Studies of Cooling Effects of Sprinkler Spray on Smoke Layer
|
|
|
- Evan Nicholson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Studies of Cooling Effects of Sprinkler Spray on Smoke Layer S.C. Li 1,2, D. Yang 1, R. Huo 1 *, L.H. Hu 1 *, Y.Z. Li 1, K.Y. Li 1 and H.B. Wang 1 1. State Key Laboratory of Fire Science University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei , China 2. Department of Fire Command The Chinese People s Armed Police Force Academy Langfang , China *Corresponding author: Tel: (86) ; Fax: (86) ; address: huoran@ustc.edu.cn; hlh@ustc.edu.cn Postal address: State Key Laboratory of Fire Science, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, , China ABSTRACT An experimental study was performed to measure the cooling of a smoke layer by water sprays. This was followed by the development of a mathematical model based on the theory of Chow and Tang. The predictions of the model agree well with the experimental measurements. Water sprays investigated in the present work provided significant cooling of the smoke layer. We observed little effect of increasing the water pressure from 50 to 100 kpa on the cooling of the smoke layer. KEYWORDS: Sprinkler spray; smoke layer; heat transfer; sprinkler cooling NOMENCLATURE LISTING c sprinkler flow coefficient S(i) surface area of droplet of diameter i (m 2 ) c p specific heat of water (kj/kg K) T temperature of smoke(k) C ps specific heat of smoke (kj/kg K) T(i) w temperature of droplet of diameter i (K) C ps2 specific heat of the smoke after sprinkler operation (kj/kg K) u velocity of hot smoke (m/s) initial horizontal component of droplet velocity C d resistance coefficient u 0 (m/s) C m sprinkler diameter coefficient U droplet velocity (m/s) d m average volume diameter of droplets (μm) U s smoke velocity (m/s) d n nozzle inner diameter (μm) v droplet vertical velocity (m/s) h heat transfer coefficient (W/m 2 k) v 0 initial vertical velocity of droplet (m/s) h(i) heat transfer coefficient of droplet of diameter i V sprinkler flow rate (m 3 /s) (kw/m 2 K) i droplet diameter (μm) W width of sprinkler chamber (m) k coefficient of thermal conductivity (W/m K) h elevation of smoke layer above ground (m) K resistance term H height of sprinkler chamber (m) m mass of water droplet (kg) T f temperature of droplet that reaches the bottom of the smoke layer (K) m p mass production rate of temperature difference between smoke and T smoke (kg/s) ambient air (K) m(i) mass of droplet of diameter i T 2 temperature difference between smoke and ambient air after sprinkler operation (K) N(i) number of droplets of y(i) probability of droplet of diameter i in log- FIRE SAFETY SCIENCE PROCEEDINGS OF THE NINTH INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM, pp COPYRIGHT 2008 INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION FOR FIRE SAFETY SCIENCE / DOI: /IAFSS.FSS
2 diameter i normal distribution Nu(i) Nusselt number of droplet of diameter i P sprinkler pressure (MPa) Greek Pr Prandtl number of air δ parameter in log-normal distribution of droplet sizes Q experimental value of sprinkler cooling (kw) α empirical coefficient Q 1 energy of smoke before sprinkler operation (kw) ρ s density of smoke (kg/m 3 ) Q 2 energy of smoke after sprinkler operation (kw) ρ w density of water (kg/m 3 ) Q c convective heat transfer (kw) σ w surface tension of water (N/m) Q cx actual heat removed by spray fraction of droplets not removed by η (kw) obstructions Re(i) Reynolds number of droplet of diameter i υ smoke kinematic viscosity (m 2 /s) S smoke circulation area (m 2 ) INTRODUCTION Automatic fire sprinkler systems are increasingly used in fire protection applications. Normally, sprinklers are installed at the ceiling. When the temperature at a sprinkler head reaches a predetermined value, the thermal element in the sprinkler activates and the water discharges from a pipe. Sprinklers control fires by four mechanisms: (1) they cool down the surface of the combustible materials; (2) they wet the surrounding material and reduce the flame spread; (3) they displace air with water vapor due to evaporation; and (4) they cool hot smoke layer and reduce its radiation [1,2]. A number of studies have been performed to investigate the effects of sprinklers on the smoke produced by a fire [3-6]. Morgan [3, 4] analyzed the heat transfer between water droplets and a hot smoke layer, using a simple model. More recent work was reported by Cooper [5, 6]. Cooper focused on the behavior of the smoke layer under sprinkler spray, and developed a physical model. Studies involving numerical modeling were later conducted by Alpert [7], Hoffmann [8], Gardiner [9] and Chow [10-12]. Chow and Tang [13] also studied the heat transfer between the sprinkler spray and hot smoke layer, both theoretically and experimentally. Temperatures at different points in smoke layer were measured, but the study was not extended to predicting the heat transfer between the smoke layer and the sprinkler spray. Their model needs further full scale validations. Starting from the theoretical analysis of Chow and Tang, in this contribution, we develop a new model for heat transfer between the hot layer and water spray. We also perform full scale experiments to validate the model. MATHEMATICAL MODEL Characterization of the sprinkler spray droplets properties Water is ejected from the sprinkler orifice and impacts onto the deflector to form a spray. We employ the log-normal distribution to characterize the droplet sizes [14]: 2 i ln 1 dm y() i = exp 2 iδ 2π 2δ - (1) 862
3 where y(i) is droplet-size distribution function, i the droplet diameter, d m average volume diameter of droplet, δ the deviation of the function, with the value of 0.56 δ The volume medium diameter of the sprinkler spray droplets is taken as [15]: 1 ( ) 3 m m n d = C We d (2) where d n is inner diameter of the nozzle, We Weber number, with the coefficient C m taken as 2.33 for ZSTP-15 sprinkler [16,17]. The Weber number is defined as: ρ We = σ 2 wu dn w (3) where U is the drop velocity, σ w the surface tension of water equal to 72.8 mn/m. Droplet velocity is taken as: V U = (4) π d n2 /4 where V is the flow rate of sprinkler. The flow rate of sprinkler can be calculated by: c 10P V = (5) where c is the sprinkler flow coefficient, with a constant value of 80 for ZSTP-15 sprinkler, and P denotes sprinkler pressure. The number of droplets with different diameters can be calculated by the following equation [3]: N() i = N i= 1 V y() i yi () 3 π i 6 (6) where N(i) is the number of droplets whose diameter is i. For a single droplet, in accordance with Newton's second law, Bullen [18] presented an equation for the droplet vertical velocity as: 863
4 2 dv dv mg Kv = m mv dt = dx (7) where m is the mass of a water droplet, K is resistance term, and v corresponds to the droplet vertical velocity. By solving equation (7), one obtains the droplet vertical velocity as a function of height: 2 mg 2 mg v = + v0 e K K 2Kx m (8) where v 0 is the droplet initial velocity. Initial horizontal velocity of sprinkler droplets is: u0 = αu (9) where u 0 is initial horizontal velocity component, α is an empirical coefficient which is taken to be 0.4. Initial droplet vertical velocity corresponds to: v = U u (10) Resistance term can be expressed by equation: K 1 2 = ρ C π i (11) 8 a d where ρ a is the density of air, and C d is drag coefficient. C d is obtained from C d = 24Re 1/2 Re < Re< Re< Re The Reynolds number of a droplet can be expressed as: ui Re( i) = (12) υ 864
5 where Re(i) is Reynolds number of a droplet of diameter i, u is the velocity of hot smoke, and υ is the kinematic viscosity of the smoke. The Nusselt number of a sprinkler droplet of diameter i is ( ) Nu( i) 2 0.4Re( i) 0.06Re( i) Pr / = + + (13) Pr is the Prandtl number of the air which is taken to be 0.7. The Nusselt number can also be expressed as: hii () Nu() i = (14) k where h(i) is convective heat transfer coefficient of the droplet whose diameter is i, k is coefficient of thermal conductivity of the air. Equation(14) can also be expressed as: hi () Nu() i k i = (15) Heat transfer between droplets and smoke For a fraction of droplets of diameter i, the energy conservation equation corresponds to [13]: dt () i w mic () p = hisi () ()( T Ti () w) (16) dt where m(i) is the mass fraction of droplets of diameter i, T(i) w the temperature of droplets of diameter i, S(i) surface area of droplets of diameter i, and T the temperature of the smoke layer. Equation 16 can be rewritten as: 3 4 () ( ) 3 π i dt i knu i vc i T T i 2 ρ = dx i π ( () ) w 2 w p w ( Ti ( ) 373 K) (17) w in Eq. 17, the x denotes vertically downward direction. The evolution of the temperature of a sprinkler droplet can be calculated by solving the above equation using the Runge/Kutta method. When the temperature of a smoke layer is high, small droplets easily reach a boiling point temperature. However, in our experiments, the thickness and the temperature of the smoke layer allow only a small fraction of water droplets to reach the boiling point. For this reason, the model neglects the evaporative cooling. The heat absorbed by a droplet of diameter i is 865
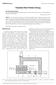
6 Q () i = m() i c ( T T ) N() i ( T 373 K) (18) c p f 0 f where T f corresponds to the temperature of the droplet that reach the bottom of the smoke layer. Equation 18 restricts the droplet temperature to below the boiling point. Although it is possible that very small droplets can start to boil during their passage through the smoke layer, the mass fraction of such droplets is small. The total heat transferred from the smoke layer to spray droplets equals: 3 N 4 i Qc = π ρwcp( Tf T0 ) N() i i= (19) where Q c is convective heat transfer, ρ w is the density of water, C p is the specific heat of water. Combining Eqs. 1, 6, 8, 15, 17-19, we can calculate the heat absorbed by water droplets that pass through smoke layer characterized by given temperature and thickness. The above calculation of the spray cooling assumes no removal of droplets by obstructions; i.e., all droplets traverse the entire smoke layer and. However, in practice, sprinklers may be located in corridors, lobbies, where substantial number of droplets are removed from the spray by collisions with walls, and do not participate in the heat exchange with the smoke layer. Therefore, the value of spray cooling calculated above needs be modified as: Q cx = η Q (20) c where Q cx denotes the actual heat removed by the spray, η is the fraction of droplets able to penetrate the smoke layer; i.e., the droplets that are not removed by obstructions. Since the area of the spray chamber is 8 m 2, and the the sprinkler coverage corresponds to 20 m 2 [19], we estimate the value of the parameter η to be 0.4. EXPERIMENTS The experimental apparatus is shown in Fig. 1. It consists of the connected combustion and sprinkler chambers. As shown in Fig. 1, pool fires were burned in the combustion chamber to generate an initial stable smoke layer in the upper region of the sprinkler chamber. The combustion chamber was 2.5 m in length, 1.22 m in width and 2.2 m in height. The opening between the combustion and sprinkler chamber was 1.22 m in width and 1.8 m in height. The dimensions of the sprinkler chamber corresponded to 4 (length) 2 (width) 2.6 (height) m. In order to ensure adequate air supply, the combustion and sprinkler chambers were equipped with vents at the bottom and side walls, as illustrated in Fig. 1. A smoke curtain with height of 2.2 m was installed below the ceiling of the sprinkler chamber to form a smoke layer of 1 m in initial thickness. A single sprinkler was installed at the center point of the ceiling of the sprinkler chamber. Two thermocouples trees, each with 12 thermocouples, were located symmetrically 1 m away from the sprinkler. We used K-type thermocouples, 0.3 mm in diameter, and accurate to ±1. The vertical interval between the thermocouples was 0.15 m. In order to minimize the cooling of the thermocouple by the water spray, a 866
7 thin reverse U shaped metal shield was installed above the thermocouples. These metal shields prevented water from the sprinkler reaching the thermocouples directly. The dimensions of the thermocouples trees are shown in Fig. 1. ZSTP-15 sprinkler with the nozzle diameter of 12.7 mm was used for all experiments. A pressure reducing valve and a pressure transmitter were installed on the water pipe to control the operating pressure of the sprinkler with an accuracy of MPa. In total 16 tests were conducted with the smoke layer generated by diesel (heat of combustion of 42 MJ/kg) pool fires of four sizes. The transient mass of the fuel was measured by a weighting system with six strain gauges, capable of measuring mass of up to 60 kg. The heat release rates of the pool fires were calculated from the mass loss rates of the fuel with the combustion efficiency assumed to be 75% of that calculated from the heat of combustion. Table 1 summarized the heat release rates for all experiments. The sprinkler spray was discharged at the same time after the ignition. The total burning time of each test was about 600 s. The operating pressure of the sprinkler was set to 0.05, or 0.1 MPa. The heat release rate of the pool fire was measured by six fulcrum piezoelectric weighing platforms. These platforms measure the pressure changes, with the signal digitized by the data acquisition system and stored on a PC, providing records of fuel consumption as a function of time. By differentiating this signal, we calculated the instantaneous fuel mass consumption rate, and then the heat release rate of the pool fire. Hot wire anemometer with temperature compensation was used in experiments to measure the smoke flow velocity. Scale gauge was used to measure the thickness of the smoke layer. Measurements were performed right at the opening of the sprinkler chamber. During each experiment, the smoke flow velocity and thickness were measured every 30 s. The average values during the steady-state stage of each experiment were then deduced sprinkler chamber combustion chamber 1000 sprinkler thermocouple 100 thermocouple pool Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of the experimental rig; all dimensions are in mm. 867
8 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Variations of the smoke temperature Based on the experimental observation, the upper eight thermocouples were located in the smoke layer, and the average temperature of the smoke layer was deduced from the readings of these thermocouples. Figures 2(a) - (d) present typical temperature histories of tests The average smoke temperature was estimated from the steady state portions of the temperature histories. For Figs. 2 (a), (b), (d), we estimated the smoke temperature from the measurements between 200 and 400 s, for Fig. 2 (c), between 100 and 300 s. For all conditions, the average smoke temperatures are listed in Fig. 3. As shown in Fig. 3, smoke temperature decreased significantly after sprinkler operation. For m pool fire, the average temperature rise of the smoke is 107 K without sprinkler; whereas the sprinkler spray, generated at 0.05 MPa, decreases this temperature rise to 35.2 K. When the sprinkler pressure increases, the volume medium diameter of the sprinkler spray droplets decreases and the proportion of smaller droplets increases[15], enhancing the cooling effect of the sprinkler. For m pool fire, and spray generated at 0.05 MPa, the average temperature rise of the smoke is 29.7 K. Likewise the average temperature rise of the smoke layer is only 20.1 K for the 0.1 MPa spray. It can be also seen from Fig. 3 that the effect of water pressure is small. For example, for m pool fire, and the spray pressure of 0.05 MPa, the average temperature rise of the smoke is 9.4 K, whereas for 0.1 MPa spray, the average temperature rise of the smoke is 4.9 K smoke temperature( ) no sprinkler 0.05MPa 0.075MPa 0.1MPa smoke temperature( ) no sprinkler 0.05MPa 0.075MPa 0.1MPa Time(s) (a) m pool Time(s) (b) m pool smoke temperature( ) no sprinkler 0.05MPa 0.075MPa 0.1MPa smoke temperature( ) no sprinkler 0.05MPa 0.075MPa 0.1MPa Time(s) (c) m pool Time(s) (d) m pool Fig. 2. Temperature variation for different pool fires 868
9 Calculating heat loss from the smoke layer to the sprinkler spray The energy of the hot smoke layer before sprinkler operation can be expressed as: Q1 = mp cpsδ T = ρ s Vc s ps Δ T= ρ s USc s ps Δ T= ρ U ( H h) Wc Δ T (21) s s ps where Q 1 is the energy of smoke before sprinkler operation, m p mass production rate of smoke, c ps is specific heat of smoke, ρ s is density of smoke, T is temperature difference between smoke and ambient air, U s is smoke velocity that pass through the sprinkler chamber, S is smoke circulation area that pass through the sprinkler chamber, W is width of the sprinkler chamber, H is height of the sprinkler chamber, h is the height between smoke layer to the ground. The energy of the hot smoke layer after sprinkler operation is: ( ) Q = m c Δ T = ρ U H h Wc Δ T (22) 2 p ps2 2 s s ps2 2 where Q 2 is the energy of smoke after sprinkler operation, c ps2 is the specific heat of the smoke after sprinkler operation, T 2 is temperature difference between smoke and ambient air after sprinkler operation. The heat loss from the smoke layer to the sprinkler spray can then be deduced from the experimentally measured temperature of the smoke layer according to: Q = Q1 Q2 (23) where Q is the experimental value for heat loss from the smoke layer to the sprinkler spray. Comparison of analytical and experimental results The main experimental results are summarized in Table 1, demonstrating good agreement between the measurements and the calculations, which use the values of the parameters listed in Table Temperature rise of smoke(k) *0.25pool 0.3*0.3pool 0.5*0.5pool 0.6*0.6pool Calculated value (kw) *0.25pool 0.3*0.3pool 0.5*0.5pool 0.6*0.6pool Sprinkler pressure(mpa) Experimental value (kw) Fig. 3. Temperature rise of smoke layer versus sprinkler pressure Fig. 4. Comparison of experimental and calculated smoke layer cooling 869
10 Figure 4 compares the cooling of the smoke layer calculated by Eq with that measured experimentally. It can be seen that the sprinkler cooling increases to some extent with the operating pressure of the sprinkler. For smaller fires, the heat losses of the smoke layer predicted by the mathematical model slightly exceed the experimental measurements. The biggest error is 46% for test 8, but for larger fires, the value obtained by the mathematical model agrees fairly well with the experimental data. For the m pool fire, for the spray generated at 0.05 MPa, experimental value of the heat extracted by the spray is 54.8 kw and the model value is 54.9 kw. CONCLUSIONS We have developed a new model to calculate the heat loss from a smoke layer to a sprinkler spray. Our model is based on the theoretical analysis of Chow and Tang, applies a log-normal droplet-size distribution, function and neglects droplet boiling. A series of experiments was also conducted to verify the model. Results show that experimental measurements and calculated predictions are in good agreement. Sprinkler operation has a great effect on the smoke temperature. For the range of pressure studied in the present investigation, we found only a small effect of pressure on the cooling of the hot layer, consistent with the square root dependence of droplet diameter on pressure. The model requires further improvement. Especially, one needs to incorporate the evaporation effect. Should this effect be included, the cooling would be more than that predicted in this study. Also, the droplet size distribution function and some parameters, derived from previous studies, need to be refined. A follow-up investigation is in progress and further results will be reported in a subsequent publication. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT This work was supported by the National Key Technology R&D Program of China under Grant No. 2006BAK06B02. Table 1. Summary of the tests Test No. Ambient temperature (K) Pool size (m 2 ) Heat release rate (kw) Sprinkler operating pressure (MPa) Height of smoke layer (m) Smoke velocity (m/s) Average temperature rise of the smoke layer (K) Mass rate of smoke (kg/s) Experimental value of sprinkler cooling (kw) Test * Test * Test * Test * Test * Test * Test * Test * Test * Test * Test * Test * Test * Test * Test * Test *
11 Table 2. Input parameters of the model and results of the calculation Test No. Density of smoke( kg/m 3 ) Coefficient of thermal conductivity of the smoke (W/m K) Specific heat of smoke (kj/kg K) Prandtl number of the air Kinematical viscosity coefficient of smoke (m 2 /s) Flow rate of the sprinkler (L/s) Volume medium diameter of the droplets (μm) Model value of the sprinkler cooling (kw) Error ( kw / %) Test Test /36 Test /38 Test /46 Test Test /41 Test /34 Test /40 Test Test /32 Test /20 Test /19 Test Test /0.1 Test /-2 Test /
12 REFERENCES [1] D.J. Rasbash, Z.W. Rogowski and S.W.V. Stark.,(1960) Mechanism of Extinction of Liquid Fires with Water Vessel, Combustion and Flame 4: [2] D.J. Rasbash., Heat Transfer between Water Sprays and Flames of Freely Burning Fires, Proceeding of the Symposium- the Interaction between Fluids and Particles, International Chemical Engineering,1962,pp [3] Howard P. Morgan., (1979) Heat transfer From a Buoyant Smoke Layer Beneath a Ceiling to a Sprinkler Spray 1-A Tentative Theory, Fire and Materials 3: doi: /fam [4] Howard P. Morgan and K. Baines.,(1979) Heat transfer From a Buoyant Smoke Layer Beneath a Ceiling to a Sprinkler Spray 2 - An Experiment, Fire and Materials 3: doi: /fam [5] L.Y. Cooper.,(1995) The Interaction of an Isolated Sprinkler Spray and a Two-Layer Compartment Fire Environment. Phenomena and Model Simulations, Fire Safety Journal 25: doi: / (95) [6] L.Y. Cooper.,(1995) The Interaction of an Isolated Sprinkler Spray and a Two-Layer Compartment Fire Environment, International Journal Heat and Mass Transfer 38: doi: / (94) [7] Alpert R L.,(1985) Numerical modeling of the interaction between automatic sprinkler sprays, Fire Safety Journal 9: doi: / (85) [8] Hoffmann N F, Galea E R, Markatos N C.,(1989) Mathematical Modeling of the Fire Sprinkler Systems, Applied Mathematical Modeling 13: [9] Gardiner A J., The Mathematical Modeling of the Interaction Between Sprinkler Sprays and the Thermally Buoyant Layers of the Gas from Fires. PhD dissertation, South Bank Polytechnic, London, United Kingdom, [10] Chow W K, Fong N K.,(1991) Numerical Simulation on Cooling of the Fire-induced Air Flow by Sprinkler Water Spray, Fire safety Journal 17: doi: / (91)90023-r. [11] Chow W K, Fong N K.,(1993) Numerical Studies on the Interaction of Sprinklers and the Hot Layer,Architectural Science review 36: [12] Chow W K, Cheung Y L.,(1994) Simulation of Sprinkler-hot Layer Interaction Using a Field Model. Fire and Material, 18: doi: /fam [13] W.K.Chow and Anderson C.Tang.,(1994) Experimental Studies on Sprinkler Water Spray-Smoke Layer Interaction, Journal of Applied Fire Science 4: [14] Subramaniam S.,(2001) Statistical Modeling of Sprays Using the Droplet Distribution Function, Physics of Fluids13. [15] J.M.Prahl and B. Wendt.,(1988) Discharge Distribution Performance for an Axisymmetric Model of a Fire Sprinkler Head, Fire Safety Journal 14: doi: / (88) [16] Yu H Z., Investigation of Spray Patterns of Selected Sprinklers with the FMRC Drop Size Measuring System, Fire Safety Science Proceedings of the First International Symposium, International Association For Fire Safety Science, 1986, pp [17] Chan T S.,(1994) Measurement of Water Density and Droplet Size Distributions of Selected ESFR Sprinklers, Journal of Fire Protection Engineering 6: doi: / [18] M.L.Bullen., The Effect of a Sprinkler on the Stability of a Smoke Layer Beneath a Ceiling, Fire Research Note 1016, Fire Research Station, Borehamwood, United Kingdom,1974. [19] Code of design for sprinkler systems, China planning press, Beijing, 2001, p
EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES ON THE EFFECT OF THE FIRE POSITION ON PLUME ENTRAINMENT IN A LARGE SPACE
 , Volume, Number 4, p.138-14, 23 EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES ON THE EFFECT OF THE FIRE POSITION ON PLUME ENTRAINMENT IN A LARGE SPACE Yuanzhou Li, Ran Huo, Liang Yi and Guodong Wang State Key Laboratory of Fire
, Volume, Number 4, p.138-14, 23 EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES ON THE EFFECT OF THE FIRE POSITION ON PLUME ENTRAINMENT IN A LARGE SPACE Yuanzhou Li, Ran Huo, Liang Yi and Guodong Wang State Key Laboratory of Fire
ZONE MODEL VERIFICATION BY ELECTRIC HEATER
 , Volume 6, Number 4, p.284-290, 2004 ZONE MODEL VERIFICATION BY ELECTRIC HEATER Y.T. Chan Department of Building Services Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China ABSTRACT Selecting
, Volume 6, Number 4, p.284-290, 2004 ZONE MODEL VERIFICATION BY ELECTRIC HEATER Y.T. Chan Department of Building Services Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China ABSTRACT Selecting
4th International Conference on Sensors, Measurement and Intelligent Materials (ICSMIM 2015)
 4th International Conference on Sensors, Measurement and Intelligent Materials (ICSMIM 2015) Multi-stage Series Heat Pump Drying System with Dehumidification Simulation and Experiment Verification Chao
4th International Conference on Sensors, Measurement and Intelligent Materials (ICSMIM 2015) Multi-stage Series Heat Pump Drying System with Dehumidification Simulation and Experiment Verification Chao
Global Journal of Engineering Science and Research Management
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THEORETICAL STUDY OF MINIATURE VAPOR COMPRESSION CYCLE USING MICROCHANNEL CONDENSER Issam M. Ali Aljubury*, Ahmed Q. Mohammed, Marwa S. Neama * Mechanical Eng. Dept. College of Engineering,
EXPERIMENTAL AND THEORETICAL STUDY OF MINIATURE VAPOR COMPRESSION CYCLE USING MICROCHANNEL CONDENSER Issam M. Ali Aljubury*, Ahmed Q. Mohammed, Marwa S. Neama * Mechanical Eng. Dept. College of Engineering,
PRELIMINARY STUDIES ON MECHANICAL SMOKE EXHAUSTS IN LARGE SPACE BUILDING FIRES
 PRELIMINARY STUDIES ON MECHANICAL SMOKE EXHAUSTS IN LARGE SPACE BUILDING FIRES R. Huo a, Y. Li a, W. Fan a and W. Chow b a. State Key Laboratory of Fire Science, CHINA b. The Hong Kong Polytechnic University
PRELIMINARY STUDIES ON MECHANICAL SMOKE EXHAUSTS IN LARGE SPACE BUILDING FIRES R. Huo a, Y. Li a, W. Fan a and W. Chow b a. State Key Laboratory of Fire Science, CHINA b. The Hong Kong Polytechnic University
RADIATION BLOCKAGE EFFECTS BY WATER CURTAIN
 , Volume 6, Number 4, p.248-254, 04 RADIATION BLOCKAGE EFFECTS BY WATER CURTAIN C.L. Choi Department of Building Services Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China ABSTRACT Water
, Volume 6, Number 4, p.248-254, 04 RADIATION BLOCKAGE EFFECTS BY WATER CURTAIN C.L. Choi Department of Building Services Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China ABSTRACT Water
Falling Film Heat Exchangers for Solar Water Heaters
 Y.C., G.L. Morrison and M. Behnia School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering University of New South Wales Sydney 2052 AUSTRALIA E-mail: yens@student.unsw.edu.au Abstract The characteristics of
Y.C., G.L. Morrison and M. Behnia School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering University of New South Wales Sydney 2052 AUSTRALIA E-mail: yens@student.unsw.edu.au Abstract The characteristics of
A Mathematical Model of the Drag Component of a Sprinkler Spray Adjacent to Horizontal Smoke Vents
 A Mathematical Model of the Drag Component of a Sprinkler Spray Adjacent to Horizontal Smoke Vents K. Y. LI* AND M. J. SPEARPOINT Department of Civil and Natural Resources Engineering University of Canterbury,
A Mathematical Model of the Drag Component of a Sprinkler Spray Adjacent to Horizontal Smoke Vents K. Y. LI* AND M. J. SPEARPOINT Department of Civil and Natural Resources Engineering University of Canterbury,
and vent height on mechanical smoke exhaust efficiency
 Experimental investigation on influence of smoke venting velocity and vent height on mechanical smoke exhaust efficiency Ji Jie a, Li Kaiyuan b, Zhong Wei c, *, Huo Ran a a State Key Laboratory of Fire
Experimental investigation on influence of smoke venting velocity and vent height on mechanical smoke exhaust efficiency Ji Jie a, Li Kaiyuan b, Zhong Wei c, *, Huo Ran a a State Key Laboratory of Fire
A Numerical study of the Fire-extinguishing Performance of Water Mist in an Opening Machinery Space
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 31 (2012) 734 738 International Conference on Advances in Computational Modeling and Simulation A Numerical study of the Fire-extinguishing
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 31 (2012) 734 738 International Conference on Advances in Computational Modeling and Simulation A Numerical study of the Fire-extinguishing
EXPERIMENTAL AND CFD STUDIES ON SURFACE CONDENSATION
 Eighth International IBPSA Conference Eindhoven, Netherlands August 11-14, 2003 EXPERIMENTAL AND CFD STUDIES ON SURFACE CONDENSATION Liu Jing 1, Yoshihiro Aizawa 2, Hiroshi Yoshino 3 1 School of Municipal
Eighth International IBPSA Conference Eindhoven, Netherlands August 11-14, 2003 EXPERIMENTAL AND CFD STUDIES ON SURFACE CONDENSATION Liu Jing 1, Yoshihiro Aizawa 2, Hiroshi Yoshino 3 1 School of Municipal
NUMERICAL STUDIES ON BARE CABIN FIRES WITH OPERATION OF SMOKE EXTRACTION SYSTEM
 , Volume 11, Number 2, p.43-48, 2012 NUMERICAL STUDIES ON BARE CABIN FIRES WITH OPERATION OF SMOKE EXTRACTION SYSTEM Q. Kui Institute of Building Fire Research, China Academy of Building Research, Beijing,
, Volume 11, Number 2, p.43-48, 2012 NUMERICAL STUDIES ON BARE CABIN FIRES WITH OPERATION OF SMOKE EXTRACTION SYSTEM Q. Kui Institute of Building Fire Research, China Academy of Building Research, Beijing,
Experimental study on heat transfer characteristics of horizontal concentric tube using twisted wire brush inserts
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 416, P-ISSN 2347 5161 216 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Experimental
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 416, P-ISSN 2347 5161 216 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Experimental
ENSC 388: Engineering Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer
 ENSC 388: Engineering Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer Experiment 3: Free and Forced Convection Objective Determination of heat transfer coefficient for free and forced convection for different geometries.
ENSC 388: Engineering Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer Experiment 3: Free and Forced Convection Objective Determination of heat transfer coefficient for free and forced convection for different geometries.
An experimental study of the impact of tunnel suppression on tunnel ventilation
 An experimental study of the impact of tunnel suppression on tunnel ventilation Yoon J. Ko and George Hadjisophocleous Civil and Environmental Engineering, Carleton University 1125 Colonel By Drive, Ottawa,
An experimental study of the impact of tunnel suppression on tunnel ventilation Yoon J. Ko and George Hadjisophocleous Civil and Environmental Engineering, Carleton University 1125 Colonel By Drive, Ottawa,
Simple Equations for Predicting Smoke Filling Time in Fire Rooms with Irregular Ceilings
 Fire Science and Technorogy Vol.24 No.4(2005) 165-178 165 Simple Equations for Predicting Smoke Filling Time in Fire Rooms with Irregular Ceilings Jun-ichi Yamaguchi 1, Takeyoshi Tanaka 2 1 Technical Research
Fire Science and Technorogy Vol.24 No.4(2005) 165-178 165 Simple Equations for Predicting Smoke Filling Time in Fire Rooms with Irregular Ceilings Jun-ichi Yamaguchi 1, Takeyoshi Tanaka 2 1 Technical Research
Experimental Study to Evaluate Smoke Stratification and Layer Height in Highly Ventilated Compartments
 Experimental Study to Evaluate Smoke Stratification and Layer Height in Highly Ventilated Compartments Jason Huczek a, Marc Janssens a, Kentaro Onaka b, Stephen Turner c a SwRI, 6220 Culebra Road, San
Experimental Study to Evaluate Smoke Stratification and Layer Height in Highly Ventilated Compartments Jason Huczek a, Marc Janssens a, Kentaro Onaka b, Stephen Turner c a SwRI, 6220 Culebra Road, San
Physical Mechanism of Convection. Conduction and convection are similar in that both mechanisms require the presence of a material medium.
 Convection 1 Physical Mechanism of Convection Conduction and convection are similar in that both mechanisms require the presence of a material medium. But they are different in that convection requires
Convection 1 Physical Mechanism of Convection Conduction and convection are similar in that both mechanisms require the presence of a material medium. But they are different in that convection requires
The Experimental Study and Simplified Model of. Water Mist Absorbing Heat Radiation
 Advanced Materials Research Submitted: 2014-06-15 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vols. 1008-1009, pp 886-891 Accepted: 2014-06-16 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.1008-1009.886 Online: 2014-08-13 2014 Trans Tech Publications,
Advanced Materials Research Submitted: 2014-06-15 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vols. 1008-1009, pp 886-891 Accepted: 2014-06-16 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.1008-1009.886 Online: 2014-08-13 2014 Trans Tech Publications,
Thermal Design of Condenser Using Ecofriendly Refrigerants R404A-R508B for Cascade Refrigeration System
 Thermal Design of Condenser Using Ecofriendly Refrigerants R404A-R508B for Cascade Refrigeration System A D Parekh, and P R Tailor Abstract Because of damaging effect of CFC refrigerants on stratospheric
Thermal Design of Condenser Using Ecofriendly Refrigerants R404A-R508B for Cascade Refrigeration System A D Parekh, and P R Tailor Abstract Because of damaging effect of CFC refrigerants on stratospheric
THERMAL PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF GREENHOUSE SOLAR DRYER UNDER PASSIVE MODE
 THERMAL PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF GREENHOUSE SOLAR DRYER UNDER PASSIVE MODE Pushpendra Singh 1, Vipin Shrivastava 2 1,2 Mechanical Engineering Department, Lakshmi Narain College of Technology (India) ABSTRACT
THERMAL PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF GREENHOUSE SOLAR DRYER UNDER PASSIVE MODE Pushpendra Singh 1, Vipin Shrivastava 2 1,2 Mechanical Engineering Department, Lakshmi Narain College of Technology (India) ABSTRACT
A Monte Carlo Approach for the Design of Thermal Fire Detection System
 A Monte Carlo Approach for the Design of Thermal Fire Detection System Walter W. Yuen Department of Mechanical & Environmental Engineering University of California at Santa Barbara California, USA and
A Monte Carlo Approach for the Design of Thermal Fire Detection System Walter W. Yuen Department of Mechanical & Environmental Engineering University of California at Santa Barbara California, USA and
STUDY ON TEMPERATURE, RH AND AIR FLOW VELOCITY DISTRIBUTION INSIDE THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT SOLAR DRYER
 STUDY ON TEMPERATURE, RH AND AIR FLOW VELOCITY DISTRIBUTION INSIDE THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT SOLAR DRYER WULANDANI, D., K. ABDULLAH, E. HARTULISTIYOSO Department of Agricultural Engineering, Faculty of Agricultural
STUDY ON TEMPERATURE, RH AND AIR FLOW VELOCITY DISTRIBUTION INSIDE THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT SOLAR DRYER WULANDANI, D., K. ABDULLAH, E. HARTULISTIYOSO Department of Agricultural Engineering, Faculty of Agricultural
Theoritical Analysis For Miniature Vapor Compression Cycle Performance Using Microchannel And Finned Tube Condenser
 Theoritical Analysis For Miniature Vapor Compression Cycle Performance Using Microchannel And Finned Tube Condenser Issam Mohammed Ali Ahmed Qasim Mohammed Marwa Sallah Neama Mechanical Eng. Dept Air-
Theoritical Analysis For Miniature Vapor Compression Cycle Performance Using Microchannel And Finned Tube Condenser Issam Mohammed Ali Ahmed Qasim Mohammed Marwa Sallah Neama Mechanical Eng. Dept Air-
Performance Enhancement of Refrigeration Cycle by Employing a Heat Exchanger
 Performance Enhancement of Refrigeration Cycle by Employing a Heat Exchanger Shoeb Inamdar 1, H. S. Farkade 2 P.G. Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Govt. College of Engg. Amravati. Maharashtra,
Performance Enhancement of Refrigeration Cycle by Employing a Heat Exchanger Shoeb Inamdar 1, H. S. Farkade 2 P.G. Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Govt. College of Engg. Amravati. Maharashtra,
ijcrr Vol 04 issue 07 Category: Research Received on:06/02/12 Revised on:17/02/12 Accepted on:02/03/12
 EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF THE EFFECT OF FIN GEOMETRY ON HEAT TRANSFER RATE THROUGH THE REFRIGERATOR CONDENSER ijcrr Vol 04 issue 07 Category: Research Received on:06/02/12 Revised on:17/02/12 Accepted on:02/03/12
EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF THE EFFECT OF FIN GEOMETRY ON HEAT TRANSFER RATE THROUGH THE REFRIGERATOR CONDENSER ijcrr Vol 04 issue 07 Category: Research Received on:06/02/12 Revised on:17/02/12 Accepted on:02/03/12
Development of a Transient Simulation Model of a Freezer Part II: Comparison of Experimental Data with Model
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 199 Development of a Transient Simulation Model of a Freezer Part II: Comparison
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 199 Development of a Transient Simulation Model of a Freezer Part II: Comparison
Using FDS Modelling to Establish Performance Criteria for Water Mist Systems on Very Large Fires in Tunnels
 Using FDS Modelling to Establish Performance Criteria for Water Mist Systems on Very Large Fires in Tunnels Jack R. Mawhinney, P. Eng., FSFPE Javier J. Trelles, Ph.D. Authors & acknowledgement J. R. Mawhinney
Using FDS Modelling to Establish Performance Criteria for Water Mist Systems on Very Large Fires in Tunnels Jack R. Mawhinney, P. Eng., FSFPE Javier J. Trelles, Ph.D. Authors & acknowledgement J. R. Mawhinney
WATER MIST FIRE PROTECTION SYSTEMS FOR INDUSTRIAL CABLE TUNNELS AND TURBINE HALLS
 WATER MIST FIRE PROTECTION SYSTEMS FOR INDUSTRIAL CABLE TUNNELS AND TURBINE HALLS Jukka Vaari 1, Amit Lior 2 1 2 VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland, Espoo, Finland Marioff Corporation Oy, Vantaa,
WATER MIST FIRE PROTECTION SYSTEMS FOR INDUSTRIAL CABLE TUNNELS AND TURBINE HALLS Jukka Vaari 1, Amit Lior 2 1 2 VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland, Espoo, Finland Marioff Corporation Oy, Vantaa,
OPTIMIZATION OF VENTILATION MODE OF SMOKE CONTROL SYSTEM IN HIGH-RISE BUILDING FIRE
 OPTIMIZATION OF VENTILATION MODE OF SMOKE CONTROL SYSTEM IN HIGH-RISE BUILDING FIRE 1 RU ZHOU, 2 WEI ZHANG 1 School of Urban Construction and Safety Engineering, Nanjing University of Technology, Nanjing
OPTIMIZATION OF VENTILATION MODE OF SMOKE CONTROL SYSTEM IN HIGH-RISE BUILDING FIRE 1 RU ZHOU, 2 WEI ZHANG 1 School of Urban Construction and Safety Engineering, Nanjing University of Technology, Nanjing
CHAPTER 2 EXPERIMENTAL APPARATUS AND PROCEDURES
 CHAPTER 2 EXPERIMENTAL APPARATUS AND PROCEDURES The experimental system established in the present study to investigate the transient flow boiling heat transfer and associated bubble characteristics of
CHAPTER 2 EXPERIMENTAL APPARATUS AND PROCEDURES The experimental system established in the present study to investigate the transient flow boiling heat transfer and associated bubble characteristics of
A NETWORK MODEL OF SIMULATING SMOKE MOVEMENT IN BUILDINGS
 , Volume 3, Number 4, p.151-157, 2001 A NETWORK MODEL OF SIMULATING SMOKE MOVEMENT IN BUILDINGS F. Liu and X.Z. Fu Faculty of Urban Construction and Environmental Engineering Chongqing University, Chongqing
, Volume 3, Number 4, p.151-157, 2001 A NETWORK MODEL OF SIMULATING SMOKE MOVEMENT IN BUILDINGS F. Liu and X.Z. Fu Faculty of Urban Construction and Environmental Engineering Chongqing University, Chongqing
A Study on the 2-D Temperature Distribution of the Strip due to Induction Heater
 , pp.1-5 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2015.90.01 A Study on the 2-D Temperature Distribution of the Strip due to Induction Heater Jong-Hyun Lee 1, Jin-Taek Kim 1, Sung-Hyuk Lim 2, Do-Gyun Jung 2, Hyeong-Jin
, pp.1-5 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2015.90.01 A Study on the 2-D Temperature Distribution of the Strip due to Induction Heater Jong-Hyun Lee 1, Jin-Taek Kim 1, Sung-Hyuk Lim 2, Do-Gyun Jung 2, Hyeong-Jin
Shalaby Institute of Fire Protection Heyrothsberge, Germany.
 International Water Mist Conference November 3-4, 2010, Prague, Czech Republic The Influence of Droplet Size of Water Mist on Extinguishment Fire Plume Dr.Hemdan Shalaby Institute of Fire Protection Heyrothsberge,
International Water Mist Conference November 3-4, 2010, Prague, Czech Republic The Influence of Droplet Size of Water Mist on Extinguishment Fire Plume Dr.Hemdan Shalaby Institute of Fire Protection Heyrothsberge,
Experimental Investigation of Elliptical Tube Bank Cross Flow Heat Exchanger with Inline Arrangement & 45 Angle of Attack
 Experimental Investigation of Elliptical Tube Bank Cross Flow Heat Exchanger with Inline Arrangement & 45 Angle of Attack #1 Digvijay A. Shelar, #2 N.S. Gohel, #3 R. S. Jha #1 Mechanical Engineering Department,
Experimental Investigation of Elliptical Tube Bank Cross Flow Heat Exchanger with Inline Arrangement & 45 Angle of Attack #1 Digvijay A. Shelar, #2 N.S. Gohel, #3 R. S. Jha #1 Mechanical Engineering Department,
Smoldering Propagation Characteristics of Flexible Polyurethane Foam under Different Air Flow Rates
 Smoldering Propagation Characteristics of Flexible Polyurethane Foam under Different Air Flow Rates Zhou Y., Fei Y.*, Hu S. Q. Nanjing Tech University, College of Fire Safety Science and Engineering &
Smoldering Propagation Characteristics of Flexible Polyurethane Foam under Different Air Flow Rates Zhou Y., Fei Y.*, Hu S. Q. Nanjing Tech University, College of Fire Safety Science and Engineering &
A STUDY ON COMPACT HEAT EXCHANGERS AND PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS
 A STUDY ON COMPACT HEAT EXCHANGERS AND PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS V. BHOGESWARA RAO Research Scholar Email:pallivayala@gmail.com Dr. S. CHAKRADHAR GOUD Principal, Sri Sarada Institute of Science and Technology
A STUDY ON COMPACT HEAT EXCHANGERS AND PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS V. BHOGESWARA RAO Research Scholar Email:pallivayala@gmail.com Dr. S. CHAKRADHAR GOUD Principal, Sri Sarada Institute of Science and Technology
Experimental investigation of Hybrid Nanofluid on wickless heat pipe heat exchanger thermal performance
 Experimental investigation of Hybrid Nanofluid on wickless heat pipe heat exchanger thermal performance #1 Jaydev S. Bade, #2 Dr. Nitin U. Korde 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Savitribai Phule
Experimental investigation of Hybrid Nanofluid on wickless heat pipe heat exchanger thermal performance #1 Jaydev S. Bade, #2 Dr. Nitin U. Korde 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Savitribai Phule
Experimental Investigate on the Performance of High Temperature Heat Pump Using Scroll Compressor
 Experimental Investigate on the Performance of High Temperature Heat Pump Using Scroll Compressor Mingyue Huang a, Xiangfei Liang a,b *, Rong Zhuang a a Gree Electric Appliances, Inc.of Zhuhai,Zhuhai 519070,China
Experimental Investigate on the Performance of High Temperature Heat Pump Using Scroll Compressor Mingyue Huang a, Xiangfei Liang a,b *, Rong Zhuang a a Gree Electric Appliances, Inc.of Zhuhai,Zhuhai 519070,China
ME 410 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING SYSTEMS LABORATORY MASS & ENERGY BALANCES IN PSYCHROMETRIC PROCESSES EXPERIMENT 3
 ME 410 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING SYSTEMS LABORATORY MASS & ENERGY BALANCES IN PSYCHROMETRIC PROCESSES EXPERIMENT 3 1. OBJECTIVE The objective of this experiment is to observe four basic psychrometric processes
ME 410 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING SYSTEMS LABORATORY MASS & ENERGY BALANCES IN PSYCHROMETRIC PROCESSES EXPERIMENT 3 1. OBJECTIVE The objective of this experiment is to observe four basic psychrometric processes
MODELLING AND OPTIMIZATION OF DIRECT EXPANSION AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM FOR COMMERCIAL BUILDING ENERGY SAVING
 MODELLING AND OPTIMIZATION OF DIRECT EXPANSION AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM FOR COMMERCIAL BUILDING ENERGY SAVING V. Vakiloroaya*, J.G. Zhu, and Q.P. Ha School of Electrical, Mechanical and Mechatronic Systems,
MODELLING AND OPTIMIZATION OF DIRECT EXPANSION AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM FOR COMMERCIAL BUILDING ENERGY SAVING V. Vakiloroaya*, J.G. Zhu, and Q.P. Ha School of Electrical, Mechanical and Mechatronic Systems,
SIMULATION ANALYSIS ON THE FRESH AIR HANDLING UNIT WITH LIQUID DESICCANT TOTAL HEAT RECOVERY
 SIMULATION ANALYSIS ON THE FRESH AIR HANDLING UNIT WITH LIQUID DESICCANT TOTAL HEAT RECOVERY Xiaoyun Xie, Yidan Tang, Xiaoqin Yi, Shuanqiang Liu,Yi Jiang Department of Building Science and Technology,
SIMULATION ANALYSIS ON THE FRESH AIR HANDLING UNIT WITH LIQUID DESICCANT TOTAL HEAT RECOVERY Xiaoyun Xie, Yidan Tang, Xiaoqin Yi, Shuanqiang Liu,Yi Jiang Department of Building Science and Technology,
ME 410 MECHA ICAL E GI EERI G SYSTEMS LABORATORY
 ME 410 MECHA ICAL E GI EERI G SYSTEMS LABORATORY MASS & E ERGY BALA CES I PSYCHROMETRIC PROCESSES EXPERIME T 3 1. OBJECTIVE The object of this experiment is to observe four basic psychrometric processes
ME 410 MECHA ICAL E GI EERI G SYSTEMS LABORATORY MASS & E ERGY BALA CES I PSYCHROMETRIC PROCESSES EXPERIME T 3 1. OBJECTIVE The object of this experiment is to observe four basic psychrometric processes
INFLUENCE OF SOLAR RADIATION AND VENTILATION CONDITIONS ON HEAT BALANCE AND THERMAL COMFORT CONDITIONS IN LIVING-ROOMS
 INFLUENCE OF SOLAR RADIATION AND VENTILATION CONDITIONS ON HEAT BALANCE AND THERMAL COMFORT CONDITIONS IN LIVING-ROOMS Staņislavs GENDELIS, Andris JAKOVIČS Laboratory for mathematical modelling of environmental
INFLUENCE OF SOLAR RADIATION AND VENTILATION CONDITIONS ON HEAT BALANCE AND THERMAL COMFORT CONDITIONS IN LIVING-ROOMS Staņislavs GENDELIS, Andris JAKOVIČS Laboratory for mathematical modelling of environmental
Performance Enhancement of Refrigeration Cycle by Employing a Heat Exchanger
 Performance Enhancement of Refrigeration Cycle by Employing a Heat Exchanger Abstract Shoeb J. Inamdar 1 H.S. Farkade 2 M. Tech student. (Thermal Engineering) 1, Asst. Professor 2 Department of Mechanical
Performance Enhancement of Refrigeration Cycle by Employing a Heat Exchanger Abstract Shoeb J. Inamdar 1 H.S. Farkade 2 M. Tech student. (Thermal Engineering) 1, Asst. Professor 2 Department of Mechanical
Design and Development of Water Cooled Condenser for Domestic Refrigerator
 Design and Development of Water Cooled Condenser for Domestic Refrigerator Anil S. Patil Research PG Student, GF s Godavari College of Engineering, Jalgaon Dr. Atul A Patil Assot. Prof. GF s Godavari College
Design and Development of Water Cooled Condenser for Domestic Refrigerator Anil S. Patil Research PG Student, GF s Godavari College of Engineering, Jalgaon Dr. Atul A Patil Assot. Prof. GF s Godavari College
Experimental Room Fire Studies with Perforated Suspended Ceiling
 Experimental Room Fire Studies with Perforated Suspended Ceiling FIONA S.C. TSUI 1, W.K. CHOW 1, N.K. FONG 1, Y. GAO 2, H. DONG 2, and G.W. ZOU 2 1 Research Centre for Fire Engineering Department of Building
Experimental Room Fire Studies with Perforated Suspended Ceiling FIONA S.C. TSUI 1, W.K. CHOW 1, N.K. FONG 1, Y. GAO 2, H. DONG 2, and G.W. ZOU 2 1 Research Centre for Fire Engineering Department of Building
2. HEAT EXCHANGERS MESA
 1. INTRODUCTION Multiport minichannel and microchannel aluminium tubes are becoming more popular as components in heat exchangers. These heat exchangers are used in various industrial applications and
1. INTRODUCTION Multiport minichannel and microchannel aluminium tubes are becoming more popular as components in heat exchangers. These heat exchangers are used in various industrial applications and
REVIEW ON WATER MIST FIRE SUPPRESSION SYSTEM
 , Volume 5, Number 4, p.170-175, 2003 REVIEW ON WATER MIST FIRE SUPPRESSION SYSTEM N. Zhu Department of Building Services Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China ABSTRACT Water
, Volume 5, Number 4, p.170-175, 2003 REVIEW ON WATER MIST FIRE SUPPRESSION SYSTEM N. Zhu Department of Building Services Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China ABSTRACT Water
Mathematical Simulation of Longan Fruit Drying
 Mathematical Simulation of Longan Fruit Drying Aree Achariyaviriya, Somchart Soponronnarit and Jirawan Tiansuwan ABSTRACT The objectives of this study were to develop a mathematical model and to simulate
Mathematical Simulation of Longan Fruit Drying Aree Achariyaviriya, Somchart Soponronnarit and Jirawan Tiansuwan ABSTRACT The objectives of this study were to develop a mathematical model and to simulate
Seyedeh Sepideh Ghaffari 1 & Seyed Ali Jazayeri 2
 Modern Applied Science; Vol. 9, No. 13; 2015 ISSN 1913-1844 E-ISSN 1913-1852 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education The Design of a Shell-Tube Heat Exchanger as Evaporator an Absorption
Modern Applied Science; Vol. 9, No. 13; 2015 ISSN 1913-1844 E-ISSN 1913-1852 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education The Design of a Shell-Tube Heat Exchanger as Evaporator an Absorption
Investigating the Effects of Sprinkler Sprays on Fire-Induced Doorway Flows: A Two-Part Study. Jeremiah Crocker and Dr. Bin Xiao New Technology Team
 Jeremiah Crocker and Dr. Bin Xiao New Technology Team Copyright 2010 Tyco Fire Suppression & Building Products. All rights reserved. The products and specifications published herein are for general evaluation
Jeremiah Crocker and Dr. Bin Xiao New Technology Team Copyright 2010 Tyco Fire Suppression & Building Products. All rights reserved. The products and specifications published herein are for general evaluation
Scientific Principals and Analytical Model. Charcoal Cooler. Lisa Crofoot MECH 425, Queens University
 Scientific Principals and Analytical Model Charcoal Cooler Lisa Crofoot MECH 425, Queens University 1.0 Scientific Principles Evaporative cooling is based on the principle that water requires heat energy
Scientific Principals and Analytical Model Charcoal Cooler Lisa Crofoot MECH 425, Queens University 1.0 Scientific Principles Evaporative cooling is based on the principle that water requires heat energy
EFFECTIVE UTILIZATION OF SOLAR ENERGY IN AIR DRYER
 International Journal of Mechanical and Production Engineering Research and Development (IJMPERD) ISSN 2249-6890 Vol. 3, Issue 1, Mar 2013, 133-142 TJPRC Pvt Ltd. EFFECTIVE UTILIZATION OF SOLAR ENERGY
International Journal of Mechanical and Production Engineering Research and Development (IJMPERD) ISSN 2249-6890 Vol. 3, Issue 1, Mar 2013, 133-142 TJPRC Pvt Ltd. EFFECTIVE UTILIZATION OF SOLAR ENERGY
Experimental Study on Performance of Double pipe Length on Instantaneous Air Source Heat Pump Water Heater. Yin Shaoyou 1, a
 International Symposium on Energy Science and Chemical Engineering (ISESCE 2015) Experimental Study on Performance of Double pipe Length on Instantaneous Air Source Heat Pump Water Heater Yin Shaoyou 1,
International Symposium on Energy Science and Chemical Engineering (ISESCE 2015) Experimental Study on Performance of Double pipe Length on Instantaneous Air Source Heat Pump Water Heater Yin Shaoyou 1,
Performance Study of Triple Concentric Pipe Heat Exchanger
 Performance Study of Triple Concentric Pipe Heat Exchanger #1 Pravin M. Linge, #2 A. B. Korane, #3 V. N. Kapatkar #123 Mechanical Engineering Department, Sinhgad College of Engineering, SPPU, Pune, India
Performance Study of Triple Concentric Pipe Heat Exchanger #1 Pravin M. Linge, #2 A. B. Korane, #3 V. N. Kapatkar #123 Mechanical Engineering Department, Sinhgad College of Engineering, SPPU, Pune, India
Feasibility Study of Condensation Heat Exchanger with Helical Tubes for a Passive Auxiliary Feedwater System
 Feasibility Study of Condensation Heat Exchanger with Helical Tubes for a Passive Auxiliary Feedwater System Kwanghee Seo 1) and Taewan Kim 2)* 1) KEPCO Engineering & Construction Company. INC., 269 Hyeoksin-ro,
Feasibility Study of Condensation Heat Exchanger with Helical Tubes for a Passive Auxiliary Feedwater System Kwanghee Seo 1) and Taewan Kim 2)* 1) KEPCO Engineering & Construction Company. INC., 269 Hyeoksin-ro,
PREDICTION OF THE PRESSURE DROP OF CO 2 IN AN EVAPORATOR USED FOR AIR COOLING ABSTRACT 1. INTRODUCTION 2. EXPERIMENTAL SET-UP AND PROCEDURE
 PREDICTION OF THE PRESSURE DROP OF CO 2 IN AN EVAPORATOR USED FOR AIR COOLING M. POIRIER, D. GIGUÈRE, Z. AIDOUN, M. OUZZANE Natural Resources Canada, CANMET Energy Technology Centre-Varennes 1615, Lionel
PREDICTION OF THE PRESSURE DROP OF CO 2 IN AN EVAPORATOR USED FOR AIR COOLING M. POIRIER, D. GIGUÈRE, Z. AIDOUN, M. OUZZANE Natural Resources Canada, CANMET Energy Technology Centre-Varennes 1615, Lionel
Module 5: Combustion Technology. Lecture 38: Combustion Burners
 1 P age Module 5: Combustion Technology Lecture 38: Combustion Burners 2 P age Keywords : Atmospheric burner, atomizer, rotating cup burner, swirl type burner, nozzle design 5.7 Combustion Burners Types
1 P age Module 5: Combustion Technology Lecture 38: Combustion Burners 2 P age Keywords : Atmospheric burner, atomizer, rotating cup burner, swirl type burner, nozzle design 5.7 Combustion Burners Types
Heat Transfer in Evacuated Tubular Solar Collectors
 Heat Transfer in Evacuated Tubular Solar Collectors Graham L. Morrison, Indra Budihardjo and Masud Behnia School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering University of New South Wales Sydney 2052 Australia
Heat Transfer in Evacuated Tubular Solar Collectors Graham L. Morrison, Indra Budihardjo and Masud Behnia School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering University of New South Wales Sydney 2052 Australia
Experimental Study on the Effects of Compression Parameters on Molding Quality of Dried Fish Floss
 Experimental Study on the Effects of Compression arameters on Molding Quality of Dried Fish Floss Hongmei Xu, Li Zong, Ling Li, and Jing Zhang College of Engineering and Technology, Huazhong Agricultural
Experimental Study on the Effects of Compression arameters on Molding Quality of Dried Fish Floss Hongmei Xu, Li Zong, Ling Li, and Jing Zhang College of Engineering and Technology, Huazhong Agricultural
Effect of the Use Pattern on Performance of Heat Pump Water Heater
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering July 2018 Effect of the Use Pattern on Performance of Heat Pump Water Heater
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering July 2018 Effect of the Use Pattern on Performance of Heat Pump Water Heater
Numerical Studies On The Performance Of Methanol Based Air To Air Heat Pipe Heat Exchanger
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA) IJCRGG ISSN 0974-4290 Vol.5, No.2, pp 925-934, April-June 2013 ICGSEE-2013[14th 16th March 2013] International Conference on Global Scenario in Environment
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA) IJCRGG ISSN 0974-4290 Vol.5, No.2, pp 925-934, April-June 2013 ICGSEE-2013[14th 16th March 2013] International Conference on Global Scenario in Environment
International Forum on Energy, Environment Science and Materials (IFEESM 2015)
 The Comparison and Analysis of Humidity Environment between Floor and Ceiling Radiant Cooling Systems that Combined with Displacement Ventilation Kai SUN 1 a *, Chuan-hui ZHOU 1 1 College of Urban Construction,
The Comparison and Analysis of Humidity Environment between Floor and Ceiling Radiant Cooling Systems that Combined with Displacement Ventilation Kai SUN 1 a *, Chuan-hui ZHOU 1 1 College of Urban Construction,
Conceptual Design of a Better Heat Pump Compressor for Northern Climates
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1976 Conceptual Design of a Better Heat Pump Compressor for Northern Climates D. Squarer
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1976 Conceptual Design of a Better Heat Pump Compressor for Northern Climates D. Squarer
Analysis of the influence of open door size on fire smoke diffusion law in protective engineering
 Analysis of the influence of open door size on fire smoke diffusion law in protective engineering Abstract Zheli Xing a, Jinfeng Mao b, Chaofeng Li c and Jin Zhou d PLA University of Science and Technology,
Analysis of the influence of open door size on fire smoke diffusion law in protective engineering Abstract Zheli Xing a, Jinfeng Mao b, Chaofeng Li c and Jin Zhou d PLA University of Science and Technology,
Implementation and testing of a model for the calculation of equilibrium between components of a refrigeration installation
 Implementation and testing of a model for the calculation of equilibrium between components of a refrigeration installation Marco Alexandre Onofre Dias This paper presents a model that was implemented
Implementation and testing of a model for the calculation of equilibrium between components of a refrigeration installation Marco Alexandre Onofre Dias This paper presents a model that was implemented
Characterization of a Heat Sink with Embedded Heat Pipe with Variable Heat Dissipating Source Placement for Power Electronics Applications
 Characterization of a Heat Sink with Embedded Heat Pipe with Variable Heat Dissipating Source Placement for Power Electronics Applications Neda Mansouri, Cliff Weasner and Ahmed Zaghlol Mersen Canada Toronto
Characterization of a Heat Sink with Embedded Heat Pipe with Variable Heat Dissipating Source Placement for Power Electronics Applications Neda Mansouri, Cliff Weasner and Ahmed Zaghlol Mersen Canada Toronto
Heat Transfer Analysis of Vapor Compression System Using Nano Cuo-R134a
 2011 International Conference on Advanced Materials Engineering IPCSIT vol.15 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Heat Transfer Analysis of Vapor Compression System Using Nano Cuo-R134a Eed Abdel-Hafez
2011 International Conference on Advanced Materials Engineering IPCSIT vol.15 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Heat Transfer Analysis of Vapor Compression System Using Nano Cuo-R134a Eed Abdel-Hafez
Numerical investigation on the effect of channelled and unchannelled screens on smoke contamination in atriums upper balconies with open upstand
 Numerical investigation on the effect of channelled and unchannelled screens on smoke contamination in atriums upper balconies with open upstand Mohammed Mutafi 1, Mohammad Nasif 1*, William Pao 1 and
Numerical investigation on the effect of channelled and unchannelled screens on smoke contamination in atriums upper balconies with open upstand Mohammed Mutafi 1, Mohammad Nasif 1*, William Pao 1 and
Gandhinagar Institute of Technology Mechanical Engineering (Thermal Engineering) Semester II. Design of Heat Exchange Equipments [ ]
![Gandhinagar Institute of Technology Mechanical Engineering (Thermal Engineering) Semester II. Design of Heat Exchange Equipments [ ] Gandhinagar Institute of Technology Mechanical Engineering (Thermal Engineering) Semester II. Design of Heat Exchange Equipments [ ]](/thumbs/78/77331028.jpg) Experiment 1 Study of fundamentals of Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer associated with Heat Exchangers Review questions (1) Significance of dimensionless numbers. (2) Define overall heat transfer coefficient.
Experiment 1 Study of fundamentals of Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer associated with Heat Exchangers Review questions (1) Significance of dimensionless numbers. (2) Define overall heat transfer coefficient.
A Simulation Study on the Energy Efficiency of Gas-Burned Boilers in Heating Systems
 International Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 2015; 4(6): 327-332 Published online December 5, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijepe) doi: 10.11648/j.ijepe.20150406.11 ISSN: 2326-957X
International Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 2015; 4(6): 327-332 Published online December 5, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijepe) doi: 10.11648/j.ijepe.20150406.11 ISSN: 2326-957X
Fluidised-Bed Paddy Drying
 RESEARCH ARTICLE ScienceAsia 25 (1999) : 51-56 Fluidised-Bed Paddy Drying Somchart Soponronnarit School of Energy and Materials, King Mongkut's University of Technology Thonburi, Suksawat 48 Road, Bangkok
RESEARCH ARTICLE ScienceAsia 25 (1999) : 51-56 Fluidised-Bed Paddy Drying Somchart Soponronnarit School of Energy and Materials, King Mongkut's University of Technology Thonburi, Suksawat 48 Road, Bangkok
Analysis of Constant Pressure and Constant Area Mixing Ejector Expansion Refrigeration System using R-1270 as Refrigerant
 Analysis of Constant Pressure and Constant Area Mixing Ejector Expansion Refrigeration System using R-1270 as Refrigerant Ravi Verma 1, Sharad Chaudhary 2 1, 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, IET
Analysis of Constant Pressure and Constant Area Mixing Ejector Expansion Refrigeration System using R-1270 as Refrigerant Ravi Verma 1, Sharad Chaudhary 2 1, 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, IET
An Experimental Study on Evacuated Tube Solar Collector for Heating of Air in India Avadhesh Yadav, V.K. Bajpai
 Vol:5, No:7, 211 An Experimental Study on Evacuated Tube Solar Collector for Heating of Air in India Avadhesh Yadav, V.K. Bajpai International Science Index, Mechanical and Mechatronics Engineering Vol:5,
Vol:5, No:7, 211 An Experimental Study on Evacuated Tube Solar Collector for Heating of Air in India Avadhesh Yadav, V.K. Bajpai International Science Index, Mechanical and Mechatronics Engineering Vol:5,
TITLE: Improvement in Heat Transfer Rate and Dynamics of Shrouded Fanned Radiator System
 TITLE: Improvement in Heat Transfer Rate and Dynamics of Shrouded Fanned Radiator System Prof. G.L.Allampallewar 1, Divyal P. Bagul 2, Abhiraj S. Galande 3, Amol M. Rathod 4, Ketan R. Behere 5. 1 Assistant
TITLE: Improvement in Heat Transfer Rate and Dynamics of Shrouded Fanned Radiator System Prof. G.L.Allampallewar 1, Divyal P. Bagul 2, Abhiraj S. Galande 3, Amol M. Rathod 4, Ketan R. Behere 5. 1 Assistant
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION. In the modern life, electronic equipments have made their way
 1 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION In the modern life, electronic equipments have made their way in to practically every part, which is from electronic gadgets to high power computers. Electronic components have
1 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION In the modern life, electronic equipments have made their way in to practically every part, which is from electronic gadgets to high power computers. Electronic components have
THE ANALYSIS AND EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF HEAT PUMP SYSTEM USING THERMOBANK AND COS EJECTOR CYCLE
 Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Thermal Sciences 2017, 1st ACTS March 26-30, 2017, Jeju Island, Korea ACTS-P00385 THE ANALYSIS AND EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF HEAT PUMP SYSTEM USING THERMOBANK
Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Thermal Sciences 2017, 1st ACTS March 26-30, 2017, Jeju Island, Korea ACTS-P00385 THE ANALYSIS AND EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF HEAT PUMP SYSTEM USING THERMOBANK
Hot Issues in Fire Engineering 28 February 2012
 Hot Issues in Fire Engineering 28 February 2012 A Note on Cabin Fire Design for Protecting Large Halls W.K. Chow Research Centre for Fire Engineering, Department of Building Services Engineering The Hong
Hot Issues in Fire Engineering 28 February 2012 A Note on Cabin Fire Design for Protecting Large Halls W.K. Chow Research Centre for Fire Engineering, Department of Building Services Engineering The Hong
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 135 (2016 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 135 (2016 ) 439 444 Study of Grid Ceiling on Parametric Optimization Design of Automatic Sprinkler System Xiang-yu Qu a,*, Hai-yan
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 135 (2016 ) 439 444 Study of Grid Ceiling on Parametric Optimization Design of Automatic Sprinkler System Xiang-yu Qu a,*, Hai-yan
Open and Closed Door Moisture Transport and Corresponding Energy Consumption in Household Refrigerator
 18 R. Saidur et al./journal of Energy & Environment, Vol. 6, May 2007 Open and Closed Door Moisture Transport and Corresponding Energy Consumption in Household Refrigerator R. Saidur, M. A. Sattar, M.
18 R. Saidur et al./journal of Energy & Environment, Vol. 6, May 2007 Open and Closed Door Moisture Transport and Corresponding Energy Consumption in Household Refrigerator R. Saidur, M. A. Sattar, M.
FREQUENCY ENHANCEMENT OF DUAL-JUNCTION THERMOCOUPLE PROBES
 XXIII Biannual Symposium on Measuring Techniques in Turbomachinery Transonic and Supersonic Flow in FREQUENCY ENHANCEMENT OF DUAL-JUNCTION THERMOCOUPLE PROBES James Braun Purdue University Indiana, United
XXIII Biannual Symposium on Measuring Techniques in Turbomachinery Transonic and Supersonic Flow in FREQUENCY ENHANCEMENT OF DUAL-JUNCTION THERMOCOUPLE PROBES James Braun Purdue University Indiana, United
Numerical Stability Analysis of a Natural Circulation Steam Generator with a Non-uniform Heating Profile over the tube length
 Numerical Stability Analysis of a Natural Circulation Steam Generator with a Non-uniform Heating Profile over the tube length HEIMO WALTER Institute for Thermodynamics and Energy Conversion Vienna University
Numerical Stability Analysis of a Natural Circulation Steam Generator with a Non-uniform Heating Profile over the tube length HEIMO WALTER Institute for Thermodynamics and Energy Conversion Vienna University
Reducing energy consumption of airconditioning systems in moderate climates by applying indirect evaporative cooling
 Reducing energy consumption of airconditioning systems in moderate climates by applying indirect evaporative cooling Aleksandra Cichoń,*, Anna Pacak, Demis Pandelidis, and Sergey Anisimov Department of
Reducing energy consumption of airconditioning systems in moderate climates by applying indirect evaporative cooling Aleksandra Cichoń,*, Anna Pacak, Demis Pandelidis, and Sergey Anisimov Department of
Application of Evaporative Cooling in the Building Ventilated by a Solar Chimney
 Application of Evaporative Cooling in the Building Ventilated by a Solar Chimney Sudaporn Sudprasert* Faculty of Architecture and Planning, Thammasat University, Pathumthani 12121, Thailand Abstract *
Application of Evaporative Cooling in the Building Ventilated by a Solar Chimney Sudaporn Sudprasert* Faculty of Architecture and Planning, Thammasat University, Pathumthani 12121, Thailand Abstract *
Best Row Number Ratio Study of Surface Air Coolers for Segmented Handling Air-conditioning System
 International Conference on Civil, Transportation and Environment (ICCTE 201) Best Row Number Ratio Study of Surface Air Coolers for Segmented Handling Air-conditioning System Pengjie Fan1, a, Caihua Liang1,
International Conference on Civil, Transportation and Environment (ICCTE 201) Best Row Number Ratio Study of Surface Air Coolers for Segmented Handling Air-conditioning System Pengjie Fan1, a, Caihua Liang1,
Experimental Study on the Characteristics of Temperature Field of Fire Room
 Experimental Study on the Characteristics of Temperature Field of under Stack Effect in a Scaled High-rise Building Model WENXI SHI 1,2, JIE JI 1*, JINHUA SUN 1, SIUMING LO 2, LINJIE LI 1 and XIANGYONG
Experimental Study on the Characteristics of Temperature Field of under Stack Effect in a Scaled High-rise Building Model WENXI SHI 1,2, JIE JI 1*, JINHUA SUN 1, SIUMING LO 2, LINJIE LI 1 and XIANGYONG
STACK EFFECT IN LIGHT WELL OF HIGH RISE APARTMENT BUILDING
 STACK EFFECT IN LIGHT WELL OF HIGH RISE APARTMENT BUILDING H. Kotani, R. Satoh, T. Yamanaka Dept. of Architectural Engineering, School of Engineering, Osaka University, Osaka, Japan ABSTRACT The purpose
STACK EFFECT IN LIGHT WELL OF HIGH RISE APARTMENT BUILDING H. Kotani, R. Satoh, T. Yamanaka Dept. of Architectural Engineering, School of Engineering, Osaka University, Osaka, Japan ABSTRACT The purpose
STUDY ON HYBRID SYSTEM OF SOLAR POWERED WATER HEATER AND ADSORPTION ICE MAKER
 , Volume 6, Number 4, p.168-172, 2005 STUDY ON HYBRID SYSTEM OF SOLAR POWERED WATER HEATER AND ADSORPTION ICE MAKER Zhaohui Qi School of Energy Science and Engineering, Centralsouth University, Changsha,
, Volume 6, Number 4, p.168-172, 2005 STUDY ON HYBRID SYSTEM OF SOLAR POWERED WATER HEATER AND ADSORPTION ICE MAKER Zhaohui Qi School of Energy Science and Engineering, Centralsouth University, Changsha,
CFD Analysis of Fire Characteristics on Subway Junction Station
 ISGSR27 First International Symposium on Geotechnical Safety & Risk Oct. 18~19, 27 Shanghai Tongji University, China CFD Analysis of Fire Characteristics on Subway Junction Station G. H. Wu, X. Han, Q.Q.
ISGSR27 First International Symposium on Geotechnical Safety & Risk Oct. 18~19, 27 Shanghai Tongji University, China CFD Analysis of Fire Characteristics on Subway Junction Station G. H. Wu, X. Han, Q.Q.
FROSTING BEHAVIOR OF FIN-TUBE HEAT EXCHANGER ACCORDING TO REFRIGERANT FLOW TYPE
 HEFAT2012 9 th International nference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 16 18 July 2012 Malta FROSTING BEHAVIOR OF FIN-TUBE HEAT EXCHANGER ACCORDING TO REFRIGERANT FLOW TYPE Kim K.,
HEFAT2012 9 th International nference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 16 18 July 2012 Malta FROSTING BEHAVIOR OF FIN-TUBE HEAT EXCHANGER ACCORDING TO REFRIGERANT FLOW TYPE Kim K.,
Some Modeling Improvements for Unitary Air Conditioners and Heat Pumps at Off-Design Conditions
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2006 Some Modeling Improvements for Unitary Air Conditioners and Heat Pumps
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2006 Some Modeling Improvements for Unitary Air Conditioners and Heat Pumps
Effect of Louvered Strips on Heat Transfer in a Concentric Pipe Heat Exchanger
 Effect of Louvered Strips on Heat Transfer in a Concentric Pipe Heat Exchanger Somsak Pethkool 1, Smith Eiamsa-ard, Artit Ridluan and Pongjet Promvonge 1,* 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty
Effect of Louvered Strips on Heat Transfer in a Concentric Pipe Heat Exchanger Somsak Pethkool 1, Smith Eiamsa-ard, Artit Ridluan and Pongjet Promvonge 1,* 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty
The Loss prevention Council. Phase 1 report
 Phase 1 report Title: Investigation of the suitability of the Actual Delivered Density Apparatus (ADD) for the performance evaluation of standard sprinklers as described in Insurance Services project proposal
Phase 1 report Title: Investigation of the suitability of the Actual Delivered Density Apparatus (ADD) for the performance evaluation of standard sprinklers as described in Insurance Services project proposal
Study of Numerical Analysis on Smoke Exhaust Performance of Portable Smoke Exhaust Fan
 Open Journal of Fluid Dynamics, 2017, 7, 205-218 http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojfd ISSN Online: 2165-3860 ISSN Print: 2165-3852 Study of Numerical Analysis on Smoke Exhaust Performance of Portable Smoke
Open Journal of Fluid Dynamics, 2017, 7, 205-218 http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojfd ISSN Online: 2165-3860 ISSN Print: 2165-3852 Study of Numerical Analysis on Smoke Exhaust Performance of Portable Smoke
Effect of domestic storage and cooking conditions on the risk distribution in ready to cook meat products
 Effect of domestic storage and cooking conditions on the risk distribution in ready to cook meat products Bakalis S.*, Giannakourou M.C. and Taoukis P. School of Chemical Engineering, National Technical
Effect of domestic storage and cooking conditions on the risk distribution in ready to cook meat products Bakalis S.*, Giannakourou M.C. and Taoukis P. School of Chemical Engineering, National Technical
AN ANALYSIS OF THE ACTUAL THERMAL PLUMES OF KITCHEN APPLIANCES DURING COOKING MODE
 AN ANALYSIS OF THE ACTUAL THERMAL PLUMES OF KITCHEN APPLIANCES DURING COOKING MODE R Kosonen 1,*, H Koskela 2 and P Saarinen 2 1 Halton Oy, Haltonintie 1-3, 474 Kausala, Finland 2 Finnish Institute of
AN ANALYSIS OF THE ACTUAL THERMAL PLUMES OF KITCHEN APPLIANCES DURING COOKING MODE R Kosonen 1,*, H Koskela 2 and P Saarinen 2 1 Halton Oy, Haltonintie 1-3, 474 Kausala, Finland 2 Finnish Institute of
Compression of Fins pipe and simple Heat pipe Using CFD
 Compression of Fins pipe and simple Heat pipe Using CFD 1. Prof.Bhoodev Mudgal 2. Prof. Gaurav Bhadoriya (e-mail-devmudgal.mudgal@gmail.com) ABSTRACT The aim of this paper is to identify the advantages
Compression of Fins pipe and simple Heat pipe Using CFD 1. Prof.Bhoodev Mudgal 2. Prof. Gaurav Bhadoriya (e-mail-devmudgal.mudgal@gmail.com) ABSTRACT The aim of this paper is to identify the advantages
Pressure drop analysis of evaporator using refrigerants R-22, R-404A and R-407C
 drop analysis of evaporator using refrigerants R-22, R-404A and R-407C #1 Pallavi Sawkar, #2 Dr. Pradeep Patil #12 Department of Mechanical Engineering, JSPM s JSCOE, Savitribai Phule Pune University,
drop analysis of evaporator using refrigerants R-22, R-404A and R-407C #1 Pallavi Sawkar, #2 Dr. Pradeep Patil #12 Department of Mechanical Engineering, JSPM s JSCOE, Savitribai Phule Pune University,
HEFAT th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics Sun City, South Africa Paper number:pp1
 HEFAT27 5 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics Sun City, South Africa Paper number:pp PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF AIR-COOLED CONDENSER USING MICRO-FIN TUBES P.A.Patil
HEFAT27 5 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics Sun City, South Africa Paper number:pp PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF AIR-COOLED CONDENSER USING MICRO-FIN TUBES P.A.Patil
