill. One of them is happy and one of them is not.
 Name: Class: Date: Grade 11A Science Related Reading/Physics Energy Conservation Physical Processes 11A PRE READING TASK Meet Mr.A and Mr.B. They have both received their electricity bill. One of them
Name: Class: Date: Grade 11A Science Related Reading/Physics Energy Conservation Physical Processes 11A PRE READING TASK Meet Mr.A and Mr.B. They have both received their electricity bill. One of them
Week 1 Day 1-2 (combine) Thermal Energy
 Week 1 Day 1-2 (combine) Thermal Energy Heat Transfer Conduction, Convection and Radiation Thermal Energy Transfer Thermal energy transfer is heat moving from a warmer object to a cooler object. This is
Week 1 Day 1-2 (combine) Thermal Energy Heat Transfer Conduction, Convection and Radiation Thermal Energy Transfer Thermal energy transfer is heat moving from a warmer object to a cooler object. This is
Science Test: Heat Energy
 Science Test: Heat Energy Name: Date: Section 1: Vocabulary Select the word below that makes the statement correct. Then write the word in the blank. freeze conductor heat friction melt evaporate radiation
Science Test: Heat Energy Name: Date: Section 1: Vocabulary Select the word below that makes the statement correct. Then write the word in the blank. freeze conductor heat friction melt evaporate radiation
Section 9. Comparing Energy Consumption: More for Your Money. What Do You See? What Do You Think? Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Section 9 Comparing Energy Consumption: More for Your Money Section 9 Comparing Energy Consumption: More for Your Money What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Measure and compare
Section 9 Comparing Energy Consumption: More for Your Money Section 9 Comparing Energy Consumption: More for Your Money What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Measure and compare
(a) (i) Complete the following sentences using words from the box. The warm air rising from the heater transfers energy to the
 Q1.The diagram shows how one type of electric storage heater is constructed. The heater has ceramic bricks inside. The electric elements heat the ceramic bricks during the night. Later, during the daytime,
Q1.The diagram shows how one type of electric storage heater is constructed. The heater has ceramic bricks inside. The electric elements heat the ceramic bricks during the night. Later, during the daytime,
In Chapter 3 you learnt that woollen
 4 Heat In Chapter 3 you learnt that woollen clothes are made from animal fibres. You also know that cotton clothes are made from plant fibres. We wear woollen clothes during winters when it is cold outside.
4 Heat In Chapter 3 you learnt that woollen clothes are made from animal fibres. You also know that cotton clothes are made from plant fibres. We wear woollen clothes during winters when it is cold outside.
People living in the desert need to wear special clothing in order for them to keep cool.
 Heat Keep Your Cool Humans live in a number of different places, some of which can be very hot or very cold. Inuit people can live in very cold climates, because their clothing and homes help to keep them
Heat Keep Your Cool Humans live in a number of different places, some of which can be very hot or very cold. Inuit people can live in very cold climates, because their clothing and homes help to keep them
The equation which links current, potential difference and resistance is:
 Q1.An electrical circuit is shown in the figure below. (a) The current in the circuit is direct current. What is meant by direct current? Tick one box. Current that continuously changes direction. Current
Q1.An electrical circuit is shown in the figure below. (a) The current in the circuit is direct current. What is meant by direct current? Tick one box. Current that continuously changes direction. Current
Thermal Properties and Temperature
 Thermal Properties and Temperature Question Paper 5 Level IGCSE Subject Physics Exam Board CIE Topic Thermal Physics Sub-Topic Thermal Properties and Temperature Paper Type Alternative to Practical Booklet
Thermal Properties and Temperature Question Paper 5 Level IGCSE Subject Physics Exam Board CIE Topic Thermal Physics Sub-Topic Thermal Properties and Temperature Paper Type Alternative to Practical Booklet
Use each of the terms in the box to explain how heat is lost from inside a house through the window. conduction convection radiation
 Q1. The diagram shows a side view of a double-glazed window. (a) Use each of the terms in the box to explain how heat is lost from inside a house through the window. conduction convection radiation..................
Q1. The diagram shows a side view of a double-glazed window. (a) Use each of the terms in the box to explain how heat is lost from inside a house through the window. conduction convection radiation..................
Conduction, Convection, and Radiation Lab Page 1 of 5
 Conduction, Convection, and Radiation Lab Page 1 of 5 I. Objectives 1. Explain the differences among conduction, convection, and radiation. 2. Investigate thermal conductivity in common metals, convection
Conduction, Convection, and Radiation Lab Page 1 of 5 I. Objectives 1. Explain the differences among conduction, convection, and radiation. 2. Investigate thermal conductivity in common metals, convection
Use numbers given in the box to complete the following sentences. In the UK, the mains electricity supply is volts.
 DOMESTIC USES AND SAFETY PART II Q1. Use numbers given in the box to complete the following sentences. 12 50 110 230 In the UK, the mains electricity supply is volts. The frequency of the UK mains electricity
DOMESTIC USES AND SAFETY PART II Q1. Use numbers given in the box to complete the following sentences. 12 50 110 230 In the UK, the mains electricity supply is volts. The frequency of the UK mains electricity
MARIYA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL AL-JUBAIL L-8 PHYSICS WORKSHEET(Heat & energy )
 MARIYA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL AL-JUBAIL L-8 PHYSICS WORKSHEET(Heat & energy ) 1 Name... (a)fig. Shows a thermometer with a range of 10 C to 50 C. Explain what is meant by (i) the sensitivity of a thermometer,......
MARIYA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL AL-JUBAIL L-8 PHYSICS WORKSHEET(Heat & energy ) 1 Name... (a)fig. Shows a thermometer with a range of 10 C to 50 C. Explain what is meant by (i) the sensitivity of a thermometer,......
UNIQUE COLLEGE OF COMPUTER SCIENCES General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level
 UNIQUE OLLEGE OF OMPUTER SIENES General ertificate of Education Ordinary Level PHYSIS Paper 1 Multiple hoice lass II2 III2 995054/11 January 2011 91 hour dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet
UNIQUE OLLEGE OF OMPUTER SIENES General ertificate of Education Ordinary Level PHYSIS Paper 1 Multiple hoice lass II2 III2 995054/11 January 2011 91 hour dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet
Particle Model Questions 1
 Particle Model Questions 35 Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comment s: Q. Figure shows solid ice on a car s rear window. Figure Captive cookies/istock/thinkstock The glass window contains an
Particle Model Questions 35 Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comment s: Q. Figure shows solid ice on a car s rear window. Figure Captive cookies/istock/thinkstock The glass window contains an
UNIQUE SCIENCE ACADEMY
 UNIQUE SIENE AAEMY Test (Unit 1) Name :... Pap er: Physics ate :... ode: 5054 lass: I Time Allowed: 5Minutes Maximum Marks: 5 Theory Section: 1 [Total 19 Marks] 1 (a) escribe an experiment to show which
UNIQUE SIENE AAEMY Test (Unit 1) Name :... Pap er: Physics ate :... ode: 5054 lass: I Time Allowed: 5Minutes Maximum Marks: 5 Theory Section: 1 [Total 19 Marks] 1 (a) escribe an experiment to show which
THERMAL CONDUCTION. placed in a different position. Can you explain why the matches go out?
 THERMAL CONDUCTION NAME(S) Pour about 250 ml of water into a 500 ml beaker, and begin heating the beaker on a hot plate. The beaker of water will be used in a later activity. Activity #1 A Parlor Trick
THERMAL CONDUCTION NAME(S) Pour about 250 ml of water into a 500 ml beaker, and begin heating the beaker on a hot plate. The beaker of water will be used in a later activity. Activity #1 A Parlor Trick
Insulators and Conductors
 Insulators and Conductors Materials that conduct, or transfer, heat well are called thermal conductors. A thermal conductor transfers heat well because of the way its particles are arranged. Particles
Insulators and Conductors Materials that conduct, or transfer, heat well are called thermal conductors. A thermal conductor transfers heat well because of the way its particles are arranged. Particles
More heat energy means more of what type of energy? Does the mass change? So, what must change? What is the same in both containers?
 Quest Chapter 21-23 # Problem Hint 1 When a container of gas is heated, what happens to the average speed of its molecules? 1. Additional information is needed. 2. increases 3. doesn t change 4. decreases
Quest Chapter 21-23 # Problem Hint 1 When a container of gas is heated, what happens to the average speed of its molecules? 1. Additional information is needed. 2. increases 3. doesn t change 4. decreases
Heat Transfer Using words from the word boxes below, complete the paragraph about heat transfer.
 Scientist Date Period Heat Transfer Using words from the word boxes below, complete the paragraph about heat transfer. faster hot less solid fluid more energy emit warmer matter transfer absorb temperature
Scientist Date Period Heat Transfer Using words from the word boxes below, complete the paragraph about heat transfer. faster hot less solid fluid more energy emit warmer matter transfer absorb temperature
Describe the movement of the particles of helium gas inside the balloon
 Q1.The figure below shows a balloon filled with helium gas. (a) Describe the movement of the particles of helium gas inside the balloon............. (b) What name is given to the total kinetic energy and
Q1.The figure below shows a balloon filled with helium gas. (a) Describe the movement of the particles of helium gas inside the balloon............. (b) What name is given to the total kinetic energy and
Level 1 Physics, 2016
 90939 909390 1SUPERVISOR S Level 1 Physics, 2016 90939 Demonstrate understanding of aspects of heat 2.00 p.m. Tuesday 15 November 2016 Credits: Four Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with
90939 909390 1SUPERVISOR S Level 1 Physics, 2016 90939 Demonstrate understanding of aspects of heat 2.00 p.m. Tuesday 15 November 2016 Credits: Four Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with
Keep It Hot! Handout Answer Key
 Keep It Hot! Handout Answer Key Day 1: Introduction Today, you will study heat transfer by conduction and convection! Fill in the rest of these statements: Heat is the transfer or flow of thermal energy.
Keep It Hot! Handout Answer Key Day 1: Introduction Today, you will study heat transfer by conduction and convection! Fill in the rest of these statements: Heat is the transfer or flow of thermal energy.
(4)... (1) Suggest one feature of the black fuel effect lumps which make them efficient at transferring energy....
 Q1. The diagram comes from a leaflet about a coal effect gas fire. It shows how air circulates through the fire. (a) Explain in detail why the air travels from C to A. (4) (b) The black fuel effect lumps
Q1. The diagram comes from a leaflet about a coal effect gas fire. It shows how air circulates through the fire. (a) Explain in detail why the air travels from C to A. (4) (b) The black fuel effect lumps
Changes of phase usually involve a transfer of energy Evaporation
 Changes of phase usually involve a transfer of energy. The four possible forms of matter solid, liquid, gas, and plasma are called phases. Matter can change from one phase to another. The phase of matter
Changes of phase usually involve a transfer of energy. The four possible forms of matter solid, liquid, gas, and plasma are called phases. Matter can change from one phase to another. The phase of matter
Heat Energy. Heat Energy. A Science A Z Physical Series. Word Count: 1,301. Written by Felicia Brown. Visit
 Heat Energy A Science A Z Physical Series Word Count: 1,301 Heat Energy Written by Felicia Brown Visit www.sciencea-z.com www.sciencea-z.com Heat Energy Key elements Used in This Book The Big Idea: One
Heat Energy A Science A Z Physical Series Word Count: 1,301 Heat Energy Written by Felicia Brown Visit www.sciencea-z.com www.sciencea-z.com Heat Energy Key elements Used in This Book The Big Idea: One
February 18, What is heat? Touch each image to see how the water molecules react.
 What is heat? Touch each image to see how the water molecules react. Where does heat come from? Touch each image and discuss. How can motion create heat? Touch each image to view the different energy levels
What is heat? Touch each image to see how the water molecules react. Where does heat come from? Touch each image and discuss. How can motion create heat? Touch each image to view the different energy levels
(1) ... (2) Each strip has a negative charge. The cloth is left with a... charge. This is because particles called... have been transferred
 Q1. A student did an experiment with two strips of polythene. She held the strips together at one end. She rubbed down one strip with a dry cloth. Then she rubbed down the other strip with the dry cloth.
Q1. A student did an experiment with two strips of polythene. She held the strips together at one end. She rubbed down one strip with a dry cloth. Then she rubbed down the other strip with the dry cloth.
Introduction to Heat Transfer. year three Department of Mechanical Engineering College of Engineering by Dr Khaled A. Al-Farhany
 Introduction to Heat Transfer year three Department of Mechanical Engineering College of Engineering by Dr Khaled A. Al-Farhany Heat Transfer Heat always moves from a warmer place to a cooler place. Hot
Introduction to Heat Transfer year three Department of Mechanical Engineering College of Engineering by Dr Khaled A. Al-Farhany Heat Transfer Heat always moves from a warmer place to a cooler place. Hot
Heat Transfer. Heat. Thermal Energy: Heat 1
 Heat Transfer The heat is on! In this lesson, we are going to learn what heat is and how it moves from place to place. You know how they say, If you can t stand the heat, get out of the kitchen.? Well
Heat Transfer The heat is on! In this lesson, we are going to learn what heat is and how it moves from place to place. You know how they say, If you can t stand the heat, get out of the kitchen.? Well
The transfer of energy as heat can be controlled.
 FOCUS Set Learning Goals Students will Explain how energy is transferred through heat. Describe how materials are used to control the transfer of energy through heat. 3-Minute Warm-Up Display Transparency
FOCUS Set Learning Goals Students will Explain how energy is transferred through heat. Describe how materials are used to control the transfer of energy through heat. 3-Minute Warm-Up Display Transparency
Well Insulated Houses: Helping to Stay Warm in Winter and Cool in Summer
 CON EDISON WEB-BASED MIDDLE SCHOOL ACTIVITY Well Insulated Houses: Helping to Stay Warm in Winter and Cool in Summer Overview In this activity, you and your students will build two house models from discarded
CON EDISON WEB-BASED MIDDLE SCHOOL ACTIVITY Well Insulated Houses: Helping to Stay Warm in Winter and Cool in Summer Overview In this activity, you and your students will build two house models from discarded
Making a Carousel Lantern. Grade 7 Activity Plan
 Making a Carousel Lantern Grade 7 Activity Plan 1 Reviews and Updates - Carousel Lanterns Activity added by Fola Akpan in July 2017 2 Making a Carousel Lantern Objectives: 1. To compare two methods of
Making a Carousel Lantern Grade 7 Activity Plan 1 Reviews and Updates - Carousel Lanterns Activity added by Fola Akpan in July 2017 2 Making a Carousel Lantern Objectives: 1. To compare two methods of
Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
 Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation AHMAD TUSI, M.Si. Jurusan Teknik Pertnian Fakultas Pertanian UNILA Heat Transfer Heat always moves from a warmer place to a cooler place.
Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation AHMAD TUSI, M.Si. Jurusan Teknik Pertnian Fakultas Pertanian UNILA Heat Transfer Heat always moves from a warmer place to a cooler place.
Solar Matters III Teacher Page
 Solar Matters III Teacher Page We re In Hot Water Now Student Objective The student: will be able to explain how a solar thermal water heating system works will be able to explain conduction, convection
Solar Matters III Teacher Page We re In Hot Water Now Student Objective The student: will be able to explain how a solar thermal water heating system works will be able to explain conduction, convection
Saving Energy. We promote equality of opportunity in every aspect of our business in line with our objectives.
 Saving Energy We promote equality of opportunity in every aspect of our business in line with our objectives. Wiltshire Rural Housing Association Saving Energy 2015 1 SAVE ENERGY Did you know that the
Saving Energy We promote equality of opportunity in every aspect of our business in line with our objectives. Wiltshire Rural Housing Association Saving Energy 2015 1 SAVE ENERGY Did you know that the
St. Mary s Catholic High School, Dubai. Name:. SCIENCE REVISION TERM 1 (January 2017)
 St. Mary s Catholic High School, Dubai Name:. SCIENCE REVISION TERM 1 (January 2017) Date:... Year 3. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
St. Mary s Catholic High School, Dubai Name:. SCIENCE REVISION TERM 1 (January 2017) Date:... Year 3. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
M1. (a) (i) walls accept sides (of house) 1
 M. (a) (i) walls accept sides (of house) fit double glazing or close / fit curtains / fit shutters accept close windows accept keep house at a lower temperature accept fit (foam) draft excluders around
M. (a) (i) walls accept sides (of house) fit double glazing or close / fit curtains / fit shutters accept close windows accept keep house at a lower temperature accept fit (foam) draft excluders around
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE THERMODYNAMICS WHAT HAPPENS WHEN SOMETHING IS HEATED? LATENT HEAT
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE THERMODYNAMICS WHAT HAPPENS WHEN SOMETHING IS HEATED? LATENT HEAT 1 HEATS OF FUSION AND VAPORISATION From the equation containing the specific heat, it seems that we can keep on transferring
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE THERMODYNAMICS WHAT HAPPENS WHEN SOMETHING IS HEATED? LATENT HEAT 1 HEATS OF FUSION AND VAPORISATION From the equation containing the specific heat, it seems that we can keep on transferring
The diagram shows the inside of an incorrectly wired three-pin plug. What two changes need to be made so that the plug is wired correctly?
 1 (a) The diagram shows the inside of an incorrectly wired three-pin plug. (i) What two changes need to be made so that the plug is wired correctly? 1... 2... (ii) The fuse inside a plug is a safety device.
1 (a) The diagram shows the inside of an incorrectly wired three-pin plug. (i) What two changes need to be made so that the plug is wired correctly? 1... 2... (ii) The fuse inside a plug is a safety device.
Physics. Mr Rishi Gopie THERMAL ENERGY TRANSFER
 Mr Rishi Gopie THERMAL ENERGY TRANSFER Thermal Energy Transfer Thermal energy transferred from one system/region to another due to a temperature difference is called heat and there are three main ways
Mr Rishi Gopie THERMAL ENERGY TRANSFER Thermal Energy Transfer Thermal energy transferred from one system/region to another due to a temperature difference is called heat and there are three main ways
Conceptual Physics Fundamentals
 Conceptual Physics Fundamentals Chapter 9: HEAT TRANSFER AND CHANGE OF PHASE This lecture will help you understand: Conduction Convection Radiation Newton s Law of Cooling Global Warming and the Greenhouse
Conceptual Physics Fundamentals Chapter 9: HEAT TRANSFER AND CHANGE OF PHASE This lecture will help you understand: Conduction Convection Radiation Newton s Law of Cooling Global Warming and the Greenhouse
What Will Happen? If you leave a hot drink on the table and wait for a while, does the drink heat up or cool off?
 What Is Heat? What Will Happen? If you leave a hot drink on the table and wait for a while, does the drink heat up or cool off? If you leave a cold drink on the same table and wait for a while, does the
What Is Heat? What Will Happen? If you leave a hot drink on the table and wait for a while, does the drink heat up or cool off? If you leave a cold drink on the same table and wait for a while, does the
Q1. Carefully read the following extract from a safety leaflet. Then answer the questions.
 Q1. Carefully read the following extract from a safety leaflet. Then answer the questions. An RCD adaptor is an automatic safety switch. It should be used when there is a particular risk of electric shock.
Q1. Carefully read the following extract from a safety leaflet. Then answer the questions. An RCD adaptor is an automatic safety switch. It should be used when there is a particular risk of electric shock.
Station 1 1. In each box provided, use circles to represent molecules and sketch the molecular arrangement for each state of matter.
 Thermal Energy Review Station 1 1. In each box provided, use circles to represent molecules and sketch the molecular arrangement for each state of matter. 2. Label each arrow on the diagram below. These
Thermal Energy Review Station 1 1. In each box provided, use circles to represent molecules and sketch the molecular arrangement for each state of matter. 2. Label each arrow on the diagram below. These
Energy Saving Service
 Northamptonshire Energy Saving Service Useful energy saving advice booklet Advice on managing your energy bills WE RE OFFERING ALL NORTHAMPTONSHIRE RESIDENTS A FREE HOME ENERGY SERVICE SAVE MONEY ON BILLS
Northamptonshire Energy Saving Service Useful energy saving advice booklet Advice on managing your energy bills WE RE OFFERING ALL NORTHAMPTONSHIRE RESIDENTS A FREE HOME ENERGY SERVICE SAVE MONEY ON BILLS
THIRD GRADE SCIENCE (SCIENCE3_4)
 Name: Date: THIRD GRADE SCIENCE (SCIENCE3_4) 1. If you put a metal spoon in hot water, the spoon will A. melt. B. dissolve. C. get cold. D. get hot. 2. When one end of a steel rod is held in a flame, the
Name: Date: THIRD GRADE SCIENCE (SCIENCE3_4) 1. If you put a metal spoon in hot water, the spoon will A. melt. B. dissolve. C. get cold. D. get hot. 2. When one end of a steel rod is held in a flame, the
