Small Grain insect pests
|
|
|
- Paula Boone
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Small Grain insect pests SMALL GRAINS Aphids Although aphids are common in the fall and spring, populations are rarely high enough to merit treatment, especially if field are planted after the fly-free date. Description: Small oval to pear shaped soft-bodied insects with cornicles ( tailpipes ) at the back of the body. Color varies from bright green to pink to brown, depending on species. Life cycle: Aphids present during the field season are all female, and do not need to mate to reproduce; females give birth to live young. Multiple overlapping generations. Type of Damage: Sucks plant sap from leaves and stems. Heavy infestation may lead to yellowing/browning, stunting, curling of new leaves, and general weakening of plants. Aphids are also virus vectors. Scouting: See MSU Bulletin E-2549, Insect Management in Wheat and Other Small Grains, for details on the presence/absence scouting method and decision table. Management: Biological = natural enemies (ladybugs, lacewings, and wasps) and diseases generally keep populations in check. Threshold: General guideline is aphids per tiller during seedling to boot stage. Note: Although grain aphids can transmit barley yellow dwarf virus (= red leaf in oats), this is generally not a problem in the fall in Michigan. Also, insecticides usually do not stop transmission of the virus. Aphids should be sprayed only when they are numerous enough to directly threaten yield in the spring and summer. See page 10 in the seed treatment section to determine the impact of seed treatments on aphids. Baythroid 2* and XL* (1.8 to 2.4 oz) Wheat only. Cobalt* (7 to 13 oz) Wheat only Cruiser 5FS (0.75 to 1.33 oz / CWT) Wheat & Barley only Dimethoate 4 EC, 400 (0.5 to 0.75 pt) Wheat only. Dimethoate 5lb (6.4 to 9.6 oz) Wheat only Lannate LV* (0.75 to 1.5 pt) or SP* (0.25 to 0.5 lb) Malathion 5EC (1.5 pt) or 57EC (1.5 to 2 pt) Malathion 8 Aquamul (1.25 pt) or 8F (1 to 1.25 pts) Mustang Max EC* and EW* (3.2 to 4 oz) Wheat only Armyworm Armyworm outbreaks do occur in small grains, in years with heavy flights north into Michigan. Description: Caterpillars variable in color (black/brown/green), up to 1 ½ inches long. Narrow light stripe across back and broad stripes running down sides of body. Life cycle: Likely migrate to Michigan each spring. Eggs are laid on the surfaces of grasses, especially the headlands of small grains. Two to three generations per year, the first generation in late May to early June. Type of damage: Defoliation by larvae, first generation most damaging. Larvae eat leaves, stems, and sometimes the heads of small grains. Scouting: Mainly active at night and during overcast days. During the day, larvae can be found at the base of plants and under debris. Threshold: Before heading, treat when there are four or more worms per square foot. At heading (to prevent head clipping), treat when there are two or more worms per square foot For more information: MSU CAT Alert articles from 2004 May 13 Watch for cutworm and armyworm June 17 Armyworms abound 44
2 Baythroid 2* (1 to 1.8 oz) Wheat only Bt products (Dipel, Javelin, Xentari) - many products, see labels for specific rates Cobalt* (13 to 25 oz) Wheat only Entrust (1 to 2 oz) Lannate LV* (0.75 to 1.5 pt) or SP* (0.25 to 0.5 lb) Malathion 5 and 57EC (2 pt) Malathion 8F (1.0 to 1.25 pts) SMALL GRAINS Mustang Max EC* and EW* (1.76 to 4 oz) Wheat only Pyganic EC 1.4 II (16 to 64 oz) or 5.0 II (4.5 to 18 oz) Radiant SC (3 to 6 oz) Sevin 4F or XLR Plus (1 to 1.5 qt) Wheat only. Sevin 80S or 80WSP (1.25 to lb) Wheat only. Tracer (1.5 to 3 oz) Cereal Leaf Beetle Cereal leaf beetle is usually kept in check by biological control. Description: Adult up to 1/4 inch long; black body, metallic blue wing covers, a red pronotum (neck), and orange-red legs with black tarsi (feet). Eggs- very tiny, oblong; yellow to brown. Larvae- Up to ¼ inch long pale yellow to black, usually covered in fecal material to camouflage themselves. Life cycle: Adults overwinter in plant stubble and in cracks and crevices such as under tree bark. Mating occurs during warm spring temperatures and eggs are laid on the upper surface of the grain leaves. Larvae feed for about two weeks and move to the soil to pupate. These adults emerge in late June and feed for about 3 weeks, then become sedentary. One generation per year. Type of damage: Usually begins on field borders of winter grain, then goes to the preferred spring grain. Defoliation by chewing between leaf veins. Larvae feed on the surface of leaves, while adults feed on the whole leaf. This damage gives a frosted appearance to a severely infested field. Scouting: Begin when temperatures reach 60 degrees. Check 20 stems in five areas of the field. Management: Cultural- Hairy varieties are less likely to be infested. Biological- wasp parasitoids, lady beetles and various other natural enemies. Threshold: Treat when there is a combination of 3 or more eggs and larvae per plant and the larvae are fairly visible on small plants. For larger plants treat when there is one or more larvae per flag leaf. Note: First discovered in the U.S. in Berrien County Michigan, Baythroid 2* and XL* (1.0 to 1.8 oz) Wheat only Cobalt* (13 to 25 oz) Wheat only Entrust (0.5 to 2 oz) Lannate LV* (0.75 to 1.5 pt) or SP* (0.25 to 0.5 lb) Malathion 5 (1.0 to 1.5 pt) Wheat, barley, oats and rye. Malathion ULV (4 to 8 fl oz) Barley, oats, and wheat Mustang Max EC* and EW* (1.76 to 4 oz) Wheat only Radiant SC (2 to 6 oz) Sevin 4F and XLR Plus (1 qt) Wheat only. Sevin 80S and 80WSP (1.25 lb) Wheat only. Tracer (1 to 3 oz) European Corn Borer European corn borers are sometimes found in small grains tunneling in stems. The visible symptom of this damage is whitening (bleaching) of wheat heads. Generally this only occurs in years with heavy EBC populations, in scattered areas of the field. Treatment is not necessary. 45
3 Grasshoppers Grasshoppers are common in agricultural fields, but cause damage only during occasional outbreak years. Life cycle: Eggs overwinter in the soil, and nymphs hatch in June. Nymphs molt as they grow, and feeding increases with size. Females lay eggs in the soil in late summer. Type of damage: Defoliation (chewing) by nymphs and adults. Conditions favoring damage: Unplowed or fallow areas next to fields are preferred egg-laying sites, and may contribute to populations in a nearby field. Dry, warm weather often enhances survival of nymphs. Management: Cultural- plowing and cultivation to destroy eggs. Biological a fungal pathogen can kill many eggs and nymphs under wet spring conditions. Natural enemies include birds, rodents, amphibians, parasitic wasps, and ground beetles. Threshold: Treat when there are eight or more per sq yd in small plants (less than 6 in tall), or 16 or more per sq yd in taller plants. Baythroid 2* and XL* (1.8 to 2.4 oz) Wheat only Cobalt* (7 to 13 oz) Wheat only Dimethoate 4 EC, 400 (0.75 pt) Wheat only Dimethoate 4E (0.75 pts) or 267 (1.125 pts) Dimethoate 5 lb (9.6 oz) Wheat only Malathion 5 (1.5 to 2 pt) Malathion 8F (1 to 1.25 pts) or 8 Aquamul (1.25) Mustang Max EC* and EW* (3.2 to 4 oz) Wheat only Radiant SC (3 to 6 oz) Suppression Sevin 4F or XLR Plus (0.5 to 1.5 qt) Wheat only Sevin 80W or 80WSP (0.66 to 1.87 lb) Wheat only Hessian Fly Hessian fly is controlled without insecticides by planting winter wheat after adult flies are dead late summer or early fall. Fly-free dates are given below for each county (all dates are in September). For additional information, see Extension Bulletin E-2549, Insect Management in Wheat and Other Small Grains, available at county Extension offices. County Earliest seeding date (Sept) County 46 Earliest seeding date (Sept) County Earliest seeding date (Sept) Alcona 6 Hillsdale 19 Montmorency 7 Allegan 20 Huron 13 Muskegon 18 Alpena 9 Ingham 17 Newaygo 15 Antrim 4 Ionia 16 Oakland 16 Arenac 13 Iosco 7 Oceana 16 Barry 18 Isabella 11 Ogemaw 10 Bay 14 Jackson 16 Osceola 10 Benzie 16 Kalamazoo 20 Oscoda 7 Berrien 23 Kalkaska 5 Otsego 6 Branch 19 Kent 18 Ottawa 19 Calhoun 19 Lake 13 Presque Isle 8 Cass 22 Lapeer 15 Roscommon 7 Charlevoix 3 Leelanau 8 Saginaw 16 Cheboygan 4 Lenawee 25 Sanilac 15 Claire 12 Livingston 16 St. Clair 16 Clinton 17 Macomb 18 St. Joseph 23 Crawford 6 Manistee 13 Shiawassee 16 Eaton 16 Mason 13 Tuscola 15 Emmet 4 Mecosta 12 Van Buren 22 Genesee 17 Midland 15 Washtenaw 18 Gladwin 12 Missaukee 9 Wayne 18 Grand Traverse 8 Monroe 21 Wexford 9 Gratiot 15 Montcalm 15
4 Slugs Only a problem under cool and wet conditions. Type of damage: May damage seedlings by feeding on stems, cotyledons, and leaves; up to 40% defoliation can be tolerated in pre-bloom plants, but if growing point is killed, stands can be significantly reduced to the point where replanting is necessary. Conditions favoring damage: Planting into wheat stubble or other heavy crop residue; fields with a recent history of slug damage; aerial-seeded wheat exposed on the soil surface; cool, wet conditions favor slug survival and damage. Sampling/ scouting: Methods not established. Threshold: No established threshold; consider treating if slug damage threatens to reduce stand density below an acceptable level List of registered insecticides (rate per acre): Deadline MP 4 % Bait (10 to 20 lb) Snail and Slug Pellets 3.5% Bait (various products and rates) Thrips Although common on plants, CDD has never seen thrips over threshold in any field crop. Description: Adult small, slender, brown and white banded abdomen, narrow fringed wings; larva wingless, yellow/orange Life cycle: Adults move into fields in spring. Females insert eggs in plant tissue. Adults and larvae both feed on plants. Type of damage: Most obvious early in season; adult & nymph rasping/sucking mouthparts scrape cells on leaf underside, leaving silvery scratches which may turn leaves brown; young leaves may appear crinkled. Young plants can generally outgrow feeding injury Conditions favoring damage: Hot dry weather coupled with large thrips populations Management: Biological natural enemies (minute pirate bugs, predacious thrips and mites) Threshold: Rough guideline treat when 30% of plants have thrips and some drying of leaves is observed. Notes: Damage may be confused with some types of herbicide injury White Grubs White grubs, particularly European chafer, are a localized problem, often depending on soil type. White grubs build up in undisturbed soil and are damaging to crops planted in fields broken from sod. European chafer, an introduced grub species, has a history of infesting winter wheat planted after soybean. MSU field trials suggest that a grub density of 4 per square foot reduces stand, tillering, and yield of winter wheat. No insecticides are labeled for white grub control in small grains. Fall and spring plowing of old pasture or other established grasses with a season of clean fallow before a crop is planted is recommended. Winter cutworm (Noctua pronuba) The first report of damage in the U.S. by this insect was in northern Michigan in fall Life cycle: Adults (yellow underwing moths) begin to emerge in May, but some may emerge later in the summer. Moths fly at night well into October. Caterpillars are found perhaps as early as July, but are commonly found by August and September. Winter cutworms can withstand very cold conditions, feeding in fields well into fall, when nighttime temperatures dip below freezing. Even during the winter, caterpillars emerge and feed on warm days. Type of damage: Defoliation by caterpillars in the fall. Defoliated stands suffered total or severe loss the next spring (plants were lost). Conditions favoring damage: In 2007, economic damage was found in fields only in the upper 1/3 of the lower peninsula. Management: No insecticide labels specifically list winter cutworm as a target, although pyrethroids were effective in I suggest using guidelines and insecticide listed in this section for cutworm control as a baseline. 47
5 Wireworms Wireworms are a localized problem, often depending on previous crop. Description: Slender, shiny, brown caterpillar with wiry segmented body, up to 1.5 inches long. Life cycle: Immature form of click beetle; found in grasslands, sod, or fallow fields. Wireworms can spend several years in the immature stage during which they feed on newly-planted seeds as well as roots. Type of damage: Feeds on germinating seed. Sampling/ scouting: Scout for wireworms with a bait trap ( at least one week before planting. Management: Cultural spring and fall plowing of established sod is recommended before crop planted, where practical. Threshold: One or more wireworm per bait trap. See page 10 in the seed treatment section for a list of products to control wireworm Insecticides Registered for Small Grains Common Trade name name Class Recommended for: Baythroid 2 & XL cyfluthrin Pyr aphids, armyworm, CLB, & beta cutworm, Bt [for ex. Dipel Javelin, Xentari] Cobalt Cruiser 5FS Deadline MP 4 % Bait Dimethoate 4EC, 267, 4E, 400, 5lb cyfluthrin Bacillus thuringiensis PHI REI days hrs Precautions and Remarks Bio armyworm 0 4 Do Not Apply to rye. Effective only on small (1 st -2 nd stage) larvae, and with moderate populations. Full coverage is required. OP Pyr aphids, armyworm, CLB, cutworm, Maximum of 2 applications of products containing chlorpyrifos per year. Nic aphids, wireworms Seed treatment, wheat and barley Other slugs, snails Broadcast by ground or air every 3 to 4 weeks during season as needed. For best results apply in the evening, preferably after a rain or irrigation. May be fatal to dogs - use caution around pets. dimethoate OP aphids, Use in wheat and sorghum only. Maximum of two applications per season. Full coverage not required. Entrust spinosad Bio armyworm, CLB 21 4 Max 5.6 oz per acre per season. Do not allow cattle to graze unless spray is dry. Lambda-Cy EC chlorpyrifos + gamma cyhalothrin thiamethoxam metaldehyde lambdacyhalothrin Pyr See Warrior Do not apply more than 7.68 oz per acre per season. Lannate LV, SP methomyl Carb aphids, armyworm, CLB 7 48 Maximum of 4 applications per season. 48
6 Trade name Malathion 5, 57 EC, 8F,8 Aqua Common name Class Recommended for: malathion OP aphids, armyworm, CLB, PHI REI days hrs 7 12 Precautions and Remarks Mustang Max EC, EW zetacypermethrin Pyr CLB,, thrips Maximum 20 oz per acre per season. Retreatment interval = 14 days. Proaxis gamma cyhalothrin Pyr aphids, armyworm, CLB, Do not apply more than 0.48 pints per acre per season. Use on wheat only. Pyganic EC pyrethrins Bio armyworm, thrips 0 12 Listed by OMRI for use in organic production. Radiant SC spinetoram Bio armyworm, CLB, hoppers 21 grai n 3 hay fora 4 Maximum 18 oz per acre per year. Maximum 3 applications per year. Sevin 4F, XLR Plus, 50W, 80S, 80WSP Silencer carbaryl Carb armyworm, CLB, ge 21 7 Use only on wheat. Maximum of 2 applications per season. lambdacyhalothrin Pyr See Warrior Do not apply more than 7.68 oz per acre per season. Snail and Slug Pellets 3.5% Bait metaldehyde Other slugs, snails Apply every 2 weeks or as needed. Broadcast pellets and wet the soil before or after application. Do not allow pellets to contact edible portion of plant. Keep children, pets and poultry away from treated area. Tracer spinosad Other armyworm, CLB 21 4 Warrior w/ ZeonTech lambdacyhalothrin Pyr aphids, armyworm, CLB, Do not apply more than 7.68 oz per acre per season. 49
Sugar Beet Insect Pests
 Sugar Beet Insect Pests Aphids foliar Although aphids are common, they rarely cause damage. Description: Small oval to pear shaped soft-bodied insects. Color varies from bright green to pink to brown.
Sugar Beet Insect Pests Aphids foliar Although aphids are common, they rarely cause damage. Description: Small oval to pear shaped soft-bodied insects. Color varies from bright green to pink to brown.
Dry Bean Insect Pests
 Dry Bean Insect Pests DRY BEANS Aphids Although common, aphid populations are rarely high enough to cause yield loss. Description: Small oval to pear shaped soft-bodied insects. Color varies from green
Dry Bean Insect Pests DRY BEANS Aphids Although common, aphid populations are rarely high enough to cause yield loss. Description: Small oval to pear shaped soft-bodied insects. Color varies from green
Insect, Nematode, and Disease Control in Michigan Field Crops
 Insect, Nematode, and Disease Control in Michigan Field Crops MSU Bulletin E-1582 2006 Field Season Contributors: Entomology Chris DiFonzo & Michael Jewett Department of Entomology Nematology Fred Warner
Insect, Nematode, and Disease Control in Michigan Field Crops MSU Bulletin E-1582 2006 Field Season Contributors: Entomology Chris DiFonzo & Michael Jewett Department of Entomology Nematology Fred Warner
Specialty Crop Block Grant Program-Farm Bill (FY14)
 Specialty Crop Block Grant Program-Farm Bill (FY) Final Performance Report Grant Title: Nursery & Floriculture Product Mix, Sales, Energy, and Labor Survey Grant #: N00 Grantee: Nursery & Landscape Association
Specialty Crop Block Grant Program-Farm Bill (FY) Final Performance Report Grant Title: Nursery & Floriculture Product Mix, Sales, Energy, and Labor Survey Grant #: N00 Grantee: Nursery & Landscape Association
SLUGS. How to Control Slugs. Non-Chemical Controls Clean up garbage, weeds, boards, and other hiding places from your field. Remove slugs from plants.
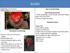 SLUGS Garden slug: Arion hortensis Little gray slug: Deroceras reticulatum How to Control Slugs Non-s Clean up garbage, weeds, boards, and other hiding places from your field. Remove slugs from plants.
SLUGS Garden slug: Arion hortensis Little gray slug: Deroceras reticulatum How to Control Slugs Non-s Clean up garbage, weeds, boards, and other hiding places from your field. Remove slugs from plants.
Crops - Commercial. Soybeans
 Banded cucumber beetle 5 Bean leaf beetle 5 Beet armyworm 3 per s Treated Sevin (Carbaryl) (4) 16 oz 0.5 8 Four beetles per sweep. Karate Z (2.08) 1.28-1.60 oz 0.02-0.025 100-80 Declare (1.25) 1.02-1.28
Banded cucumber beetle 5 Bean leaf beetle 5 Beet armyworm 3 per s Treated Sevin (Carbaryl) (4) 16 oz 0.5 8 Four beetles per sweep. Karate Z (2.08) 1.28-1.60 oz 0.02-0.025 100-80 Declare (1.25) 1.02-1.28
COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE
 COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE UNIVERSITY OF KENTUCKY COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURE ENT - 15 INSECTICIDE RECOMMENDATIONS FOR TOBACCO BEDS AND FIELDS- 1999 Prepared by Lee Townsend, Extension Entomologist These
COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE UNIVERSITY OF KENTUCKY COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURE ENT - 15 INSECTICIDE RECOMMENDATIONS FOR TOBACCO BEDS AND FIELDS- 1999 Prepared by Lee Townsend, Extension Entomologist These
INSECT MANAGEMENT (Phillip Roberts, Mike Toews, and David Buntin)
 INSECT MANAGEMENT (Phillip Roberts, Mike Toews, and David Buntin) A number of insect pests are capable of severely damaging soybeans. However, it is important to realize that soybeans can withstand considerable
INSECT MANAGEMENT (Phillip Roberts, Mike Toews, and David Buntin) A number of insect pests are capable of severely damaging soybeans. However, it is important to realize that soybeans can withstand considerable
Southeastern U.S. Vegetable Handbook eastvegetable guide/
 Southeastern U.S. Vegetable Handbook http://www.thegrower.com/south eastvegetable guide/ http://didc.blogspot.com/2007/10/funny pumpkin pictures.html Scott Stewart The University of Tennessee WTREC, Jackson
Southeastern U.S. Vegetable Handbook http://www.thegrower.com/south eastvegetable guide/ http://didc.blogspot.com/2007/10/funny pumpkin pictures.html Scott Stewart The University of Tennessee WTREC, Jackson
Potato Insects. Frank G. Zalom, Department of Entomology, UC Davis
 Potato Insects Frank G. Zalom, Department of Entomology, UC Davis Whiteflies Bemisia spp. Greenhouse whitefly (GWF) Adults- tiny, 1.5 mm long Bemisia spp. hold wings at an angle, rooflike over body, space
Potato Insects Frank G. Zalom, Department of Entomology, UC Davis Whiteflies Bemisia spp. Greenhouse whitefly (GWF) Adults- tiny, 1.5 mm long Bemisia spp. hold wings at an angle, rooflike over body, space
INSECTICIDE RECOMMENDATIONS FOR POPCORN 2018 Raul T. Villanueva, Extension Entomologist
 INSECTICIDE RECOMMENDATIONS FOR POPCORN 2018 Raul T. Villanueva, Extension Entomologist ENT 62 This publication was prepared as a guide for use in the selection of agricultural insecticides. It is not
INSECTICIDE RECOMMENDATIONS FOR POPCORN 2018 Raul T. Villanueva, Extension Entomologist ENT 62 This publication was prepared as a guide for use in the selection of agricultural insecticides. It is not
Wheat Insect Update. Kathy Flanders. Hradland, August 15, 2012
 Wheat Insect Update Kathy Flanders Hradland, August 15, 2012 West Central Alabama Hessian Fly infestations Plant symptoms April 24: 90% infested stems, average 16 flies per stem, 4 heads/ft2 Hessian fly
Wheat Insect Update Kathy Flanders Hradland, August 15, 2012 West Central Alabama Hessian Fly infestations Plant symptoms April 24: 90% infested stems, average 16 flies per stem, 4 heads/ft2 Hessian fly
INSECTICIDE RECOMMENDATIONS FOR POPCORN ENT -62 Prepared by Ric Bessin and Douglas W. Johnson, Extension Entomologists.
 INSECTICIDE RECOMMENDATIONS FOR POPCORN - 2006 ENT -62 Prepared by Ric Bessin and Douglas W. Johnson, Extension Entomologists This publication was prepared as a guide for use in the selection of agricultural
INSECTICIDE RECOMMENDATIONS FOR POPCORN - 2006 ENT -62 Prepared by Ric Bessin and Douglas W. Johnson, Extension Entomologists This publication was prepared as a guide for use in the selection of agricultural
Wheat Disease Update. Table of Contents. By Laura Sweets. Laura Sweets (573)
 Wheat Disease Update By Laura Sweets Although we have not received very many wheat samples so far this season, there have been a number of phone calls related to possible disease problems and fungicide
Wheat Disease Update By Laura Sweets Although we have not received very many wheat samples so far this season, there have been a number of phone calls related to possible disease problems and fungicide
Common Vegetable Pests
 Common Vegetable Pests Colorado Potato Beetle Yellow and black striped potato beetle. Overwinter in soil as adults. Female beetles lay batches of about 2 dozen orangeyellow eggs on the underside of the
Common Vegetable Pests Colorado Potato Beetle Yellow and black striped potato beetle. Overwinter in soil as adults. Female beetles lay batches of about 2 dozen orangeyellow eggs on the underside of the
INSECTICIDE RECOMMENDATIONS FOR POPCORN ENT -62 Raul T. Villanueva, Extension Entomologist
 INSECTICIDE RECOMMENDATIONS FOR POPCORN - 2019 ENT -62 Raul T. Villanueva, Extension Entomologist This publication was prepared as a guide for use in the selection of agricultural insecticides. It is not
INSECTICIDE RECOMMENDATIONS FOR POPCORN - 2019 ENT -62 Raul T. Villanueva, Extension Entomologist This publication was prepared as a guide for use in the selection of agricultural insecticides. It is not
Fall Armyworms in Hayfields and Pastures
 Fall Armyworms in Hayfields and Pastures Fall armyworms are the most damaging insect pests of Mississippi hayfields and pastures. These caterpillars can destroy a cutting of bermudagrass in just a few
Fall Armyworms in Hayfields and Pastures Fall armyworms are the most damaging insect pests of Mississippi hayfields and pastures. These caterpillars can destroy a cutting of bermudagrass in just a few
Cucumber Beetle Biology and Control in Melons. Diane Alston Entomologist Utah State University Melon Growers Meeting Green River, UT January 31, 2006
 Cucumber Beetle Biology and Control in Melons Diane Alston Entomologist Utah State University Melon Growers Meeting Green River, UT January 31, 2006 Cucumber Beetles Chrysomelidae Leaf Beetles Western
Cucumber Beetle Biology and Control in Melons Diane Alston Entomologist Utah State University Melon Growers Meeting Green River, UT January 31, 2006 Cucumber Beetles Chrysomelidae Leaf Beetles Western
Massachusetts IPM Berry Blast 6/21/11
 Subject: Massachusetts IPM Berry Blast 6/21/11 From: Sonia Schloemann Date: Wed, 22 Jun 2011 08:38:48-0400 To: Sonia Schloemann In this Blast: STAWBERRY: STRAWBERRY
Subject: Massachusetts IPM Berry Blast 6/21/11 From: Sonia Schloemann Date: Wed, 22 Jun 2011 08:38:48-0400 To: Sonia Schloemann In this Blast: STAWBERRY: STRAWBERRY
Protecting Your Dahlias From Bugs and Other Perils. Kevin Larkin Corralitos Gardens For The Monterey Bay Dahlia Society March 2012
 Protecting Your Dahlias From Bugs and Other Perils Kevin Larkin Corralitos Gardens For The Monterey Bay Dahlia Society March 2012 Integrated Pest Management 1. Identification 2. Impact Assessment 3. Intervention
Protecting Your Dahlias From Bugs and Other Perils Kevin Larkin Corralitos Gardens For The Monterey Bay Dahlia Society March 2012 Integrated Pest Management 1. Identification 2. Impact Assessment 3. Intervention
Jerry Brust IPM Vegetable Specialist
 Organic Vegetable Pest Management Jerry Brust IPM Vegetable Specialist Insects Numbers of species Bacteria and Fungi Animals Plants Other Arthropods Insects Metamorphosis: Complete Metamorphosis: Incomplete
Organic Vegetable Pest Management Jerry Brust IPM Vegetable Specialist Insects Numbers of species Bacteria and Fungi Animals Plants Other Arthropods Insects Metamorphosis: Complete Metamorphosis: Incomplete
Crop Profile for Carrots in Ohio
 Crop Profile for Carrots in Ohio Prepared: December, 2000 General Production Information Acres in Ohio: 1350 Percent of US Acreage/Rank: 1%/11th Number of Growers: 39 Daucus carota Location of Production:
Crop Profile for Carrots in Ohio Prepared: December, 2000 General Production Information Acres in Ohio: 1350 Percent of US Acreage/Rank: 1%/11th Number of Growers: 39 Daucus carota Location of Production:
Pest Management in Vegetable Gardens. Pam Brown Extension Agent Emeritus, Gardening Coach Pampered Gardeners, LLC
 Pest Management in Vegetable Gardens Pam Brown Extension Agent Emeritus, Gardening Coach Pampered Gardeners, LLC pamperedgardeners@gmail.com Pest Management Involves: Providing proper cultural practices
Pest Management in Vegetable Gardens Pam Brown Extension Agent Emeritus, Gardening Coach Pampered Gardeners, LLC pamperedgardeners@gmail.com Pest Management Involves: Providing proper cultural practices
Pests of Landscape Trees. Wizzie Brown Texas A&M Agrilife Extension
 Pests of Landscape Trees Wizzie Brown Texas A&M Agrilife Extension Tips for pest management Always identify the insect Pest vs. beneficial Biological Control Using other organisms to control a pest Conservation
Pests of Landscape Trees Wizzie Brown Texas A&M Agrilife Extension Tips for pest management Always identify the insect Pest vs. beneficial Biological Control Using other organisms to control a pest Conservation
Practical Pest Management A workshop provided by Growing Places Volunteers Gaynor Bigelbach and Connie Grabowy
 Practical Pest Management A workshop provided by Growing Places Volunteers Gaynor Bigelbach and Connie Grabowy The first step towards building a healthy vegetable garden is regular maintenance. By keeping
Practical Pest Management A workshop provided by Growing Places Volunteers Gaynor Bigelbach and Connie Grabowy The first step towards building a healthy vegetable garden is regular maintenance. By keeping
The adult grasshoppers deposit eggs from late July through the fall. Usually only one generation of grasshoppers is produced each year.
 Grasshoppers! Posted on July 22, 2015 by vanessa.corriher Grasshoppers resting on a weed There are about 150 species of grasshoppers in the state of Texas, but 90% of the damage to crops, gardens, trees,
Grasshoppers! Posted on July 22, 2015 by vanessa.corriher Grasshoppers resting on a weed There are about 150 species of grasshoppers in the state of Texas, but 90% of the damage to crops, gardens, trees,
Lync Session 3 9/21/15
 Lync Session 3 9/21/15 Life cycles & development White grubs Sawflies Fruit flies Jessica and Linda Life cycles and development White grubs Annual Japanese beetle, masked chafers Green June beetle Multi
Lync Session 3 9/21/15 Life cycles & development White grubs Sawflies Fruit flies Jessica and Linda Life cycles and development White grubs Annual Japanese beetle, masked chafers Green June beetle Multi
Caterpillars (Lepidoptera)
 Caterpillars (Lepidoptera) Caterpillars (Lepidoptera) Mainly Families Noctuidae, Pyralidae, and Tortricidae by Dr.Richard Lindquist OARDC Dept. of Entomology The Ohio State University Many species of Lepidoptera
Caterpillars (Lepidoptera) Caterpillars (Lepidoptera) Mainly Families Noctuidae, Pyralidae, and Tortricidae by Dr.Richard Lindquist OARDC Dept. of Entomology The Ohio State University Many species of Lepidoptera
Home Vegetable Garden Insect Pest Control
 Oklahoma Cooperative Extension Service F-7313 Home Vegetable Garden Insect Pest Control Jonathan Edelson Entomology Specialist Brenda Simons Assistant Extension Specialist -Horticulture David Hillock Assistant
Oklahoma Cooperative Extension Service F-7313 Home Vegetable Garden Insect Pest Control Jonathan Edelson Entomology Specialist Brenda Simons Assistant Extension Specialist -Horticulture David Hillock Assistant
Pennsylvania Fresh-market Sweet Corn IPM. by Shelby Fleischer, Lee Young & David Biddinger 11/9/07
 Pennsylvania Fresh-market Sweet Corn IPM by Shelby Fleischer, Lee Young & David Biddinger 11/9/07 Pennsylvania sweet corn production ranks in the top ten nationally with more than 20,000 acres worth about
Pennsylvania Fresh-market Sweet Corn IPM by Shelby Fleischer, Lee Young & David Biddinger 11/9/07 Pennsylvania sweet corn production ranks in the top ten nationally with more than 20,000 acres worth about
One of the most important nut-infesting
 L-5134 2-00 Controlling the Pecan Nut Casebearer Allen Knutson and Bill Ree* One of the most important nut-infesting insect pests of pecan is the pecan nut casebearer. It is found in all pecangrowing regions
L-5134 2-00 Controlling the Pecan Nut Casebearer Allen Knutson and Bill Ree* One of the most important nut-infesting insect pests of pecan is the pecan nut casebearer. It is found in all pecangrowing regions
Biology and Management of Cucurbit Insect Pests
 Biology and of Cucurbit Insect Pests Rick Foster Purdue University The cucurbit crops are attacked by a wide variety of insects. Cucumber beetles tend to be the most important pests of cucumber and muskmelon,
Biology and of Cucurbit Insect Pests Rick Foster Purdue University The cucurbit crops are attacked by a wide variety of insects. Cucumber beetles tend to be the most important pests of cucumber and muskmelon,
Common Insect Pests of Cucurbits
 Agnote 805 No. I59 December 2003 Agdex No: 263/622 ISSN No: 0157-8243 Common Insect Pests of Cucurbits H. Brown, Entomology, Darwin INTROD UC TION Cucurbits are a major horticultural crop in the Northern
Agnote 805 No. I59 December 2003 Agdex No: 263/622 ISSN No: 0157-8243 Common Insect Pests of Cucurbits H. Brown, Entomology, Darwin INTROD UC TION Cucurbits are a major horticultural crop in the Northern
Ash. Pest Damage on. Plant Problem. September September 1 10 October September November November November 1 10
 Pest Damage on Ash March 21 31 March 11 20 March 1 10 April 21 30 April 11 20 April 1 10 May 21 31 May 11 20 May 1 10 June 21 30 June 11 20 June 1 10 July 21 31 July 11 20 July 1 10 August 21 31 August
Pest Damage on Ash March 21 31 March 11 20 March 1 10 April 21 30 April 11 20 April 1 10 May 21 31 May 11 20 May 1 10 June 21 30 June 11 20 June 1 10 July 21 31 July 11 20 July 1 10 August 21 31 August
flattened, or in groups, in crevices beneath the bark. The eggs soon hatch, and the larvae bore into the sapwood where they make tortuous
 j ^ju Agriculture Canada Publication 1718 B Major pests of birch and maple trees The birch leafminer The birch leafminer (Fenusa pusilla Lepeletier) attacks the white or paper birch (Betula papyrifera
j ^ju Agriculture Canada Publication 1718 B Major pests of birch and maple trees The birch leafminer The birch leafminer (Fenusa pusilla Lepeletier) attacks the white or paper birch (Betula papyrifera
Propagation. Pests and Diseases. Aphids
 Hibiscus, Chinese Hibiscus Hibiscus rosa-sinensis Propagation Hibiscus are normally propagated by softwood stem tip cuttings taken in late spring. Intermittent mist with soil temperatures of 70 degrees
Hibiscus, Chinese Hibiscus Hibiscus rosa-sinensis Propagation Hibiscus are normally propagated by softwood stem tip cuttings taken in late spring. Intermittent mist with soil temperatures of 70 degrees
Shade Tree Insect and Mite Pests Larry Sagers Extension Horticulture Specialist Utah State University Extension Service Thanksgiving Point Office
 Shade Tree Insect and Mite Pests Larry Sagers Extension Horticulture Specialist Utah State University Extension Service Thanksgiving Point Office Shade tree pests cause problems including: Nuisance Defoliation
Shade Tree Insect and Mite Pests Larry Sagers Extension Horticulture Specialist Utah State University Extension Service Thanksgiving Point Office Shade tree pests cause problems including: Nuisance Defoliation
INSECTS ON TOBACCO. David C. Jones SOIL INSECTS
 INSECTS ON TOBACCO David C. Jones SOIL INSECTS WIREWORMS Wireworms, the most damaging soil insect pests of tobacco, are present in the soil at transplanting. They damage tobacco by feeding and tunneling
INSECTS ON TOBACCO David C. Jones SOIL INSECTS WIREWORMS Wireworms, the most damaging soil insect pests of tobacco, are present in the soil at transplanting. They damage tobacco by feeding and tunneling
Tree Fruit IPM Advisory
 Tree Fruit IPM Advisory Weekly Orchard Pest Update, Utah State University Extension, April 7, 2010 Welcome to the 2010 tree fruit advisory season! Get ready for another great harvest of fresh - and pest-free
Tree Fruit IPM Advisory Weekly Orchard Pest Update, Utah State University Extension, April 7, 2010 Welcome to the 2010 tree fruit advisory season! Get ready for another great harvest of fresh - and pest-free
PECANS PRODUCT OVERVIEW & UPDATES
 PECANS PRODUCT OVERVIEW & UPDATES Presentation Outline List of Dow AgroSciences Pecan Products 2-3 Slides each on new products Closer & IntrepidEdge Who to contact for more info Bonus Slides on Closer
PECANS PRODUCT OVERVIEW & UPDATES Presentation Outline List of Dow AgroSciences Pecan Products 2-3 Slides each on new products Closer & IntrepidEdge Who to contact for more info Bonus Slides on Closer
IPM for Common Fruit Tree Insect Problems Diane Alston, Entomologist, Utah State University. Utah Green Industry Conference January 25, 2016
 IPM for Common Fruit Tree Insect Problems Diane Alston, Entomologist, Utah State University Utah Green Industry Conference January 25, 2016 Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Sustainable Economics, Environment,
IPM for Common Fruit Tree Insect Problems Diane Alston, Entomologist, Utah State University Utah Green Industry Conference January 25, 2016 Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Sustainable Economics, Environment,
Insect Pest Management in Louisiana Sweet Potatoes
 Insect Pest Management in Louisiana Sweet Potatoes Soil insects can pose serious problems in Louisiana sweet potato production. The majority of insect damage in sweet potatoes occurs on the root surfaces
Insect Pest Management in Louisiana Sweet Potatoes Soil insects can pose serious problems in Louisiana sweet potato production. The majority of insect damage in sweet potatoes occurs on the root surfaces
Raspberry Insect & Mite Biology & Management. Diane Alston Utah State University The 1 st Annual Utah Raspberry Meeting February 23, 2006
 Raspberry Insect & Mite Biology & Management Diane Alston Utah State University The 1 st Annual Utah Raspberry Meeting February 23, 2006 Raspberry Horntail Most common insect pest of raspberry canes in
Raspberry Insect & Mite Biology & Management Diane Alston Utah State University The 1 st Annual Utah Raspberry Meeting February 23, 2006 Raspberry Horntail Most common insect pest of raspberry canes in
Insect Pest Management in Louisiana Sweet Potatoes
 Insect Pest Management in Louisiana Sweet Potatoes Soil insect pests can be extremely problematic in Louisiana sweet potato production. The majority of insect damage in sweet potato occurs on the root
Insect Pest Management in Louisiana Sweet Potatoes Soil insect pests can be extremely problematic in Louisiana sweet potato production. The majority of insect damage in sweet potato occurs on the root
VEGETABLE INSECTS. rev. 11/04 1
 VEGETABLE INSECTS Flea Beetles Flea beetles are tiny, black, jumping insects that chew small, round holes in the leaves of young tomatoes, eggplant, potatoes and related plants, as well as spinach, beets,
VEGETABLE INSECTS Flea Beetles Flea beetles are tiny, black, jumping insects that chew small, round holes in the leaves of young tomatoes, eggplant, potatoes and related plants, as well as spinach, beets,
Potato XXII Green Peach Aphid
 Potato XXII Green Peach Aphid Whitney S. Cranshaw, Gary L. Hein Green Peach Aphid Identification (and life cycle/seasonal history) Aphids of importance to potato winter as eggs laid near buds of woody
Potato XXII Green Peach Aphid Whitney S. Cranshaw, Gary L. Hein Green Peach Aphid Identification (and life cycle/seasonal history) Aphids of importance to potato winter as eggs laid near buds of woody
Integrated pest management on vegetables for insect pests and vectors in South Texas
 Integrated pest management on vegetables for insect pests and vectors in South Texas Adrian Silva and Ismael E. Badillo-Vargas Texas A&M AgriLife Research August 2016 Insect pests of vegetables in the
Integrated pest management on vegetables for insect pests and vectors in South Texas Adrian Silva and Ismael E. Badillo-Vargas Texas A&M AgriLife Research August 2016 Insect pests of vegetables in the
Cottonwood. Pest Damage on. Plant Problem. September September 1 10 October September November November November 1 10
 Pest Damage on March 21 31 March 11 20 March 1 10 April 21 30 April 11 20 April 1 10 May 21 31 May 11 20 May 1 10 June 21 30 June 11 20 June 1 10 July 21 31 July 11 20 July 1 10 August 21 31 August 11
Pest Damage on March 21 31 March 11 20 March 1 10 April 21 30 April 11 20 April 1 10 May 21 31 May 11 20 May 1 10 June 21 30 June 11 20 June 1 10 July 21 31 July 11 20 July 1 10 August 21 31 August 11
9/25/2013. Soil pests 2: White Grubs. Sclerotized head Chewing mouthparts 3 pr segmented legs No prolegs C shaped soft body
 Soil pests 2: White Grubs Coleoptera Scarabaeidae (scarabs) Leaf feeders, decomposers, dung beetles Larvae are white grubs White Grubs Sclerotized head Chewing mouthparts 3 pr segmented legs No prolegs
Soil pests 2: White Grubs Coleoptera Scarabaeidae (scarabs) Leaf feeders, decomposers, dung beetles Larvae are white grubs White Grubs Sclerotized head Chewing mouthparts 3 pr segmented legs No prolegs
EC Entomology : Lawn Insect Control
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Historical Materials from University of Nebraska- Lincoln Extension Extension 1967 EC67-1599 Entomology : Lawn Insect Control
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Historical Materials from University of Nebraska- Lincoln Extension Extension 1967 EC67-1599 Entomology : Lawn Insect Control
Mid-late Season Pest Management for Day Neutral Strawberries. Small Fruit Conference, Julie Pond, Peerbolt Crop Management
 Mid-late Season Pest Management for Day Neutral Strawberries Small Fruit Conference, 11-29-2018 Julie Pond, Peerbolt Crop Management Pests of concern in Day Neutral production: Thrips Lygus Bug Spotted
Mid-late Season Pest Management for Day Neutral Strawberries Small Fruit Conference, 11-29-2018 Julie Pond, Peerbolt Crop Management Pests of concern in Day Neutral production: Thrips Lygus Bug Spotted
Fruit and Nuts Commercial. Peach Spray Schedule
 Dormant Scales, if present Severe Scale infestations Oil emulsion, 3% actual oil in diluted spray (follow recommendations of manufacturer). Two sprays must be conducted at least 1 week and no more than
Dormant Scales, if present Severe Scale infestations Oil emulsion, 3% actual oil in diluted spray (follow recommendations of manufacturer). Two sprays must be conducted at least 1 week and no more than
IPM for Master Gardeners. Mary Louise Flint, Ph.D. Extension Entomologist Emerita Department of Entomology University of California, Davis
 IPM for Master Gardeners Mary Louise Flint, Ph.D. Extension Entomologist Emerita Department of Entomology University of California, Davis What is IPM? Ecosystem-based strategy Focuses on long-term prevention
IPM for Master Gardeners Mary Louise Flint, Ph.D. Extension Entomologist Emerita Department of Entomology University of California, Davis What is IPM? Ecosystem-based strategy Focuses on long-term prevention
Crop Profile for Radishes in Ohio
 Prepared: December, 1999 Crop Profile for Radishes in Ohio General Production Information (Cruciferae: Raphanus sativus) Acres in Ohio: 2,130 (5) - 100% for fresh market Percent of US Acreage/Rank: 8.87%/3rd
Prepared: December, 1999 Crop Profile for Radishes in Ohio General Production Information (Cruciferae: Raphanus sativus) Acres in Ohio: 2,130 (5) - 100% for fresh market Percent of US Acreage/Rank: 8.87%/3rd
Integrated Pest Management. University of California Statewide IPM Program
 Integrated Pest Management University of California Statewide IPM Program In this presentation. Define IPM Explain what s in an IPM program How IPM can be applied to your garden and orchard Examples of
Integrated Pest Management University of California Statewide IPM Program In this presentation. Define IPM Explain what s in an IPM program How IPM can be applied to your garden and orchard Examples of
VegNet Vol. 11, No. 14. July 15, 2004 Ohio State University Extension Vegetable Crops On the WEB at: If experiencing
 VegNet Vol. 11, No. 14. July 15, 2004 Ohio State University Extension Vegetable Crops On the WEB at: http://vegnet.osu.edu If experiencing problems receiving this fax, Call 614-292-3857 In This Issue 1.
VegNet Vol. 11, No. 14. July 15, 2004 Ohio State University Extension Vegetable Crops On the WEB at: http://vegnet.osu.edu If experiencing problems receiving this fax, Call 614-292-3857 In This Issue 1.
Alfalfa Field Guide Creative Component Presentation by Lucas Westerman
 Alfalfa Field Guide Creative Component Presentation by Lucas Westerman Introduction My background CC selection CC development Research Conclusion My Background Chokio, MN Family Farm County SWCD My Background
Alfalfa Field Guide Creative Component Presentation by Lucas Westerman Introduction My background CC selection CC development Research Conclusion My Background Chokio, MN Family Farm County SWCD My Background
Rose. Pest Damage on. Plant Problem. September September September 1 10 October November November 1 10.
 Pest Damage on Rose March 21 31 March 11 20 March 1 10 April 21 30 April 11 20 April 1 10 May 21 31 May 11 20 May 1 10 June 21 30 June 11 20 June 1 10 July 21 31 July 11 20 July 1 10 August 21 31 August
Pest Damage on Rose March 21 31 March 11 20 March 1 10 April 21 30 April 11 20 April 1 10 May 21 31 May 11 20 May 1 10 June 21 30 June 11 20 June 1 10 July 21 31 July 11 20 July 1 10 August 21 31 August
Propagation. Pests and Diseases. Black twig borer (Xylosandrus compactus) Magnolia white scale (Pseudaulacaspis cockerelli)
 Magnolia, Southern Magnolia Magnolia grandiflora Propagation Magnolias are usually propagated by semi-hardwood stem tip cuttings taken in the summer. Rooting should occur in 9 weeks with IBA Quick Dip
Magnolia, Southern Magnolia Magnolia grandiflora Propagation Magnolias are usually propagated by semi-hardwood stem tip cuttings taken in the summer. Rooting should occur in 9 weeks with IBA Quick Dip
Understanding Vegetable Garden Insects. Roy Beckford Ag/Natural Resources Agent UF/IFAS Lee County Extension
 Understanding Vegetable Garden Insects Roy Beckford Ag/Natural Resources Agent UF/IFAS Lee County Extension fbeckford@leegov.com 239-533-7512 There are lots of pests out there are there? Integrated Pest
Understanding Vegetable Garden Insects Roy Beckford Ag/Natural Resources Agent UF/IFAS Lee County Extension fbeckford@leegov.com 239-533-7512 There are lots of pests out there are there? Integrated Pest
TURF. Recommendations for lawns and recreational areas not grazed by livestock.
 TURF G. Byrtus Last updated: May 2005 Recommendations for lawns and recreational areas not grazed by livestock. Important: Mow the lawn before treatment. Keep off treated lawns until dry. Important regulatory
TURF G. Byrtus Last updated: May 2005 Recommendations for lawns and recreational areas not grazed by livestock. Important: Mow the lawn before treatment. Keep off treated lawns until dry. Important regulatory
Greenhouse Pest Management. Greenhouse pests. Fungus gnat -damage by larvae
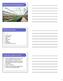 Greenhouse Pest Management Greenhouse pests Thrips Whiteflies Fungus gnats Shore flies Mites Bulb mites Aphids Mealybugs Leaf miners (rare in IN) Fungus gnat -damage by larvae Larvae (maggots) feed on
Greenhouse Pest Management Greenhouse pests Thrips Whiteflies Fungus gnats Shore flies Mites Bulb mites Aphids Mealybugs Leaf miners (rare in IN) Fungus gnat -damage by larvae Larvae (maggots) feed on
INSECT CONTROL IN COMMERCIAL TURF
 INSECT CONTROL IN COMMERCIAL TURF Will Hudson, Extension Entomologist Not all turfgrass sites are created equal. It is important to read the label on the product before purchasing an insecticide for a
INSECT CONTROL IN COMMERCIAL TURF Will Hudson, Extension Entomologist Not all turfgrass sites are created equal. It is important to read the label on the product before purchasing an insecticide for a
TOBACCO INSECT MANAGEMENT Paul J. Semtner, Retired Extension Entomologist
 TOBACCO INSECT MANAGEMENT Paul J. Semtner, Retired Extension Entomologist Several species of insects cause serious damage to tobacco in the field, the greenhouse, and in storage. Insects damage the roots,
TOBACCO INSECT MANAGEMENT Paul J. Semtner, Retired Extension Entomologist Several species of insects cause serious damage to tobacco in the field, the greenhouse, and in storage. Insects damage the roots,
Managing Insect and Mite Pests of Commercial Pecans in Texas
 E 215 9-04 Managing Insect and Mite Pests of Commercial Pecans in Texas Green lacewing adult Contents Pest management principles...3 Biological control...3 Insecticide application...4 Chemical use precautions...4
E 215 9-04 Managing Insect and Mite Pests of Commercial Pecans in Texas Green lacewing adult Contents Pest management principles...3 Biological control...3 Insecticide application...4 Chemical use precautions...4
Master Gardener Volunteer Program
 Master Gardener Volunteer Program Level 1 Training Plant Presentation-Final Exam 1. Common Name: a. Asparagus 2. Scientific name: a. Asparagus officinalis, genus of the family Asparagaceae 3. Cold hardiness
Master Gardener Volunteer Program Level 1 Training Plant Presentation-Final Exam 1. Common Name: a. Asparagus 2. Scientific name: a. Asparagus officinalis, genus of the family Asparagaceae 3. Cold hardiness
Home Vegetable Garden Insect Pest Control
 Oklahoma Cooperative Extension Service EPP-7313 Home Vegetable Garden Insect Pest Control Eric Rebek Associate Professor and State Extension Specialist Horticultural Entomology David Hillock Assistant
Oklahoma Cooperative Extension Service EPP-7313 Home Vegetable Garden Insect Pest Control Eric Rebek Associate Professor and State Extension Specialist Horticultural Entomology David Hillock Assistant
Managing Insects in Wheat with Special Reference to Cereal Aphids and Barley Yellow Dwarf
 Managing Insects in Wheat with Special Reference to Cereal Aphids and Barley Yellow Dwarf Douglas W. Johnson 1 Introduction Kentucky is located in a unique ecological situation between the cold winters
Managing Insects in Wheat with Special Reference to Cereal Aphids and Barley Yellow Dwarf Douglas W. Johnson 1 Introduction Kentucky is located in a unique ecological situation between the cold winters
Beneficial Insects. Your best buddies for pest control
 Beneficial Insects Your best buddies for pest control Convergent Lady Beetle Adults are generalist predators (especially aphids), also feed on chinch bugs, whiteflies, mites and many other soft-bodied
Beneficial Insects Your best buddies for pest control Convergent Lady Beetle Adults are generalist predators (especially aphids), also feed on chinch bugs, whiteflies, mites and many other soft-bodied
Integrated Pest Management
 Integrated Pest Management Integrated Pest Management is a term used to describe an effective and environmentally sensitive approach to pest management. IPM relies on an intimate knowledge of the life
Integrated Pest Management Integrated Pest Management is a term used to describe an effective and environmentally sensitive approach to pest management. IPM relies on an intimate knowledge of the life
Horticulture 2016 Newsletter
 Horticulture 2016 Newsletter No. 19 May 10, 2016 2021 Throckmorton Plant Science Cntr. Manhattan, KS 66506 (785) 532-6173 Video of the Week: Cantaloupe - Varieities for Small Spaces Garden Tour in Kansas
Horticulture 2016 Newsletter No. 19 May 10, 2016 2021 Throckmorton Plant Science Cntr. Manhattan, KS 66506 (785) 532-6173 Video of the Week: Cantaloupe - Varieities for Small Spaces Garden Tour in Kansas
Insect Pest Management in Eggplant
 2008 Insect Pest Management in Eggplant While eggplant production in Maryland is rather small, they are grown over the entire state to supply vegetable stands with many varieties. Because of its value
2008 Insect Pest Management in Eggplant While eggplant production in Maryland is rather small, they are grown over the entire state to supply vegetable stands with many varieties. Because of its value
Organic Growing Workshop: 10 Common Garden Insect Pests & How to Control Them Organically
 Organic Growing Workshop: 10 Common Garden Insect Pests & How to Control Them Organically Diane Alston Entomologist Utah State University Extension March 12, 2016 Common Tree Fruit Insect Pests codling
Organic Growing Workshop: 10 Common Garden Insect Pests & How to Control Them Organically Diane Alston Entomologist Utah State University Extension March 12, 2016 Common Tree Fruit Insect Pests codling
CRP Conversion: Missouri
 Water Resources: BIOEN3 Issues & Opportunities in March 2012 Bioenergy Generation Factsheet 3.2.5 CRP Conversion: Missouri As CRP contracts expire, producers must decide whether to renew the contract or
Water Resources: BIOEN3 Issues & Opportunities in March 2012 Bioenergy Generation Factsheet 3.2.5 CRP Conversion: Missouri As CRP contracts expire, producers must decide whether to renew the contract or
Science of Life Explorations
 Science of Life Explorations Biological Control and Beneficial Insects IPM uses Biological Control When is something a pest? A pest is what we call living things that are causing problems, such as insects
Science of Life Explorations Biological Control and Beneficial Insects IPM uses Biological Control When is something a pest? A pest is what we call living things that are causing problems, such as insects
Using IPM in your Ag Program- Understanding Texas Laws
 Using IPM in your Ag Program- Understanding Texas Laws What we will cover Basics of School IPM regulations IPM for Greenhouses What are biocontrols Exclusion Cultural controls Sanitation Scouting Identifying
Using IPM in your Ag Program- Understanding Texas Laws What we will cover Basics of School IPM regulations IPM for Greenhouses What are biocontrols Exclusion Cultural controls Sanitation Scouting Identifying
SEED- AND SOIL-BORNE SOYBEAN DISEASE & INSECT GUIDE
 SEED- AND SOIL-BORNE SOYBEAN DISEASE & INSECT GUIDE SEED- AND SOIL-BORNE SOYBEAN DISEASE AND INSECT GUIDE WELCOME TO SOY MASTERS LET'S REDEFINE SUCCESS IN YOUR SOYBEANS Soy Masters is about helping you
SEED- AND SOIL-BORNE SOYBEAN DISEASE & INSECT GUIDE SEED- AND SOIL-BORNE SOYBEAN DISEASE AND INSECT GUIDE WELCOME TO SOY MASTERS LET'S REDEFINE SUCCESS IN YOUR SOYBEANS Soy Masters is about helping you
Maize insect pest management. Northern grains region
 Maize insect pest management Northern grains region Compiled by Kate Charleston, March 2013 This publication has been compiled by Kate Charleston of Crop and Food Science, Queensland Department of Agriculture,
Maize insect pest management Northern grains region Compiled by Kate Charleston, March 2013 This publication has been compiled by Kate Charleston of Crop and Food Science, Queensland Department of Agriculture,
GOOD BUGS---BAD BUGS
 GOOD BUGS---BAD BUGS A happy garden is when what you think, what you know and what you do in the garden are in harmony. Gandhi As global temperatures rise, many insects are shifting their ranges northward.
GOOD BUGS---BAD BUGS A happy garden is when what you think, what you know and what you do in the garden are in harmony. Gandhi As global temperatures rise, many insects are shifting their ranges northward.
Insect Management for Onions, Leek, and Garlic 1
 ENY-467 Insect Management for Onions, Leek, and Garlic 1 S. E. Webb 2 Sweet varieties of bulbing onions, which make bulbs under short day conditions and do not store well, are by far the most common onions
ENY-467 Insect Management for Onions, Leek, and Garlic 1 S. E. Webb 2 Sweet varieties of bulbing onions, which make bulbs under short day conditions and do not store well, are by far the most common onions
Prionus root borer: biology, behavior and management. Angelita L. Acebes-Doria Tree Nut Entomology University of Georgia - Tifton
 Prionus root borer: biology, behavior and management Angelita L. Acebes-Doria Tree Nut Entomology University of Georgia - Tifton Foliage Feeders Aphids, Mites, Phylloxera, Leaffeeding caterpillars Nut
Prionus root borer: biology, behavior and management Angelita L. Acebes-Doria Tree Nut Entomology University of Georgia - Tifton Foliage Feeders Aphids, Mites, Phylloxera, Leaffeeding caterpillars Nut
Unit G: Pest Management. Lesson 4: Managing Insects
 Unit G: Pest Management Lesson 4: Managing Insects 1 Terms Ametamorphic Antennae Antibiosis control Beneficial insect Biological control Chemical control Chitin Clean culture Complete metamorphosis Cultural
Unit G: Pest Management Lesson 4: Managing Insects 1 Terms Ametamorphic Antennae Antibiosis control Beneficial insect Biological control Chemical control Chitin Clean culture Complete metamorphosis Cultural
Insect Pests. Cooperative Extension work in Agriculture and Home Economics, Gene M. Lear, director. Oregon
 Ve9etaide Insect Pests COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE OREGON STATE UNIVERSITY CORVALLIS Cooperative Extension work in Agriculture and Home Economics, Gene M. Lear, director. Oregon State University and
Ve9etaide Insect Pests COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE OREGON STATE UNIVERSITY CORVALLIS Cooperative Extension work in Agriculture and Home Economics, Gene M. Lear, director. Oregon State University and
satg WATERMELON CULTIVATION DISEASES PESTS
 satg WATERMELON CULTIVATION DISEASES PESTS Contents Cultivation Climate Requirements...4 a. Temperature...4 b. Exposure...4 Land Preparation...5 A. Soil Requirements...5 B. Propagation...5 Planting...6
satg WATERMELON CULTIVATION DISEASES PESTS Contents Cultivation Climate Requirements...4 a. Temperature...4 b. Exposure...4 Land Preparation...5 A. Soil Requirements...5 B. Propagation...5 Planting...6
Codling Moth Control at Hoch Orchard
 Codling Moth Control at Hoch Orchard April 2011 By Harry Hoch CM control on Hoch Orchard takes a truly integrated approach. There is no single silver bullet that can take care of the problem. We use a
Codling Moth Control at Hoch Orchard April 2011 By Harry Hoch CM control on Hoch Orchard takes a truly integrated approach. There is no single silver bullet that can take care of the problem. We use a
An America Rose Society Presentation 2005
 An America Rose Society Presentation 2005 IPM OF ROSE PESTS Baldo Villegas Entomologist; ARS Master Rosarian Sacramento, CA USDA (Zone 8/9) EMail: sactorose@yahoo.com Home Page: http://www.sactorose.org/
An America Rose Society Presentation 2005 IPM OF ROSE PESTS Baldo Villegas Entomologist; ARS Master Rosarian Sacramento, CA USDA (Zone 8/9) EMail: sactorose@yahoo.com Home Page: http://www.sactorose.org/
What soil characteristics are suitable for alfalfa production?
 UNIT -FORAGES Lesson 4: TEACHING Establishing and Maintaining Alfalfa PROCEDURES A Rev iew Rev iew the prev ious lessons. B. Motivation Alfalfa is the premier forage legume. It is used for hay, silage,
UNIT -FORAGES Lesson 4: TEACHING Establishing and Maintaining Alfalfa PROCEDURES A Rev iew Rev iew the prev ious lessons. B. Motivation Alfalfa is the premier forage legume. It is used for hay, silage,
Common Hop Pests & Diseases and Their Control. Rosalie Madden, MSc, P.Ag., CCA Horticulture Crops Specialist
 Common Hop Pests & Diseases and Their Control Rosalie Madden, MSc, P.Ag., CCA Horticulture Crops Specialist March 10, 2016 UVM Extension Hops Website Informational Articles Blog YouTube Videos Wiki Other
Common Hop Pests & Diseases and Their Control Rosalie Madden, MSc, P.Ag., CCA Horticulture Crops Specialist March 10, 2016 UVM Extension Hops Website Informational Articles Blog YouTube Videos Wiki Other
Winter Canola Production in Oklahoma. Heath Sanders Extension Assistant (Winter Canola) Oklahoma State University
 Winter Canola Production in Oklahoma Heath Sanders Extension Assistant (Winter Canola) Oklahoma State University Why Canola? Clean up weedy wheat fields. More profit than wheat. Breakup wheat disease cycles.
Winter Canola Production in Oklahoma Heath Sanders Extension Assistant (Winter Canola) Oklahoma State University Why Canola? Clean up weedy wheat fields. More profit than wheat. Breakup wheat disease cycles.
Common Rose and Garden Pests
 Image: http://www.insectid.ento.vt.edu Common Rose and Garden Pests 2014 1835 E. Guiberson Road, Fillmore, California 93015 (805) 524-2123 Notes Table of Contents Arthropod Pests Aphid 2 Mites 4 Thrips
Image: http://www.insectid.ento.vt.edu Common Rose and Garden Pests 2014 1835 E. Guiberson Road, Fillmore, California 93015 (805) 524-2123 Notes Table of Contents Arthropod Pests Aphid 2 Mites 4 Thrips
DIAGNOSING VEGETABLE PROBLEMS
 DIAGNOSING VEGETABLE PROBLEMS DIAGNOSING ARTHROPOD PESTS OF VEGETABLES 2 Primary Injury Types: Chewing Sap-sucking CORN EARWORM Corn: caterpillars feed on new silks & ear tips; reduce pollination & damage
DIAGNOSING VEGETABLE PROBLEMS DIAGNOSING ARTHROPOD PESTS OF VEGETABLES 2 Primary Injury Types: Chewing Sap-sucking CORN EARWORM Corn: caterpillars feed on new silks & ear tips; reduce pollination & damage
Cucurbit Powdery Mildew is Here by Sally Miller
 VegNet Vol. 13, No. 11. July 14, 2006 Ohio State University Extension Vegetable Crops On the WEB at: http://vegnet.osu.edu If experiencing problems receiving this fax, Call 614-292-3857 In This Issue 1.
VegNet Vol. 13, No. 11. July 14, 2006 Ohio State University Extension Vegetable Crops On the WEB at: http://vegnet.osu.edu If experiencing problems receiving this fax, Call 614-292-3857 In This Issue 1.
Invertebrate Pest Management in Rice
 Invertebrate Pest Management in Rice California Rice Production Workshop, 2003-1 Numerous species of invertebrate animals are found in rice fields. These species are adapted to utilize the short-term aquatic
Invertebrate Pest Management in Rice California Rice Production Workshop, 2003-1 Numerous species of invertebrate animals are found in rice fields. These species are adapted to utilize the short-term aquatic
MSU Extension Publication Archive. Scroll down to view the publication.
 MSU Extension Publication Archive Archive copy of publication, do not use for current recommendations. Up-to-date information about many topics can be obtained from your local Extension office. Common
MSU Extension Publication Archive Archive copy of publication, do not use for current recommendations. Up-to-date information about many topics can be obtained from your local Extension office. Common
Celery. Spacing. Soils. Fertilizing. Transplants. Pesticide Use in Greenhouses. Harvesting
 Celery Spacing Typical spacing for celery is rows 2 feet apart with plants 6 inches apart in row. One plant per square foot. Soils Traditionally, celery has been grown on muck soils, but it can be grown
Celery Spacing Typical spacing for celery is rows 2 feet apart with plants 6 inches apart in row. One plant per square foot. Soils Traditionally, celery has been grown on muck soils, but it can be grown
STALK ROTS. When to look for: Mid-August to Early October
 Figure 19. Lodging of corn plants due to stalk rot damage. Photo courtesy of MAFRI. Figure 20. Shredding of internal tissues of a corn stalk by a stalk rot pathogen. Photo courtesy of MAFRI. STALK ROTS
Figure 19. Lodging of corn plants due to stalk rot damage. Photo courtesy of MAFRI. Figure 20. Shredding of internal tissues of a corn stalk by a stalk rot pathogen. Photo courtesy of MAFRI. STALK ROTS
Maple. Pest Damage on. Plant Problem. September September September 1 10 October November November 1 10.
 Pest Damage on March 21 31 March 11 20 March 1 10 April 21 30 April 11 20 April 1 10 May 21 31 May 11 20 May 1 10 June 21 30 June 11 20 June 1 10 July 21 31 July 11 20 July 1 10 August 21 31 August 11
Pest Damage on March 21 31 March 11 20 March 1 10 April 21 30 April 11 20 April 1 10 May 21 31 May 11 20 May 1 10 June 21 30 June 11 20 June 1 10 July 21 31 July 11 20 July 1 10 August 21 31 August 11
 Plant Pests People depend on plants for many reasons. They provide food, wood, fibers for clothing, even oxygen for us to breathe. We grow plants for these and many more useful products as well as for
Plant Pests People depend on plants for many reasons. They provide food, wood, fibers for clothing, even oxygen for us to breathe. We grow plants for these and many more useful products as well as for
ROOT CROPS. 3-4 year crop rotation.
 ROOT CROPS VARIETIES Parsnips: Radishes: SPACING Parsnips: Radishes: FERTILIZING Ruby Queen, Crosby Greentop, Red Ace, Asgrow Wonder, Rosette. Imperator: Premium, First Class, Avenger, Apache, Condor,
ROOT CROPS VARIETIES Parsnips: Radishes: SPACING Parsnips: Radishes: FERTILIZING Ruby Queen, Crosby Greentop, Red Ace, Asgrow Wonder, Rosette. Imperator: Premium, First Class, Avenger, Apache, Condor,
Frank A. Hale, Ph.D. Professor Entomology and Plant Pathology and David L. Cook Extension Agent II, Davidson County
 Frank A. Hale, Ph.D. Professor Entomology and Plant Pathology and David L. Cook Extension Agent II, Davidson County Multipurpose Fruit Spray These are mixtures containing a fungicide (captan) and either
Frank A. Hale, Ph.D. Professor Entomology and Plant Pathology and David L. Cook Extension Agent II, Davidson County Multipurpose Fruit Spray These are mixtures containing a fungicide (captan) and either
