Mathematical modelling, moisture diffusion and specific energy consumption of thin layer microwave drying of olive pomace
|
|
|
- Asher Lane
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Food Research Journal 22(2): (2015) Journal homepage: Mathematical modelling, moisture diffusion and specific energy consumption of thin layer microwave drying of olive pomace Article history Received: 2 March 2014 Received in revised form: 28 January 2015 Accepted: 7 February 2015 Keywords Olive pomace Microwave drying Modeling Effective moisture diffusivity Specific energy consumption Sadi, T. and * Meziane, S. Laboratory of Applied Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Sciences, University Mouloud Mammeri, B.P N 17 RP, Tizi-Ouzou, Algeria Abstract In this study, the effects of microwave drying power on drying kinetics, effective moisture diffusivity, and specific energy consumption of olive pomace were studied at three different microwave power levels of 170, 360 and 510 W. Increasing microwave power resulted in a considerable decrease in drying time. The experimental data for moisture loss was converted to moisture ratios and fitted to eleven thin layer drying mathematical models to describe the drying process. Among the models tested, the Midilli et al. and Diffusion Approch models were found to be the most appropriate in describing microwave drying kinetics of olive pomace. The effective moisture diffusivity values varied from 3.55 x 10-9 to x 10-9 m 2 /s and increased with increase in microwave power. The activation energy was calculated using an exponential expression based on Arrhenius equation and was found to be W/g. The specific energy consumption values were in the range of to MJ/kg [H 2 O], under applied drying conditions. All Rights Reserved Introduction Agricultural products are characterized with high initial moisture content. Drying is one of the oldest and most widely used methods of food preservation. It is based on removal of moisture contained in the product by means a complicated process involving simultaneous heat and mass transfer (Krokida et al., 2003; Yilbas et al., 2003). Drying of agricultural products can be performed using different drying methods (solar drying, hot air drying, microwave drying, infrared drying, etc.). In particular, the conventional hot air drying processes was the most common method used. However, this drying technique has a number of disadvantages such as poor quality of dried products, low energy efficiency and a long drying time (Maskan, 2000; Soysal and Oztekin, 2001). The microwave technology is widely applied to treat various kinds of raw materials and products including food, fruits, vegetables, wood, etc. In drying agricultural products, microwave drying has gained much popularity as an alternative drying method in the last few years, due to high potential in improving process efficiency and quality of dried products. Some of the recent studies focus on fruits, vegetables, and the by-products of agricultural industry such as parsely (Soysal, 2004; Soysal et al., 2006), garlic cloves (Sharma, 2006), nettles leave (Alibas, 2007), okra (Dadali et al., 2007), mint leaves (Ozbek and Dadali, 2007; Therdthai and Zhou, 2009), spinach (Ozkan et al. 2007), apple pomace (Wang et al., 2007), red pepper (Soysal et al., 2009), whole fruit Chinese jujube (Wang et al., 2009), purslane (Demirhan and Ozbek, 2010), rosehips (Evin, 2011a), white mulberry (Evin, 2011b), Pandanus leaves (Rayaguru and Routray, 2011), coriander leaves (Sarimeseli, 2011), liquorice root (Balbay and Sahin, 2012), Gundelia tournefortii L. (Evin, 2012), mango ginger (Krishna Murthy and Manohar, 2012) and potato slices (Darvishi et al., 2013). This alternative method of drying presents several advantages including shortening drying time, high energy efficiency, high quality finished products, and uniform heating due to the penetration of microwaves into the body of the product (Yongsawatdigul and Gunasekaran, 1996; Soysal, 2004; Vadivambal and Jayas, 2007; Wang et al., 2007; Soysal et al., 2009; Therdthai and Zhou, 2009). On the other hand, microwave drying is known to lead low quality product when it s not appropriately applied (Yongsawatdigul and Gunasekaran, 1996; Soysal et al., 2009). Microwave drying differs fundamentally from the conventional hot-air drying. Microwaves are a form of electromagnetic energy with frequencies that lie between 300 MHz and 300 GHz, generated by magnetrons under the combined force of an electric and a magnetic field perpendicular to each other. During microwave drying, the water molecules of the product to be dried readily absorb this energy, which *Corresponding author. smmeziane@yahoo.fr
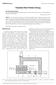
2 495 Sadi and Meziane/IFRJ 22(2): is converted to heat. Thus, the water vaporizes and diffuses through the product to the surface where it s led away. Olive production is a significant agriculture activity in the countries of the Mediterranean basin with important environmental, social and economic implications. Olive pomace is an important biomass by-product of olive oil industry, which can be used in very large amounts at very low cost. It is composed of a mixture of olive pulp and olive stones and it has been widely used as an animal feed supplement (Molina-Alcaide and Yáñez-Ruiz, 2008), energy source (Skoulou et al., 2009), fertilizer (Altieri and Esposito, 2010) and in many industrial purposes. However, this seasonal product is quite perishable due to its high moisture content, which can reach 65% depending on the olive oil extraction process used. It s then essential to dry this abundant agricultural waste quickly up to certain level, at which microbial spoilage and deterioration chemical reactions are greatly minimized. Therefore, the study on drying olive pomace is of great significance for recycling resource and environmental protection. Most of the previous studies on drying of olive pomace have focused on convective hot-air drying (Doymaz et al., 2004; Akgun and Doymaz, 2005; Jumah et al., 2011; Meziane, 2011; Vega-Galvez et al., 2011). In all these studies, the mathematical modeling of drying curves and the effects of drying on drying kinetics, effective moisture diffusivity were investigated. Other methods such as the drying using microwave and infrared energy (Gogus and Maskan, 2001, Celma et al., 2008) were also used. In their study, Gogus and Maskan (2001) studied the effects of microwave power, thickness and temperature on the drying kinetics of olive pomace in a combined microwave-fan assisted convection oven. However, to our knowledge, there is no available report regarding the effect of microwave power on effective moisture diffusivity and energy consumption during microwave drying of olive pomace. In this study, attention is focused on the microwave drying kinetics of olive pomace over a microwave power range of 170 to 510 W. Several thin layerdrying models were fitted to the experimental data of moisture ratio versus drying time in order to evaluate a suitable form of the drying kinetics curves for olive pomace. The influence of microwave power on the drying kinetics, moisture diffusivity and energy consumption was studied. Materials and Methods Raw material Fresh olive pomace was obtained from local continuous three-phase centrifugal system. The initial moisture content of the sample was approximately 45.02% (wb) and average particle diameter of 1.2 mm. The sample was kept in air tight plastic bottles and stored at a temperature of 4 C until the drying process. Drying equipment and experimental procedure The drying experiments were performed in a domestic digital microwave oven (whirlpool; MWO 611) presented in Figure 1. Figure 1. Schematic diagram of microwave dryer 1: microwave drying chamber; 2: control panel of the microwave; 3: time and power display; 4: sample; 5: glass stem; 6: aeration; 7: bracket; 8: digital balance It consists of a microwave generator with maximum output of 850 W at a frequency of 2450 MHz. The oven is fitted with a controller to set the microwave output power and the time of processing. The dimensions of the microwave inner cavity were 220 x 354 x 358 mm. An electronic balance (JA5003, Shanghai Balance Instrument Factory, China) with accuracy of ±0.01 g was positioned on a bracket on the top of the microwave oven for mass determination. Drying experiments were carried out at three microwave powers of 170, 340 and 510 W. Before each run, the microwave oven was set to operating drying power by heating 500 ml of water in a glass beaker for few min. The Petri-dish in glass (6 mm depth and 95 mm diameter) containing the sample with initial load of about g and thickness of 6 mm was then placed on the tray, which was suspended on the balance with a glass stem out through a hole in the center of chamber ceiling. Moisture loss in the sample was continuously measured by using an electronic balance and recorded at 2 min intervals for drying experiments with the microwave powers of 170 and 350 W, and at 1 min intervals for experiments with 510 W. Drying
3 Sadi and Meziane/IFRJ 22(2): process continued till the moisture content of olive pomace was reduced to about 7.0% (wb). After, the glass Petri-dish containing the dried sample was placed in an oven set at 105 C for 24 hours in order to determine its dry matter. Each drying run was carried out in triplicate and average value was reported. Modelling of drying curves In this study, the microwave experimental drying data of olive pomace at three power levels were fitted to the eleven commonly used thin layer drying mathematical models (Ertekin and Yaldiz, 2004; Sacilik et al., 2006; Akpinar and Bicer, 2008), listed in Table 1. In these models, MR represents the dimensionless moisture ratio expressed as follow: (1) where, M t is the moisture content of the sample at any time (kg water/kg dry matter), M e is the equilibrium moisture content of the sample (kg water/kg dry matter) and M 0 is its initial moisture content (kg water/kg dry matter). The values of M e are relatively small compared with M t or M t /M 0 for long drying time (Akgun and Doymaz, 2005). Thus, moisture ratio can be simplified to MR = M t /M 0. The non-linear regression analysis was performed using Statistica 5.0 software (Statsoft, USA) to fit the experimental data to the eleven selected mathematical models available in literature. The coefficient of determination (R 2 ) is one of the primary criteria in order to evaluate the fit quality of selected models. In addition to R 2, reduced chi-square (χ 2 ) and root mean square error (RMSE) are used to determine suitability of the fit. The reduced chi-square and the root mean square error can be calculated as follows: (2) (3) where MR ei is the ith experimental moisture ratio, MR pi is the ith predicted moisture ratio, N is the number of observations and z is the number of constants in a model. The higher the R 2 values and the lower the χ 2 and RMSE values, the better is the goodness of fit (Ertekin and Yaldiz, 2004; Doymaz and Ismail, 2011). The drying rate (DR) is expressed as the amount of the evaporated moisture over time. The drying rate (kg moisture/kg dry solid min) of olive pomace was computed using the following equation: (4) where M t+ t is the moisture ratio at t+ t. Effective moisture diffusivity and activation energy The effective moisture diffusivity can be defined from Fick s second law of diffusion (Eq. 5), which describes the movement of moisture within the solid. (5) where D eff is the effective moisture diffusivity (m 2 /s), M is the material moisture content (kg/kg of dry solid), and t is the time (s). An analytical solution of this law in the case of drying an infinite slab of thin layer, assuming moisture migration being by diffusion, one-dimensional moisture movement, uniform initial moisture distribution, negligible shrinkage, constant moisture diffusivity, and negligible external resistance to heat and mass transfer can be developed in the form of the following equation (Crank, 1975): (6) where D eff is the effective moisture diffusivity (m 2 s -1 ), L is the half-thickness of the product being dried (m) and t is the time (s). For long drying periods, Eq. (6) can be further simplified to only the first term of the series (n=0). Thus, simplified Eq. (6) is written in a logarithmic form as follows (Chen, 2007; Doymaz and Ismail, 2011): (7) The effective moisture diffusivity was calculated by using the method of slopes. From Eq. (7), a plot of ln (MR) versus time gives a straight line with a slope of: (8) The energy of activation in the microwave dryer was calculated using the Arrhenius exponential model (Dadali et al., 2007; Ozbek and Dadali, 2007; Darvishi et al., 2013). (9) where D eff0 is the pre-exponential factor (m 2 /s); P is the microwave output power (W), m is the average mass of raw sample (g), and E a is the activation energy (W/g). The linear form of Eq.(10) can be obtained by applying the logarithms as: (10)
4 497 Sadi and Meziane/IFRJ 22(2): Both Arrhenius parameters (E a and D eff0 ) can be estimated from the slope (-E a ) and intercept ln(d eff0 ) of the plot ln D eff versus (m/p). Specific energy consumption Effect of microwave drying power on the energy efficiency of microwave drying was evaluated by the specific energy consumption (SEC). This energy, expressed in (MJ/kg[H 2 O]), was calculated as the energy needed to evaporate a unit mass of water (Yongsawatdigul and Gunasekaran, 1996; Soysal et al., 2006). (11) where m w is the mass of evaporated water (kg) and t is the time interval (s). Results and Discussion Analysis of drying curves The experimental data for moisture loss were converted to dimensionless moisture ratio and plotted against time. Figure 2 presents the drying curves [MR=f(t)] for microwave drying of olive pomace at different microwave powers. was found to be shortened by 64% with the increase of microwave power from 360 W to 900 W for microwave drying of parsley (Soysal, 2004). This time was reduced by 76% in the power range from 180 to 900 W for microwave drying of mint leaves (Ozbeck and Dadali, 2007) and by 88% working at 800 W instead of 90 W for rosehips (Evin, 2011a). By working at 900W instead of 180 W, Dadali et al. (2007) showed that the drying time was shortened by 72% for microwave drying of okra. Alibas (2007) reported that the required time for microwave drying of nettle leaves at 500 W was 1.5 times longer than that at 850 W. Ozkan et al. (2007) studied microwave drying of spinach. The authors were observed that the drying time at 90 W microwave power level was times longer than that for 1000 W. Furthermore, the results obtained in this present study showed that as compared to convective hot air drying of olive pomace performed in a tunnel dryer at 90 C (Meziane and Mesbahi, 2012), the drying time to achieve the required final moisture content of about 7% can be reduced by 8-fold by working at microwave output power of 510 W. Figure 3. Drying rate versus moisture ratio of olive pomace at different microwave powers Figure 2. Microwave drying kinetics of olive pomace at different microwave powers As show this figure, the drying process is characterized by a progressive decrease in moisture ratio with drying time depending on the microwave output power. As expected, the total drying time showed a substantial reduction as microwave drying power was increased. Indeed, the total drying times to reach the final moisture ratio of the pomace were 42, 16 and 7 min at 170, 340, 510 W, respectively. The required drying time for microwave drying at 170 W was 6 times longer than that at 510 W. This indicates that an increasing microwave power strongly accelerates the drying process, thus greatly shortening the drying time. Similar finding was reported for microwave drying of many biological products by many researchers. Thus, the drying time Drying rate curves [DR=f(MR)] for olive pomace at different microwave power are shown in Figure 3. The drying rate decreased continuously with decreasing moisture ratio, indicating that microwave drying of olive pomace took place only during the falling rate period. This observation is in agreement with previous reports on thin layer microwave drying of bioproducts (Wang et al., 2007; Evin, 2011a, 2011b; Balbay and Şahin, 2012; Evin, 2012; Darvishi et al., 2013). In this drying period, the drying process was controlled by diffusion of moisture from the interior of solid to the surface. Drying rate increased also with microwave power level. This can be explained by rapid heating of the product, thus accelerating moisture migration toward the surface of the product where it s carried away.
5 Sadi and Meziane/IFRJ 22(2): Table 1. Statistical analysis of the eleven models fitted to the drying data for thin layer microwave drying of olive pomace Mathematical modelling of drying curves The experimental data for moisture loss were converted to dimensionless moisture ratios and fitted to eleven thin layer drying mathematical models to describe the microwave drying behaviour of olive pomace. The values of the determination coefficient (R 2 ), the reduced chi-square (χ 2 ) and the root mean square error (RMSE) for different microwave powers determined by nonlinear regression analysis are presented in Table 1. For all the models, the statistical parameter estimations showed that R 2, χ 2 and RMSE values were ranged from to , to , and to , respectively, within the experimental range of study. Based on higher value of R 2, and lower values of χ 2 and RMSE the Page, Wang and Singh, Diffusion approach, Logarithmic and Midilli et al. models gave a good fit to the experimental data with R 2 values greater than in all cases. However, the Midilli et al. model (2003) gave comparatively the highest R 2 value ( ) and the lowest χ 2 ( ) and RMSE ( ) values at microwave power levels of 340 and 510 W. For the low power level of 170 W, the highest R 2 value ( ) and the lowest RMSE ( ) and χ 2 ( ) values were found for the Diffusion approach model. Note that for this power, seven models (Page, Diffusion approach, Logarithmic, Two-term, Henderson and Pabis, Modified Henderson and Pabis and Midilli et al. models) gave an excellent fit to the experimental results with determination coefficients greater than In their study Gogus and Maskan (2001) tested two models, i.e. the empirical Page s model and the diffusion model (Lewis) to describe the drying process of olive pomace in a combined microwavefan assisted convection oven. They found that Lewis model provides a good fit to the experimental data. The Midilli et al. model has also been suggested by many researchers to describe the drying behavior kinetics of biological materials dried using different drying methods such as microwave drying (Soysal et al., 2006; Ozbek and Dadali, 2007; Demirhan and Ozbek, 2010; Sarimeseli, 2011; Evin, 2012; Darvishi et al., 2013), infrared drying (Celma et al., 2009), hot air drying (Ertekin and Yaldiz, 2004; Akpinar, 2006; Wang et al., 2009; Amiri Chayjan et al., 2011; Meziane, 2011; Mihindukulasuriya and Jayasuriya, 2013) and natural sun drying (Akpinar and Bicer, 2008). Calculation of effective moisture diffusivity and activation energy In the literature, no report was found relating
6 499 Sadi and Meziane/IFRJ 22(2): Table 2. Effective moisture diffusivity values of some agricultural products to investigation of the effective moisture diffusivity (D eff ) for olive pomace under microwave drying conditions. In this study, the effective moisture diffusivity values of the pomace for different levels of microwave power were calculated using the slope derived from the linear regression ln(mr) versus drying time (Eq.8). The plots gave straight lines with high determination coefficients ranging between and The Deff values obtained, presented in Table 2, ranged from 3.55 x 10-9 to x 10-9 m 2 s -1. These values are comparable with diffusivities obtained for the microwave drying of agricultural products, which are reported in Table 2. As expected, microwave drying power had an appreciable effect on the diffusivity of olive pomace, which increased vigorously with increases in drying power from 170 to 510 W. Indeed, the value of Deff at 540 W is about 2.6 times higher than at 340 W and 5.8 times higher than at 170 W. Thus, the drying rate can be hastened and drying time can be shortened by using higher microwave powers, which increase effective moisture diffusivity. Same trend was observed for microwave drying of white mulberry (Evin, 2011b), fresh apple pomace (Wang et al., 2007) and potato slices (Darvishi et al., 2013). Moreover, the Deff values are substantially higher that those obtained during drying of the pomace using a tunnel-type dryer at drying air temperatures of 50, 60, 70, 90 C (Meziane and Mesbahi, 2012). Indeed, the diffusivity value at microwave drying power level of 510 W was about 8-fold higher than in the drying by means of hot air steam at 90 C. The relationship between effective moisture diffusivity and microwave power can be expressed as follow: D = 6 x10-14 P x P + 2 x 10-9 R 2 =1 (12) The activation energy (E a ) of drying process of olive pomace calculated from the slope of the linearized Arrhenius relationship was found to be W/g, with a determination coefficient of This value is similar to the reported value for microwave drying of mango ginger (21.6 kw kg 1 ) (Krishna Murthy and Manohar, 2012), but it s higher than the value obtained in the microwave drying of okra (5.54 W/g) (Dadali et al., 2007), mint leaves ( W g -1 ) (Ozbek and Dadali, 2007), Pandanus amaryllifolius leaves (13.6 W/g) (Rayaguru and Routray, 2011) and potato slices ( W/g) (Darvishi et al., 2013). Calculation of specific energy consumption The specific energy consumption values for the drying of olive pomace at different microwave powers of 170, 340 and 510 W were 52.56, and MJ/kg evaporated water, respectively. The SEC decreased by approximately 51.8% when the microwave power increased from 170 to 510 W. Similar trends were reported for microwave drying of parseley (5.10 to 4.18 MJ kg -1 [H 2 O]), with microwave power ranging from 297 to 489 W (Soysal et al., 2006) and slices potato slices (5.882 to MJ/kg water), in the microwave power range of W (Darvishi et al., 2013). Wang et al. (2009) studied the microwave drying of whole fruit Chinese jujube. It was shown that energy consumption decreased from 2.07 to 1.35 kwh as microwave power increased from 45 to 135 W. On the other hand, the specific energy consumption in microwave drying of garlic cloves at 40 W of microwave power output was MJ/kg of water removed, resulting in about a 70% energy saving as compared to convective drying processes (Sharma and Prasad, 2006). Conclusions Microwave drying of olive pomace was investigated at microwave powers of 170, 340 and 510 W. It was observed that microwave drying took place in the falling rate period. Drying time up to the moisture content of about 7.0% (wb) can be reduced 7-fold by working at 510 W instead of 170 W. The Midilli et al. drying model was considered to be the best model for describing the drying behavior of olive pomace for the high drying powers considered here, whereas for the low power level of 170 W, the Diffusion approach model seems to be the most adequate. The effective moisture diffusivity value, which ranged between 3.55 x 10-9 and x10-9 m 2 s -1, increased with the increase in microwave power. The activation energy was found to be W/g. The specific energy consumption decreased from
7 Sadi and Meziane/IFRJ 22(2): to MJ/kg [H 2 O] as the microwave power increased from 170 to 510 W. References Akgun, N. A. and Doymaz, I Modeling of olive cake thin-layer drying process. Journal of Food Engineering 68(4): Akpinar, E. K Determination of suitable thin layer drying curve model for some vegetables and fruits. Journal of Food Engineering 73(1): Akpinar, E. K. and Bicer, Y Mathematical modelling of thin layer drying process of long green pepper in solar dryer and under open sun. Energy Conversion and Management 49(6): Alibas, I Energy consumption and colour characteristics of nettle leaves during microwave, vacuum and convective drying. Biosystems Engineering 96(4): Altieri, R. and Esposito, A Evaluation of the fertilizing effect of olive mill waste compost in short-term crops. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation 64(2): Amiri Chayjan, R., Amiri Parian, J. and Esna-Ashari, M Modeling of moisture diffusivity, activation energy and specific energy consumption of high moisture corn in a fixed and fluidized bed convective dryer. Spanish Journal of Agricultural Research 9(1): Balbay, A. and Şahin, O Microwave drying kinetics of a thin-layer liquorice root. Drying Technology 30(8): Chen, X. D Moisture Diffusivity in Food and Biological Materials. Drying Technology 25(7-8): Crank, J The mathematics of diffusion. 2nd ed. Oxford (UK): Clarendon Press. Dadali, G., Dilek Kilic, A. and Ozbek, B Estimatioin of effective moisture diffusivity of okra for microwave drying. Drying Technology 25(9): Darvishi, H., Asl, A. R., Asghar, A., Najafi, G. and Gazori, H. A Mathematical modeling, moisture diffusion, energy consumption and efficiency of thin layer drying of potato slices. Journal of Food Processing and Technology 4(3): 215. Demirhan, E. and Özbek, B Drying kinetics and effective moisture diffusivity of purslane undergoing microwave heat treatment. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering 27(5): Doymaz, I., Gorel, O. and Akgun, N. A Drying characteristics of the solid by-product of olive oil extraction. Biosystems Engineering 88(2): Doymaz, I. and Ismail, O Drying characteristics of sweet cherry. Food and bioproducts processing 89(1): Evin, D. 2011a. Investigation on the drying kinetics of sliced and whole rosehips at different moisture contents under microwave treatment. Scientific Research and Essays 6(11): Evin, D. 2011b. Microwave drying and moisture diffusivity of white mulberry: experimental and mathematical modeling. Journal of mechanical science and technology 25(10): Evin, D Thin layer drying kinetics of Gundelia tournefortii L. Food and bioproducts processing 90(2): Ertekin, C. and Yaldiz, O Drying of eggplant and selection of a suitable thin layer drying model. Journal of Food Engineering 63(3): Gogus, F. and Maskan, M Drying of olive pomace by a combined microwave-fan assisted convection oven. Nahrung/Food 45(2): Jumah, R., Al-Kteimat, E., Al-Hamad, A. and Telfah, E Constant and intermittent drying characteristics of olive cake. Drying Technology 25(9): Krishna Murthy, T. P. and Manohar, B Microwave drying of mango ginger (Curcuma amada Roxb) prediction of drying kinetics by mathematical modelling and artificial neural network. International Journal of Food Science and Technology 47(6): Krokida, M. K., Karathanos, V. T., Maroulis, Z. B. and Marinos-Kouris, D Drying kinetics of some vegetables. Journal of Food Engineering 59(4): Maskan, M Microwave/air and microwave finish drying of banana. Journal of Food Engineering 44(2): Midilli, A., Kucuk, H. and Yapar, Z A new model for single layer drying. Drying Technology 20(7): Mihindukulasuriya, S. D. F. and Jayasuriya, H. P. W Mathematical modeling of drying characteristics of chilli in hot air oven and fluidized bed dryers. Agricultural Engineering International: CIGR Journal 15(1): Meziane, S Drying kinetics of olive pomace in a fluidized bed dryer. Energy Conversion and Management 52(3): Meziane, S. and Mesbahi, N Determination of moisture diffusivity and activation energy in thin layer drying of olive pomace. International Journal of Food Engineering, 8, Article 34. Molina-Alcaide, E. and Yáñez-Ruiz, D. R Potential use of olive by-products in ruminant feeding: A review. Animal Feed Science and Technology 147(1-3): Ozbek, B. and Dadali, G Thin-layer drying characteristics and modelling of mint leaves undergoing microwave treatment. Journal of Food Engineering 83(4): Ozkan, I. A., Akbudak, B. and Akbudak, N Microwave drying characteristics of spinach. Journal of Food Engineering 78(2): Rayaguru, K. and Routray, W Microwave drying kinetics and quality characteristics of aromatic Pandanus amaryllifolius leaves. International Food Research Journal 18(3): Ruiz Celma, A., Rojas, S. and Lopez-Rodrıguez, F.
8 501 Sadi and Meziane/IFRJ 22(2): Mathematical modelling of thin-layer infrared drying of wet olive husk. Chemical Engineering and Processing 47(9-10): Sacilik, K., Keskin, R. and Elicin, A. K Mathematical modeling of solar tunnel drying of thin layer organic tomato. Journal of Food Engineering 73(3): Sarimeseli, A Microwave drying characteristics of coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) leaves. Energy Conversion and Management 52(2): Sharma, G. P. and Prasad, S Specific energy consumption in microwave drying of garlic cloves. Energy 31(12): Skoulou, V., Swiderski, A., Yang, W. and Zabaniotou, A Process characteristics and products of olive kernel high temperature steam gasification (HTSG). Bioresource Technology 100(8): Soysal, Y. and Oztekin, S PH Postharvest Technology: Comparison of seven equilibrium moisture content equations for some medicinal and aromatic plants. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research 78(1): Soysal, Y Microwave drying characteristics of parsley. Biosystems Engineering 89(2): Soysal, Y., Oztekin, S. and Eren, O Microwave drying of parsley: Modelling, Kinetics, and Energy aspects. Biosystems Engineering 93(4): Soysal, Y., Ayhan, Z., Esturk, O. and Arıkan, M. F Intermittent microwave convective drying of red pepper: Drying kinetics, physical (colour and texture) and sensory quality. Biosystems engineering 103(4): Therdthai, N. and Zhou, W Characterization of microwave vacuum drying and hot air drying of mint leaves (Mentha cordifolia Opiz ex Fresen). Journal of Food Engineering 91(3): Vadivambal, R. and Jayas, D. S Changes in quality of microwave-treated agricultural products - a review. Biosystems Engineering 98(1): Vega-Galvez, A., Miranda, M., Diaz, L. P., Lopez, L., Rodriguez, K. and Di Scala, K Effective moisture diffusivity determination and mathematical modelling of the drying curves of the olive-waste cake. Bioresource Technology 101(19): Wang, Z., Sun, J., Chen, F., Liao, X. and Hu, X Mathematical modelling on thin layer microwave drying of apple pomace with and without hot air predrying. Journal of Food Engineering 80(2): Wang, Z. F., Fang, S. Z. and Hu, X. S Effective diffusivities and energy consumption of whole fruit Chinese jujube (Zizyphus jujuba Miller) in Microwave Drying. Drying technology 27(10): Yilbas, B., Hussain, M. and Dincer, I Heat and moisture diffusion in slab products due to convective boundary condition. Heat and Mass Transfer 39(5-6): Yongsawatdigul, J. and Gunasekaran, S Microwave-vacuum drying of cranberries, Part II: Quality evaluation. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation 20(2):
An Experimental Study on Drying of Pistacia Terebinthus in a Fixed Bed Dryer
 Copyright 2013 Tech Science Press FDMP, vol.9, no.1, pp.1-10, 2013 An Experimental Study on Drying of Pistacia Terebinthus in a Fixed Bed Dryer A. Balbay 1, H. Ülker 2 and Ö. Şahin 3 Abstract: In this
Copyright 2013 Tech Science Press FDMP, vol.9, no.1, pp.1-10, 2013 An Experimental Study on Drying of Pistacia Terebinthus in a Fixed Bed Dryer A. Balbay 1, H. Ülker 2 and Ö. Şahin 3 Abstract: In this
Drying Kinetics Modelling of Basil in Microwave Dryer
 AGRICULTURAL COMMUNICATIONS, 2015, 3(4): 37 44. Drying Kinetics Modelling of Basil in Microwave Dryer ESMAEEL SEYEDABADI Department of Agronomy, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Zabol, Zabol, Iran.
AGRICULTURAL COMMUNICATIONS, 2015, 3(4): 37 44. Drying Kinetics Modelling of Basil in Microwave Dryer ESMAEEL SEYEDABADI Department of Agronomy, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Zabol, Zabol, Iran.
Influence of temperature and drying air velocity on the kinetics of convective drying in the food industry
 Influence of temperature and drying air velocity on the kinetics of convective drying in the food industry Ing. Michal Pěnička Project leader: Doc. Pavel Hoffman CSc. Abstract The aim of this study was
Influence of temperature and drying air velocity on the kinetics of convective drying in the food industry Ing. Michal Pěnička Project leader: Doc. Pavel Hoffman CSc. Abstract The aim of this study was
Energy consumption and mathematical modeling of microwave drying of potato slices
 94 March, 01 Agric Eng Int: CIGR Journal Open access at http://www.cigrjournal.org Vol. 14, o.1 Energy consumption and mathematical modeling of microwave drying of potato slices Hosain Darvishi (Department
94 March, 01 Agric Eng Int: CIGR Journal Open access at http://www.cigrjournal.org Vol. 14, o.1 Energy consumption and mathematical modeling of microwave drying of potato slices Hosain Darvishi (Department
Characteristics of sunflower seed drying and microwave energy consumption
 Int. Agrophys., 2013, 27, 127-132 doi: 10.2478/v10247-012-0077-8 INTERNATIONAL Agrophysics www.international-agrophysics.org Characteristics of sunflower seed drying and microwave energy consumption H.
Int. Agrophys., 2013, 27, 127-132 doi: 10.2478/v10247-012-0077-8 INTERNATIONAL Agrophysics www.international-agrophysics.org Characteristics of sunflower seed drying and microwave energy consumption H.
DETERMINATION OF THE EFFECTIVE MOISTURE DIFFUSIVITY OF RED PEPPER IN A MICROWAVE CONVEYOR DRYER
 DETERMINATION OF THE EFFECTIVE MOISTURE DIFFUSIVITY OF RED PEPPER IN A MICROWAVE CONVEYOR DRYER Soner ÇELEN +, Ugur AKYOL +, Aytaç MORALAR + + NAMIK KEMAL UNIVERSITY, Çorlu, Tekirda, Turkey. Abstract.
DETERMINATION OF THE EFFECTIVE MOISTURE DIFFUSIVITY OF RED PEPPER IN A MICROWAVE CONVEYOR DRYER Soner ÇELEN +, Ugur AKYOL +, Aytaç MORALAR + + NAMIK KEMAL UNIVERSITY, Çorlu, Tekirda, Turkey. Abstract.
Cassava Chip Drying by Using a Small-Scale Hot-Air Microwave Oven
 American Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences 6 (2): 211-215, 2013 ISSN: 1941-7020 2014 P. Wilaipon, This open access article is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) 3.0 license
American Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences 6 (2): 211-215, 2013 ISSN: 1941-7020 2014 P. Wilaipon, This open access article is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) 3.0 license
A New Approach for Modeling of Hot Air-microwave Thin Layer Drying of Soybean
 A New Approach for Modeling of Hot Air-microwave Thin Layer Drying of Soybean Dariush Zare, Assistant Professor, Agricultural Engineering Dept., Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran. M. Ranjbaran, M. Javidi,
A New Approach for Modeling of Hot Air-microwave Thin Layer Drying of Soybean Dariush Zare, Assistant Professor, Agricultural Engineering Dept., Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran. M. Ranjbaran, M. Javidi,
Drying of apple slices (var. Golab) and effect on moisture diffusivity and activation energy
 POJ 3(3):97-10 (010) ISSN:1836-3644 Drying of apple slices (var. Golab) and effect on moisture diffusivity and activation energy *E. Meisami-asl, S. Rafiee, A. Keyhani and A. Tabatabaeefar Department of
POJ 3(3):97-10 (010) ISSN:1836-3644 Drying of apple slices (var. Golab) and effect on moisture diffusivity and activation energy *E. Meisami-asl, S. Rafiee, A. Keyhani and A. Tabatabaeefar Department of
Evaluation and Selection of Thin-layer Models for Drying Kinetics of Apricot (cv.nasiry)
 1 Evaluation and Selection of Thin-layer Models for Drying Kinetics of Apricot (cv.nasiry) E. Mirzaee 1, S. Rafiee 1, A. Keyhani 1 1 Agricultural Machinery Engineering Dept., Faculty of Agricultural Engineering
1 Evaluation and Selection of Thin-layer Models for Drying Kinetics of Apricot (cv.nasiry) E. Mirzaee 1, S. Rafiee 1, A. Keyhani 1 1 Agricultural Machinery Engineering Dept., Faculty of Agricultural Engineering
Drying Kinetics of Chilli Pepper in a force Convection Indirect Solar Drying
 Drying Kinetics of Chilli Pepper in a force Convection Indirect Solar Drying M.I. FADHEL 1, S. SHAUNMUGANATHAN 1, M.A. AlGHOUL 2, MALEK ALI 1, K. SOPIAN 2 & A. ZAHARIM 2 1 Faculty of Engineering and Technology,
Drying Kinetics of Chilli Pepper in a force Convection Indirect Solar Drying M.I. FADHEL 1, S. SHAUNMUGANATHAN 1, M.A. AlGHOUL 2, MALEK ALI 1, K. SOPIAN 2 & A. ZAHARIM 2 1 Faculty of Engineering and Technology,
Thin layer tea drying experimentation with biomass fuelled producer gas
 In the previous Chapter, we had discussed the details procedure of selection and characterization of biomass as prospective fuel for tea processing through gasification. We found that fuel properties of
In the previous Chapter, we had discussed the details procedure of selection and characterization of biomass as prospective fuel for tea processing through gasification. We found that fuel properties of
Review of the Drying Kinetics of Olive Oil Mill Wastes: Biomass Recovery
 Review of the Drying Kinetics of Olive Oil Mill Wastes: Biomass Recovery Francisco J. Gómez-de la Cruz, a, * Pedro J. Casanova-Peláez, b Rafael López-García, a and Fernando Cruz-Peragón a The drying kinetics
Review of the Drying Kinetics of Olive Oil Mill Wastes: Biomass Recovery Francisco J. Gómez-de la Cruz, a, * Pedro J. Casanova-Peláez, b Rafael López-García, a and Fernando Cruz-Peragón a The drying kinetics
Thin-layer drying of some Sri Lankan paddy varieties under low humid conditions
 36 Thin-layer drying of some Sri Lankan paddy varieties under low humid conditions A.K. Shyamali, H.H.E. Jayaweera and T.R. Ariyaratne Centre for Instrument Development, Department of Physics, University
36 Thin-layer drying of some Sri Lankan paddy varieties under low humid conditions A.K. Shyamali, H.H.E. Jayaweera and T.R. Ariyaratne Centre for Instrument Development, Department of Physics, University
Mathematical modeling of drying characteristics of chilli in hot air oven and fluidized bed dryers
 154 March, 2013 Agric Eng Int: CIGR Journal Open access at http://www.cigrjournal.org Vol. 15, No.1 Mathematical modeling of drying characteristics of chilli in hot air oven and fluidized bed dryers S.
154 March, 2013 Agric Eng Int: CIGR Journal Open access at http://www.cigrjournal.org Vol. 15, No.1 Mathematical modeling of drying characteristics of chilli in hot air oven and fluidized bed dryers S.
MICROWAVE DRYING OF ALOE VERA (ALOE BARBADENSIS MILLER): MATHEMATICAL MODELING, KINETICS AND MASS TRANSFER ASPECTS
 MICROWAVE DRYING OF ALOE VERA (ALOE BARBADENSIS MILLER): MATHEMATICAL MODELING, KINETICS AND MASS TRANSFER ASPECTS G. Srinivasan 1, R.Baskar 2 1 Assistant Professor (Sr.Gr.), Department of Chemical Engineering,
MICROWAVE DRYING OF ALOE VERA (ALOE BARBADENSIS MILLER): MATHEMATICAL MODELING, KINETICS AND MASS TRANSFER ASPECTS G. Srinivasan 1, R.Baskar 2 1 Assistant Professor (Sr.Gr.), Department of Chemical Engineering,
Drying Characteristics of Carrot and Green Pumpkin Slices in Waste Heat Dryer
 Original Article J. of Biosystems Eng. 37(1):36-43. (2012. 2) http://dx.doi.org/10.5307/jbe.2012.37.1.036 Journal of Biosystems Engineering eissn : 2234-1862 pissn : 1738-1266 Drying Characteristics of
Original Article J. of Biosystems Eng. 37(1):36-43. (2012. 2) http://dx.doi.org/10.5307/jbe.2012.37.1.036 Journal of Biosystems Engineering eissn : 2234-1862 pissn : 1738-1266 Drying Characteristics of
DRYING CHARACTERISTICS OF PAPAYA (CARICA PAPAYA L.) DURING MICROWAVE-VACUUM TREATMENT
 International Journal of Engineering and Technology, Vol., No.,, pp. - DRYING CHARACTERISTICS OF PAPAYA (CARICA PAPAYA L.) DURING MICROWAVE-VACUUM TREATMENT Nurul Asyikin Md Zaki, Ida Idayu Muhamad and
International Journal of Engineering and Technology, Vol., No.,, pp. - DRYING CHARACTERISTICS OF PAPAYA (CARICA PAPAYA L.) DURING MICROWAVE-VACUUM TREATMENT Nurul Asyikin Md Zaki, Ida Idayu Muhamad and
Mathematical modeling of thin layer microwave drying kinetics of elephant foot yam (Amorphophallus paeoniifolius)
 International Food Research Journal 21(3): 1081-1087 (2014) Journal homepage: http://www.ifrj.upm.edu.my Mathematical modeling of thin layer microwave drying kinetics of elephant foot yam (Amorphophallus
International Food Research Journal 21(3): 1081-1087 (2014) Journal homepage: http://www.ifrj.upm.edu.my Mathematical modeling of thin layer microwave drying kinetics of elephant foot yam (Amorphophallus
Influence Collector Inclination of Solar Dryer on Apple Golab Chips Drying
 ORIGIAL SCIETIFIC PAPER 101 Influence Collector Inclination of Solar Dryer on Apple Golab Chips Drying Omid Reza ROUSTAPOUR 1( ) Hamid Reza GAZOR 2 Summary Thin layer of apple chips ( Golab ) with 73.4%
ORIGIAL SCIETIFIC PAPER 101 Influence Collector Inclination of Solar Dryer on Apple Golab Chips Drying Omid Reza ROUSTAPOUR 1( ) Hamid Reza GAZOR 2 Summary Thin layer of apple chips ( Golab ) with 73.4%
INFLUENCE OF DRYING CONDITIONS ON THE MOISTURE DIFFUSION DURING SINGLE STAGE AND TWO STAGE FLUIDIZED BED DRYING OF BOVINE INTESTINE FOR PET FOOD
 INFLUENCE OF DRYING CONDITIONS ON THE MOISTURE DIFFUSION DURING SINGLE STAGE AND TWO STAGE FLUIDIZED BED DRYING OF BOVINE INTESTINE FOR PET FOOD O. Alves-Filho 1, W. Senadeera, T. Eikevik 1 1 Norwegian
INFLUENCE OF DRYING CONDITIONS ON THE MOISTURE DIFFUSION DURING SINGLE STAGE AND TWO STAGE FLUIDIZED BED DRYING OF BOVINE INTESTINE FOR PET FOOD O. Alves-Filho 1, W. Senadeera, T. Eikevik 1 1 Norwegian
ANALYSIS OF THE DRYING KINETICS OF S. BARTOLOMEU PEARS FOR DIFFERENT DRYING SYSTEMS
 ISSN: 1579-4377 ANALYSIS OF THE DRYING KINETICS OF S. BARTOLOMEU PEARS FOR DIFFERENT DRYING SYSTEMS RAQUEL P. F. GUINÉ Departamento de Indústrias Alimentares, Escola Superior Agrária de Viseu, Instituto
ISSN: 1579-4377 ANALYSIS OF THE DRYING KINETICS OF S. BARTOLOMEU PEARS FOR DIFFERENT DRYING SYSTEMS RAQUEL P. F. GUINÉ Departamento de Indústrias Alimentares, Escola Superior Agrária de Viseu, Instituto
THE THIN LAYER DRYING OF TEMU PUTIH HERB
 The 6 th Asia-Pacific Drying Conference (ADC2009) October 19-21, 2009, Bangkok, Thailand THE THIN LAYER DRYING OF TEMU PUTIH HERB *Lamhot P. MANALU 1,2, Armansyah H. TAMBUNAN 3, Leopold O. NELWAN 3 and
The 6 th Asia-Pacific Drying Conference (ADC2009) October 19-21, 2009, Bangkok, Thailand THE THIN LAYER DRYING OF TEMU PUTIH HERB *Lamhot P. MANALU 1,2, Armansyah H. TAMBUNAN 3, Leopold O. NELWAN 3 and
MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF MICROWAVE ASSISTED FLUIDIZED BED DRYING OF HAZELNUTS
 MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF MICROWAVE ASSISTED FLUIDIZED BED DRYING OF HAZELNUTS Narjes Malekjani (a), Zahra Emam-Djomeh (b), Seyed Hassan Hashemabadi (c), Gholam Reza Askari (d) (a), (b), (d) Department
MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF MICROWAVE ASSISTED FLUIDIZED BED DRYING OF HAZELNUTS Narjes Malekjani (a), Zahra Emam-Djomeh (b), Seyed Hassan Hashemabadi (c), Gholam Reza Askari (d) (a), (b), (d) Department
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECT OF DRYING AIR RELATIVE HUMIDITY IN DRYING KINETICS OF KIWI
 Academic Journal of Science, CD-ROM. ISSN: 2165-6282 :: 2(1):1 10 (2013) EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECT OF DRYING AIR RELATIVE HUMIDITY IN DRYING KINETICS OF KIWI Soner en and Selçuk Dar c Selçuk
Academic Journal of Science, CD-ROM. ISSN: 2165-6282 :: 2(1):1 10 (2013) EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECT OF DRYING AIR RELATIVE HUMIDITY IN DRYING KINETICS OF KIWI Soner en and Selçuk Dar c Selçuk
Mathematical Simulation of Longan Fruit Drying
 Mathematical Simulation of Longan Fruit Drying Aree Achariyaviriya, Somchart Soponronnarit and Jirawan Tiansuwan ABSTRACT The objectives of this study were to develop a mathematical model and to simulate
Mathematical Simulation of Longan Fruit Drying Aree Achariyaviriya, Somchart Soponronnarit and Jirawan Tiansuwan ABSTRACT The objectives of this study were to develop a mathematical model and to simulate
Study of the Drying Kinetics of Baccaurea angulata Merr. (Belimbing Dayak) Fruit
 Study of the Drying Kinetics of Baccaurea angulata Merr. (Belimbing Dayak) Fruit DAYAG FREDALIA BASRI, AHMAD FUDHOLI *, MOHD HAFIDZ RUSLA, M. A. ALGHOUL School of Diagnostic and Applied Health Sciences,
Study of the Drying Kinetics of Baccaurea angulata Merr. (Belimbing Dayak) Fruit DAYAG FREDALIA BASRI, AHMAD FUDHOLI *, MOHD HAFIDZ RUSLA, M. A. ALGHOUL School of Diagnostic and Applied Health Sciences,
The influence of the combined microwave power and hot air ventilation on the drying kinetics and colour quality of tomato slices
 African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 11(87), pp. 15353-15364, 30 October, 2012 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb DOI: 10.5897/AJB11.318 ISSN 1684 5315 2012 Academic Journals Full
African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 11(87), pp. 15353-15364, 30 October, 2012 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb DOI: 10.5897/AJB11.318 ISSN 1684 5315 2012 Academic Journals Full
Drying Kinetics of Oyster Mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus) in a Convective Hot Air Dryer
 J. Agr. Sci. Tech. (011) Vol. 13: 655-664 Drying Kinetics of Oyster Mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus) in a Convective Hot Air Dryer Y. Tulek 1 ABSTRACT The objective of this study was to investigate the drying
J. Agr. Sci. Tech. (011) Vol. 13: 655-664 Drying Kinetics of Oyster Mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus) in a Convective Hot Air Dryer Y. Tulek 1 ABSTRACT The objective of this study was to investigate the drying
The Effect of Quantity of Salt on the Drying Characteristics of Fresh Noodles
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Agriculture and Agricultural Science Procedia 2 ( 2014 ) 207 211 ST26943, 2nd International Conference on Agricultural and Food Engineering, CAFEi2014
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Agriculture and Agricultural Science Procedia 2 ( 2014 ) 207 211 ST26943, 2nd International Conference on Agricultural and Food Engineering, CAFEi2014
Solar Drying Kinetics of Cassava Slices in a Mixed Flow Dryer
 DOI: 10.1515/ata-015-000 Acta Technologica Agriculturae 4/015 Acta Technologica Agriculturae 4 Nitra, Slovaca Universitas Agriculturae Nitriae, 015, pp. 10 107 Solar Drying Kinetics of Cassava Slices in
DOI: 10.1515/ata-015-000 Acta Technologica Agriculturae 4/015 Acta Technologica Agriculturae 4 Nitra, Slovaca Universitas Agriculturae Nitriae, 015, pp. 10 107 Solar Drying Kinetics of Cassava Slices in
Development of a Simulation Model for the Hybrid Solar Dryers as Alternative Sustainable Drying System for Herbal and Medicinal Plants
 Development of a Simulation Model for the Hybrid Solar Dryers as Alternative Sustainable Drying System for Herbal and Medicinal Plants Ali, S.A. and A.H. Bahnasawy Agric. Eng. Dept., Moshtohor Agric. College
Development of a Simulation Model for the Hybrid Solar Dryers as Alternative Sustainable Drying System for Herbal and Medicinal Plants Ali, S.A. and A.H. Bahnasawy Agric. Eng. Dept., Moshtohor Agric. College
Thin layer drying models for sweet potato in tray dryer
 Thin layer drying models for sweet potato in tray dryer A. S. Olawale *, S. O. Omole (Department of Chemical Engineering, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria) Abstract: Sweet potato is increasingly
Thin layer drying models for sweet potato in tray dryer A. S. Olawale *, S. O. Omole (Department of Chemical Engineering, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria) Abstract: Sweet potato is increasingly
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 6, June ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 6, June-2015 1009 Selection of Optimum Temperature and Thin Layer Drying Kinetics of Maize for Production of Quality Seeds Mosharaf
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 6, June-2015 1009 Selection of Optimum Temperature and Thin Layer Drying Kinetics of Maize for Production of Quality Seeds Mosharaf
4th International Conference on Sensors, Measurement and Intelligent Materials (ICSMIM 2015)
 4th International Conference on Sensors, Measurement and Intelligent Materials (ICSMIM 2015) Multi-stage Series Heat Pump Drying System with Dehumidification Simulation and Experiment Verification Chao
4th International Conference on Sensors, Measurement and Intelligent Materials (ICSMIM 2015) Multi-stage Series Heat Pump Drying System with Dehumidification Simulation and Experiment Verification Chao
Thin-Layer Drying Characteristics of Banana Slices in a Force Convection Indirect Solar Drying
 Thin-Layer Drying Characteristics of Banana Slices in a Force Convection Indirect Solar Drying M. I. FADHEL, RAMEZ ABDULWASEA ABDO, B. F. YOUSIF, AZAMI ZAHARIM 3 AND K. SOPIAN 3 Faculty of Engineering
Thin-Layer Drying Characteristics of Banana Slices in a Force Convection Indirect Solar Drying M. I. FADHEL, RAMEZ ABDULWASEA ABDO, B. F. YOUSIF, AZAMI ZAHARIM 3 AND K. SOPIAN 3 Faculty of Engineering
Sitesh Kumar Pandey1, Richa Soni2, Abhishek Shrivastav3 1,3
 IJEEE Volume Spl. Issue (6) Mathematical ing of Thin Layer Drying Process of Red Chili in Solar Dryer Under Open Sun Sitesh Kumar Pey Richa Soni Abhishek Shrivastav Mechanical Engineering Deptt. C.I.E.T
IJEEE Volume Spl. Issue (6) Mathematical ing of Thin Layer Drying Process of Red Chili in Solar Dryer Under Open Sun Sitesh Kumar Pey Richa Soni Abhishek Shrivastav Mechanical Engineering Deptt. C.I.E.T
Mathematical modelling of thin-layer drying of carrot
 Int. Agrophysics, 2009, 23, 313-317 INTERNATIONAL Agrophysics www.international-agrophysics.org Mathematical modelling of thin-layer drying of carrot M. Aghbashlo*, M.H. Kianmehr, S. Khani, and M. Ghasemi
Int. Agrophysics, 2009, 23, 313-317 INTERNATIONAL Agrophysics www.international-agrophysics.org Mathematical modelling of thin-layer drying of carrot M. Aghbashlo*, M.H. Kianmehr, S. Khani, and M. Ghasemi
Food Research (2019) : pp - pp Journal homepage:
 Food Research (2019) : pp - pp Journal homepage: http://www.myfoodresearch.com Drying characteristics of fish cracker under different drying techniques 1,* Abdullah, S., 1 Musa, N., 2 Rukunudin, I.H. and
Food Research (2019) : pp - pp Journal homepage: http://www.myfoodresearch.com Drying characteristics of fish cracker under different drying techniques 1,* Abdullah, S., 1 Musa, N., 2 Rukunudin, I.H. and
Experimental & Analytical Investigation on Modified Solar Dryer with Recirculation of Air
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 4 (2013), pp. 441-448 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Experimental & Analytical
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 4 (2013), pp. 441-448 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Experimental & Analytical
Variable far infrared radiation (VFIR) technique for cubic carrot drying
 International Journal of Renewable Energy, Vol. 7, No. 2, July - December 2012 Variable far infrared radiation (VFIR) technique for cubic carrot drying Sirinuch Chindaruksa a *, Pisit Maneechot b, Seishu
International Journal of Renewable Energy, Vol. 7, No. 2, July - December 2012 Variable far infrared radiation (VFIR) technique for cubic carrot drying Sirinuch Chindaruksa a *, Pisit Maneechot b, Seishu
Solar Drying of Fruits and Vegetables
 Solar Drying of Fruits and Vegetables Y. Baradey 1, M. N. A. Hawlader 2, A. F. Ismail 3, M. Hrairi 4, M. I. Rapi 5 1,2,3 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, International Islamic
Solar Drying of Fruits and Vegetables Y. Baradey 1, M. N. A. Hawlader 2, A. F. Ismail 3, M. Hrairi 4, M. I. Rapi 5 1,2,3 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, International Islamic
Design and Fabrication of Experimental Dryer for Studying Agricultural Products
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF AGRICULTURE & BIOLOGY ISSN Print: 1560 8530; ISSN Online: 1814 9596 07-84/AWB/008/10 1 61 65 http://www.fspublishers.org Full Length Article Design and Fabrication of Dryer for
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF AGRICULTURE & BIOLOGY ISSN Print: 1560 8530; ISSN Online: 1814 9596 07-84/AWB/008/10 1 61 65 http://www.fspublishers.org Full Length Article Design and Fabrication of Dryer for
Exergy Analysis of Heat Pump Dryer
 12 MAHASARAKHAM INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 4, NO. 1, JANUARY-JUNE 2018 ergy Analysis of Heat Pump Dryer Nattapol Poomsa-ad 1,*, Lamul Wiset 2 and Khanuengnit Chapchaimoh 3 1,*
12 MAHASARAKHAM INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 4, NO. 1, JANUARY-JUNE 2018 ergy Analysis of Heat Pump Dryer Nattapol Poomsa-ad 1,*, Lamul Wiset 2 and Khanuengnit Chapchaimoh 3 1,*
Design and Experimental Studies on Modified Solar Dryer
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 8, Number 1 (2015), pp. 43-47 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Design and Experimental
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 8, Number 1 (2015), pp. 43-47 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Design and Experimental
Microwave Assisted Hot Air Ventilation Drying of Tomato Slices
 2011 International Conference on Food Engineering and Biotechnology IPCBEE vol.9 (2011) (2011)IACSIT Press, Singapoore Microwave Assisted Hot Air Ventilation Drying of Tomato Slices Tilahun Seyoum Workneh
2011 International Conference on Food Engineering and Biotechnology IPCBEE vol.9 (2011) (2011)IACSIT Press, Singapoore Microwave Assisted Hot Air Ventilation Drying of Tomato Slices Tilahun Seyoum Workneh
Investigation of microwave application in agricultural production drying
 41 / 14 Investigation of microwave application in agricultural production drying Ehsan Yarionsorudi, Amin Alamloo, Atabak Movafegi 1 Department of Electrical Engineering,College of Technical & Engineering,Tabriz
41 / 14 Investigation of microwave application in agricultural production drying Ehsan Yarionsorudi, Amin Alamloo, Atabak Movafegi 1 Department of Electrical Engineering,College of Technical & Engineering,Tabriz
An Investigation on Drying of Millets in A Microwave Oven
 An Investigation on Drying of Millets in A Microwave Oven G. B. Radhika 1, S.V. Satyanarayana, D. G. Rao 3 1 B.V.Raju Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, India Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University
An Investigation on Drying of Millets in A Microwave Oven G. B. Radhika 1, S.V. Satyanarayana, D. G. Rao 3 1 B.V.Raju Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, India Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University
PROCESSING OF VEGETABLES IN A SOLAR DRYER IN ARID AREAS
 PROCESSING OF VEGETABLES IN A SOLAR DRYER IN ARID AREAS N. M. Nahar Central Arid Zone Research Institute, Jodhpur 342003, India Email:nmnahar@gmail.com Fax: 91-291-2788706 Abstract When the production
PROCESSING OF VEGETABLES IN A SOLAR DRYER IN ARID AREAS N. M. Nahar Central Arid Zone Research Institute, Jodhpur 342003, India Email:nmnahar@gmail.com Fax: 91-291-2788706 Abstract When the production
Drying principles and general considerations
 Drying principles and general considerations Drying Mechanisms In the process of drying heat is necessary to evaporate moisture from the grain and a flow of air is needed to carry away the evaporated moisture.
Drying principles and general considerations Drying Mechanisms In the process of drying heat is necessary to evaporate moisture from the grain and a flow of air is needed to carry away the evaporated moisture.
MODEL AND SIMULATION OF DEEP-BED CLOVE DRYING: EFFECT OF FERMENTED TREATMENT
 - Vol. 15, No. 1, April 21 MODEL AND SIMULATION OF DEEP-BED CLOVE DRYING: EFFECT OF FERMENTED TREATMENT Agus Supriatna ~omantri' Abstract This paper describes the prediction of deep-bed clove drying. This
- Vol. 15, No. 1, April 21 MODEL AND SIMULATION OF DEEP-BED CLOVE DRYING: EFFECT OF FERMENTED TREATMENT Agus Supriatna ~omantri' Abstract This paper describes the prediction of deep-bed clove drying. This
Thermal Performance Of Low Cost Solar Bamboo Dryer
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol.5, No.2, pp 1041-1045, April-June 2013 ICGSEE-2013[14 th 16 th March 2013] International Conference on Global Scenario
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol.5, No.2, pp 1041-1045, April-June 2013 ICGSEE-2013[14 th 16 th March 2013] International Conference on Global Scenario
INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT TEMPERING PERIOD AND VACUUM CONDITIONS ON THE RICE GRAIN BREAKAGE IN A THIN LAYER DRYER
 INFLUENCE OF TEMPERING PERIOD AND VACUUM CONDITIONS ON THE RICE GRAIN BREAKAGE Cercetări Agronomice în Moldova Vol. XLVI, No. 4 (156) / 2013 INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT TEMPERING PERIOD AND VACUUM CONDITIONS
INFLUENCE OF TEMPERING PERIOD AND VACUUM CONDITIONS ON THE RICE GRAIN BREAKAGE Cercetări Agronomice în Moldova Vol. XLVI, No. 4 (156) / 2013 INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT TEMPERING PERIOD AND VACUUM CONDITIONS
Effect of different air velocities on convective thin-layer drying of alfalfa for livestock feeding
 Agronomy Research 15(3), 737 744, 2017 Effect of different air velocities on convective thin-layer drying of alfalfa for livestock feeding P. Kic Czech University of Life Sciences Prague, Faculty of Engineering,
Agronomy Research 15(3), 737 744, 2017 Effect of different air velocities on convective thin-layer drying of alfalfa for livestock feeding P. Kic Czech University of Life Sciences Prague, Faculty of Engineering,
Microwave Drying Characteristics, Kineticsand Drying Quality of Onion Slices (Allium CepaL.)
 AENSI Journals Advances in Environmental Biology ISSN-1995-0756 EISSN-1998-1066 Journal home page: http://www.aensiweb.com/aeb/ Microwave Drying Characteristics, Kineticsand Drying Quality of Onion Slices
AENSI Journals Advances in Environmental Biology ISSN-1995-0756 EISSN-1998-1066 Journal home page: http://www.aensiweb.com/aeb/ Microwave Drying Characteristics, Kineticsand Drying Quality of Onion Slices
International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research e-issn No.: , Date: 2-4 July, 2015
 International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com e-issn No.:2349-9745, Date: 2-4 July, 2015 Modeling Moisture Ratio of High Moisture Potato Slices in Forced Convection
International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com e-issn No.:2349-9745, Date: 2-4 July, 2015 Modeling Moisture Ratio of High Moisture Potato Slices in Forced Convection
Nahid Aghilinategh, Shahin Rafiee, Abolfazl Gholikhani, Soleiman Hosseinpur, Mahmoud Omid, Seyed S. Mohtasebi & Neda Maleki
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A comparative study of dried apple using hot air, intermittent and continuous microwave: evaluation of kinetic parameters and physicochemical quality attributes Nahid Aghilinategh, Shahin
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A comparative study of dried apple using hot air, intermittent and continuous microwave: evaluation of kinetic parameters and physicochemical quality attributes Nahid Aghilinategh, Shahin
Drying of Fruits, Vegetables, Spices and Medicinal Plants with a Mixed-Mode Solar Drying System with Internal Reflectors
 Drying of Fruits, Vegetables, Spices and Medicinal Plants with a Mixed-Mode Solar Drying System with Internal Reflectors Jatinkumar Patel, Pandit Deendayal Petroleum University, India Anurag Mudgal, Pandit
Drying of Fruits, Vegetables, Spices and Medicinal Plants with a Mixed-Mode Solar Drying System with Internal Reflectors Jatinkumar Patel, Pandit Deendayal Petroleum University, India Anurag Mudgal, Pandit
Drying Kinetics and Inversion Temperature in a Low-Pressure Superheated Steam-Drying System
 Drying Kinetics and Inversion Temperature in a Low-Pressure Superheated Steam-Drying System P. Suvarnakuta, S. Devahastin,*, S. Soponronnarit, and A. S. Mujumdar Department of Food Engineering and School
Drying Kinetics and Inversion Temperature in a Low-Pressure Superheated Steam-Drying System P. Suvarnakuta, S. Devahastin,*, S. Soponronnarit, and A. S. Mujumdar Department of Food Engineering and School
KERONE (AN ISO 9001: 2008 CERTIFIED COMPANY)
 KERONE (AN ISO 9001: 2008 CERTIFIED COMPANY) Role of Agriculture and Allied Sector in Indian Economy Largest economic sector, plays a significant role in socio-economic development of India. More than
KERONE (AN ISO 9001: 2008 CERTIFIED COMPANY) Role of Agriculture and Allied Sector in Indian Economy Largest economic sector, plays a significant role in socio-economic development of India. More than
Mathematical Modeling on Hot Air Drying of Thin Layer Fresh Tilapia Fillets
 Original paper Section: Food Technology Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci., 2013, Vol. 63, No. 1, pp. 25-34 DOI: 10.2478/v10222 012 0065 5 http://journal.pan.olsztyn.pl Mathematical Modeling on Hot Air Drying of
Original paper Section: Food Technology Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci., 2013, Vol. 63, No. 1, pp. 25-34 DOI: 10.2478/v10222 012 0065 5 http://journal.pan.olsztyn.pl Mathematical Modeling on Hot Air Drying of
Performance and Evaluation of Pop Can Solar Dryer for Batch Products
 American Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy Vol. 4, No. 1, 2018, pp. 1-7 http://www.aiscience.org/journal/ajrse ISSN: 2381-7437 (Print); ISSN: 2381-7445 (Online) Performance and Evaluation of
American Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy Vol. 4, No. 1, 2018, pp. 1-7 http://www.aiscience.org/journal/ajrse ISSN: 2381-7437 (Print); ISSN: 2381-7445 (Online) Performance and Evaluation of
Performance Investigation and Development of Solar Dryer Tunnel Type Apparatus of Cocoa
 Performance Investigation and Development of Solar Dryer Tunnel Type Apparatus of Cocoa Darwin Harun*, Hasan Akhyar and Razali Thaib Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, Faculty of Engineering,
Performance Investigation and Development of Solar Dryer Tunnel Type Apparatus of Cocoa Darwin Harun*, Hasan Akhyar and Razali Thaib Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, Faculty of Engineering,
Study of the Drying Kinetics of Lemon Grass
 American Journal of Applied Sciences 6 (6): 1070-1075, 2009 ISS 1546-9239 2009 Science Publications Study of the Drying Kinetics of Lemon Grass Mustafa Ibrahim, K. Sopian and W.R.W. Daud Solar Energy Research
American Journal of Applied Sciences 6 (6): 1070-1075, 2009 ISS 1546-9239 2009 Science Publications Study of the Drying Kinetics of Lemon Grass Mustafa Ibrahim, K. Sopian and W.R.W. Daud Solar Energy Research
Drying Parawood with Superheated Steam
 American Journal of Applied Sciences 4 (4): 215-219, 2007 ISSN 1546-9239 2007 Science Publications Drying Parawood with Superheated Steam Surachai Bovornsethanan and Somchai Wongwises Department of Mechanical
American Journal of Applied Sciences 4 (4): 215-219, 2007 ISSN 1546-9239 2007 Science Publications Drying Parawood with Superheated Steam Surachai Bovornsethanan and Somchai Wongwises Department of Mechanical
Mathematical Modelling of Thin Layer Drying Kinetics of Amla-Beet Root Shreds
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.221
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.221
DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION OF FORCED/NATURAL CONVECTION SOLAR VEGETABLE DRYER WITH HEAT STORAGE
 DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION OF FORCED/NATURAL CONVECTION SOLAR VEGETABLE DRYER WITH HEAT STORAGE Gutti Babagana, Kiman Silas and Mustafa B. G. Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Maiduguri, Borno,
DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION OF FORCED/NATURAL CONVECTION SOLAR VEGETABLE DRYER WITH HEAT STORAGE Gutti Babagana, Kiman Silas and Mustafa B. G. Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Maiduguri, Borno,
Thin Layer Mathematical Modelling of Cob Maize in a Natural Convection Solar Drier
 Energy and Environment Research; Vol. 7, No. 2; 2017 ISSN 1927-0569 E-ISSN 1927-0577 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Thin Layer Mathematical Modelling of Cob Maize in a Natural Convection
Energy and Environment Research; Vol. 7, No. 2; 2017 ISSN 1927-0569 E-ISSN 1927-0577 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Thin Layer Mathematical Modelling of Cob Maize in a Natural Convection
Experimental Analysis of Open, Simple and Modified Greenhouse Dryers for Drying Potato Flakes under Forced Convection
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Experimental Analysis of Open, Simple and Modified Greenhouse Dryers for Drying Potato Flakes under Forced Convection Tanuj Kumar Sahu 1, Vishal Gupta 2, Ajay Kumar Singh 3
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Experimental Analysis of Open, Simple and Modified Greenhouse Dryers for Drying Potato Flakes under Forced Convection Tanuj Kumar Sahu 1, Vishal Gupta 2, Ajay Kumar Singh 3
Convective drying of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum graecum L.) leaves
 International J. Seed Spices 7(), July 017:93-98 Convective drying of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum graecum L.) leaves P. D. Jawake, V. D. Mudgal* and D. Rajpurohit College of Technology and Engineering,
International J. Seed Spices 7(), July 017:93-98 Convective drying of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum graecum L.) leaves P. D. Jawake, V. D. Mudgal* and D. Rajpurohit College of Technology and Engineering,
Analysis of Energy Consumption for Biomass Drying Process
 Environment. Technology. Resources, Rezekne, Latvia Proceedings of the 10 th International Scientific and Practical Conference. Volume II, 317-322 Analysis of Energy Consumption for Biomass Drying Process
Environment. Technology. Resources, Rezekne, Latvia Proceedings of the 10 th International Scientific and Practical Conference. Volume II, 317-322 Analysis of Energy Consumption for Biomass Drying Process
Drying characteristics of Air Dried Sheet (ADS) Rubber
 Paper Code: ee11 characteristics of Air Dried Sheet (ADS) Rubber Y. Tirawanichakul 1*, W. Suchonpanit 2 and S. Tirawanichakul 3 1 Plasma and Energy Technology Research Laboratory, Department of Physics,
Paper Code: ee11 characteristics of Air Dried Sheet (ADS) Rubber Y. Tirawanichakul 1*, W. Suchonpanit 2 and S. Tirawanichakul 3 1 Plasma and Energy Technology Research Laboratory, Department of Physics,
Key Words: Microalgae; Solar Dryer; Exergy Analysis; Energy Analysis;
 ENERGY AND EXERGY ANALYSES OF A MICROALGAE SOLAR DRYER FOR BIODIESEL PRODUCTION Eunice A. Doblada 1a, Aristotle T. Ubando 1b,2, Alvin B. Culaba 1c,2 1 Mechanical Engineering Department, DLSU-Manila 2 Center
ENERGY AND EXERGY ANALYSES OF A MICROALGAE SOLAR DRYER FOR BIODIESEL PRODUCTION Eunice A. Doblada 1a, Aristotle T. Ubando 1b,2, Alvin B. Culaba 1c,2 1 Mechanical Engineering Department, DLSU-Manila 2 Center
Drying Kinetics of Sliced Pineapples in a Solar Conduction Dryer
 Energy and Environment Research; Vol. 7, No. 2; 2017 ISSN 1927-0569 E-ISSN 1927-0577 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Drying Kinetics of Sliced Pineapples in a Solar Conduction Dryer
Energy and Environment Research; Vol. 7, No. 2; 2017 ISSN 1927-0569 E-ISSN 1927-0577 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Drying Kinetics of Sliced Pineapples in a Solar Conduction Dryer
CLOVER DRYING PROCESS BY FORCED CONVECTION
 CLOVER DRYING PROCESS BY FORCED CONVECTION Pavel Kic Czech University of Life Sciences Prague kic@tf.czu.cz Abstract. The aim of this paper is to inform about the experimental and theoretical investigations
CLOVER DRYING PROCESS BY FORCED CONVECTION Pavel Kic Czech University of Life Sciences Prague kic@tf.czu.cz Abstract. The aim of this paper is to inform about the experimental and theoretical investigations
15 Microwave Drying. Unauthenticated Download Date 11/3/18 12:04 PM
 15 Microwave Drying Many products must be dried before they can be stored or used. For example, drying of animal fodder helps preserve its quality and avoid spontaneous combustion during storage in hay
15 Microwave Drying Many products must be dried before they can be stored or used. For example, drying of animal fodder helps preserve its quality and avoid spontaneous combustion during storage in hay
Mathematical modeling and polysaccharide content of Ganoderma lucidum by hot air impingement drying
 An ASABE Meeting Presentation Paper Number: 131619320 Mathematical modeling and polysaccharide content of Ganoderma lucidum by hot air impingement drying Jun-Wen Bai, Hong-Wei Xiao, Zheng Lou, Zhen-Jiang
An ASABE Meeting Presentation Paper Number: 131619320 Mathematical modeling and polysaccharide content of Ganoderma lucidum by hot air impingement drying Jun-Wen Bai, Hong-Wei Xiao, Zheng Lou, Zhen-Jiang
Thin Layer Drying and Modelling of Poultry Litter Briquettes
 Energy and Environment Research; Vol. 9, No. ; 29 ISSN 927-569 E-ISSN 927-577 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Thin Layer Drying and Modelling of Poultry Litter Briquettes Mogomotsi
Energy and Environment Research; Vol. 9, No. ; 29 ISSN 927-569 E-ISSN 927-577 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Thin Layer Drying and Modelling of Poultry Litter Briquettes Mogomotsi
Effect of Magnetic Field on Convective Drying Of Ceramic Clay
 International Journal of Engineering and Technology Volume 5 No. 7, July, 2015 Effect of Magnetic Field on Convective Drying Of Ceramic Clay A.A Dare 1, L. I Onu 2, R Akinoso 3 1 Department of Mechanical
International Journal of Engineering and Technology Volume 5 No. 7, July, 2015 Effect of Magnetic Field on Convective Drying Of Ceramic Clay A.A Dare 1, L. I Onu 2, R Akinoso 3 1 Department of Mechanical
Hot Air-Microwave Combined Drying Characteristics of Gypsum Board. Won-Pyo Chun, Sung-Il Kim, and Ki-Woo Lee 1
 European Drying Conference - EuroDrying'11 Palma. Balearic Island, Spain, 26-28 October 11 Hot Air-Microwave Combined Drying Characteristics of Gypsum Board Won-Pyo Chun, Sung-Il Kim, and Ki-Woo Lee 1
European Drying Conference - EuroDrying'11 Palma. Balearic Island, Spain, 26-28 October 11 Hot Air-Microwave Combined Drying Characteristics of Gypsum Board Won-Pyo Chun, Sung-Il Kim, and Ki-Woo Lee 1
Review Article Solar Drying Technology: Potentials and Developments
 Ashdin Publishing Journal of Fundamentals of Renewable Energy and Applications Vol. 2 (2012), Article ID R120302, 5 pages doi:10.4303/jfrea/r120302 ASHDIN publishing Review Article Solar Drying Technology:
Ashdin Publishing Journal of Fundamentals of Renewable Energy and Applications Vol. 2 (2012), Article ID R120302, 5 pages doi:10.4303/jfrea/r120302 ASHDIN publishing Review Article Solar Drying Technology:
MODELING DRYING CHARACTERISTICS OF MORINGA (MORINGA OLEIFERA) LEAVES UNDER A MECHANICAL CONVECTIVE CABINET DRYER
 MODELING DRYING CHARACTERISTICS OF MORINGA (MORINGA OLEIFERA) LEAVES UNDER A MECHANICAL CONVECTIVE CABINET DRYER Ayoola Patrick Olalusi*, Goodluck Ehis Odiase Department of Agricultural and Environmental
MODELING DRYING CHARACTERISTICS OF MORINGA (MORINGA OLEIFERA) LEAVES UNDER A MECHANICAL CONVECTIVE CABINET DRYER Ayoola Patrick Olalusi*, Goodluck Ehis Odiase Department of Agricultural and Environmental
Convective Drying of Apple: Mathematical Modeling and Determination of some Quality Parameters
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF AGRICULTURE & BIOLOGY ISSN Print: 1560 8530; ISSN Online: 1814 9596 09 15/ZSA/010/1 171 178 http://www.fspublishers.org Full Length Article Convective Drying of Apple: Mathematical
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF AGRICULTURE & BIOLOGY ISSN Print: 1560 8530; ISSN Online: 1814 9596 09 15/ZSA/010/1 171 178 http://www.fspublishers.org Full Length Article Convective Drying of Apple: Mathematical
All rights reserved, Armando B. Corripio, PhD, PE, Solid Dryer Design Introduction Continuous Dryer Design...
 Solid Dryer Design All rights reserved, Armando B. Corripio, PhD, PE, 2014 Contents Solid Dryer Design... 1 Introduction... 2 1. Continuous Dryer Design... 3 1.1 Mass Balances... 4 1.2 Temperature Profiles...
Solid Dryer Design All rights reserved, Armando B. Corripio, PhD, PE, 2014 Contents Solid Dryer Design... 1 Introduction... 2 1. Continuous Dryer Design... 3 1.1 Mass Balances... 4 1.2 Temperature Profiles...
Specific Energy Consumption of Heat Pump Drying System
 Mindanao Journal of Science and Technology Vol.14 (2016) 131-145 Specific Energy Consumption of Heat Pump Drying System Adonis A. Closas 1* and Eliseo P. Villanueva 2 1 College of Engineering and Architecture
Mindanao Journal of Science and Technology Vol.14 (2016) 131-145 Specific Energy Consumption of Heat Pump Drying System Adonis A. Closas 1* and Eliseo P. Villanueva 2 1 College of Engineering and Architecture
DRYING OF LONGAN: ITS DRYING KINETICS AND PERFORMANCE OF LONGAN DRYERS. By Niroot Lamlert
 DRYING OF LONGAN: ITS DRYING KINETICS AND PERFORMANCE OF LONGAN DRYERS By Niroot Lamlert A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY Department of
DRYING OF LONGAN: ITS DRYING KINETICS AND PERFORMANCE OF LONGAN DRYERS By Niroot Lamlert A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY Department of
Heat and Mass Transfer in Fibrous Materials. Theory and Applications. A.K. Haghi S. Thomas L.A. Pothan ATLANTIC PUBLISHERS & DISTRIBUTORS (P) LTD
 Heat and Mass Transfer in Fibrous Materials Theory and Applications A.K. Haghi S. Thomas L.A. Pothan ATLANTIC PUBLISHERS & DISTRIBUTORS (P) LTD Preface v Nomenclature (Part 1) xii PART 1 THEORY 1. Basic
Heat and Mass Transfer in Fibrous Materials Theory and Applications A.K. Haghi S. Thomas L.A. Pothan ATLANTIC PUBLISHERS & DISTRIBUTORS (P) LTD Preface v Nomenclature (Part 1) xii PART 1 THEORY 1. Basic
DRYING AND COLOR CHARACTERISTICS OF CORIANDER FOLIAGE USING CONVECTIVE THIN- LAYER AND MICROWAVE DRYING
 DRYING AND COLOR CHARACTERISTICS OF CORIANDER FOLIAGE USING CONVECTIVE THIN- LAYER AND MICROWAVE DRYING M. Shaw, V. Meda, L. Tabil Jr. and A. Opoku Department of Agricultural and Bioresource Engineering,
DRYING AND COLOR CHARACTERISTICS OF CORIANDER FOLIAGE USING CONVECTIVE THIN- LAYER AND MICROWAVE DRYING M. Shaw, V. Meda, L. Tabil Jr. and A. Opoku Department of Agricultural and Bioresource Engineering,
Fluidised-Bed Paddy Drying
 RESEARCH ARTICLE ScienceAsia 25 (1999) : 51-56 Fluidised-Bed Paddy Drying Somchart Soponronnarit School of Energy and Materials, King Mongkut's University of Technology Thonburi, Suksawat 48 Road, Bangkok
RESEARCH ARTICLE ScienceAsia 25 (1999) : 51-56 Fluidised-Bed Paddy Drying Somchart Soponronnarit School of Energy and Materials, King Mongkut's University of Technology Thonburi, Suksawat 48 Road, Bangkok
Specific Energy Consumption comparative study of Hot Air dryer and Heat Pump dryer for highland drying process Sayompon Srina
 Specific Energy Consumption comparative study of Hot Air dryer and Heat Pump dryer for highland drying process Sayompon Srina Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, King Mongkut
Specific Energy Consumption comparative study of Hot Air dryer and Heat Pump dryer for highland drying process Sayompon Srina Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, King Mongkut
Available online at I-SEEC Proceeding - Science and Engineering (2013) 19 26
 Available online at www.iseec2012.com I-SEEC 2012 Proceeding - Science and Engineering (2013) 19 26 Proceeding Science and Engineering www.iseec2012.com Science and Engineering Symposium 4 th International
Available online at www.iseec2012.com I-SEEC 2012 Proceeding - Science and Engineering (2013) 19 26 Proceeding Science and Engineering www.iseec2012.com Science and Engineering Symposium 4 th International
Mango Sheet Drying by the Solar Dryer Combine with Electric Coil
 Mango Sheet Drying by the Solar Dryer Combine with Electric Coil Narin Koolnapadol, Rajabhat Rajanagarindra University, Thailand Chatchawan Nimrotham, Rajabhat Rajanagarindra University, Thailand The Asian
Mango Sheet Drying by the Solar Dryer Combine with Electric Coil Narin Koolnapadol, Rajabhat Rajanagarindra University, Thailand Chatchawan Nimrotham, Rajabhat Rajanagarindra University, Thailand The Asian
Activation Energy Kinetics in Thin Layer Drying of Basil Leaves
 Activation Energy Kinetics in Thin Layer Drying of Basil Leaves N. C. Shahi 1, Anupama Singh 2, A. E. Kate 3 1 Ph. D Scholar, Department of Post Harvest Process & Food Engineering, College of Technology
Activation Energy Kinetics in Thin Layer Drying of Basil Leaves N. C. Shahi 1, Anupama Singh 2, A. E. Kate 3 1 Ph. D Scholar, Department of Post Harvest Process & Food Engineering, College of Technology
Low-pressure microwave heating system for drying of swiftlet bird s nest
 3 rd International conference on agricultural and food engineering Low-pressure microwave heating system for drying of swiftlet bird s nest Mudtorlep Nisoa Plasma technology for agricultural application
3 rd International conference on agricultural and food engineering Low-pressure microwave heating system for drying of swiftlet bird s nest Mudtorlep Nisoa Plasma technology for agricultural application
Experimental study on heat transfer characteristics of horizontal concentric tube using twisted wire brush inserts
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 416, P-ISSN 2347 5161 216 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Experimental
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 416, P-ISSN 2347 5161 216 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Experimental
Performance Evaluation of Solar Tunnel Dryer for Drying of Garlic.
 ISSN: 2347-4688, Vol. 05, No.(2) 2017, Pg.220-226 Current Agriculture Research Journal An International Open Access, Peer Reviewed Journal www.agriculturejournal.org Performance Evaluation of Solar Tunnel
ISSN: 2347-4688, Vol. 05, No.(2) 2017, Pg.220-226 Current Agriculture Research Journal An International Open Access, Peer Reviewed Journal www.agriculturejournal.org Performance Evaluation of Solar Tunnel
Heat Transfer Analysis of Vapor Compression System Using Nano Cuo-R134a
 2011 International Conference on Advanced Materials Engineering IPCSIT vol.15 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Heat Transfer Analysis of Vapor Compression System Using Nano Cuo-R134a Eed Abdel-Hafez
2011 International Conference on Advanced Materials Engineering IPCSIT vol.15 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Heat Transfer Analysis of Vapor Compression System Using Nano Cuo-R134a Eed Abdel-Hafez
Effective Moisture Diffusivity and Activation Energy Estimation of Cucumber Fruit Slices Using a Refractance Window TM Dryer
 A.A. Akinola et al.: Effective Moisture Diffusivity and Activation Energy Estimation of Cucumber Fruit Slices Using a Refractance Window TM Dryer 11 ISSN 1000 794 The Journal of the Association of Professional
A.A. Akinola et al.: Effective Moisture Diffusivity and Activation Energy Estimation of Cucumber Fruit Slices Using a Refractance Window TM Dryer 11 ISSN 1000 794 The Journal of the Association of Professional
Reducing energy consumption of airconditioning systems in moderate climates by applying indirect evaporative cooling
 Reducing energy consumption of airconditioning systems in moderate climates by applying indirect evaporative cooling Aleksandra Cichoń,*, Anna Pacak, Demis Pandelidis, and Sergey Anisimov Department of
Reducing energy consumption of airconditioning systems in moderate climates by applying indirect evaporative cooling Aleksandra Cichoń,*, Anna Pacak, Demis Pandelidis, and Sergey Anisimov Department of
Simulation Of Pneumatic Drying: Influence Of Particle Diameter And Solid Loading Ratio
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol.4, No.4, pp 1633-1641, Oct-Dec 2012 Simulation Of Pneumatic Drying: Influence Of Particle Diameter And Solid Loading
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol.4, No.4, pp 1633-1641, Oct-Dec 2012 Simulation Of Pneumatic Drying: Influence Of Particle Diameter And Solid Loading
