Energy consumption and mathematical modeling of microwave drying of potato slices
|
|
|
- Scott Neal
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 94 March, 01 Agric Eng Int: CIGR Journal Open access at Vol. 14, o.1 Energy consumption and mathematical modeling of microwave drying of potato slices Hosain Darvishi (Department of Mechanical Engineering, Shahre Ray Branch, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran) Abstract: Abstract: In this research, drying characteristics and energy requirements for microwave drying of potato slices were reported at four microwave power densities, 5, 10, 15 and 0 W/g. During the experiments, potato slices were dried to the final moisture content of 0.08 from.94 (kgh O/kgdry matter). The experimental data were fitted to six drying models: Linear, Lewis, Henderson and Pabis, Wang and Singh, Page, and Midilli et al. models. The models were compared using the coefficient of determination, root mean square error and reduced chi-square. The Midilli et al. model best described the drying curve of potato slices. The effective moisture diffusivity was determined by using Fick s second law and was observed to lie between and m /s for the potato samples. The minimum and the maximum energy requirements for drying of potato slices were also determined as 4. MJ/kgH O and MJ/kgH O for 15 and 5 W/g, respectively. Keywords: potato, drying, mathematical model, effective diffusivity, energy consumption Citation: Hosain Darvishi. 01. Energy consumption and mathematical modeling of microwave drying of potato slices. Agric Eng Int: CIGR Journal, 14(1): Introduction Microwave heating is based on the transformation of alternating electromagnetic field energy into thermal energy by affecting the polar molecules of a material. Compared with hot air drying, microwave reduces the decline in quality, and provides rapid and effective heat distribution in the material as well (Diaz et al., 003). Tippayawong et al. (008) reported that the conventional practice results in low overall efficiency, approximately 30% and around 35% 45% of energy input is wasted as hot gas exhaust. In microwave drying, the quick absorption of energy by water molecules causes rapid evaporation of water, resulting in high drying rates of the food. The drying time can be greatly reduced by applying the microwave energy to the dried material. Received date: Accepted date: Corresponding Author: Hosain Darvishi, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Shahre Ray Branch, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran. Tel: (+98) ; Hosaindarvishi@gmail.com; Due to the concentrated energy of a microwave drying system, only 0% 35% of the floor space is required, as compared to conventional heating and drying equipment (Vadivambal and Jayas, 007; Maskan, 000). Also, it has also been suggested that microwave energy should be applied in the falling rate period for drying (Maskan, 000). In the drying industry, the most important aim is to use lowest energy to extract the most moisture for obtaining optimum product storing conditions. Akpinaret al. (005) found that the potato slices are sufficiently dried in the ranges between 60 and 80 and 0% 10% relative humidity at 1and 1.5 m/s of drying air velocity during 10 1 h despite the exergy losses of kj/s. Bakal et al. (011) investigated the effect of air temperature and two different shapes (cubical and cylindrical) with 3 aspect ratio of each shape on the drying kinetics of potato in a fluidized bed dryer. They reported that the Page model best described the drying behaviour of potatoes. Similar results were reported by Senadeera et al. (003) for potatoes. McMinn et al. (003) carried out an extensive study of the effect of key process parameters on the drying
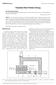
2 March, 01 Energy consumption and mathematical modeling of microwave drying of potato slices Vol. 14, o.1 95 characteristics of potato samples dried using microwave and combined microwave convective techniques. Reyes et al. (007) found that the type of dryers and the drying temperature had a strong effect on drying rate and on the colour and the porosity of the dried potato slices, while the rehydration capacity and the maximum penetration force were not affected. Hatamipour et al. (007) studied the effect of various pretreatments (tray dryer, with and without air circulation, and fluidized bed dryer) on the shrinkage and colour properties of six varieties of sweet potatoes. The effect of air conditions (air temperature, air humidity and air velocity) and characteristic sample size on drying kinetics of potatoes was examined during air drying by Krokida et al. (003). Leeratanarak et al. (006) investigated drying of potato slices using both low-pressure superheated steam drying and hot air drying. Pimpaporn et al. (007) studied the influence of various pretreatments and drying temperature on the low-pressure superheated steam drying kinetics and quality parameters of dried potato chips. Khraisheh et al. (004) studied the quality and structural changes of potatoes during microwave and convective drying. They reported that air drying led to higher structural changes than in the case of microwave drying. Caixeta et al. (00) found that the potato chips dried at higher steam temperatures and high convective heat transfer coefficients had less shrinkage, higher porosity, darker color, and lower vitamin C content. As little research has been performed on the effect of power density on energy consumption and drying efficiency in microwave drying method, the present research is focused on this issue. The aim of this research was (i) to determine the influence of microwave power density on the energy consumption and drying kinetics during microwave dehydration and (ii) to fit the experimental moisture data to six mathematical models. Average initial moisture content of potato samples were determined by using a standard oven method at 105± for 6 h (Aghbashlo et al., 009) and were found to be ±0.35% (w.b.).. Experimental set-up and methods Figure 1 shows the diagram of the microwave drying system. The drying apparatus used was consisted of a laboratory microwave oven (M945, Samsung Electronics Ins) with features of 30 V, 50 Hz with a frequency of 450 MHz and a digital balance (GF-600, A & D, Japan) with accuracy of ±0.01 g. The area on which microwave drying was carried out was mm in size. The microwave dryer was operated by a control terminal which could control both microwave power level and emission time. In order to weigh the samples without taking them out of the oven, a weighing system was integrated to the oven. A sample tray in the microwave oven chamber was suspended on the balance with a nylon wire through a ventilation hole in the centre of the chamber ceiling. Moisture loss of the sample was recorded by means of a weighing system at 15 s intervals during drying using software for the balance. The oven has a fan for air flow in drying chamber and cooling of magnetron. The moisture from drying cavity was removed with this fan by passing it through the openings on the right side of the oven wall to the outer atmosphere. The drying trial was carried out at four different microwave power densities being 5, 10, 15 and 0 W/g. Each drying process was applied until the initial moisture ratio was reduced to about 0.08 (kg water/kg dry matter). Materials and methods.1 Materials Potatoes were purchased from a local market, in Tehran, Iran. The samples were stored in a refrigerator at 4 until used. The potatoes were washed with tap water, peeled and sliced into chips of 0.5±0.03 mm thick. Figure 1 Schematic diagram of microwave dryer
3 96 March Agric Eng Int: CIGR Journal Open access at Vol. 14, o.1.3 Energy consumption and drying efficiency Energy consumption by the microwave oven equals: t Qt P (1) 60 where, Q t represents total energy consumption in each drying bout, kwh; P is the microwave power, kw; and t is drying time, min. The microwave drying efficiency was calculated as the ratio of the heat energy utilized for evaporating water from the sample to the heat supplied by the microwave oven (Soysal, 004; Yongsawatdigul and Gunasekaran, 1996). m w w 100 () 60 Pt where, η is the microwave drying efficiency, %; m w is the mass of evaporated water, kg; and λ w is the latent heat of vaporization of water, kj/kg. The latent heat of vaporization of water at the evaporating temperature of 100 was taken as 57, kj/kg (Hayes, 1987). The specific energy consumption was calculated as the energy needed to evaporate a unit mass of water (Mousa and Farid, 00; Soysal et al., 006) Pt Qs (3) m where, Q s is the specific energy consumption, MJ/kgH O..4 Moisture ratio and mathematical modeling The moisture ratio (MR) was calculated using the Equation (4): M w M t e MR M 0 M e where, MR is the moisture ratio (dimensionless); M t is the moisture content at t, kgh O/kgdry matter); M e is the equilibrium moisture content, kgh O/kg dry matter; and M 0 is the initial moisture content, kgh O/kg dry matter. The value of M e is relatively small compared with M t or M 0. Therefore, the moisture ratio (MR) was simplified to M t /M 0. Six semi-empirical models were applied to fit the experimental moisture data because they are widely used in drying agriculture products and they are equalities that explain the characteristic of the drying method in a safe way, as listed in Table 1. The terms used to evaluate the goodness of the fit of the tested models to the experimental data were the coefficient of determination (R ), root mean (4) square error (RMSE) and the reduced chi-square (χ ) between the experimental and predicted moisture ratio values. The statistical parameters were calculated using the following equations: R 1 i1 i1 ( MR MR ) pre, i exp, i ( MR MR ) pre, i exp, i (5) MRpre, i MR i exp, i (6) ( ) 1 z RMSE 1 ( MR ) 1 pre, i MR i exp, i (7) where, MR exp is the experimental moisture ratio; MR per is the predicted moisture ratio; Z and are numbers of constants and observations, respectively. The best model describing the thin-layer drying characteristics of potato slices was chosen based on the higher value of R and lower values of χ and RMSE. Table 1 Mathematical models given by various authors for drying curves Model name Model References Linear MR = 1+bt - Lewis MR = exp(-kt) Bruce (1985) Henderson and Pabis MR =aexp(-kt) Henderson and Pabis (1961) Page MR = exp(-kt n ) Page (1949) Midilli et al. MR =aexp(-kt n )+bt Midilli et al. (00) Wang and Singh MR = 1+bt+at Wang and Singh (1978) ote: k, n, a, and b are the model constants..5 Effective moisture diffusivity Fick s law of diffusion incorporated with drying experiments has been widely used to determine the moisture diffusivity of various fruits and other biological materials: t M D eff M The solution of Fick s equation, with the assumption of moisture migration being by diffusion, negligible shrinkage, constant diffusion coefficients and temperature and for a slab: M 8 1 (n1) Deff t R exp t (9) M0 n0 (n1) 4L where, D eff is the effective moisture diffusivity, m /s; t is the drying time, s; L is the half-thickness of a thin layer (8)
4 March, 01 Energy consumption and mathematical modeling of microwave drying of potato slices Vol. 14, o.1 97 sample, m; and n is a positive integer. For long drying time, only the first term of this series is significant, and then the solution becomes: M t 8 D eff MR exp t (10) M0 4L This could be further simplified to a straight-line equation as: 8 D eff ln( MR) ln t (11) 4L The effective moisture diffusivity is determined by plotting the experimental drying data in terms of ln(mr) versus drying time with a slope of: D eff Slope (1) 4L.6 Drying rate The drying rate is expressed as the amount of the evaporated moisture over time. The drying rate of potato slices was calculated using the following equation: M DR l M t tt t (13) where, DR is the drying rate, kgh O/kgdry matter min). 3 Results and discussion 3.1 Drying kinetics of potato slices The potato slices were dried as a single layer with thickness of 5 mm at the drying microwave power densities of 5, 10, 15 and 0 W/g in a microwave dryer. The variations in moisture ratio of the potato slices as a function of drying time at different power densities are presented in Figure. It can be seen that the moisture content of the potato slices decreased with the increase in drying time. It only took 3, 5.75, 3.5 and.5 min to dry potato samples from an initial moisture ratio (MR) of 1 to a final moisture ratio (MR) of 0.08at 5, 10, 15 and 0 W/g of drying power densities, respectively. It indicated that increasing the drying power density decreases the drying time. The decrease in drying time with an increase in the drying microwave power density has been reported for many foodstuffs, such as carrots (Sumnu et al., 005), nettle leaves (Alibas, 007), peaches (Wang and Sheng, 006), tomato pomace (Al-Harahsheh et al., 009), onions (Arslan and Ozcan, 010), and mint leaves (Ozbek and Dadali, 007). Figure Drying curves of moisture ratio with drying time at different microwave power densities The drying rates versus average moisture content and drying time curves of potato slices are illustrated in Figure 3 and Figure 4. The drying rates decreased continually with the decrease in moisture content and increased with the microwave power and thus decreasing drying time. The results indicated that mass transfer within the sample was more rapidly during higher microwave power heating because more heat was generated within the sample creating a large vapor pressure difference between the center and the surface of the product due to characteristic microwave volumetric heating. It was observed that the drying rates were higher at the beginning of the drying operation, when the product moisture content was higher. The moisture content of the material was very high during the initial phase of the drying which resulted in a higher absorption of microwave power and higher drying rates due to the higher moisture diffusion. As the drying Figure 3 Variations of drying rate as a function of time for microwave drying of potato slices
5 98 March Agric Eng Int: CIGR Journal Open access at Vol. 14, o.1 Figure 4 Variations of drying rate as a function of moisture content for microwave drying of potato slices progressed, the loss of moisture in the product caused a decrease in the absorption of microwave power and resulted in a fall in the drying rate. Higher drying rates were obtained at higher microwave output powers. Thus, the microwave output power had a crucial effect on the drying rate (Soysal, 004). It was observed that there was a period with a constant drying rate at 5 W/g, and the drying processed at 10, 15 and 0 W/g represented a falling-rate drying period. 3. Evaluation of the models on-linear regression was used to obtain each parameter value of every model. The statistical results from the models are summarized in Table. In all cases, the statistical parameter estimations showed that R, χ and RMSE values were ranged from to 1, to , and to 0.781, respectively. Based on higher R, and lower values of χ and RMSE, it can be concluded that Midilli et al. model gave best results than the other models. Thus, it was selected to represent the thin layer drying characteristics of potato slices. Table Results of statistical analysis on the modeling of moisture contents and drying time for the microwave dried potato slices Model name P/W g -1 Model constants R χ RMSE 0 a = Linear Lewis Henderson and Pabis Page Midilli et al. Wang and Singh 15 a = a = a = k = k = k = k = a = 1.655, k = a = 1.519, k = a = 1.501, k = a = 1.34, k = k = 0.417, n = k = 0.391, n = k = 0.145, n = k = 0.017, n = a = 1.013, b = , k = 0.378, n = a = 1.01, b = , k = 0.354, n = a = 1.019, b = -0.08, k = 0.150, n = a = 1.013, b = , k = 0.0, n = a = , b = a = , b = a = , b = a = 0.000, b = Figure 5 compares experimental data with those predicted with the Midilli et al. model for potato slices at 5, 10, 15 and 0 W/g. There was a very good agreement between the experimental and predicted moisture ratio
6 March, 01 Energy consumption and mathematical modeling of microwave drying of potato slices Vol. 14, o.1 99 values, which closely banded around a 45 straight line. The Midilli et al. model has also been suggested by others to describe the infrared drying of tomatoes (Celma et al., 009), fluidized bed drying of olive pomace (Meziane, 011), sun, oven, and microwave oven drying of savory leaves (Arslan and Ozcan, 011), thin layer drying of eggplants (Ertekin and Yaldiz, 004), thin layer drying of potato, apple and pumpkin slices (Akpinar, 006), and mint leaves (Doymaz, 006). Figure 5 Comparison of experimental moisture ratio with predicted moisture ratio by Midilli et al. 3.3 Effective moisture diffusivity The effective moisture diffusivity was calculated by using the method of slopes. According to the experimental data obtained at different drying power densities, the logarithm of moisture ratio values, ln(mr), were plotted against drying time (t). The linearity of the relationship between ln(mr) and the drying time is illustrated in Figure 6. The values of effective moisture diffusivity are presented in Table 3, and obtaining values between and m /s. The D eff values reported herein are within the general range of to 10 9 m /s for food materials (Madamba et al., 1996). As expected, the effective moisture diffusivity values increased greatly with the increase in drying power density because of increasing in the vapor pressure inside the samples. This might be explained by the increased heating energy, which would increase the activity of the water molecules leading to higher moisture diffusivity when samples were dried at higher microwave power density. Similar results are found to correspond well with those existing in the literature, such as to m /s for fluidized bed drying of potatoes (Bakal et al., 011), to m /s freeze-drying of sweet potato cubes with far-infrared (Lin et al., 005), to m /s for thin-layer drying of potato slices in length of continuous band dryer (Aghbashlo et al., 009), and to m /s, to m /s, and to m /s for convective, microwave and combined drying of potato cylinders, respectively (McMinn et al., 003). The differences between the results can be explained by effect of drying methods, types, composition, and tissue characteristics of the potatoes and the proposed model used for calculation. Table 3 Moisture diffusivity coefficient values for microwave drying of potato slices P/W g -1 D eff /m s Figure 6 Plot of ln(mr) versus drying time used for the determination of effective moisture diffusivity 3.4 Energy consumption Figure 7 shows the variations of drying efficiency values for potato samples drying under microwave heating. Results showed that the drying efficiency values decreased continuously with time and increased as the power density and moisture content were increased. The average drying efficiency, total energy requirement for a charge of the dryer and the energy needed for drying of potato slices are given Figure 8. As it is understood from these figures,
7 100 March Agric Eng Int: CIGR Journal Open access at Vol. 14, o.1 the minimum specific energy ( MJ/kgH O) and maximum drying efficiency (6.4%) was computed for drying potato slices at microwave power density of 15 W/g. The minimum drying efficiency (1.38%) and Figure 7 Variations of drying efficiency as a function of time for microwave drying of potato slices Figure 8 Average values of drying efficiency and energy consumption during microwave drying of potato slices maximum specific energy ( MJ/kgH O) was computed at 5 W/g. Besides, the energy consumption decreasing with increasing drying microwave power output was more effective on energy requirement. The best result with regard to energy consumption and drying efficiency was obtained from 15 W/g power density level among all drying power density levels. The specific energy consumption obtained in the drying process using 15 W/g power density level was.5-fold lower than 5 W/g power density level. One of many reasons might be that the drying time is longer under lower power, hence results in a increase in energy consumption. 4 Conclusions The drying kinetics of the potato slices was investigated in a microwave dryer as a single layer at the drying microwave power densities of 5, 10, 15 and 0 W/g. The entire drying took place in a falling rate period at 10, 15 and 0 W/g, and took place in a constant period at 5 W/g. The moisture content and drying rates were influenced by the drying power density. Increases in drying power density caused decreases in drying time and increases in the drying rate. The effective diffusivity increased with the increase in the drying power density. Based on non-linear regression analysis, the Midilli et al. model was considered adequate to describe the thin-layer drying behavior of potato slices. The effective diffusivity varied from to m /s over the microwave power densities ranged from 5 to 0 W/g. According to the results, it can be said that 15 W/g must be selected for drying potato slices. Specific energy consumption and drying efficiency at this level were 4. MJ/kg[H O] and 53.54%, respectively. References Aghbashlo, M., M.H.Kianmehr, and A.Arabhosseini Modeling of thin-layer drying of potato slices in length of continuous band dryer. Energy Conversion and Management, 50(5): Akpinar, E.K Determination of suitable thin layer drying curve model for some vegetables and fruits. Journal of Food Engineering, 73(1): Akpinar, E.K., A.Midilli, and Y.Bicer Energy and exergy of potato drying process via cyclone type dryer. Energy Conversion and Management, 46(15-16): Al-Harahsheh, M., A. Al-Muhtaseb, and T.R.A.Magee Microwave drying kinetics of tomato pomace: Effect of osmotic dehydration. Chemical Engineering and Processing, 48(1):
8 March, 01 Energy consumption and mathematical modeling of microwave drying of potato slices Vol. 14, o Alibas, I Energy consumption and colour characteristics of nettle leaves during microwave, vacuum and convective drying. Biosystems Engineering, 96(4): Arslan, D., and M.M.Ozcan Study the effect of sun, oven and microwave drying on quality of onion slices. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 43(7): Arslan, D., and M.M. Ozcan Evaluation of drying methods with respect to drying kinetics, mineral content, and color characteristics of savory leaves. Food Bioprocess Technology, DOI /s y. Bakal, S.B., P.G.Sharma, S.P.Sonawan, and R.C.Verma Kinetics of potato drying using fluidized bed dryer.journal Food Science Technology, DOI /s x. Bruce, D.M Exposed-layer barley drying, three models fitted to new data up to 150 C.Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 3(4): Caixeta, A.T., R.Moreira, and M.E.Castell-Perez. 00. Impingement drying of potato chips. Journal of Food Process Engineering, 5(1): Celma, A.R., F.Cuadros, and L.F.Rodriguez Characterisation of industrial tomato by-products from infrared drying process. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 87(4): Diaz, G.R., J.Martı nez-monzo, P.Fito, and A.Chiralt Modelling of dehydration rehydration of orange slices in combined microwave/air drying. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 4(): Doymaz, I Thin-layer drying behaviour of mint leaves. Journal of Food Engineering, 74(3): Ertekin, C., and O.Yaldiz Drying of eggplant and selection of a suitable thin layer drying model. Journal of Food Engineering, 63(3): Hatamipour, M.S., H.Kazemi, A.ooraliv,andA.ozarpoor Drying characteristics of sex varieties of sweet potatoes in different dryers. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 85(C3): Hayes, G.D Food Engineering Data Handbook. England:Longman Scientific and Technical. Henderson, S.M., and S.Pabis Grain drying theory II: Temperature effects on drying coefficients. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 6: Khraisheh, M.A.M., W.A.M.McMinn, and T.R.A.Magee Quality and structural changes in starchy foods during microwave and convective drying. Food Research International, 37(5): Krokida, M.K., V.T.Karathanos, Z. B.Maroulis, and D.Marinos-Kouris Drying kinetics of some vegetables. Journal of Food Engineering, 59(4): Leeratanarak,., S.Devahastin, and.chiewchan Drying kinetics and quality of potato chips undergoing different drying techniques. Journal of Food Engineering, 77(3): Lin, P.Y., J.H.Tsen, and V.A.E.King Effects of far-infrared radiation on the freeze-drying of sweet potato. Journal of Food Engineering, 68(): Madamba, P.S., R. H. Driscoll, and K. A. Buckle The thin-layer drying characteristics of garlic slices. Journal of Food Engineering, 9(1): Maskan, M Microwave/air and microwave finish drying of banana. Journal of Food Engineering, 44(): McMinn, W.A.M., M.A.M.Khraisheh, and T.R.A.Magee Modelling the mass transfer during convective, microwave and combined microwave-convective drying of solid slabs and cylinders. Food Research International, 36(9-10): Meziane, S Drying kinetics of olive pomace in a fluidized bed dryer. Energy Conversion and Management, 5(3): Midilli, A., H.Kucuk, and Z.Yapar. 00. A new model for single layer drying. Drying Technology, 0(10): Mousa,., and M.Farid. 00. Microwave vacuum drying of banana slices. Drying Technology, 0(10): Ozbek, B., and G. Dadali Thin-layer drying characteristics and modeling of mint leaves undergoing microwave treatment. Journal of Food Engineering, 83(4): Page, G.E Factors influencing the maximum rates of air drying shelled corn in thin layers. M.S. thesis.department of Mechanical Engineering, Purdue University, Purdue, USA. Pimpaporn, P., S.Devahastin, and. Chiewchan Effects of combined pretreatments on drying kinetics and quality of potato chips undergoing low-pressure superheated steam drying. Journal of Food Engineering, 81(): Reyes, A., S.Ceron, R.Zuniga, and P.Moyano A comparative study of microwave-assisted air drying of potato slices. Biosystems Engineering, 98(3): Senadeera, W., B.R.Bhandari, G.Young, and B.Wijesinghe Influence of shapes of selected vegetable materials on drying kinetics during fluidized bed drying. Journal of Food Engineering, 58(3): Soysal, A Microwave Drying Characteristics of Parsley. Biosystems Engineering, 89(): Soysal, A., S.Oztekin, and O.Eren Microwave drying of parsley: modelling, kinetics, and energy aspects. Biosystems Engineering, 93(4): Sumnu, G., E.M.Turabi, and M.Oztop Drying of carrots in microwave and halogen lamp microwave combination ovens. LWT, 38(5): Tippayawong,., C.Tantakitti, and S.Thavornun Energy efficiency improvements in longan drying practice. Energy, 33(7):
9 10 March Agric Eng Int: CIGR Journal Open access at Vol. 14, o.1 Vadivambal, R., and D.S.Jayas Changes in quality of microwave-treated agricultural products-a review. Biosystems Engineering, 98(1): Wang, C.Y., and R.P.Singh Use of variable equilibrium moisture content in modeling rice drying. Transactions of American Society of Agricultural Engineers, 11: Wang, J., and K.Sheng Far-infrared and microwave drying of peach. LWT, 39(3): Wang, Z., J.Sun, F.Chen, X.Liao, and X.Hu Mathematical modelling on thin layer microwave drying of apple pomace with and without hot air pre-drying. Journal of Food Engineering, 80(): Yongsawatdigul, J., and S.Gunasekaran Microwavevacuum drying of cranberries, Part II: Quality evaluation. Journal of Food Process Engineering, 0(1):
Influence of temperature and drying air velocity on the kinetics of convective drying in the food industry
 Influence of temperature and drying air velocity on the kinetics of convective drying in the food industry Ing. Michal Pěnička Project leader: Doc. Pavel Hoffman CSc. Abstract The aim of this study was
Influence of temperature and drying air velocity on the kinetics of convective drying in the food industry Ing. Michal Pěnička Project leader: Doc. Pavel Hoffman CSc. Abstract The aim of this study was
An Experimental Study on Drying of Pistacia Terebinthus in a Fixed Bed Dryer
 Copyright 2013 Tech Science Press FDMP, vol.9, no.1, pp.1-10, 2013 An Experimental Study on Drying of Pistacia Terebinthus in a Fixed Bed Dryer A. Balbay 1, H. Ülker 2 and Ö. Şahin 3 Abstract: In this
Copyright 2013 Tech Science Press FDMP, vol.9, no.1, pp.1-10, 2013 An Experimental Study on Drying of Pistacia Terebinthus in a Fixed Bed Dryer A. Balbay 1, H. Ülker 2 and Ö. Şahin 3 Abstract: In this
Cassava Chip Drying by Using a Small-Scale Hot-Air Microwave Oven
 American Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences 6 (2): 211-215, 2013 ISSN: 1941-7020 2014 P. Wilaipon, This open access article is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) 3.0 license
American Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences 6 (2): 211-215, 2013 ISSN: 1941-7020 2014 P. Wilaipon, This open access article is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) 3.0 license
A New Approach for Modeling of Hot Air-microwave Thin Layer Drying of Soybean
 A New Approach for Modeling of Hot Air-microwave Thin Layer Drying of Soybean Dariush Zare, Assistant Professor, Agricultural Engineering Dept., Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran. M. Ranjbaran, M. Javidi,
A New Approach for Modeling of Hot Air-microwave Thin Layer Drying of Soybean Dariush Zare, Assistant Professor, Agricultural Engineering Dept., Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran. M. Ranjbaran, M. Javidi,
Characteristics of sunflower seed drying and microwave energy consumption
 Int. Agrophys., 2013, 27, 127-132 doi: 10.2478/v10247-012-0077-8 INTERNATIONAL Agrophysics www.international-agrophysics.org Characteristics of sunflower seed drying and microwave energy consumption H.
Int. Agrophys., 2013, 27, 127-132 doi: 10.2478/v10247-012-0077-8 INTERNATIONAL Agrophysics www.international-agrophysics.org Characteristics of sunflower seed drying and microwave energy consumption H.
Drying Kinetics Modelling of Basil in Microwave Dryer
 AGRICULTURAL COMMUNICATIONS, 2015, 3(4): 37 44. Drying Kinetics Modelling of Basil in Microwave Dryer ESMAEEL SEYEDABADI Department of Agronomy, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Zabol, Zabol, Iran.
AGRICULTURAL COMMUNICATIONS, 2015, 3(4): 37 44. Drying Kinetics Modelling of Basil in Microwave Dryer ESMAEEL SEYEDABADI Department of Agronomy, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Zabol, Zabol, Iran.
Evaluation and Selection of Thin-layer Models for Drying Kinetics of Apricot (cv.nasiry)
 1 Evaluation and Selection of Thin-layer Models for Drying Kinetics of Apricot (cv.nasiry) E. Mirzaee 1, S. Rafiee 1, A. Keyhani 1 1 Agricultural Machinery Engineering Dept., Faculty of Agricultural Engineering
1 Evaluation and Selection of Thin-layer Models for Drying Kinetics of Apricot (cv.nasiry) E. Mirzaee 1, S. Rafiee 1, A. Keyhani 1 1 Agricultural Machinery Engineering Dept., Faculty of Agricultural Engineering
Mathematical modelling, moisture diffusion and specific energy consumption of thin layer microwave drying of olive pomace
 International Food Research Journal 22(2): 494-501 (2015) Journal homepage: http://www.ifrj.upm.edu.my Mathematical modelling, moisture diffusion and specific energy consumption of thin layer microwave
International Food Research Journal 22(2): 494-501 (2015) Journal homepage: http://www.ifrj.upm.edu.my Mathematical modelling, moisture diffusion and specific energy consumption of thin layer microwave
DRYING CHARACTERISTICS OF PAPAYA (CARICA PAPAYA L.) DURING MICROWAVE-VACUUM TREATMENT
 International Journal of Engineering and Technology, Vol., No.,, pp. - DRYING CHARACTERISTICS OF PAPAYA (CARICA PAPAYA L.) DURING MICROWAVE-VACUUM TREATMENT Nurul Asyikin Md Zaki, Ida Idayu Muhamad and
International Journal of Engineering and Technology, Vol., No.,, pp. - DRYING CHARACTERISTICS OF PAPAYA (CARICA PAPAYA L.) DURING MICROWAVE-VACUUM TREATMENT Nurul Asyikin Md Zaki, Ida Idayu Muhamad and
Mathematical modelling of thin-layer drying of carrot
 Int. Agrophysics, 2009, 23, 313-317 INTERNATIONAL Agrophysics www.international-agrophysics.org Mathematical modelling of thin-layer drying of carrot M. Aghbashlo*, M.H. Kianmehr, S. Khani, and M. Ghasemi
Int. Agrophysics, 2009, 23, 313-317 INTERNATIONAL Agrophysics www.international-agrophysics.org Mathematical modelling of thin-layer drying of carrot M. Aghbashlo*, M.H. Kianmehr, S. Khani, and M. Ghasemi
DETERMINATION OF THE EFFECTIVE MOISTURE DIFFUSIVITY OF RED PEPPER IN A MICROWAVE CONVEYOR DRYER
 DETERMINATION OF THE EFFECTIVE MOISTURE DIFFUSIVITY OF RED PEPPER IN A MICROWAVE CONVEYOR DRYER Soner ÇELEN +, Ugur AKYOL +, Aytaç MORALAR + + NAMIK KEMAL UNIVERSITY, Çorlu, Tekirda, Turkey. Abstract.
DETERMINATION OF THE EFFECTIVE MOISTURE DIFFUSIVITY OF RED PEPPER IN A MICROWAVE CONVEYOR DRYER Soner ÇELEN +, Ugur AKYOL +, Aytaç MORALAR + + NAMIK KEMAL UNIVERSITY, Çorlu, Tekirda, Turkey. Abstract.
Design and Fabrication of Experimental Dryer for Studying Agricultural Products
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF AGRICULTURE & BIOLOGY ISSN Print: 1560 8530; ISSN Online: 1814 9596 07-84/AWB/008/10 1 61 65 http://www.fspublishers.org Full Length Article Design and Fabrication of Dryer for
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF AGRICULTURE & BIOLOGY ISSN Print: 1560 8530; ISSN Online: 1814 9596 07-84/AWB/008/10 1 61 65 http://www.fspublishers.org Full Length Article Design and Fabrication of Dryer for
Variable far infrared radiation (VFIR) technique for cubic carrot drying
 International Journal of Renewable Energy, Vol. 7, No. 2, July - December 2012 Variable far infrared radiation (VFIR) technique for cubic carrot drying Sirinuch Chindaruksa a *, Pisit Maneechot b, Seishu
International Journal of Renewable Energy, Vol. 7, No. 2, July - December 2012 Variable far infrared radiation (VFIR) technique for cubic carrot drying Sirinuch Chindaruksa a *, Pisit Maneechot b, Seishu
Drying of apple slices (var. Golab) and effect on moisture diffusivity and activation energy
 POJ 3(3):97-10 (010) ISSN:1836-3644 Drying of apple slices (var. Golab) and effect on moisture diffusivity and activation energy *E. Meisami-asl, S. Rafiee, A. Keyhani and A. Tabatabaeefar Department of
POJ 3(3):97-10 (010) ISSN:1836-3644 Drying of apple slices (var. Golab) and effect on moisture diffusivity and activation energy *E. Meisami-asl, S. Rafiee, A. Keyhani and A. Tabatabaeefar Department of
Drying Characteristics of Carrot and Green Pumpkin Slices in Waste Heat Dryer
 Original Article J. of Biosystems Eng. 37(1):36-43. (2012. 2) http://dx.doi.org/10.5307/jbe.2012.37.1.036 Journal of Biosystems Engineering eissn : 2234-1862 pissn : 1738-1266 Drying Characteristics of
Original Article J. of Biosystems Eng. 37(1):36-43. (2012. 2) http://dx.doi.org/10.5307/jbe.2012.37.1.036 Journal of Biosystems Engineering eissn : 2234-1862 pissn : 1738-1266 Drying Characteristics of
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECT OF DRYING AIR RELATIVE HUMIDITY IN DRYING KINETICS OF KIWI
 Academic Journal of Science, CD-ROM. ISSN: 2165-6282 :: 2(1):1 10 (2013) EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECT OF DRYING AIR RELATIVE HUMIDITY IN DRYING KINETICS OF KIWI Soner en and Selçuk Dar c Selçuk
Academic Journal of Science, CD-ROM. ISSN: 2165-6282 :: 2(1):1 10 (2013) EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECT OF DRYING AIR RELATIVE HUMIDITY IN DRYING KINETICS OF KIWI Soner en and Selçuk Dar c Selçuk
Mathematical modeling of drying characteristics of chilli in hot air oven and fluidized bed dryers
 154 March, 2013 Agric Eng Int: CIGR Journal Open access at http://www.cigrjournal.org Vol. 15, No.1 Mathematical modeling of drying characteristics of chilli in hot air oven and fluidized bed dryers S.
154 March, 2013 Agric Eng Int: CIGR Journal Open access at http://www.cigrjournal.org Vol. 15, No.1 Mathematical modeling of drying characteristics of chilli in hot air oven and fluidized bed dryers S.
Thin-layer drying of some Sri Lankan paddy varieties under low humid conditions
 36 Thin-layer drying of some Sri Lankan paddy varieties under low humid conditions A.K. Shyamali, H.H.E. Jayaweera and T.R. Ariyaratne Centre for Instrument Development, Department of Physics, University
36 Thin-layer drying of some Sri Lankan paddy varieties under low humid conditions A.K. Shyamali, H.H.E. Jayaweera and T.R. Ariyaratne Centre for Instrument Development, Department of Physics, University
INFLUENCE OF DRYING CONDITIONS ON THE MOISTURE DIFFUSION DURING SINGLE STAGE AND TWO STAGE FLUIDIZED BED DRYING OF BOVINE INTESTINE FOR PET FOOD
 INFLUENCE OF DRYING CONDITIONS ON THE MOISTURE DIFFUSION DURING SINGLE STAGE AND TWO STAGE FLUIDIZED BED DRYING OF BOVINE INTESTINE FOR PET FOOD O. Alves-Filho 1, W. Senadeera, T. Eikevik 1 1 Norwegian
INFLUENCE OF DRYING CONDITIONS ON THE MOISTURE DIFFUSION DURING SINGLE STAGE AND TWO STAGE FLUIDIZED BED DRYING OF BOVINE INTESTINE FOR PET FOOD O. Alves-Filho 1, W. Senadeera, T. Eikevik 1 1 Norwegian
Drying Kinetics of Chilli Pepper in a force Convection Indirect Solar Drying
 Drying Kinetics of Chilli Pepper in a force Convection Indirect Solar Drying M.I. FADHEL 1, S. SHAUNMUGANATHAN 1, M.A. AlGHOUL 2, MALEK ALI 1, K. SOPIAN 2 & A. ZAHARIM 2 1 Faculty of Engineering and Technology,
Drying Kinetics of Chilli Pepper in a force Convection Indirect Solar Drying M.I. FADHEL 1, S. SHAUNMUGANATHAN 1, M.A. AlGHOUL 2, MALEK ALI 1, K. SOPIAN 2 & A. ZAHARIM 2 1 Faculty of Engineering and Technology,
The Effect of Quantity of Salt on the Drying Characteristics of Fresh Noodles
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Agriculture and Agricultural Science Procedia 2 ( 2014 ) 207 211 ST26943, 2nd International Conference on Agricultural and Food Engineering, CAFEi2014
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Agriculture and Agricultural Science Procedia 2 ( 2014 ) 207 211 ST26943, 2nd International Conference on Agricultural and Food Engineering, CAFEi2014
Thin layer drying models for sweet potato in tray dryer
 Thin layer drying models for sweet potato in tray dryer A. S. Olawale *, S. O. Omole (Department of Chemical Engineering, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria) Abstract: Sweet potato is increasingly
Thin layer drying models for sweet potato in tray dryer A. S. Olawale *, S. O. Omole (Department of Chemical Engineering, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria) Abstract: Sweet potato is increasingly
Sitesh Kumar Pandey1, Richa Soni2, Abhishek Shrivastav3 1,3
 IJEEE Volume Spl. Issue (6) Mathematical ing of Thin Layer Drying Process of Red Chili in Solar Dryer Under Open Sun Sitesh Kumar Pey Richa Soni Abhishek Shrivastav Mechanical Engineering Deptt. C.I.E.T
IJEEE Volume Spl. Issue (6) Mathematical ing of Thin Layer Drying Process of Red Chili in Solar Dryer Under Open Sun Sitesh Kumar Pey Richa Soni Abhishek Shrivastav Mechanical Engineering Deptt. C.I.E.T
Study of the Drying Kinetics of Baccaurea angulata Merr. (Belimbing Dayak) Fruit
 Study of the Drying Kinetics of Baccaurea angulata Merr. (Belimbing Dayak) Fruit DAYAG FREDALIA BASRI, AHMAD FUDHOLI *, MOHD HAFIDZ RUSLA, M. A. ALGHOUL School of Diagnostic and Applied Health Sciences,
Study of the Drying Kinetics of Baccaurea angulata Merr. (Belimbing Dayak) Fruit DAYAG FREDALIA BASRI, AHMAD FUDHOLI *, MOHD HAFIDZ RUSLA, M. A. ALGHOUL School of Diagnostic and Applied Health Sciences,
The influence of the combined microwave power and hot air ventilation on the drying kinetics and colour quality of tomato slices
 African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 11(87), pp. 15353-15364, 30 October, 2012 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb DOI: 10.5897/AJB11.318 ISSN 1684 5315 2012 Academic Journals Full
African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 11(87), pp. 15353-15364, 30 October, 2012 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb DOI: 10.5897/AJB11.318 ISSN 1684 5315 2012 Academic Journals Full
Thin layer tea drying experimentation with biomass fuelled producer gas
 In the previous Chapter, we had discussed the details procedure of selection and characterization of biomass as prospective fuel for tea processing through gasification. We found that fuel properties of
In the previous Chapter, we had discussed the details procedure of selection and characterization of biomass as prospective fuel for tea processing through gasification. We found that fuel properties of
Hot Air-Microwave Combined Drying Characteristics of Gypsum Board. Won-Pyo Chun, Sung-Il Kim, and Ki-Woo Lee 1
 European Drying Conference - EuroDrying'11 Palma. Balearic Island, Spain, 26-28 October 11 Hot Air-Microwave Combined Drying Characteristics of Gypsum Board Won-Pyo Chun, Sung-Il Kim, and Ki-Woo Lee 1
European Drying Conference - EuroDrying'11 Palma. Balearic Island, Spain, 26-28 October 11 Hot Air-Microwave Combined Drying Characteristics of Gypsum Board Won-Pyo Chun, Sung-Il Kim, and Ki-Woo Lee 1
Investigation of microwave application in agricultural production drying
 41 / 14 Investigation of microwave application in agricultural production drying Ehsan Yarionsorudi, Amin Alamloo, Atabak Movafegi 1 Department of Electrical Engineering,College of Technical & Engineering,Tabriz
41 / 14 Investigation of microwave application in agricultural production drying Ehsan Yarionsorudi, Amin Alamloo, Atabak Movafegi 1 Department of Electrical Engineering,College of Technical & Engineering,Tabriz
ANALYSIS OF THE DRYING KINETICS OF S. BARTOLOMEU PEARS FOR DIFFERENT DRYING SYSTEMS
 ISSN: 1579-4377 ANALYSIS OF THE DRYING KINETICS OF S. BARTOLOMEU PEARS FOR DIFFERENT DRYING SYSTEMS RAQUEL P. F. GUINÉ Departamento de Indústrias Alimentares, Escola Superior Agrária de Viseu, Instituto
ISSN: 1579-4377 ANALYSIS OF THE DRYING KINETICS OF S. BARTOLOMEU PEARS FOR DIFFERENT DRYING SYSTEMS RAQUEL P. F. GUINÉ Departamento de Indústrias Alimentares, Escola Superior Agrária de Viseu, Instituto
An Investigation on Drying of Millets in A Microwave Oven
 An Investigation on Drying of Millets in A Microwave Oven G. B. Radhika 1, S.V. Satyanarayana, D. G. Rao 3 1 B.V.Raju Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, India Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University
An Investigation on Drying of Millets in A Microwave Oven G. B. Radhika 1, S.V. Satyanarayana, D. G. Rao 3 1 B.V.Raju Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, India Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University
Drying Parawood with Superheated Steam
 American Journal of Applied Sciences 4 (4): 215-219, 2007 ISSN 1546-9239 2007 Science Publications Drying Parawood with Superheated Steam Surachai Bovornsethanan and Somchai Wongwises Department of Mechanical
American Journal of Applied Sciences 4 (4): 215-219, 2007 ISSN 1546-9239 2007 Science Publications Drying Parawood with Superheated Steam Surachai Bovornsethanan and Somchai Wongwises Department of Mechanical
MICROWAVE DRYING OF ALOE VERA (ALOE BARBADENSIS MILLER): MATHEMATICAL MODELING, KINETICS AND MASS TRANSFER ASPECTS
 MICROWAVE DRYING OF ALOE VERA (ALOE BARBADENSIS MILLER): MATHEMATICAL MODELING, KINETICS AND MASS TRANSFER ASPECTS G. Srinivasan 1, R.Baskar 2 1 Assistant Professor (Sr.Gr.), Department of Chemical Engineering,
MICROWAVE DRYING OF ALOE VERA (ALOE BARBADENSIS MILLER): MATHEMATICAL MODELING, KINETICS AND MASS TRANSFER ASPECTS G. Srinivasan 1, R.Baskar 2 1 Assistant Professor (Sr.Gr.), Department of Chemical Engineering,
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 6, June ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 6, June-2015 1009 Selection of Optimum Temperature and Thin Layer Drying Kinetics of Maize for Production of Quality Seeds Mosharaf
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 6, June-2015 1009 Selection of Optimum Temperature and Thin Layer Drying Kinetics of Maize for Production of Quality Seeds Mosharaf
Solar Drying Kinetics of Cassava Slices in a Mixed Flow Dryer
 DOI: 10.1515/ata-015-000 Acta Technologica Agriculturae 4/015 Acta Technologica Agriculturae 4 Nitra, Slovaca Universitas Agriculturae Nitriae, 015, pp. 10 107 Solar Drying Kinetics of Cassava Slices in
DOI: 10.1515/ata-015-000 Acta Technologica Agriculturae 4/015 Acta Technologica Agriculturae 4 Nitra, Slovaca Universitas Agriculturae Nitriae, 015, pp. 10 107 Solar Drying Kinetics of Cassava Slices in
Influence Collector Inclination of Solar Dryer on Apple Golab Chips Drying
 ORIGIAL SCIETIFIC PAPER 101 Influence Collector Inclination of Solar Dryer on Apple Golab Chips Drying Omid Reza ROUSTAPOUR 1( ) Hamid Reza GAZOR 2 Summary Thin layer of apple chips ( Golab ) with 73.4%
ORIGIAL SCIETIFIC PAPER 101 Influence Collector Inclination of Solar Dryer on Apple Golab Chips Drying Omid Reza ROUSTAPOUR 1( ) Hamid Reza GAZOR 2 Summary Thin layer of apple chips ( Golab ) with 73.4%
4th International Conference on Sensors, Measurement and Intelligent Materials (ICSMIM 2015)
 4th International Conference on Sensors, Measurement and Intelligent Materials (ICSMIM 2015) Multi-stage Series Heat Pump Drying System with Dehumidification Simulation and Experiment Verification Chao
4th International Conference on Sensors, Measurement and Intelligent Materials (ICSMIM 2015) Multi-stage Series Heat Pump Drying System with Dehumidification Simulation and Experiment Verification Chao
Mathematical Simulation of Longan Fruit Drying
 Mathematical Simulation of Longan Fruit Drying Aree Achariyaviriya, Somchart Soponronnarit and Jirawan Tiansuwan ABSTRACT The objectives of this study were to develop a mathematical model and to simulate
Mathematical Simulation of Longan Fruit Drying Aree Achariyaviriya, Somchart Soponronnarit and Jirawan Tiansuwan ABSTRACT The objectives of this study were to develop a mathematical model and to simulate
MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF MICROWAVE ASSISTED FLUIDIZED BED DRYING OF HAZELNUTS
 MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF MICROWAVE ASSISTED FLUIDIZED BED DRYING OF HAZELNUTS Narjes Malekjani (a), Zahra Emam-Djomeh (b), Seyed Hassan Hashemabadi (c), Gholam Reza Askari (d) (a), (b), (d) Department
MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF MICROWAVE ASSISTED FLUIDIZED BED DRYING OF HAZELNUTS Narjes Malekjani (a), Zahra Emam-Djomeh (b), Seyed Hassan Hashemabadi (c), Gholam Reza Askari (d) (a), (b), (d) Department
Food Research (2019) : pp - pp Journal homepage:
 Food Research (2019) : pp - pp Journal homepage: http://www.myfoodresearch.com Drying characteristics of fish cracker under different drying techniques 1,* Abdullah, S., 1 Musa, N., 2 Rukunudin, I.H. and
Food Research (2019) : pp - pp Journal homepage: http://www.myfoodresearch.com Drying characteristics of fish cracker under different drying techniques 1,* Abdullah, S., 1 Musa, N., 2 Rukunudin, I.H. and
Thin Layer Mathematical Modelling of Cob Maize in a Natural Convection Solar Drier
 Energy and Environment Research; Vol. 7, No. 2; 2017 ISSN 1927-0569 E-ISSN 1927-0577 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Thin Layer Mathematical Modelling of Cob Maize in a Natural Convection
Energy and Environment Research; Vol. 7, No. 2; 2017 ISSN 1927-0569 E-ISSN 1927-0577 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Thin Layer Mathematical Modelling of Cob Maize in a Natural Convection
Drying Kinetics and Inversion Temperature in a Low-Pressure Superheated Steam-Drying System
 Drying Kinetics and Inversion Temperature in a Low-Pressure Superheated Steam-Drying System P. Suvarnakuta, S. Devahastin,*, S. Soponronnarit, and A. S. Mujumdar Department of Food Engineering and School
Drying Kinetics and Inversion Temperature in a Low-Pressure Superheated Steam-Drying System P. Suvarnakuta, S. Devahastin,*, S. Soponronnarit, and A. S. Mujumdar Department of Food Engineering and School
THERMAL PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF GREENHOUSE SOLAR DRYER UNDER PASSIVE MODE
 THERMAL PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF GREENHOUSE SOLAR DRYER UNDER PASSIVE MODE Pushpendra Singh 1, Vipin Shrivastava 2 1,2 Mechanical Engineering Department, Lakshmi Narain College of Technology (India) ABSTRACT
THERMAL PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF GREENHOUSE SOLAR DRYER UNDER PASSIVE MODE Pushpendra Singh 1, Vipin Shrivastava 2 1,2 Mechanical Engineering Department, Lakshmi Narain College of Technology (India) ABSTRACT
Microwave Assisted Hot Air Ventilation Drying of Tomato Slices
 2011 International Conference on Food Engineering and Biotechnology IPCBEE vol.9 (2011) (2011)IACSIT Press, Singapoore Microwave Assisted Hot Air Ventilation Drying of Tomato Slices Tilahun Seyoum Workneh
2011 International Conference on Food Engineering and Biotechnology IPCBEE vol.9 (2011) (2011)IACSIT Press, Singapoore Microwave Assisted Hot Air Ventilation Drying of Tomato Slices Tilahun Seyoum Workneh
KERONE (AN ISO 9001: 2008 CERTIFIED COMPANY)
 KERONE (AN ISO 9001: 2008 CERTIFIED COMPANY) Role of Agriculture and Allied Sector in Indian Economy Largest economic sector, plays a significant role in socio-economic development of India. More than
KERONE (AN ISO 9001: 2008 CERTIFIED COMPANY) Role of Agriculture and Allied Sector in Indian Economy Largest economic sector, plays a significant role in socio-economic development of India. More than
All rights reserved, Armando B. Corripio, PhD, PE, Solid Dryer Design Introduction Continuous Dryer Design...
 Solid Dryer Design All rights reserved, Armando B. Corripio, PhD, PE, 2014 Contents Solid Dryer Design... 1 Introduction... 2 1. Continuous Dryer Design... 3 1.1 Mass Balances... 4 1.2 Temperature Profiles...
Solid Dryer Design All rights reserved, Armando B. Corripio, PhD, PE, 2014 Contents Solid Dryer Design... 1 Introduction... 2 1. Continuous Dryer Design... 3 1.1 Mass Balances... 4 1.2 Temperature Profiles...
Experimental Investigation of a Heat Pump Assisted Fluidized Bed Dryer
 GRD Journals- Global Research and Development Journal for Engineering Volume 2 Issue 6 May 2017 ISSN: 2455-5703 Experimental Investigation of a Heat Pump Assisted Fluidized Bed Dryer Gokul G Nair Dr. Jeoju
GRD Journals- Global Research and Development Journal for Engineering Volume 2 Issue 6 May 2017 ISSN: 2455-5703 Experimental Investigation of a Heat Pump Assisted Fluidized Bed Dryer Gokul G Nair Dr. Jeoju
Development of a Simulation Model for the Hybrid Solar Dryers as Alternative Sustainable Drying System for Herbal and Medicinal Plants
 Development of a Simulation Model for the Hybrid Solar Dryers as Alternative Sustainable Drying System for Herbal and Medicinal Plants Ali, S.A. and A.H. Bahnasawy Agric. Eng. Dept., Moshtohor Agric. College
Development of a Simulation Model for the Hybrid Solar Dryers as Alternative Sustainable Drying System for Herbal and Medicinal Plants Ali, S.A. and A.H. Bahnasawy Agric. Eng. Dept., Moshtohor Agric. College
Experimental & Analytical Investigation on Modified Solar Dryer with Recirculation of Air
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 4 (2013), pp. 441-448 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Experimental & Analytical
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 4 (2013), pp. 441-448 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Experimental & Analytical
Drying Kinetics of Oyster Mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus) in a Convective Hot Air Dryer
 J. Agr. Sci. Tech. (011) Vol. 13: 655-664 Drying Kinetics of Oyster Mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus) in a Convective Hot Air Dryer Y. Tulek 1 ABSTRACT The objective of this study was to investigate the drying
J. Agr. Sci. Tech. (011) Vol. 13: 655-664 Drying Kinetics of Oyster Mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus) in a Convective Hot Air Dryer Y. Tulek 1 ABSTRACT The objective of this study was to investigate the drying
THE THIN LAYER DRYING OF TEMU PUTIH HERB
 The 6 th Asia-Pacific Drying Conference (ADC2009) October 19-21, 2009, Bangkok, Thailand THE THIN LAYER DRYING OF TEMU PUTIH HERB *Lamhot P. MANALU 1,2, Armansyah H. TAMBUNAN 3, Leopold O. NELWAN 3 and
The 6 th Asia-Pacific Drying Conference (ADC2009) October 19-21, 2009, Bangkok, Thailand THE THIN LAYER DRYING OF TEMU PUTIH HERB *Lamhot P. MANALU 1,2, Armansyah H. TAMBUNAN 3, Leopold O. NELWAN 3 and
Prediction of Soil Infiltration Rate Based on Sand Content of Soil
 Agricultural Engineering Research Journal 3 (): 0-4, 013 ISSN 18-3906 IDOSI Publications, 013 DOI: 10.589/idosi.aerj.013.3..1109 Prediction of Soil Infiltration Rate Based on Sand Content of Soil 1 1 Majid
Agricultural Engineering Research Journal 3 (): 0-4, 013 ISSN 18-3906 IDOSI Publications, 013 DOI: 10.589/idosi.aerj.013.3..1109 Prediction of Soil Infiltration Rate Based on Sand Content of Soil 1 1 Majid
INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT TEMPERING PERIOD AND VACUUM CONDITIONS ON THE RICE GRAIN BREAKAGE IN A THIN LAYER DRYER
 INFLUENCE OF TEMPERING PERIOD AND VACUUM CONDITIONS ON THE RICE GRAIN BREAKAGE Cercetări Agronomice în Moldova Vol. XLVI, No. 4 (156) / 2013 INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT TEMPERING PERIOD AND VACUUM CONDITIONS
INFLUENCE OF TEMPERING PERIOD AND VACUUM CONDITIONS ON THE RICE GRAIN BREAKAGE Cercetări Agronomice în Moldova Vol. XLVI, No. 4 (156) / 2013 INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT TEMPERING PERIOD AND VACUUM CONDITIONS
Drying principles and general considerations
 Drying principles and general considerations Drying Mechanisms In the process of drying heat is necessary to evaporate moisture from the grain and a flow of air is needed to carry away the evaporated moisture.
Drying principles and general considerations Drying Mechanisms In the process of drying heat is necessary to evaporate moisture from the grain and a flow of air is needed to carry away the evaporated moisture.
Specific Energy Consumption comparative study of Hot Air dryer and Heat Pump dryer for highland drying process Sayompon Srina
 Specific Energy Consumption comparative study of Hot Air dryer and Heat Pump dryer for highland drying process Sayompon Srina Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, King Mongkut
Specific Energy Consumption comparative study of Hot Air dryer and Heat Pump dryer for highland drying process Sayompon Srina Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, King Mongkut
Experimental Analysis of Open, Simple and Modified Greenhouse Dryers for Drying Potato Flakes under Forced Convection
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Experimental Analysis of Open, Simple and Modified Greenhouse Dryers for Drying Potato Flakes under Forced Convection Tanuj Kumar Sahu 1, Vishal Gupta 2, Ajay Kumar Singh 3
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Experimental Analysis of Open, Simple and Modified Greenhouse Dryers for Drying Potato Flakes under Forced Convection Tanuj Kumar Sahu 1, Vishal Gupta 2, Ajay Kumar Singh 3
Review of the Drying Kinetics of Olive Oil Mill Wastes: Biomass Recovery
 Review of the Drying Kinetics of Olive Oil Mill Wastes: Biomass Recovery Francisco J. Gómez-de la Cruz, a, * Pedro J. Casanova-Peláez, b Rafael López-García, a and Fernando Cruz-Peragón a The drying kinetics
Review of the Drying Kinetics of Olive Oil Mill Wastes: Biomass Recovery Francisco J. Gómez-de la Cruz, a, * Pedro J. Casanova-Peláez, b Rafael López-García, a and Fernando Cruz-Peragón a The drying kinetics
Drying Kinetics of Sliced Pineapples in a Solar Conduction Dryer
 Energy and Environment Research; Vol. 7, No. 2; 2017 ISSN 1927-0569 E-ISSN 1927-0577 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Drying Kinetics of Sliced Pineapples in a Solar Conduction Dryer
Energy and Environment Research; Vol. 7, No. 2; 2017 ISSN 1927-0569 E-ISSN 1927-0577 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Drying Kinetics of Sliced Pineapples in a Solar Conduction Dryer
Solar Drying of Fruits and Vegetables
 Solar Drying of Fruits and Vegetables Y. Baradey 1, M. N. A. Hawlader 2, A. F. Ismail 3, M. Hrairi 4, M. I. Rapi 5 1,2,3 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, International Islamic
Solar Drying of Fruits and Vegetables Y. Baradey 1, M. N. A. Hawlader 2, A. F. Ismail 3, M. Hrairi 4, M. I. Rapi 5 1,2,3 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, International Islamic
Effect of Magnetic Field on Convective Drying Of Ceramic Clay
 International Journal of Engineering and Technology Volume 5 No. 7, July, 2015 Effect of Magnetic Field on Convective Drying Of Ceramic Clay A.A Dare 1, L. I Onu 2, R Akinoso 3 1 Department of Mechanical
International Journal of Engineering and Technology Volume 5 No. 7, July, 2015 Effect of Magnetic Field on Convective Drying Of Ceramic Clay A.A Dare 1, L. I Onu 2, R Akinoso 3 1 Department of Mechanical
Exergy Analysis of Heat Pump Dryer
 12 MAHASARAKHAM INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 4, NO. 1, JANUARY-JUNE 2018 ergy Analysis of Heat Pump Dryer Nattapol Poomsa-ad 1,*, Lamul Wiset 2 and Khanuengnit Chapchaimoh 3 1,*
12 MAHASARAKHAM INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 4, NO. 1, JANUARY-JUNE 2018 ergy Analysis of Heat Pump Dryer Nattapol Poomsa-ad 1,*, Lamul Wiset 2 and Khanuengnit Chapchaimoh 3 1,*
Corn drying experiments by pilot dryer
 Agronomy Research Biosystem Engineering Special Issue 1, 91-97, 2011 Corn drying experiments by pilot dryer L. Kocsis, M. Herdovics, J. Deákvári and L. Fenyvesi Hungarian Institute of Agricultural Engineering,
Agronomy Research Biosystem Engineering Special Issue 1, 91-97, 2011 Corn drying experiments by pilot dryer L. Kocsis, M. Herdovics, J. Deákvári and L. Fenyvesi Hungarian Institute of Agricultural Engineering,
International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research e-issn No.: , Date: 2-4 July, 2015
 International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com e-issn No.:2349-9745, Date: 2-4 July, 2015 Modeling Moisture Ratio of High Moisture Potato Slices in Forced Convection
International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com e-issn No.:2349-9745, Date: 2-4 July, 2015 Modeling Moisture Ratio of High Moisture Potato Slices in Forced Convection
Drying characteristics of Air Dried Sheet (ADS) Rubber
 Paper Code: ee11 characteristics of Air Dried Sheet (ADS) Rubber Y. Tirawanichakul 1*, W. Suchonpanit 2 and S. Tirawanichakul 3 1 Plasma and Energy Technology Research Laboratory, Department of Physics,
Paper Code: ee11 characteristics of Air Dried Sheet (ADS) Rubber Y. Tirawanichakul 1*, W. Suchonpanit 2 and S. Tirawanichakul 3 1 Plasma and Energy Technology Research Laboratory, Department of Physics,
Convective Drying of Apple: Mathematical Modeling and Determination of some Quality Parameters
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF AGRICULTURE & BIOLOGY ISSN Print: 1560 8530; ISSN Online: 1814 9596 09 15/ZSA/010/1 171 178 http://www.fspublishers.org Full Length Article Convective Drying of Apple: Mathematical
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF AGRICULTURE & BIOLOGY ISSN Print: 1560 8530; ISSN Online: 1814 9596 09 15/ZSA/010/1 171 178 http://www.fspublishers.org Full Length Article Convective Drying of Apple: Mathematical
Mathematical modeling and polysaccharide content of Ganoderma lucidum by hot air impingement drying
 An ASABE Meeting Presentation Paper Number: 131619320 Mathematical modeling and polysaccharide content of Ganoderma lucidum by hot air impingement drying Jun-Wen Bai, Hong-Wei Xiao, Zheng Lou, Zhen-Jiang
An ASABE Meeting Presentation Paper Number: 131619320 Mathematical modeling and polysaccharide content of Ganoderma lucidum by hot air impingement drying Jun-Wen Bai, Hong-Wei Xiao, Zheng Lou, Zhen-Jiang
Drying paddy by microwave vibro-fluidized bed drying using single mode applicator
 WFL Publisher Science and Technology Meri-Rastilantie 3 B, FI-00980 Helsinki, Finland e-mail: info@world-food.net Journal of Food, Agriculture & Environment Vol.9 (2): 50-54. 2011 www.world-food.net Drying
WFL Publisher Science and Technology Meri-Rastilantie 3 B, FI-00980 Helsinki, Finland e-mail: info@world-food.net Journal of Food, Agriculture & Environment Vol.9 (2): 50-54. 2011 www.world-food.net Drying
Scientific Principals and Analytical Model. Charcoal Cooler. Lisa Crofoot MECH 425, Queens University
 Scientific Principals and Analytical Model Charcoal Cooler Lisa Crofoot MECH 425, Queens University 1.0 Scientific Principles Evaporative cooling is based on the principle that water requires heat energy
Scientific Principals and Analytical Model Charcoal Cooler Lisa Crofoot MECH 425, Queens University 1.0 Scientific Principles Evaporative cooling is based on the principle that water requires heat energy
Drying characteristics and mathematical model of ultrasound assisted hot-air
 124 August, 2015 Int J Agric & Biol Eng Open Access at http://www.ijabe.org Vol. 8 No.4 Drying characteristics and mathematical model of ultrasound assisted hot-air drying of carrots Luo Denglin *, Liu
124 August, 2015 Int J Agric & Biol Eng Open Access at http://www.ijabe.org Vol. 8 No.4 Drying characteristics and mathematical model of ultrasound assisted hot-air drying of carrots Luo Denglin *, Liu
Fluidised-Bed Paddy Drying
 RESEARCH ARTICLE ScienceAsia 25 (1999) : 51-56 Fluidised-Bed Paddy Drying Somchart Soponronnarit School of Energy and Materials, King Mongkut's University of Technology Thonburi, Suksawat 48 Road, Bangkok
RESEARCH ARTICLE ScienceAsia 25 (1999) : 51-56 Fluidised-Bed Paddy Drying Somchart Soponronnarit School of Energy and Materials, King Mongkut's University of Technology Thonburi, Suksawat 48 Road, Bangkok
Performance Comparison of Ejector Expansion Refrigeration Cycle with Throttled Expansion Cycle Using R-170 as Refrigerant
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 7, July 2014 1 Performance Comparison of Ejector Expansion Refrigeration Cycle with Throttled Expansion Cycle Using R-170
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 7, July 2014 1 Performance Comparison of Ejector Expansion Refrigeration Cycle with Throttled Expansion Cycle Using R-170
Solar Drying Techniques And Performance Analysis: A Review
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X PP. 35-39 www.iosrjournals.org Solar Drying Techniques And Performance Analysis: A Review A.C. Jambhulkar,
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X PP. 35-39 www.iosrjournals.org Solar Drying Techniques And Performance Analysis: A Review A.C. Jambhulkar,
Performance and Evaluation of Pop Can Solar Dryer for Batch Products
 American Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy Vol. 4, No. 1, 2018, pp. 1-7 http://www.aiscience.org/journal/ajrse ISSN: 2381-7437 (Print); ISSN: 2381-7445 (Online) Performance and Evaluation of
American Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy Vol. 4, No. 1, 2018, pp. 1-7 http://www.aiscience.org/journal/ajrse ISSN: 2381-7437 (Print); ISSN: 2381-7445 (Online) Performance and Evaluation of
DRYING OF LONGAN: ITS DRYING KINETICS AND PERFORMANCE OF LONGAN DRYERS. By Niroot Lamlert
 DRYING OF LONGAN: ITS DRYING KINETICS AND PERFORMANCE OF LONGAN DRYERS By Niroot Lamlert A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY Department of
DRYING OF LONGAN: ITS DRYING KINETICS AND PERFORMANCE OF LONGAN DRYERS By Niroot Lamlert A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY Department of
Comparison Simulation between Ventilation and Recirculation of Solar Desiccant Cooling System by TRNSYS in Hot and Humid Area
 Comparison Simulation between Ventilation and Recirculation of Solar Desiccant Cooling System by TRNSYS in Hot and Humid Area MMS DEZFOULI, SOHIF MAT, K.SOPIAN Solar Energy Research Institute (SERI, Universiti
Comparison Simulation between Ventilation and Recirculation of Solar Desiccant Cooling System by TRNSYS in Hot and Humid Area MMS DEZFOULI, SOHIF MAT, K.SOPIAN Solar Energy Research Institute (SERI, Universiti
Specific Energy Consumption of Heat Pump Drying System
 Mindanao Journal of Science and Technology Vol.14 (2016) 131-145 Specific Energy Consumption of Heat Pump Drying System Adonis A. Closas 1* and Eliseo P. Villanueva 2 1 College of Engineering and Architecture
Mindanao Journal of Science and Technology Vol.14 (2016) 131-145 Specific Energy Consumption of Heat Pump Drying System Adonis A. Closas 1* and Eliseo P. Villanueva 2 1 College of Engineering and Architecture
Heat Pump Assisted Drying - Freeze Drying Technology
 Heat Pump Assisted Drying - Freeze Drying Technology Trygve M. Eikevik Professor Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) Department of Energy and Process Engineering E-mail: trygve.m.eikevik@ntnu.no
Heat Pump Assisted Drying - Freeze Drying Technology Trygve M. Eikevik Professor Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) Department of Energy and Process Engineering E-mail: trygve.m.eikevik@ntnu.no
Study of the Drying Kinetics of Lemon Grass
 American Journal of Applied Sciences 6 (6): 1070-1075, 2009 ISS 1546-9239 2009 Science Publications Study of the Drying Kinetics of Lemon Grass Mustafa Ibrahim, K. Sopian and W.R.W. Daud Solar Energy Research
American Journal of Applied Sciences 6 (6): 1070-1075, 2009 ISS 1546-9239 2009 Science Publications Study of the Drying Kinetics of Lemon Grass Mustafa Ibrahim, K. Sopian and W.R.W. Daud Solar Energy Research
Thin-Layer Drying Models for Dehumidified Hot Air Drying of Germinated Brown Rice
 Thin-Layer Drying Models for Dehumidified Hot Air Drying of Germinated Brown Rice Palida Suvanvisan 1, Ekkapong Cheevitsopon 2, Jiraporn Sripinyowanich Jongyingcharoen 1 * 1 Curriculum of Agricultural
Thin-Layer Drying Models for Dehumidified Hot Air Drying of Germinated Brown Rice Palida Suvanvisan 1, Ekkapong Cheevitsopon 2, Jiraporn Sripinyowanich Jongyingcharoen 1 * 1 Curriculum of Agricultural
Analysis of Energy Consumption for Biomass Drying Process
 Environment. Technology. Resources, Rezekne, Latvia Proceedings of the 10 th International Scientific and Practical Conference. Volume II, 317-322 Analysis of Energy Consumption for Biomass Drying Process
Environment. Technology. Resources, Rezekne, Latvia Proceedings of the 10 th International Scientific and Practical Conference. Volume II, 317-322 Analysis of Energy Consumption for Biomass Drying Process
PERFORMANCE OF FORCED CONVECTION EVACUATED TUBE SOLAR GRAIN DRYER. BOOKER ONYANGO OSODO B. Ed.(TECH); M. Phil (Tech. Ed) (J98/25749/2011)
 PERFORMANCE OF FORCED CONVECTION EVACUATED TUBE SOLAR GRAIN DRYER BOOKER ONYANGO OSODO B. Ed.(TECH); M. Phil (Tech. Ed) (J98/25749/2011) A research Proposal Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
PERFORMANCE OF FORCED CONVECTION EVACUATED TUBE SOLAR GRAIN DRYER BOOKER ONYANGO OSODO B. Ed.(TECH); M. Phil (Tech. Ed) (J98/25749/2011) A research Proposal Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF A DRYER FOR PROCESSED LOCUST BEAN CONDIMENTS
 Agrosearch (2014) Volume 14(2):103-112 http://dx.doi.org/10.4314/agrosh.v14i2.2 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF A DRYER FOR PROCESSED LOCUST BEAN CONDIMENTS Adamade, C. A. 2 and Olaoye, J. O. 1 Department of
Agrosearch (2014) Volume 14(2):103-112 http://dx.doi.org/10.4314/agrosh.v14i2.2 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF A DRYER FOR PROCESSED LOCUST BEAN CONDIMENTS Adamade, C. A. 2 and Olaoye, J. O. 1 Department of
HUMIDITY RELATIONSHIP DETERMINATED IN THE DRYING CEREAL SEED FLUIDIZED BED
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. 2 (51) - 2009 Series I: Engineering Sciences HUMIDITY RELATIONSHIP DETERMINATED IN THE DRYING CEREAL SEED FLUIDIZED BED C.D. CERNĂIANU 1 A.E.STĂNCUŢ
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. 2 (51) - 2009 Series I: Engineering Sciences HUMIDITY RELATIONSHIP DETERMINATED IN THE DRYING CEREAL SEED FLUIDIZED BED C.D. CERNĂIANU 1 A.E.STĂNCUŢ
STACK EFFECT IN LIGHT WELL OF HIGH RISE APARTMENT BUILDING
 STACK EFFECT IN LIGHT WELL OF HIGH RISE APARTMENT BUILDING H. Kotani, R. Satoh, T. Yamanaka Dept. of Architectural Engineering, School of Engineering, Osaka University, Osaka, Japan ABSTRACT The purpose
STACK EFFECT IN LIGHT WELL OF HIGH RISE APARTMENT BUILDING H. Kotani, R. Satoh, T. Yamanaka Dept. of Architectural Engineering, School of Engineering, Osaka University, Osaka, Japan ABSTRACT The purpose
Mathematical Modeling on Hot Air Drying of Thin Layer Fresh Tilapia Fillets
 Original paper Section: Food Technology Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci., 2013, Vol. 63, No. 1, pp. 25-34 DOI: 10.2478/v10222 012 0065 5 http://journal.pan.olsztyn.pl Mathematical Modeling on Hot Air Drying of
Original paper Section: Food Technology Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci., 2013, Vol. 63, No. 1, pp. 25-34 DOI: 10.2478/v10222 012 0065 5 http://journal.pan.olsztyn.pl Mathematical Modeling on Hot Air Drying of
Mathematical Modelling of Thin Layer Drying Kinetics of Amla-Beet Root Shreds
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.221
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.221
Drying rate 1. Section B to C of the curve, known as the constant rate periods, represents removal of unbound water from the product.
 Drying rate 1 Drying process of a material can be described as a series of steps in which drying rate plays a key role. Following figure shows typical drying rate curve for a constant drying conditions.
Drying rate 1 Drying process of a material can be described as a series of steps in which drying rate plays a key role. Following figure shows typical drying rate curve for a constant drying conditions.
Nahid Aghilinategh, Shahin Rafiee, Abolfazl Gholikhani, Soleiman Hosseinpur, Mahmoud Omid, Seyed S. Mohtasebi & Neda Maleki
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A comparative study of dried apple using hot air, intermittent and continuous microwave: evaluation of kinetic parameters and physicochemical quality attributes Nahid Aghilinategh, Shahin
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A comparative study of dried apple using hot air, intermittent and continuous microwave: evaluation of kinetic parameters and physicochemical quality attributes Nahid Aghilinategh, Shahin
Heat and Mass Transfer in Fibrous Materials. Theory and Applications. A.K. Haghi S. Thomas L.A. Pothan ATLANTIC PUBLISHERS & DISTRIBUTORS (P) LTD
 Heat and Mass Transfer in Fibrous Materials Theory and Applications A.K. Haghi S. Thomas L.A. Pothan ATLANTIC PUBLISHERS & DISTRIBUTORS (P) LTD Preface v Nomenclature (Part 1) xii PART 1 THEORY 1. Basic
Heat and Mass Transfer in Fibrous Materials Theory and Applications A.K. Haghi S. Thomas L.A. Pothan ATLANTIC PUBLISHERS & DISTRIBUTORS (P) LTD Preface v Nomenclature (Part 1) xii PART 1 THEORY 1. Basic
CLOVER DRYING PROCESS BY FORCED CONVECTION
 CLOVER DRYING PROCESS BY FORCED CONVECTION Pavel Kic Czech University of Life Sciences Prague kic@tf.czu.cz Abstract. The aim of this paper is to inform about the experimental and theoretical investigations
CLOVER DRYING PROCESS BY FORCED CONVECTION Pavel Kic Czech University of Life Sciences Prague kic@tf.czu.cz Abstract. The aim of this paper is to inform about the experimental and theoretical investigations
Effective moisture diffusivity during hot air solar drying of tomato slices
 Res. Agr. Eng. Vol. 62, 26 (): 5 23 Effective moisture diffusivity during hot air solar drying of tomato slices H. Samimi. Akhijani, A. Arabhosseini, M.H. Kianmehr Department of Agrotechnology, University
Res. Agr. Eng. Vol. 62, 26 (): 5 23 Effective moisture diffusivity during hot air solar drying of tomato slices H. Samimi. Akhijani, A. Arabhosseini, M.H. Kianmehr Department of Agrotechnology, University
Analysis of Constant Pressure and Constant Area Mixing Ejector Expansion Refrigeration System using R-1270 as Refrigerant
 Analysis of Constant Pressure and Constant Area Mixing Ejector Expansion Refrigeration System using R-1270 as Refrigerant Ravi Verma 1, Sharad Chaudhary 2 1, 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, IET
Analysis of Constant Pressure and Constant Area Mixing Ejector Expansion Refrigeration System using R-1270 as Refrigerant Ravi Verma 1, Sharad Chaudhary 2 1, 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, IET
Subscripts 1-4 States of the given system Comp Compressor Cond Condenser E Evaporator vol Volumetric G Gas L Liquid
 Simulation Analysis of Compression Refrigeration Cycle with Different Refrigerants P.Thangavel, Dr.P.Somasundaram, T.Sivakumar, C.Selva Kumar, G.Vetriselvan Abstract --- In this analysis, the performance
Simulation Analysis of Compression Refrigeration Cycle with Different Refrigerants P.Thangavel, Dr.P.Somasundaram, T.Sivakumar, C.Selva Kumar, G.Vetriselvan Abstract --- In this analysis, the performance
Simulation Of Pneumatic Drying: Influence Of Particle Diameter And Solid Loading Ratio
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol.4, No.4, pp 1633-1641, Oct-Dec 2012 Simulation Of Pneumatic Drying: Influence Of Particle Diameter And Solid Loading
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol.4, No.4, pp 1633-1641, Oct-Dec 2012 Simulation Of Pneumatic Drying: Influence Of Particle Diameter And Solid Loading
Volume 10 No. 3 March THIN LAYER DRYING KINETICS OF AMARANTH (Amaranthus cruentus) GRAINS IN A NATURAL CONVECTION SOLAR TENT DRYER.
 THIN LAYER DRYING KINETICS OF AMARANTH (Amaranthus cruentus) GRAINS IN A NATURAL CONVECTION SOLAR TENT DRYER Ronoh EK 1*, Kanali CL 1, Mailutha JT 1 and D Shitanda 1 Erick Ronoh * Corresponding author,
THIN LAYER DRYING KINETICS OF AMARANTH (Amaranthus cruentus) GRAINS IN A NATURAL CONVECTION SOLAR TENT DRYER Ronoh EK 1*, Kanali CL 1, Mailutha JT 1 and D Shitanda 1 Erick Ronoh * Corresponding author,
Novel process for the drying of sugar cubes applying microwave technology
 AVH Association 8 th Symposium Reims, March 2 Novel process for the drying of sugar cubes applying microwave technology H.M. TORRINGA, H.P.M NEIJNENS 2. Agrotechnological Research Institute, P.O. Box 7,
AVH Association 8 th Symposium Reims, March 2 Novel process for the drying of sugar cubes applying microwave technology H.M. TORRINGA, H.P.M NEIJNENS 2. Agrotechnological Research Institute, P.O. Box 7,
Donald G. Mercer, Ph.D., P.Eng. Department of Food Science University of Guelph. Donald G. Mercer 2012
 Donald G. Mercer, Ph.D., P.Eng. Department of Food Science University of Guelph Donald G. Mercer 2012 1 Objectives Introductory Observations Why do we dry food products? How do we dry food products? Factors
Donald G. Mercer, Ph.D., P.Eng. Department of Food Science University of Guelph Donald G. Mercer 2012 1 Objectives Introductory Observations Why do we dry food products? How do we dry food products? Factors
PROCESSING OF VEGETABLES IN A SOLAR DRYER IN ARID AREAS
 PROCESSING OF VEGETABLES IN A SOLAR DRYER IN ARID AREAS N. M. Nahar Central Arid Zone Research Institute, Jodhpur 342003, India Email:nmnahar@gmail.com Fax: 91-291-2788706 Abstract When the production
PROCESSING OF VEGETABLES IN A SOLAR DRYER IN ARID AREAS N. M. Nahar Central Arid Zone Research Institute, Jodhpur 342003, India Email:nmnahar@gmail.com Fax: 91-291-2788706 Abstract When the production
Effect of domestic storage and cooking conditions on the risk distribution in ready to cook meat products
 Effect of domestic storage and cooking conditions on the risk distribution in ready to cook meat products Bakalis S.*, Giannakourou M.C. and Taoukis P. School of Chemical Engineering, National Technical
Effect of domestic storage and cooking conditions on the risk distribution in ready to cook meat products Bakalis S.*, Giannakourou M.C. and Taoukis P. School of Chemical Engineering, National Technical
Drying of Fruits, Vegetables, Spices and Medicinal Plants with a Mixed-Mode Solar Drying System with Internal Reflectors
 Drying of Fruits, Vegetables, Spices and Medicinal Plants with a Mixed-Mode Solar Drying System with Internal Reflectors Jatinkumar Patel, Pandit Deendayal Petroleum University, India Anurag Mudgal, Pandit
Drying of Fruits, Vegetables, Spices and Medicinal Plants with a Mixed-Mode Solar Drying System with Internal Reflectors Jatinkumar Patel, Pandit Deendayal Petroleum University, India Anurag Mudgal, Pandit
Effect of Relative Humidity on Oven Temperature of Locally Design Solar Carbinet Dryer
 Global Journal of Science Frontier Research Physics and Space Science Volume 13 Issue 1 Version 1.0 Year Type : Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc.
Global Journal of Science Frontier Research Physics and Space Science Volume 13 Issue 1 Version 1.0 Year Type : Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc.
