Effective moisture diffusivity during hot air solar drying of tomato slices
|
|
|
- Martina Small
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Res. Agr. Eng. Vol. 62, 26 (): 5 23 Effective moisture diffusivity during hot air solar drying of tomato slices H. Samimi. Akhijani, A. Arabhosseini, M.H. Kianmehr Department of Agrotechnology, University of Tehran, College of Abouraihan, Tehran, Iran Abstract Samimi. Akhijani H., Arabhosseini A., Kianmehr M.H. (26): Effective moisture diffusivity during hot air solar drying of tomato slices. Res. Agr. Eng., 62: Mathematical modelling and effective moisture diffusivity of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) was studied during hot air solar drying. An experimental solar dryer with a swivel collector was used for experiments. The collector followed the solar radiation using a precious sensor. Drying experiments were performed in a thin layer hot air drying at slice thicknesses of 3, 5 and 7 mm and air velocities of.5, and 2 m/s. The experimental data were fitted to different mathematical moisture ratio models and the Page model was selected as the best model according to correlation coefficient R 2, chi-square χ 2 and root mean square error (RMSE) parameters. The maximum values of moisture diffusivity was m 2 /s at air velocity of 2 m/s and slice thickness of 7 mm while the minimum value of the moisture diffusivity was.58 9 m 2 /s at air velocity of.5 m/s and slice thickness of 3 mm. Keywords: falling rate period; Fick s second law; mathematical models; solar dryer; swivel collector Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) is one of the vegetables, which is a good source of macro minerals such as Na, K, Ca, Mg, P, S and micro minerals as Mn, Fe, Cu, Zn and Se (Oyeta et al. 22). Tomato is generally produced in moderate-warm climate zones (Davies, Hobson 98). Iran is the seventh highest tomato-producing country in the world. In 22, the total cultivation in Iran was about 6, ha and the total production was about 6 million tons (FA- OSTAT 24), which is mostly produced in the East Azerbaijan province, especially in Azarshahr city. Tomato is one of the main sources for fresh using and processing industries and its production creates job opportunities and supplies some parts of the market in dry form. The dry form refers to the removal of relatively small amount of moisture from a solid or nearly solid material by evaporation (Aghbashloo et al. 28). Solar drying could be a possible solution for the dehydration of food and agricultural products (Taheri et al. 2). Solar drying is a process where moisture content, drying air temperature and product temperature change simultaneously along with the two basic inputs to the system i.e. the solar radiation and the ambient temperature. The drying rate is affected by ambient climatic conditions which include temperature, relative humidity, sunshine hours, available solar radiation, wind velocity, frequency and duration of rain showers during the drying period (Chandra Shahi et al. 2). The most important feature of solar dryers is that the product does not include any kind of preservatives or other added chemical stuffs, which allows its use for people suffering from various allergic reactions from these (Akpinar et al. 23). Azarshahr city is situated in the Azerbaijan province at 45.8 E longitude and 37.4 N latitude having altitude of,45 m above mean sea level. The sunshine period of East Azerbaijan is about 2,852 h/year with a max. of 45 h/month in July and a min. of 5
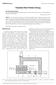
2 Vol. 62, 26 (): 5 23 Res. Agr. Eng. 23 h/month in January. Max. solar radiation is about 4.9 kwh/m 2 per day. Because of the proper solar radiations in this area, solar energy is the main source for drying of fruits and vegetables. Properly designed solar drying systems must be taken into account for drying requirements of specific crops, energy efficiency requirements, and cost-effectiveness (Steinfeld, Segal 986). Simulation models are needed in the design and operation of solar dryers. Several researchers have already developed simulation models for solar drying systems such as design theory for simple solar rice dryer (Exell 98), solar drying of rough rice (Zaman, Bala 989), testing of a new solar dryer and mathematical modelling of thin layer drying of sultana grapes (Yaldiz et al. 2). Moreover thermodynamic analysis, particularly moisture diffusivity and exergy analysis, has appeared to be essential tools for the design, analysis and optimisation of thermal system (Dincer, Sahin 24). Exergy is defined as the maxi. amount of work which can be produced by a stream of matter, heat or work as it comes to equilibrium with a reference environment (Dincer 22). Exergy analysis, as is known, evaluates the available energy at different points in a system. In the design of a system, the exergy method provides the useful information to choose the appropriate component design and operation procedure. Exergy is the measure of the potential of a stream to cause change, as a consequence of not being completely stable relative to the reference environment (Sami et al. 2). To calculate the energy and exergy of the drying process, finding the moisture diffusivity of drying of crops is essential. Several studies have been reported about exergetic and moisture diffusivity analysis on the thin layer vegetable and fruit solar dryers, such as barberries (Aghbashloo et al. 28), seedless grapes (Doymaz, Pala 22), pumpkin slices (Doymaz 26), apple pomace (Wang et al. 22), candle nuts (Tarigan et al. 26), red pepper (Akpinar et al. 23), green olive (Colak, Hepbasli 27), coroba slices (Corzo et al. 28) and mulberry (Akbulut, Durmus 2). The objectives of this study are mathematical modelling of drying kinetics and the effective moisture diffusivity for thin-layer drying of tomato slices in a solar indirect cabinet dryer with swivel absorber plate and to evaluate the influence of air condition on moisture diffusivity for thin-layer drying of tomato slices. MATERIAL AND METHODS Sample preparation. Fresh harvested tomatoes were purchased from a local farm at Azarshahr city, East Azerbaijan province. The tomatoes were packed and stored in the refrigerator at +5 C to prevent undesired changes. Before each experiment, certain amount of tomatoes was cut in slices with thicknesses of 3, 5 and 7 mm. The average diameter of the samples was about 7 ± 2 mm. About g of tomato slices with three replicates were dried in a hot oven at 5 ± 2 C for six hours until the mass did not change between two weighing intervals (AOAC 984). The samples were weighed by using a digital balance with an accuracy of.5 g and a capacity of,5 g. The initial moisture content was about 93.6% (w.b.). For each drying experiment, about 8 g of samples were placed in the sample trays and put in the cabinet of the dryer. Drying conditions. A laboratory scale solar dryer of the static-tray type, was developed at the Agriculture Machinery Laboratory of the Azarshahr Research Centre and was used for experiments (Fig. ). Basically, the main divisions of the developed dryer are top collector and bottom drying chamber. The separated sections of energy collec- Fig.. The laboratory scale of the solar swivel dryer collector; 2 isolated drying cabinet; 3 DC motor; 4 solar panel; 5 location of fan; 6 location of swivel; 7 location of sensor 6
3 Res. Agr. Eng. Vol. 62, 26 (): 5 23 Table. Thin layer drying models for describing drying of tomato slices No. Model Mathematical equation Reference MR = exp( kt) Lewis Lewis (92) 2 MR = exp( kt n ) Page Page (949) 3 MR = a exp( kt) Henderson and Pabis Henderson and Pabis (96) 4 MR = a exp( kt) + c Logarithmic Togrul and Pehlivan (24) 5 MR = a exp( k t) + b exp( k 2 t) Two term Verma et al. (985) 6 MR = a exp( kt) + ( a) exp( kat) Approximation of diffusion Sharaf-Elden et al. (98) 7 MR = + at + bt 2 Wang and Singh Yaldiz et al. (2) MR moisture ratio; a, b, c, k, n constants of the equation; t drying time tion and drying area help to avoid direct exposure of the product to the sun, thereby retaining the original colour for the dried products even at the end of the drying process. The absorber plate is made of steel sheet with dimensions of,8 9 mm and thickness of 2 mm. The plate was painted black to increase the solar absorption capacity. All the walls were isolated using glass wool and covered by aluminium foil to suppress heat losses. The glazing was a single layer of 4 mm thick transparent glass sheet with a surface area of,8 mm by 98 mm. The distance between absorber plate and glazing was 8 mm. By assembling a controlling system, a direct current (DC) motor (235; Daiichi-Kasei, Ymashina-ku, Japan), a precious photocell and a proper mechanism, the absorber would rotate by changing the solar radiation angle, therefore more energy will be absorbed by the solar panel. By a fan the air passes through the panel and moves to the cabinet via the orifice which is connected to the inlet of the cabinet dryer. The dryer cabinet was made of mm thick wooden plates (MDF) mm 3. All sides of the cabinet were insulated by 4 mm glass wool which is covered with aluminium foil. The cabinet consists of five perforated polyethylene trays to load the material to be dried. The size of a single tray was mm. The trays were divided into two compartments each having two trays. A double layered door packed with rock wool insulation was provided in front of the dryer. The location of the axial fan was on the top of the cabinet, the opposite side from where the hot air entered. The dryer was installed in an environment with the relative air humidity of about 8 24% and the ambient air temperature of about C. An automatic temperature controller with an accuracy of ±. C was used to fix the drying air temperature. The air velocity was controlled by controlling the speed of the fan and the required air velocity was regulated by using an anemometer Yk-25AM model (Lutron, Taipei, Taiwan). The experiments were carried out at three levels of air velocity,.5, and 2 m/s. The solar radiation intensity was measured by using a solarimeter (SL, 2; Meratex, Košice, Slovakia) with an accuracy of ± W/m 2. During the experiments, the temperature of ambient air, drying chamber, absorber plate, dryer outlet, cover glass and inlet air were measured using T type thermocouples. The output data were recorded by a digital thermometer (DL- 96A; Lutron, Taipei, Taiwan) that was connected to a computer using RS232 cable and recorded the temperature at required point every 3 minutes. The ambient relative humidity was measured every hour by a digital hygrometer (HT.36; Lutron, Taipei, Taiwan), with an accuracy of.%. The samples in the dryer were weighed at 3 min intervals using an electronic digital weighing balance (±.5 g). Theoretical principles. The moisture ratio of tomato slices during the drying experiments was found using Eq. (): MR = M/M () where: MR moisture ratio M moisture content at any time (kg water/kg dry mater) M initial moisture content (kg water/kg dry mater) The experimental data were fitted to seven different moisture ratio equations in order to select the most appropriate model for describing drying of tomato slices (Table ). The correlation coefficient (R 2 ) was one of the primary criteria to select the best equation to account for variation in the solar drying curves of the 7
4 Vol. 62, 26 (): 5 23 = ((MMMM ) (MMMM ) PP zz Res. Agr. Eng. dried samples. In addition, reduced chi-square (χ 2 ) and root mean square error (RMSE) were other criteria to select the best mathematical model. Chisquare and RMSE were calculated using the following equations: χ = χ = RMSE = RMSE = PP PP ((MMMM "# ) (MMMM "# ) ) ((MMMM PP "# ) (MMMM zz "# ) ) PP zz ((MMMM "# ) (MMMM "# ) ) ((MMMM "# ) (MMMM "# ) ) (2) (3) where: MM = 8 (2nn ) MM π exp = MM = 8 (2nn ) 4LL MM π (2nn ) exp (2nn ) π MR exp,i i th experimental moisture ratio 4LL MR pre,i i th predicted moisture ratio P number MMMM = 8 π exp π DDt MMMM = 8 of observations π exp π DDt z number of constants 4LL 4LL (Aghbashloo et al. 29; Yaldiz et al. 2) Ln MMMM = Ln 8 π π DDDD Ln MMMM = Ln 8 π π DDDD The relationship between 4LL the 4LL constants and the drying variables like slice thickness and drying air velocity was also determined kk = π DD for the best suitable model. The effects of 4LLtemperature and air velocity on equation constants were investigated by the simple linear, polynomial, logarithmic, exponential and power regression models (Guarte 996). The drying rate of tomato slices was calculated using Eq. (4) (Kavak Akpinar 22): DR = (M t + dt M t )/dt (4) where: M t+dt moisture content at the time t + dt (kg water/kg dry mater) M t moisture content at the time t (kg water/kg dry mater) t drying χ = time ((MMMM (min) "# ) (MMMM "# ) ) PP zz Crank using the Fick s second law proposed Eq. (5) for the effective moisture diffusivity for an RMSE = ((MMMM infinite slab (Crank PP 975): "# ) (MMMM "# ) ) MMMM = MM = 8 MM π (2nn ) exp (2nn ) π DDDD 4LL MMMM = 8 π exp π DDt where: 4LL n number of terms taken into consideration t time of drying (s) Ln MMMM = Ln 8 π π DDDD D effective moisture diffusivity (m 2 /s) 4LL L half thickness of the slice (m) 8 kk = π DD 4LL (5) = ((MMMM PP "# ) (MMMM In this study the thickness of the tomato slices SE = ((MMMM ) (MMMM was 7 ± PP. mm. For longer times, the terms other 8 (2nn than the first approach exp are equal to zero. Neglecting higher terms of the Eq. (5), we have: (2nn ) = 8 (2nn π MMMM = 8 exp (2nn π exp ) π DDt (6) 4LL The MMMM Eq. = (6) 8 n MMMM = Ln 8 can be simplified π π DDDD to a straight-line π equation as Eq. exp π DDt 4LL (7): 4LL Ln MMMM = Ln kk = π DD 8 π π DDDD 4LL (7) 4LL The diffusion coefficient kk = π DD is obtained by plotting experimental drying 4LL data in terms of Ln(MR) versus time (s) (Mirzaee et al. 29; Rasouli et al. 2). The slope (k ) was calculated by plotting Ln(MR) versus time according to Eq. (8): k = π 2 D/4L 2 (8) RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Variation of solar radiation during the day is shown in Fig. 2 for the days when experiments are done. The solar radiation increased by time and reached the max. level at around 3 pm. The solar radiation was fluctuating during the days and varied from 5 95 W/m 2. The Fig. 2 also shows the Day 2 Day 5 Day 9 Day Day Day 43 Day Day 76 Ambient Day 8 temp Day Day 23 Day Day 546 Day Day 897,2 Temp below the samples Day Day 3 4 Ambient Day 6 temp 7 Day Temp 9 b Day,2 5 Day 8 Ambie 8 Solar radiation(w/m 2 ), Time (h) Fig. 2. Variation of solar radiation in 9 days, mean ambient temperature and temperature below the samples during the day Temprature ( C)
5 Res. Agr. Eng. Vol. 62, 26 (): 5 23 (a) Moisture ratio Moisture ratio (b) Moisture ratio m/s m/s.5 m/s Pre 2m/s Pre m/s Pre.5m/s.2.2 (c) Time (min) a Time (min). Moisture ratio Time (min) Fig. 3. Drying of tomato slices (3, 5, 7 mm) and fitted curves of the Page model at air velocity of (a) 2 m/s, (b) m/s and (c).5 m/s variation of ambient temperature and temperature below the samples in the cabinet. Average temperatures were considered for charting (Fig. 2). The max. air temperature at the dryer inlet was 69. C at ambient air temperature of 36 C and solar radiance level of 952 W/m 2. The temperature of the collector consequently increased the temperature in the cabinet because of rotation of the collector and more energy absorbed (Fig. 2). The moisture ratio versus drying time for different levels of tomato slice thickness is shown in Fig. 3 for air velocities of 2, and.5 m/s respectively. The total drying time at.5 m/s was almost.2.26 times longer than 2 m/s for the samples with the same slice thickness. The drying time at constant air velocity increased about.3 2. times when the slice thickness changed from 3 to 7 mm and the effect of slice thickness on drying time was significant. The Page Table 2. Constants for the Page model and values of correlation coefficient (R 2 ), RMSE and χ 2 Slices thickness Air velocity (m/s) k 5 n R 2 RMSE χ mm mm mm RMSE root mean square error; k, n constants of the Page model; χ 2 chi-square 9
6 Vol. 62, 26 (): 5 23 Res. Agr. Eng. (a) Ln(MR) Time(s), a (c) Time(s), (b) Ln(MR) Time(s), m/s 2 m/s 3.5m/s b Ln(MR) Fig. 4. Ln(MR) versus time for thin-layer solar drying of tomato slices with thickness of (a) 3 mm, (b) 5 mm and (c) 7 mm model was the best mathematical model for describing the drying kinetics of tomato slices. The drying c process took place in the falling rate period. Drying rate decreased continuously with moisture content or drying time. These results are in agreement with the observations of earlier researchers (Diamante, Munro 993; Yaldiz et al. 2, Aghbashloo et al. 29). During the drying process, internal mass transfer occurs with liquid diffusion, vapour diffusion and capillary forces in the interior region of the product and water evaporates as it reaches the surface (Aghbashloo et al. 29). Moisture removal has capillarity movement when the water content of tomato slices is high. Then, water removal occurs through capillary forces to the surface of the fruit. Free moisture evaporates from the fruit surface as the drying process progresses and so shrinkage occurs. Pores and free spaces lose and thus the rates (a) Moisture diffusivity 9 (m 2 /s) mm 4 5mm 3 7mm Air velocity (m/s) a m/s 2 m/s.5m/s Slice thickness (mm) Fig 5. Moisture diffusivity (D) of tomato slices at (a) different air velocity for different levels of slice thickness and (b) different thicknesses at three levels of air velocity 2 (b) Moisture diffusivity 9 (m 2 /s) b
7 Res. Agr. Eng. Vol. 62, 26 (): 5 23 Table 3. Fitted equations for moisture diffusivity (D) for each slice thickness Slice thickness (mm) (l = 2 L) Equation 9 R 2 3 D = 4.85e.8ν D = 2.62e.36ν D =.38e.279ν.9994 l slice thickness (m); L half slice thickness; R 2 correlation coefficient; e neperian number; ν air velocity (m/s) of water removal and heat transfer decrease significantly. Multiple regression analysis was performed in the MATLAB computer programme (Version 23) environment. The best model describing the thin-layer drying kinetics was selected based on the highest R 2 average values and the lowest χ 2 and RMSE average values. The Page model showed the best fit to the experimental data and the best agreement for thin-layer drying curves. Table 2 shows the fitting results of statistical parameters (R, χ 2 and RMSE) and constant values k and n for the Page model using the experimental data values. The constant values of Page model for different conditions were regressed against air condition using multiple regressions. Regression analysis for these parameters yielded the following relationships at the significance level of %: k = ( 3.9ν ν.7(2L) ν L L 7.36) 5 ; R 2 =.9254 (9) n =.7ν 2.9ν +.2νL.34L + 4.3; R 2 =.9543 () where: k,n constant of Page model ν velocity of drying (m/s) L half thickness of the slice (m) The Ln(MR) versus time (s) for different level of air velocity is shown in Fig. 4 for slice thicknesses of 3, 5 and 7 mm, respectively. All the figures show that the drying of tomato occurred in falling rate period, in other words the liquid diffusion is by the dry wing force controlling the drying process, and therefore the curves are straight lines. Plotted curves show that the increase in velocity increases the slop of straight line, in other words the effective Table 4. Fitted equations for moisture diffusivity (D) for each air velocity Air velocity (m/s) Equation 9 R 2.5 D =.4(2L) D =.97(2L) D =.93(2L) for abbreviations see Table 3 moisture diffusivity increases, whereas the effect of thickness on the slope is adverse. The effective moisture diffusivity was calculated using Eq. (8). The results are plotted in Fig. 5. The Fig. 5a shows that the moisture diffusivity of tomato slices increased by increasing air velocity for each slice thickness. Similar results are reported by the other researchers (Aghbashloo et al. 28; Mirzaee et al. 29; Rasouli et al. 2). The linear equations were fitted to estimate the values of moisture diffusivity. The fitted equations and related correlation coefficients (R 2 ) are reported in Table 3. Fig. 5b shows that the max. value of the moisture diffusivity was m 2 /s at 2 m/s air velocity and 7 mm slice thickness while the min. value of the moisture diffusivity was.58 9 m 2 /s at.5 m/s air velocity and 3 mm slice thickness. Generally, the value of moisture diffusion (D) changes in the range of 9 m 2 /s for food materials (Babalis, Belessiotis 24; Aghbashlo et al. 28; Rasouli D (m 2 /s) Air velocity (m/s) Slice thickness (mm) Fig 6. Effect of slice thickness and air velocity on moisture diffusivity (D) of tomato slices
8 Vol. 62, 26 (): 5 23 Res. Agr. Eng. et al. 2). Table 4 contains linear equation and related correlation coefficient (R 2 ), for different air velocity. In all levels of air velocity, the value of D increased linearly by increasing the slice thickness. In Fig. 6 the value of the moisture diffusivity is plotted versus slice thickness of tomato and air velocity by using multiple regression analyses. The fitted parabolic equation and corresponding R 2 are also reported (Eq. ). k,n ν L D = ( L 3.97ν.72L ν 2 ) 9 ; R 2 =.9826 () constants of Page model velocity of drying (m/s) half thickness of the slice (m) CONCLUSION The Page model showed the best fit to the experimental data with the highest average values of R 2 and the lowest average values of χ 2 and RMSE. The effective moisture diffusivity for tomato slices varied from.58 9 to m 2 /s. The effective moisture diffusivity increased with increasing air velocity and sample thickness. More moisture absorbed at higher air velocity (2 m/s), consequently the moisture gradient of the sample with ambient temperature increases and causes an increase in moisture diffusivity. In thicker slices (7 mm), the hot air hardly passes through the samples and decreases the moisture gradient and moisture diffusivity. The best method to reduce the drying time is to decrease the vapour pressure around the sample in the dryer and take the expelled moisture away from the product surface; this is accomplished with selection of proper thickness and hot-air velocity around the surface of tomato slices. References Aghbashloo M., Kianmehr M.H., Samimi-Akhijahani H. (28): Influence of drying conditions on the effective moisture diffusivity, energy of activation and energy consumption during the thin-layer drying of beriberi fruit (Berberidaceae). Energy Conversion Management, 49: Aghbashloo M., Kianmehr M.H., Samimi-Akhijahani H. (29): Evaluation of thin-layer drying models for describing kinetics of barberries (Barberries vulgaris). Journal of Food Process Engineering, 32: Akbulut A., Durmus A. (2): Energy and exergy analyses of thin layer drying of mulberry in a forced solar dryer. Energy, 35: AOAC (984): Official Methods of Analysis. Washington, DC, Association of Official Analytical Chemists Press. Akpinar E., Midilli A., Bicer Y. (23): Single layer drying behavior of potato slices in a convective cyclone and mathematical modeling. Energy Conversion Management, 44: Babalis J., Belessiotis V.G. (24): Influence of the drying conditions on the drying contents and moisture diffusivity during the thin layer drying of figs. Journal of Food Engineering, 65: Chandra Shahi N., Khan J., Lohani U., Singh A., Kumar A. (2): Development of polyhouse type solar dryer for Kashmir valley. Journal of Food Engineering, 48: Colak N., Hepbasli A. (27): Performance analysis of drying of green olive in a tray dryer. Journal of Food Engineering, 8: Corzo O., Bracho N., Vasquez A., Pereira A. (28): Energy and exergy analyses of thin layer drying of coroba slices. Journal of Food Engineering, 86: 5 6. Crank J. (975): Mathematics of Diffusions. London, Oxford University Press. Davies J.N., Hobson G.E. (98): The constituents of tomato fruit the influence of environment, nutrition and genotype. CRC Critical Review in Food Science and Nutrition, 5: Diamante L.M., Munro P.A. (993): Mathematical modelling of the thin layer solar drying of sweet potato slices. Solar Energy, 5: Dincer I., Sahin A.Z. (24): A new model for thermodynamics analysis of a drying process. Intermational Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 47: Dincer I. (22): On energetic, energetic and environmental aspects of drying systems. International Journal of Energy Research, 26: Doymaz I., Pala M. (22): The effects of dipping pretreatment on air-drying rates of seedless grapes. Journal of Food Engineering, 52: Doymaz I. (26): The kinetics of forced convective air-drying of pumpkin slices. Journal of Food Engineering, 79: Exell R.H.B. (98): Basic design theory for simple solar rice dryer. Renewable Energy Review, :. FAOSTAT (22): Available at Guarte R.C. (996): Modeling the drying behaviour of copra and development of a natural convection dryer for production of high quality copra in the Philippines.[PhD. Thesis 287], Hohenheim University, Stuttgart, Germany. Henderson S.M., Pabis S. (96): Grain drying theory:. Temperature affection drying coefficient. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 6:
9 Res. Agr. Eng. Vol. 62, 26 (): 5 23 Kavak Akpinar E. (22): The Development of a Cyclone Type Dryer for Agricultural Products. [PhD. Thesis.] Firat University, Elazig. Mirzaee E., Rafiee S., Keyhani A., Emam-Djomeh Z. (29): Determining of moisture diffusivity and activation energy in drying of apricots. Research of Agricultural Engineering, 55: 4 2. Lewis W.K. (92): The rate of drying of solid materials. Industrial Engineering Chemistry, 3: Oyeta Y., Folake L., Muyiwa F. (22): Phytochemical and nutrient/antinutrient interactions in cherry tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) fruits. International Journal of Advanced Biological Research, 2: Page G.E. (949): Factors influencing the maximum rates of air drying shelled corn in thin layers. [MSc. Thesis.] Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN. Rasouli M., Seiiedlou S., Ghasemzadeh H.R., Nalbandi H. (2): Influence of drying conditions on the effective moisture diffusivity and energy of activation during the hot air drying of garlic. Australian Journal of Agricultural Engineering, 2: 96. Sami S., Etesami N., Rahimi A. (2): Energy and exergy analysis of an indirect solar cabinet dryer based on mathematical modeling results. Energy, 36: Sharaf-Elden Y.I., Blaisdell J.L., Hamdy M.Y. (98): A model for ear corn drying. Transactions of ASAE, 5: Steinfeld A., Segal I. (986): A simulation model for solar thin layer drying process. Drying Technology, 4: Taheri-Garavand A., Rafiee S., Keyhani A. (2): Effective moisture diffusivity and activation energy of tomato in thin layer dryer during hot air drying. International Transaction Journal of Engineering, Management and Applied Sciences and Technologies, 2: Tarigan E., Prateepchaikul G., Yamseangsung R., Sirichote A., Tekasakul P. (26): Drying characteristics of unshelled kernels of candle nuts. Journal of Food Engineering, 79: Togrul I.T., Pehlivan D. (24): Modelling of thin-layer drying kinetics of some fruits under open-air sun drying process. Journal of Food Engineering, 65: Verma L.R., Bucklin R.A., Endan J.B., Wratten F.T. (985): Effects of drying air parameters on rice drying models. Transaction of ASAE, 28: Wang Z., Sun J., Liao X., Chen F., Zhao G., Wu J. (22): Mathematical modeling on hot air drying of thin layer apple pomace. Journal of Food Engineering, 4: Yaldiz O., Ertekin C., Uzun H.I. (2): Mathematical modeling of thin layer solar drying of sultana grapes. Energy, 26: Zaman M.A., Bala B.K. (989): Thin layer solar drying of rough rice. Solar Energy, 42: Received for publication December 4, 24 Accepted after correction April 3, 25 Corresponding author: Akbar Arabhosseini, University of Tehran, College of Abouraihan, Imam Reza blvd., Pakdasht, Iran; ahosseini@ut.ac.ir 23
Evaluation and Selection of Thin-layer Models for Drying Kinetics of Apricot (cv.nasiry)
 1 Evaluation and Selection of Thin-layer Models for Drying Kinetics of Apricot (cv.nasiry) E. Mirzaee 1, S. Rafiee 1, A. Keyhani 1 1 Agricultural Machinery Engineering Dept., Faculty of Agricultural Engineering
1 Evaluation and Selection of Thin-layer Models for Drying Kinetics of Apricot (cv.nasiry) E. Mirzaee 1, S. Rafiee 1, A. Keyhani 1 1 Agricultural Machinery Engineering Dept., Faculty of Agricultural Engineering
Mathematical modelling of thin-layer drying of carrot
 Int. Agrophysics, 2009, 23, 313-317 INTERNATIONAL Agrophysics www.international-agrophysics.org Mathematical modelling of thin-layer drying of carrot M. Aghbashlo*, M.H. Kianmehr, S. Khani, and M. Ghasemi
Int. Agrophysics, 2009, 23, 313-317 INTERNATIONAL Agrophysics www.international-agrophysics.org Mathematical modelling of thin-layer drying of carrot M. Aghbashlo*, M.H. Kianmehr, S. Khani, and M. Ghasemi
An Experimental Study on Drying of Pistacia Terebinthus in a Fixed Bed Dryer
 Copyright 2013 Tech Science Press FDMP, vol.9, no.1, pp.1-10, 2013 An Experimental Study on Drying of Pistacia Terebinthus in a Fixed Bed Dryer A. Balbay 1, H. Ülker 2 and Ö. Şahin 3 Abstract: In this
Copyright 2013 Tech Science Press FDMP, vol.9, no.1, pp.1-10, 2013 An Experimental Study on Drying of Pistacia Terebinthus in a Fixed Bed Dryer A. Balbay 1, H. Ülker 2 and Ö. Şahin 3 Abstract: In this
Influence of temperature and drying air velocity on the kinetics of convective drying in the food industry
 Influence of temperature and drying air velocity on the kinetics of convective drying in the food industry Ing. Michal Pěnička Project leader: Doc. Pavel Hoffman CSc. Abstract The aim of this study was
Influence of temperature and drying air velocity on the kinetics of convective drying in the food industry Ing. Michal Pěnička Project leader: Doc. Pavel Hoffman CSc. Abstract The aim of this study was
Thin-layer drying of some Sri Lankan paddy varieties under low humid conditions
 36 Thin-layer drying of some Sri Lankan paddy varieties under low humid conditions A.K. Shyamali, H.H.E. Jayaweera and T.R. Ariyaratne Centre for Instrument Development, Department of Physics, University
36 Thin-layer drying of some Sri Lankan paddy varieties under low humid conditions A.K. Shyamali, H.H.E. Jayaweera and T.R. Ariyaratne Centre for Instrument Development, Department of Physics, University
Drying Kinetics of Chilli Pepper in a force Convection Indirect Solar Drying
 Drying Kinetics of Chilli Pepper in a force Convection Indirect Solar Drying M.I. FADHEL 1, S. SHAUNMUGANATHAN 1, M.A. AlGHOUL 2, MALEK ALI 1, K. SOPIAN 2 & A. ZAHARIM 2 1 Faculty of Engineering and Technology,
Drying Kinetics of Chilli Pepper in a force Convection Indirect Solar Drying M.I. FADHEL 1, S. SHAUNMUGANATHAN 1, M.A. AlGHOUL 2, MALEK ALI 1, K. SOPIAN 2 & A. ZAHARIM 2 1 Faculty of Engineering and Technology,
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 6, June ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 6, June-2015 1009 Selection of Optimum Temperature and Thin Layer Drying Kinetics of Maize for Production of Quality Seeds Mosharaf
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 6, June-2015 1009 Selection of Optimum Temperature and Thin Layer Drying Kinetics of Maize for Production of Quality Seeds Mosharaf
Experimental & Analytical Investigation on Modified Solar Dryer with Recirculation of Air
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 4 (2013), pp. 441-448 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Experimental & Analytical
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 4 (2013), pp. 441-448 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Experimental & Analytical
Design and Fabrication of Experimental Dryer for Studying Agricultural Products
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF AGRICULTURE & BIOLOGY ISSN Print: 1560 8530; ISSN Online: 1814 9596 07-84/AWB/008/10 1 61 65 http://www.fspublishers.org Full Length Article Design and Fabrication of Dryer for
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF AGRICULTURE & BIOLOGY ISSN Print: 1560 8530; ISSN Online: 1814 9596 07-84/AWB/008/10 1 61 65 http://www.fspublishers.org Full Length Article Design and Fabrication of Dryer for
Study of the Drying Kinetics of Baccaurea angulata Merr. (Belimbing Dayak) Fruit
 Study of the Drying Kinetics of Baccaurea angulata Merr. (Belimbing Dayak) Fruit DAYAG FREDALIA BASRI, AHMAD FUDHOLI *, MOHD HAFIDZ RUSLA, M. A. ALGHOUL School of Diagnostic and Applied Health Sciences,
Study of the Drying Kinetics of Baccaurea angulata Merr. (Belimbing Dayak) Fruit DAYAG FREDALIA BASRI, AHMAD FUDHOLI *, MOHD HAFIDZ RUSLA, M. A. ALGHOUL School of Diagnostic and Applied Health Sciences,
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECT OF DRYING AIR RELATIVE HUMIDITY IN DRYING KINETICS OF KIWI
 Academic Journal of Science, CD-ROM. ISSN: 2165-6282 :: 2(1):1 10 (2013) EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECT OF DRYING AIR RELATIVE HUMIDITY IN DRYING KINETICS OF KIWI Soner en and Selçuk Dar c Selçuk
Academic Journal of Science, CD-ROM. ISSN: 2165-6282 :: 2(1):1 10 (2013) EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECT OF DRYING AIR RELATIVE HUMIDITY IN DRYING KINETICS OF KIWI Soner en and Selçuk Dar c Selçuk
Influence Collector Inclination of Solar Dryer on Apple Golab Chips Drying
 ORIGIAL SCIETIFIC PAPER 101 Influence Collector Inclination of Solar Dryer on Apple Golab Chips Drying Omid Reza ROUSTAPOUR 1( ) Hamid Reza GAZOR 2 Summary Thin layer of apple chips ( Golab ) with 73.4%
ORIGIAL SCIETIFIC PAPER 101 Influence Collector Inclination of Solar Dryer on Apple Golab Chips Drying Omid Reza ROUSTAPOUR 1( ) Hamid Reza GAZOR 2 Summary Thin layer of apple chips ( Golab ) with 73.4%
Drying Characteristics of Carrot and Green Pumpkin Slices in Waste Heat Dryer
 Original Article J. of Biosystems Eng. 37(1):36-43. (2012. 2) http://dx.doi.org/10.5307/jbe.2012.37.1.036 Journal of Biosystems Engineering eissn : 2234-1862 pissn : 1738-1266 Drying Characteristics of
Original Article J. of Biosystems Eng. 37(1):36-43. (2012. 2) http://dx.doi.org/10.5307/jbe.2012.37.1.036 Journal of Biosystems Engineering eissn : 2234-1862 pissn : 1738-1266 Drying Characteristics of
Experimental Analysis of Open, Simple and Modified Greenhouse Dryers for Drying Potato Flakes under Forced Convection
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Experimental Analysis of Open, Simple and Modified Greenhouse Dryers for Drying Potato Flakes under Forced Convection Tanuj Kumar Sahu 1, Vishal Gupta 2, Ajay Kumar Singh 3
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Experimental Analysis of Open, Simple and Modified Greenhouse Dryers for Drying Potato Flakes under Forced Convection Tanuj Kumar Sahu 1, Vishal Gupta 2, Ajay Kumar Singh 3
Thin Layer Mathematical Modelling of Cob Maize in a Natural Convection Solar Drier
 Energy and Environment Research; Vol. 7, No. 2; 2017 ISSN 1927-0569 E-ISSN 1927-0577 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Thin Layer Mathematical Modelling of Cob Maize in a Natural Convection
Energy and Environment Research; Vol. 7, No. 2; 2017 ISSN 1927-0569 E-ISSN 1927-0577 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Thin Layer Mathematical Modelling of Cob Maize in a Natural Convection
Sitesh Kumar Pandey1, Richa Soni2, Abhishek Shrivastav3 1,3
 IJEEE Volume Spl. Issue (6) Mathematical ing of Thin Layer Drying Process of Red Chili in Solar Dryer Under Open Sun Sitesh Kumar Pey Richa Soni Abhishek Shrivastav Mechanical Engineering Deptt. C.I.E.T
IJEEE Volume Spl. Issue (6) Mathematical ing of Thin Layer Drying Process of Red Chili in Solar Dryer Under Open Sun Sitesh Kumar Pey Richa Soni Abhishek Shrivastav Mechanical Engineering Deptt. C.I.E.T
A New Approach for Modeling of Hot Air-microwave Thin Layer Drying of Soybean
 A New Approach for Modeling of Hot Air-microwave Thin Layer Drying of Soybean Dariush Zare, Assistant Professor, Agricultural Engineering Dept., Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran. M. Ranjbaran, M. Javidi,
A New Approach for Modeling of Hot Air-microwave Thin Layer Drying of Soybean Dariush Zare, Assistant Professor, Agricultural Engineering Dept., Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran. M. Ranjbaran, M. Javidi,
Thermal Performance Of Low Cost Solar Bamboo Dryer
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol.5, No.2, pp 1041-1045, April-June 2013 ICGSEE-2013[14 th 16 th March 2013] International Conference on Global Scenario
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol.5, No.2, pp 1041-1045, April-June 2013 ICGSEE-2013[14 th 16 th March 2013] International Conference on Global Scenario
Mathematical modeling of drying characteristics of chilli in hot air oven and fluidized bed dryers
 154 March, 2013 Agric Eng Int: CIGR Journal Open access at http://www.cigrjournal.org Vol. 15, No.1 Mathematical modeling of drying characteristics of chilli in hot air oven and fluidized bed dryers S.
154 March, 2013 Agric Eng Int: CIGR Journal Open access at http://www.cigrjournal.org Vol. 15, No.1 Mathematical modeling of drying characteristics of chilli in hot air oven and fluidized bed dryers S.
Development of a Simulation Model for the Hybrid Solar Dryers as Alternative Sustainable Drying System for Herbal and Medicinal Plants
 Development of a Simulation Model for the Hybrid Solar Dryers as Alternative Sustainable Drying System for Herbal and Medicinal Plants Ali, S.A. and A.H. Bahnasawy Agric. Eng. Dept., Moshtohor Agric. College
Development of a Simulation Model for the Hybrid Solar Dryers as Alternative Sustainable Drying System for Herbal and Medicinal Plants Ali, S.A. and A.H. Bahnasawy Agric. Eng. Dept., Moshtohor Agric. College
Cassava Chip Drying by Using a Small-Scale Hot-Air Microwave Oven
 American Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences 6 (2): 211-215, 2013 ISSN: 1941-7020 2014 P. Wilaipon, This open access article is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) 3.0 license
American Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences 6 (2): 211-215, 2013 ISSN: 1941-7020 2014 P. Wilaipon, This open access article is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) 3.0 license
Exergy Analysis of Heat Pump Dryer
 12 MAHASARAKHAM INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 4, NO. 1, JANUARY-JUNE 2018 ergy Analysis of Heat Pump Dryer Nattapol Poomsa-ad 1,*, Lamul Wiset 2 and Khanuengnit Chapchaimoh 3 1,*
12 MAHASARAKHAM INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 4, NO. 1, JANUARY-JUNE 2018 ergy Analysis of Heat Pump Dryer Nattapol Poomsa-ad 1,*, Lamul Wiset 2 and Khanuengnit Chapchaimoh 3 1,*
International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research e-issn No.: , Date: 2-4 July, 2015
 International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com e-issn No.:2349-9745, Date: 2-4 July, 2015 Modeling Moisture Ratio of High Moisture Potato Slices in Forced Convection
International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com e-issn No.:2349-9745, Date: 2-4 July, 2015 Modeling Moisture Ratio of High Moisture Potato Slices in Forced Convection
Thin layer tea drying experimentation with biomass fuelled producer gas
 In the previous Chapter, we had discussed the details procedure of selection and characterization of biomass as prospective fuel for tea processing through gasification. We found that fuel properties of
In the previous Chapter, we had discussed the details procedure of selection and characterization of biomass as prospective fuel for tea processing through gasification. We found that fuel properties of
Drying Kinetics of Oyster Mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus) in a Convective Hot Air Dryer
 J. Agr. Sci. Tech. (011) Vol. 13: 655-664 Drying Kinetics of Oyster Mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus) in a Convective Hot Air Dryer Y. Tulek 1 ABSTRACT The objective of this study was to investigate the drying
J. Agr. Sci. Tech. (011) Vol. 13: 655-664 Drying Kinetics of Oyster Mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus) in a Convective Hot Air Dryer Y. Tulek 1 ABSTRACT The objective of this study was to investigate the drying
Drying of apple slices (var. Golab) and effect on moisture diffusivity and activation energy
 POJ 3(3):97-10 (010) ISSN:1836-3644 Drying of apple slices (var. Golab) and effect on moisture diffusivity and activation energy *E. Meisami-asl, S. Rafiee, A. Keyhani and A. Tabatabaeefar Department of
POJ 3(3):97-10 (010) ISSN:1836-3644 Drying of apple slices (var. Golab) and effect on moisture diffusivity and activation energy *E. Meisami-asl, S. Rafiee, A. Keyhani and A. Tabatabaeefar Department of
Drying Kinetics of Sliced Pineapples in a Solar Conduction Dryer
 Energy and Environment Research; Vol. 7, No. 2; 2017 ISSN 1927-0569 E-ISSN 1927-0577 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Drying Kinetics of Sliced Pineapples in a Solar Conduction Dryer
Energy and Environment Research; Vol. 7, No. 2; 2017 ISSN 1927-0569 E-ISSN 1927-0577 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Drying Kinetics of Sliced Pineapples in a Solar Conduction Dryer
INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT TEMPERING PERIOD AND VACUUM CONDITIONS ON THE RICE GRAIN BREAKAGE IN A THIN LAYER DRYER
 INFLUENCE OF TEMPERING PERIOD AND VACUUM CONDITIONS ON THE RICE GRAIN BREAKAGE Cercetări Agronomice în Moldova Vol. XLVI, No. 4 (156) / 2013 INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT TEMPERING PERIOD AND VACUUM CONDITIONS
INFLUENCE OF TEMPERING PERIOD AND VACUUM CONDITIONS ON THE RICE GRAIN BREAKAGE Cercetări Agronomice în Moldova Vol. XLVI, No. 4 (156) / 2013 INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT TEMPERING PERIOD AND VACUUM CONDITIONS
Thin-Layer Drying Characteristics of Banana Slices in a Force Convection Indirect Solar Drying
 Thin-Layer Drying Characteristics of Banana Slices in a Force Convection Indirect Solar Drying M. I. FADHEL, RAMEZ ABDULWASEA ABDO, B. F. YOUSIF, AZAMI ZAHARIM 3 AND K. SOPIAN 3 Faculty of Engineering
Thin-Layer Drying Characteristics of Banana Slices in a Force Convection Indirect Solar Drying M. I. FADHEL, RAMEZ ABDULWASEA ABDO, B. F. YOUSIF, AZAMI ZAHARIM 3 AND K. SOPIAN 3 Faculty of Engineering
The Effect of Quantity of Salt on the Drying Characteristics of Fresh Noodles
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Agriculture and Agricultural Science Procedia 2 ( 2014 ) 207 211 ST26943, 2nd International Conference on Agricultural and Food Engineering, CAFEi2014
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Agriculture and Agricultural Science Procedia 2 ( 2014 ) 207 211 ST26943, 2nd International Conference on Agricultural and Food Engineering, CAFEi2014
Design and development of mixed mode natural convection solar dryer
 08; 7(3): 30-307 E-ISSN: 78-436 P-ISSN: 349-834 JPP 08; 7(3): 30-307 Received: 05-03-08 Accepted: 0-04-08 Divyasree Arepally J Venkata Lavanya G Manikanth Reddy Venkat Reddy Kamidi D Mahender Reddy N Gangadhar
08; 7(3): 30-307 E-ISSN: 78-436 P-ISSN: 349-834 JPP 08; 7(3): 30-307 Received: 05-03-08 Accepted: 0-04-08 Divyasree Arepally J Venkata Lavanya G Manikanth Reddy Venkat Reddy Kamidi D Mahender Reddy N Gangadhar
Available online Journal of Scientific and Engineering Research, 2018, 5(10): Research Article
 Available online www.jsaer.com, 2018, 5(10):59-65 Research Article ISSN: 2394-2630 CODEN(USA): JSERBR Evaluation of Temperature and Relative Humidity Stratifications in a Solar Drying Chamber Maytham AL-NEAMA*
Available online www.jsaer.com, 2018, 5(10):59-65 Research Article ISSN: 2394-2630 CODEN(USA): JSERBR Evaluation of Temperature and Relative Humidity Stratifications in a Solar Drying Chamber Maytham AL-NEAMA*
Drying of Fruits, Vegetables, Spices and Medicinal Plants with a Mixed-Mode Solar Drying System with Internal Reflectors
 Drying of Fruits, Vegetables, Spices and Medicinal Plants with a Mixed-Mode Solar Drying System with Internal Reflectors Jatinkumar Patel, Pandit Deendayal Petroleum University, India Anurag Mudgal, Pandit
Drying of Fruits, Vegetables, Spices and Medicinal Plants with a Mixed-Mode Solar Drying System with Internal Reflectors Jatinkumar Patel, Pandit Deendayal Petroleum University, India Anurag Mudgal, Pandit
Performance and Evaluation of Pop Can Solar Dryer for Batch Products
 American Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy Vol. 4, No. 1, 2018, pp. 1-7 http://www.aiscience.org/journal/ajrse ISSN: 2381-7437 (Print); ISSN: 2381-7445 (Online) Performance and Evaluation of
American Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy Vol. 4, No. 1, 2018, pp. 1-7 http://www.aiscience.org/journal/ajrse ISSN: 2381-7437 (Print); ISSN: 2381-7445 (Online) Performance and Evaluation of
Solar Drying Techniques And Performance Analysis: A Review
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X PP. 35-39 www.iosrjournals.org Solar Drying Techniques And Performance Analysis: A Review A.C. Jambhulkar,
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X PP. 35-39 www.iosrjournals.org Solar Drying Techniques And Performance Analysis: A Review A.C. Jambhulkar,
Mathematical Modeling on Hot Air Drying of Thin Layer Fresh Tilapia Fillets
 Original paper Section: Food Technology Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci., 2013, Vol. 63, No. 1, pp. 25-34 DOI: 10.2478/v10222 012 0065 5 http://journal.pan.olsztyn.pl Mathematical Modeling on Hot Air Drying of
Original paper Section: Food Technology Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci., 2013, Vol. 63, No. 1, pp. 25-34 DOI: 10.2478/v10222 012 0065 5 http://journal.pan.olsztyn.pl Mathematical Modeling on Hot Air Drying of
ANALYSIS OF THE DRYING KINETICS OF S. BARTOLOMEU PEARS FOR DIFFERENT DRYING SYSTEMS
 ISSN: 1579-4377 ANALYSIS OF THE DRYING KINETICS OF S. BARTOLOMEU PEARS FOR DIFFERENT DRYING SYSTEMS RAQUEL P. F. GUINÉ Departamento de Indústrias Alimentares, Escola Superior Agrária de Viseu, Instituto
ISSN: 1579-4377 ANALYSIS OF THE DRYING KINETICS OF S. BARTOLOMEU PEARS FOR DIFFERENT DRYING SYSTEMS RAQUEL P. F. GUINÉ Departamento de Indústrias Alimentares, Escola Superior Agrária de Viseu, Instituto
THE THIN LAYER DRYING OF TEMU PUTIH HERB
 The 6 th Asia-Pacific Drying Conference (ADC2009) October 19-21, 2009, Bangkok, Thailand THE THIN LAYER DRYING OF TEMU PUTIH HERB *Lamhot P. MANALU 1,2, Armansyah H. TAMBUNAN 3, Leopold O. NELWAN 3 and
The 6 th Asia-Pacific Drying Conference (ADC2009) October 19-21, 2009, Bangkok, Thailand THE THIN LAYER DRYING OF TEMU PUTIH HERB *Lamhot P. MANALU 1,2, Armansyah H. TAMBUNAN 3, Leopold O. NELWAN 3 and
Mathematical Modelling of Thin Layer Drying Kinetics of Amla-Beet Root Shreds
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.221
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.221
Mathematical Simulation of Longan Fruit Drying
 Mathematical Simulation of Longan Fruit Drying Aree Achariyaviriya, Somchart Soponronnarit and Jirawan Tiansuwan ABSTRACT The objectives of this study were to develop a mathematical model and to simulate
Mathematical Simulation of Longan Fruit Drying Aree Achariyaviriya, Somchart Soponronnarit and Jirawan Tiansuwan ABSTRACT The objectives of this study were to develop a mathematical model and to simulate
Drying Kinetics Modelling of Basil in Microwave Dryer
 AGRICULTURAL COMMUNICATIONS, 2015, 3(4): 37 44. Drying Kinetics Modelling of Basil in Microwave Dryer ESMAEEL SEYEDABADI Department of Agronomy, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Zabol, Zabol, Iran.
AGRICULTURAL COMMUNICATIONS, 2015, 3(4): 37 44. Drying Kinetics Modelling of Basil in Microwave Dryer ESMAEEL SEYEDABADI Department of Agronomy, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Zabol, Zabol, Iran.
An Investigation on Drying of Millets in A Microwave Oven
 An Investigation on Drying of Millets in A Microwave Oven G. B. Radhika 1, S.V. Satyanarayana, D. G. Rao 3 1 B.V.Raju Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, India Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University
An Investigation on Drying of Millets in A Microwave Oven G. B. Radhika 1, S.V. Satyanarayana, D. G. Rao 3 1 B.V.Raju Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, India Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University
MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF MICROWAVE ASSISTED FLUIDIZED BED DRYING OF HAZELNUTS
 MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF MICROWAVE ASSISTED FLUIDIZED BED DRYING OF HAZELNUTS Narjes Malekjani (a), Zahra Emam-Djomeh (b), Seyed Hassan Hashemabadi (c), Gholam Reza Askari (d) (a), (b), (d) Department
MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF MICROWAVE ASSISTED FLUIDIZED BED DRYING OF HAZELNUTS Narjes Malekjani (a), Zahra Emam-Djomeh (b), Seyed Hassan Hashemabadi (c), Gholam Reza Askari (d) (a), (b), (d) Department
INFLUENCE OF DRYING CONDITIONS ON THE MOISTURE DIFFUSION DURING SINGLE STAGE AND TWO STAGE FLUIDIZED BED DRYING OF BOVINE INTESTINE FOR PET FOOD
 INFLUENCE OF DRYING CONDITIONS ON THE MOISTURE DIFFUSION DURING SINGLE STAGE AND TWO STAGE FLUIDIZED BED DRYING OF BOVINE INTESTINE FOR PET FOOD O. Alves-Filho 1, W. Senadeera, T. Eikevik 1 1 Norwegian
INFLUENCE OF DRYING CONDITIONS ON THE MOISTURE DIFFUSION DURING SINGLE STAGE AND TWO STAGE FLUIDIZED BED DRYING OF BOVINE INTESTINE FOR PET FOOD O. Alves-Filho 1, W. Senadeera, T. Eikevik 1 1 Norwegian
Solar Drying Kinetics of Cassava Slices in a Mixed Flow Dryer
 DOI: 10.1515/ata-015-000 Acta Technologica Agriculturae 4/015 Acta Technologica Agriculturae 4 Nitra, Slovaca Universitas Agriculturae Nitriae, 015, pp. 10 107 Solar Drying Kinetics of Cassava Slices in
DOI: 10.1515/ata-015-000 Acta Technologica Agriculturae 4/015 Acta Technologica Agriculturae 4 Nitra, Slovaca Universitas Agriculturae Nitriae, 015, pp. 10 107 Solar Drying Kinetics of Cassava Slices in
THERMAL PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF GREENHOUSE SOLAR DRYER UNDER PASSIVE MODE
 THERMAL PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF GREENHOUSE SOLAR DRYER UNDER PASSIVE MODE Pushpendra Singh 1, Vipin Shrivastava 2 1,2 Mechanical Engineering Department, Lakshmi Narain College of Technology (India) ABSTRACT
THERMAL PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF GREENHOUSE SOLAR DRYER UNDER PASSIVE MODE Pushpendra Singh 1, Vipin Shrivastava 2 1,2 Mechanical Engineering Department, Lakshmi Narain College of Technology (India) ABSTRACT
Review Article Solar Drying Technology: Potentials and Developments
 Ashdin Publishing Journal of Fundamentals of Renewable Energy and Applications Vol. 2 (2012), Article ID R120302, 5 pages doi:10.4303/jfrea/r120302 ASHDIN publishing Review Article Solar Drying Technology:
Ashdin Publishing Journal of Fundamentals of Renewable Energy and Applications Vol. 2 (2012), Article ID R120302, 5 pages doi:10.4303/jfrea/r120302 ASHDIN publishing Review Article Solar Drying Technology:
Thin layer drying models for sweet potato in tray dryer
 Thin layer drying models for sweet potato in tray dryer A. S. Olawale *, S. O. Omole (Department of Chemical Engineering, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria) Abstract: Sweet potato is increasingly
Thin layer drying models for sweet potato in tray dryer A. S. Olawale *, S. O. Omole (Department of Chemical Engineering, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria) Abstract: Sweet potato is increasingly
Design, Construction and Testing of Simple Solar Maize Dryer
 Leonardo Electronic Journal of Practices and Technologies ISSN 1583-1078 Issue 13, July-December 2008 p. 122-130 Design, Construction and Testing of Simple Solar Maize Dryer Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Leonardo Electronic Journal of Practices and Technologies ISSN 1583-1078 Issue 13, July-December 2008 p. 122-130 Design, Construction and Testing of Simple Solar Maize Dryer Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Corn drying experiments by pilot dryer
 Agronomy Research Biosystem Engineering Special Issue 1, 91-97, 2011 Corn drying experiments by pilot dryer L. Kocsis, M. Herdovics, J. Deákvári and L. Fenyvesi Hungarian Institute of Agricultural Engineering,
Agronomy Research Biosystem Engineering Special Issue 1, 91-97, 2011 Corn drying experiments by pilot dryer L. Kocsis, M. Herdovics, J. Deákvári and L. Fenyvesi Hungarian Institute of Agricultural Engineering,
Drying characteristics of Air Dried Sheet (ADS) Rubber
 Paper Code: ee11 characteristics of Air Dried Sheet (ADS) Rubber Y. Tirawanichakul 1*, W. Suchonpanit 2 and S. Tirawanichakul 3 1 Plasma and Energy Technology Research Laboratory, Department of Physics,
Paper Code: ee11 characteristics of Air Dried Sheet (ADS) Rubber Y. Tirawanichakul 1*, W. Suchonpanit 2 and S. Tirawanichakul 3 1 Plasma and Energy Technology Research Laboratory, Department of Physics,
Study of the Drying Kinetics of Lemon Grass
 American Journal of Applied Sciences 6 (6): 1070-1075, 2009 ISS 1546-9239 2009 Science Publications Study of the Drying Kinetics of Lemon Grass Mustafa Ibrahim, K. Sopian and W.R.W. Daud Solar Energy Research
American Journal of Applied Sciences 6 (6): 1070-1075, 2009 ISS 1546-9239 2009 Science Publications Study of the Drying Kinetics of Lemon Grass Mustafa Ibrahim, K. Sopian and W.R.W. Daud Solar Energy Research
Numerical investigation of a solar greenhouse tunnel drier for drying of copra
 Numerical investigation of a solar greenhouse tunnel drier for drying of copra S. Sadodin a, T. T. Kashani a,* a Department of Energy Conversion, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Semnan University, Semnan,
Numerical investigation of a solar greenhouse tunnel drier for drying of copra S. Sadodin a, T. T. Kashani a,* a Department of Energy Conversion, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Semnan University, Semnan,
Convective Drying of Apple: Mathematical Modeling and Determination of some Quality Parameters
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF AGRICULTURE & BIOLOGY ISSN Print: 1560 8530; ISSN Online: 1814 9596 09 15/ZSA/010/1 171 178 http://www.fspublishers.org Full Length Article Convective Drying of Apple: Mathematical
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF AGRICULTURE & BIOLOGY ISSN Print: 1560 8530; ISSN Online: 1814 9596 09 15/ZSA/010/1 171 178 http://www.fspublishers.org Full Length Article Convective Drying of Apple: Mathematical
MODEL AND SIMULATION OF DEEP-BED CLOVE DRYING: EFFECT OF FERMENTED TREATMENT
 - Vol. 15, No. 1, April 21 MODEL AND SIMULATION OF DEEP-BED CLOVE DRYING: EFFECT OF FERMENTED TREATMENT Agus Supriatna ~omantri' Abstract This paper describes the prediction of deep-bed clove drying. This
- Vol. 15, No. 1, April 21 MODEL AND SIMULATION OF DEEP-BED CLOVE DRYING: EFFECT OF FERMENTED TREATMENT Agus Supriatna ~omantri' Abstract This paper describes the prediction of deep-bed clove drying. This
Drying of agricultural products using forced convection indirect solar dryer
 International Refereed Journal of Engineering and Science (IRJES) ISSN (Online) 2319-183X, (Print) 2319-1821 Volume 6, Issue 8 (August 2017), PP.47-54 Drying of agricultural products using forced convection
International Refereed Journal of Engineering and Science (IRJES) ISSN (Online) 2319-183X, (Print) 2319-1821 Volume 6, Issue 8 (August 2017), PP.47-54 Drying of agricultural products using forced convection
Volume 10 No. 3 March THIN LAYER DRYING KINETICS OF AMARANTH (Amaranthus cruentus) GRAINS IN A NATURAL CONVECTION SOLAR TENT DRYER.
 THIN LAYER DRYING KINETICS OF AMARANTH (Amaranthus cruentus) GRAINS IN A NATURAL CONVECTION SOLAR TENT DRYER Ronoh EK 1*, Kanali CL 1, Mailutha JT 1 and D Shitanda 1 Erick Ronoh * Corresponding author,
THIN LAYER DRYING KINETICS OF AMARANTH (Amaranthus cruentus) GRAINS IN A NATURAL CONVECTION SOLAR TENT DRYER Ronoh EK 1*, Kanali CL 1, Mailutha JT 1 and D Shitanda 1 Erick Ronoh * Corresponding author,
Performance Evaluation of Solar Tunnel Dryer for Drying of Garlic.
 ISSN: 2347-4688, Vol. 05, No.(2) 2017, Pg.220-226 Current Agriculture Research Journal An International Open Access, Peer Reviewed Journal www.agriculturejournal.org Performance Evaluation of Solar Tunnel
ISSN: 2347-4688, Vol. 05, No.(2) 2017, Pg.220-226 Current Agriculture Research Journal An International Open Access, Peer Reviewed Journal www.agriculturejournal.org Performance Evaluation of Solar Tunnel
Specific Energy Consumption of Heat Pump Drying System
 Mindanao Journal of Science and Technology Vol.14 (2016) 131-145 Specific Energy Consumption of Heat Pump Drying System Adonis A. Closas 1* and Eliseo P. Villanueva 2 1 College of Engineering and Architecture
Mindanao Journal of Science and Technology Vol.14 (2016) 131-145 Specific Energy Consumption of Heat Pump Drying System Adonis A. Closas 1* and Eliseo P. Villanueva 2 1 College of Engineering and Architecture
Drying principles and general considerations
 Drying principles and general considerations Drying Mechanisms In the process of drying heat is necessary to evaporate moisture from the grain and a flow of air is needed to carry away the evaporated moisture.
Drying principles and general considerations Drying Mechanisms In the process of drying heat is necessary to evaporate moisture from the grain and a flow of air is needed to carry away the evaporated moisture.
THE GLASS TRANSITION TEMPERATURE CONCEPT IN RICE DRYING AND TEMPERING: EFFECT ON DRYING RATE
 THE GLASS TRANSITION TEMPERATURE CONCEPT IN RICE DRYING AND TEMPERING: EFFECT ON DRYING RATE A. G. Cnossen, T. J. Siebenmorgen, W. Yang ABSTRACT. Research on rice drying and tempering has shown that high
THE GLASS TRANSITION TEMPERATURE CONCEPT IN RICE DRYING AND TEMPERING: EFFECT ON DRYING RATE A. G. Cnossen, T. J. Siebenmorgen, W. Yang ABSTRACT. Research on rice drying and tempering has shown that high
Mathematical modeling and polysaccharide content of Ganoderma lucidum by hot air impingement drying
 An ASABE Meeting Presentation Paper Number: 131619320 Mathematical modeling and polysaccharide content of Ganoderma lucidum by hot air impingement drying Jun-Wen Bai, Hong-Wei Xiao, Zheng Lou, Zhen-Jiang
An ASABE Meeting Presentation Paper Number: 131619320 Mathematical modeling and polysaccharide content of Ganoderma lucidum by hot air impingement drying Jun-Wen Bai, Hong-Wei Xiao, Zheng Lou, Zhen-Jiang
Design and Experimental Studies on Modified Solar Dryer
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 8, Number 1 (2015), pp. 43-47 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Design and Experimental
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 8, Number 1 (2015), pp. 43-47 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Design and Experimental
DRYING PERFORMANCE OF ROTATING AND SOLAR TUNNEL DRYER FOR PRODUCTION OF QUALITY DRIED FISH
 Progress. Agric. 20(1 & 2) : 173-181, 2009 ISSN 1017-8139 DRYING PERFORMANCE OF ROTATING AND SOLAR TUNNEL DRYER FOR PRODUCTION OF QUALITY DRIED FISH S. Sultana, Shikha, M. N. Islam and M. Kamal* 1 Department
Progress. Agric. 20(1 & 2) : 173-181, 2009 ISSN 1017-8139 DRYING PERFORMANCE OF ROTATING AND SOLAR TUNNEL DRYER FOR PRODUCTION OF QUALITY DRIED FISH S. Sultana, Shikha, M. N. Islam and M. Kamal* 1 Department
Characteristics of sunflower seed drying and microwave energy consumption
 Int. Agrophys., 2013, 27, 127-132 doi: 10.2478/v10247-012-0077-8 INTERNATIONAL Agrophysics www.international-agrophysics.org Characteristics of sunflower seed drying and microwave energy consumption H.
Int. Agrophys., 2013, 27, 127-132 doi: 10.2478/v10247-012-0077-8 INTERNATIONAL Agrophysics www.international-agrophysics.org Characteristics of sunflower seed drying and microwave energy consumption H.
Food Research (2019) : pp - pp Journal homepage:
 Food Research (2019) : pp - pp Journal homepage: http://www.myfoodresearch.com Drying characteristics of fish cracker under different drying techniques 1,* Abdullah, S., 1 Musa, N., 2 Rukunudin, I.H. and
Food Research (2019) : pp - pp Journal homepage: http://www.myfoodresearch.com Drying characteristics of fish cracker under different drying techniques 1,* Abdullah, S., 1 Musa, N., 2 Rukunudin, I.H. and
Variable far infrared radiation (VFIR) technique for cubic carrot drying
 International Journal of Renewable Energy, Vol. 7, No. 2, July - December 2012 Variable far infrared radiation (VFIR) technique for cubic carrot drying Sirinuch Chindaruksa a *, Pisit Maneechot b, Seishu
International Journal of Renewable Energy, Vol. 7, No. 2, July - December 2012 Variable far infrared radiation (VFIR) technique for cubic carrot drying Sirinuch Chindaruksa a *, Pisit Maneechot b, Seishu
Rice is generally harvested at a moisture content
 RELATING DRYING RATE CONSTANT TO HEAD RICE YIELD REDUCTION OF LONG-GRAIN RICE H. Chen, T. J. Siebenmorgen, B. P. Marks ABSTRACT. Long-grain rough rice was dried at various rates and durations and milled
RELATING DRYING RATE CONSTANT TO HEAD RICE YIELD REDUCTION OF LONG-GRAIN RICE H. Chen, T. J. Siebenmorgen, B. P. Marks ABSTRACT. Long-grain rough rice was dried at various rates and durations and milled
Design and Optimization of Domestic Solar Dryer
 Science Journal of Energy Engineering 2017; 5(6): 130-135 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/sjee doi: 10.11648/j.sjee.20170506.11 ISSN: 2376-810X (Print); ISSN: 2376-8126 (Online) Review Article
Science Journal of Energy Engineering 2017; 5(6): 130-135 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/sjee doi: 10.11648/j.sjee.20170506.11 ISSN: 2376-810X (Print); ISSN: 2376-8126 (Online) Review Article
PERFORMANCE OF FORCED CONVECTION EVACUATED TUBE SOLAR GRAIN DRYER. BOOKER ONYANGO OSODO B. Ed.(TECH); M. Phil (Tech. Ed) (J98/25749/2011)
 PERFORMANCE OF FORCED CONVECTION EVACUATED TUBE SOLAR GRAIN DRYER BOOKER ONYANGO OSODO B. Ed.(TECH); M. Phil (Tech. Ed) (J98/25749/2011) A research Proposal Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
PERFORMANCE OF FORCED CONVECTION EVACUATED TUBE SOLAR GRAIN DRYER BOOKER ONYANGO OSODO B. Ed.(TECH); M. Phil (Tech. Ed) (J98/25749/2011) A research Proposal Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
DETERMINATION OF THE EFFECTIVE MOISTURE DIFFUSIVITY OF RED PEPPER IN A MICROWAVE CONVEYOR DRYER
 DETERMINATION OF THE EFFECTIVE MOISTURE DIFFUSIVITY OF RED PEPPER IN A MICROWAVE CONVEYOR DRYER Soner ÇELEN +, Ugur AKYOL +, Aytaç MORALAR + + NAMIK KEMAL UNIVERSITY, Çorlu, Tekirda, Turkey. Abstract.
DETERMINATION OF THE EFFECTIVE MOISTURE DIFFUSIVITY OF RED PEPPER IN A MICROWAVE CONVEYOR DRYER Soner ÇELEN +, Ugur AKYOL +, Aytaç MORALAR + + NAMIK KEMAL UNIVERSITY, Çorlu, Tekirda, Turkey. Abstract.
Effect of Magnetic Field on Convective Drying Of Ceramic Clay
 International Journal of Engineering and Technology Volume 5 No. 7, July, 2015 Effect of Magnetic Field on Convective Drying Of Ceramic Clay A.A Dare 1, L. I Onu 2, R Akinoso 3 1 Department of Mechanical
International Journal of Engineering and Technology Volume 5 No. 7, July, 2015 Effect of Magnetic Field on Convective Drying Of Ceramic Clay A.A Dare 1, L. I Onu 2, R Akinoso 3 1 Department of Mechanical
Fluidised-Bed Paddy Drying
 RESEARCH ARTICLE ScienceAsia 25 (1999) : 51-56 Fluidised-Bed Paddy Drying Somchart Soponronnarit School of Energy and Materials, King Mongkut's University of Technology Thonburi, Suksawat 48 Road, Bangkok
RESEARCH ARTICLE ScienceAsia 25 (1999) : 51-56 Fluidised-Bed Paddy Drying Somchart Soponronnarit School of Energy and Materials, King Mongkut's University of Technology Thonburi, Suksawat 48 Road, Bangkok
DEVELOPMENT AND PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF A LOCALLY FABRICATED PORTABLE SOLAR TUNNEL DRYER FOR DRYING OF FRUITS, VEGETABLES AND MEDICINAL PLANTS
 Genetic diversity in chestnuts of Kashmir valley Pak. J. Agri. Sci., Vol. 50(3), 493-498; 2013 ISSN (Print) 0552-9034, ISSN (Online) 2076-0906 http://www.pakjas.com.pk DEVELOPMENT AND PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
Genetic diversity in chestnuts of Kashmir valley Pak. J. Agri. Sci., Vol. 50(3), 493-498; 2013 ISSN (Print) 0552-9034, ISSN (Online) 2076-0906 http://www.pakjas.com.pk DEVELOPMENT AND PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
Analysis of Constant Pressure and Constant Area Mixing Ejector Expansion Refrigeration System using R-1270 as Refrigerant
 Analysis of Constant Pressure and Constant Area Mixing Ejector Expansion Refrigeration System using R-1270 as Refrigerant Ravi Verma 1, Sharad Chaudhary 2 1, 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, IET
Analysis of Constant Pressure and Constant Area Mixing Ejector Expansion Refrigeration System using R-1270 as Refrigerant Ravi Verma 1, Sharad Chaudhary 2 1, 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, IET
[Harikeishnan*et al., 5(7): July, 2016] ISSN: IC Value: 3.00 Impact Factor: 4.116
![[Harikeishnan*et al., 5(7): July, 2016] ISSN: IC Value: 3.00 Impact Factor: 4.116 [Harikeishnan*et al., 5(7): July, 2016] ISSN: IC Value: 3.00 Impact Factor: 4.116](/thumbs/75/72180927.jpg) IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY COMPUTATIONAL STUDIES ON PERFORMANCE OF A MIXED MODE SOLAR DRYER WITH THERMAL STORAGE Harikrishnan P. V. *, Richu Zachariah Electrical
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY COMPUTATIONAL STUDIES ON PERFORMANCE OF A MIXED MODE SOLAR DRYER WITH THERMAL STORAGE Harikrishnan P. V. *, Richu Zachariah Electrical
DRYING OF LONGAN: ITS DRYING KINETICS AND PERFORMANCE OF LONGAN DRYERS. By Niroot Lamlert
 DRYING OF LONGAN: ITS DRYING KINETICS AND PERFORMANCE OF LONGAN DRYERS By Niroot Lamlert A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY Department of
DRYING OF LONGAN: ITS DRYING KINETICS AND PERFORMANCE OF LONGAN DRYERS By Niroot Lamlert A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY Department of
Performance Evaluation of Reversible Air Flow Drying in Circulating Dryer
 Performance Evaluation of Reversible Air Flow Drying in Circulating Dryer Dai-Chyi Wang 1 and Yeun-Chung Lee 2 Abstract In Taiwan, rice is harvested with high moisture content (above 27%) and must be immediately
Performance Evaluation of Reversible Air Flow Drying in Circulating Dryer Dai-Chyi Wang 1 and Yeun-Chung Lee 2 Abstract In Taiwan, rice is harvested with high moisture content (above 27%) and must be immediately
Numerical Studies On The Performance Of Methanol Based Air To Air Heat Pipe Heat Exchanger
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA) IJCRGG ISSN 0974-4290 Vol.5, No.2, pp 925-934, April-June 2013 ICGSEE-2013[14th 16th March 2013] International Conference on Global Scenario in Environment
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA) IJCRGG ISSN 0974-4290 Vol.5, No.2, pp 925-934, April-June 2013 ICGSEE-2013[14th 16th March 2013] International Conference on Global Scenario in Environment
Rough rice should be dried to a certain moisture
 fpe 1599 ms 7/9/01 3:33 PM Page 1709 ASTUDY OF HEAD RICE YIELD REDUCTION OF LONG- AND MEDIUM-GRAIN RICE VARIETIES IN RELATION TO VARIOUS HARVEST AND DRYING CONDITIONS J. Fan, T. J. Siebenmorgen, W. Yang
fpe 1599 ms 7/9/01 3:33 PM Page 1709 ASTUDY OF HEAD RICE YIELD REDUCTION OF LONG- AND MEDIUM-GRAIN RICE VARIETIES IN RELATION TO VARIOUS HARVEST AND DRYING CONDITIONS J. Fan, T. J. Siebenmorgen, W. Yang
Prediction of Soil Infiltration Rate Based on Sand Content of Soil
 Agricultural Engineering Research Journal 3 (): 0-4, 013 ISSN 18-3906 IDOSI Publications, 013 DOI: 10.589/idosi.aerj.013.3..1109 Prediction of Soil Infiltration Rate Based on Sand Content of Soil 1 1 Majid
Agricultural Engineering Research Journal 3 (): 0-4, 013 ISSN 18-3906 IDOSI Publications, 013 DOI: 10.589/idosi.aerj.013.3..1109 Prediction of Soil Infiltration Rate Based on Sand Content of Soil 1 1 Majid
Energy consumption and mathematical modeling of microwave drying of potato slices
 94 March, 01 Agric Eng Int: CIGR Journal Open access at http://www.cigrjournal.org Vol. 14, o.1 Energy consumption and mathematical modeling of microwave drying of potato slices Hosain Darvishi (Department
94 March, 01 Agric Eng Int: CIGR Journal Open access at http://www.cigrjournal.org Vol. 14, o.1 Energy consumption and mathematical modeling of microwave drying of potato slices Hosain Darvishi (Department
DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION OF FORCED/NATURAL CONVECTION SOLAR VEGETABLE DRYER WITH HEAT STORAGE
 DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION OF FORCED/NATURAL CONVECTION SOLAR VEGETABLE DRYER WITH HEAT STORAGE Gutti Babagana, Kiman Silas and Mustafa B. G. Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Maiduguri, Borno,
DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION OF FORCED/NATURAL CONVECTION SOLAR VEGETABLE DRYER WITH HEAT STORAGE Gutti Babagana, Kiman Silas and Mustafa B. G. Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Maiduguri, Borno,
A COMPARATIVE EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THERMAL PERFORMANCE OF THREE DIFFERENT SOLAR AIR HEATERS
 A COMPARATIVE EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THERMAL PERFORMANCE OF THREE DIFFERENT SOLAR AIR HEATERS 1 AFJAUL ANSARI, 2 MD. ALAMGIR, 3 HARI KUMAR SINGH, 4 GYANESH GUPTA, 5 SARVESH KUMAR SINGH 1,2,3,4,5
A COMPARATIVE EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THERMAL PERFORMANCE OF THREE DIFFERENT SOLAR AIR HEATERS 1 AFJAUL ANSARI, 2 MD. ALAMGIR, 3 HARI KUMAR SINGH, 4 GYANESH GUPTA, 5 SARVESH KUMAR SINGH 1,2,3,4,5
Performance Evaluation of a Mixed-Mode Solar Dryer
 Performance Evaluation of a Mixed-Mode Solar Dryer Bukola O. Bolaji and Ayoola P. Olalusi* Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Agriculture Abeokuta, Ogun State, Nigeria Email: ayoolalusi@yahoo.co.uk>
Performance Evaluation of a Mixed-Mode Solar Dryer Bukola O. Bolaji and Ayoola P. Olalusi* Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Agriculture Abeokuta, Ogun State, Nigeria Email: ayoolalusi@yahoo.co.uk>
Effect of Air Velocity and Pre Treatment on Drying Characteristics of Tomato Slices during Solar Tunnel Drying
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 6 (2017) pp. 573-580 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.606.067
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 6 (2017) pp. 573-580 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.606.067
Performance Evaluation of a Mixed-Mode Tomato Solar Dryer and Modeling of the Dying Process
 Nigerian Journal of Solar Energy, Vol. 27, 2016. Solar Energy Society of Nigeria (SESN) 2016. All rights reserved. Performance Evaluation of a Mixed-Mode Tomato Solar Dryer and Modeling of the Dying Process
Nigerian Journal of Solar Energy, Vol. 27, 2016. Solar Energy Society of Nigeria (SESN) 2016. All rights reserved. Performance Evaluation of a Mixed-Mode Tomato Solar Dryer and Modeling of the Dying Process
14 Drying. I Basic relations and definitions. Oldřich Holeček, Martin Kohout
 14 Drying Oldřich Holeček, Martin Kohout I Basic relations and definitions Drying is a process which is used for removing the liquid from the solid material. In standard chemical engineering practice drying
14 Drying Oldřich Holeček, Martin Kohout I Basic relations and definitions Drying is a process which is used for removing the liquid from the solid material. In standard chemical engineering practice drying
Solar Drying of Fruits and Vegetables
 Solar Drying of Fruits and Vegetables Y. Baradey 1, M. N. A. Hawlader 2, A. F. Ismail 3, M. Hrairi 4, M. I. Rapi 5 1,2,3 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, International Islamic
Solar Drying of Fruits and Vegetables Y. Baradey 1, M. N. A. Hawlader 2, A. F. Ismail 3, M. Hrairi 4, M. I. Rapi 5 1,2,3 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, International Islamic
HUMIDITY RELATIONSHIP DETERMINATED IN THE DRYING CEREAL SEED FLUIDIZED BED
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. 2 (51) - 2009 Series I: Engineering Sciences HUMIDITY RELATIONSHIP DETERMINATED IN THE DRYING CEREAL SEED FLUIDIZED BED C.D. CERNĂIANU 1 A.E.STĂNCUŢ
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. 2 (51) - 2009 Series I: Engineering Sciences HUMIDITY RELATIONSHIP DETERMINATED IN THE DRYING CEREAL SEED FLUIDIZED BED C.D. CERNĂIANU 1 A.E.STĂNCUŢ
ANALYSIS OF THERMAL PERFORMANCE OF SOLAR AIR DRYER FOR THREE DIFFERENT ABSORBER PLATES
 ANALYSIS OF THERMAL PERFORMANCE OF SOLAR AIR DRYER FOR THREE DIFFERENT ABSORBER PLATES 1 BALIRAM KUMAR, 2 VIKAS KUMAR, 3 HARI KUMAR SINGH Centre of Excellence Renewable and Sustainable Energy studies,
ANALYSIS OF THERMAL PERFORMANCE OF SOLAR AIR DRYER FOR THREE DIFFERENT ABSORBER PLATES 1 BALIRAM KUMAR, 2 VIKAS KUMAR, 3 HARI KUMAR SINGH Centre of Excellence Renewable and Sustainable Energy studies,
DRYING BEHAVIORS OF WATER HYACINTH BY MULTI-TRAY SOLAR DRYER
 Egypt. J. Agric. Res., 92 (1), 2014 273 DRYING BEHAVIORS OF WATER HYACINTH BY MULTI-TRAY SOLAR DRYER SHOUGHY M. I., A. F. ABDRABOH and A. B. EL-NAGAR Agric. Eng. Res. Inst. (AEnRI), ARC Dokki, Giza, Egypt.
Egypt. J. Agric. Res., 92 (1), 2014 273 DRYING BEHAVIORS OF WATER HYACINTH BY MULTI-TRAY SOLAR DRYER SHOUGHY M. I., A. F. ABDRABOH and A. B. EL-NAGAR Agric. Eng. Res. Inst. (AEnRI), ARC Dokki, Giza, Egypt.
Performance of a small-scale greenhouse solar dryer for drying long peppers of Ban Khokamin Community Enterprise Loei Province, Thailand
 S NRU J ou r n al of S ci e n ce an d Tech n ol og y 8 ( 2 ) M ay Au gu s t ( 2 0 16 ) 2 68 2 74 SNRU Jour nal of Science and Technology J o u r n a l h o m e p a g e : s n r u j s t. s n r u. a c. t h
S NRU J ou r n al of S ci e n ce an d Tech n ol og y 8 ( 2 ) M ay Au gu s t ( 2 0 16 ) 2 68 2 74 SNRU Jour nal of Science and Technology J o u r n a l h o m e p a g e : s n r u j s t. s n r u. a c. t h
Performance Enhancement of Inclined Bubbling Fluidized Bed Paddy Dryer by Design Modification
 Performance Enhancement of Inclined Bubbling Fluidized Bed Paddy Dryer by Design Modification Phyu Phyu Thant, P. Mahanta, P.S. Robi Abstract Present paper discusses the bed inclination and passive inserts
Performance Enhancement of Inclined Bubbling Fluidized Bed Paddy Dryer by Design Modification Phyu Phyu Thant, P. Mahanta, P.S. Robi Abstract Present paper discusses the bed inclination and passive inserts
A STUDY ON DRYING OF AMLA USING A HYBRID SOLAR DRYER
 ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization, Volume 2, Special Issue
ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization, Volume 2, Special Issue
Shortcut Model for Predicting Refrigeration Cycle Performance
 17 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 5, 15 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Sharifah Rafidah Wan Alwi, Jun Yow Yong, Xia Liu Copyright 15, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l.,
17 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 5, 15 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Sharifah Rafidah Wan Alwi, Jun Yow Yong, Xia Liu Copyright 15, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l.,
4th International Conference on Sensors, Measurement and Intelligent Materials (ICSMIM 2015)
 4th International Conference on Sensors, Measurement and Intelligent Materials (ICSMIM 2015) Multi-stage Series Heat Pump Drying System with Dehumidification Simulation and Experiment Verification Chao
4th International Conference on Sensors, Measurement and Intelligent Materials (ICSMIM 2015) Multi-stage Series Heat Pump Drying System with Dehumidification Simulation and Experiment Verification Chao
ME 410 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING SYSTEMS LABORATORY MASS & ENERGY BALANCES IN PSYCHROMETRIC PROCESSES EXPERIMENT 3
 ME 410 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING SYSTEMS LABORATORY MASS & ENERGY BALANCES IN PSYCHROMETRIC PROCESSES EXPERIMENT 3 1. OBJECTIVE The objective of this experiment is to observe four basic psychrometric processes
ME 410 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING SYSTEMS LABORATORY MASS & ENERGY BALANCES IN PSYCHROMETRIC PROCESSES EXPERIMENT 3 1. OBJECTIVE The objective of this experiment is to observe four basic psychrometric processes
PROCESSING OF VEGETABLES IN A SOLAR DRYER IN ARID AREAS
 PROCESSING OF VEGETABLES IN A SOLAR DRYER IN ARID AREAS N. M. Nahar Central Arid Zone Research Institute, Jodhpur 342003, India Email:nmnahar@gmail.com Fax: 91-291-2788706 Abstract When the production
PROCESSING OF VEGETABLES IN A SOLAR DRYER IN ARID AREAS N. M. Nahar Central Arid Zone Research Institute, Jodhpur 342003, India Email:nmnahar@gmail.com Fax: 91-291-2788706 Abstract When the production
Comparison of Energy and Cost Analysis of Two Different Industrial Corn Drying Plants Using Solid Fuel
 Comparison of Energy and Cost Analysis of Two Different Industrial Corn Drying Plants Using Solid Fuel FatihÜnal, HüsamettinBulut, Ahmet Kahraman Assistant Professor, Department of Machine, MardinArtuklu
Comparison of Energy and Cost Analysis of Two Different Industrial Corn Drying Plants Using Solid Fuel FatihÜnal, HüsamettinBulut, Ahmet Kahraman Assistant Professor, Department of Machine, MardinArtuklu
