CAPACITY BUILDING GUIDELINES IN URBAN AND REGIONAL PLANNING FOR MUNICIPAL ENGINEERS AND ENGINEERING STAFF WITHIN MUNICIPALITIES.
|
|
|
- Sharlene Flynn
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CAPACITY BUILDING GUIDELINES IN URBAN AND REGIONAL PLANNING FOR MUNICIPAL ENGINEERS AND ENGINEERING STAFF WITHIN MUNICIPALITIES. Ms. I. Jansen van Rensburg & Prof. C.B. Schoeman Masters Student in Urban and Regional Planning North West University (Potchefstroom Campus) Unit for Environmental Sciences and Management North West University (Potchefstroom Campus) ABSTRACT Urban and Regional Planning responsibilities have been assumed by newly established and existing local municipalities. Of these municipalities, many does not have the financial means to employ full-time Urban and Regional Planners to manage these responsibilities. Recognizing the need for capacity building in physical development planning at all levels, including all local-, district- and national authorities, for equipping them with a user friendly and comprehensive user guideline, the project will assist in carrying out their Urban and Regional Planning duties and associated responsibilities. The project is proposed to serve in this need although it is not aimed at training engineering staff to become Urban and Regional Planners but rather to enable them to engage with planning specialists. The purpose of this project is to provide an understanding of Urban and Regional Planning and associated practices, the policy and legislative framework that it accompanies and the implications it has for spatial development, transportation, the environment, land development and layout planning, the provision of engineering services and housing, sustainable development, statutory planning processes, etc. A basic knowledge of this will build capacity within staff working in related disciplines. The project will also inform all parties involved of the changes SPLUMA will bring and attempt to guide them through the transition from the old legislation towards an integrated approach. Thus the project will contribute to changing the face of the Municipal Engineer from an Urban and Regional Planning perspective. The interface between Urban and Regional Planners and Municipal Engineers and its staff is contextualised and formalized through this project. Contents: Part 1: Orientation and Context Prof. C.B. Schoeman Unit for Environmental Sciences and Management North West University (Potchefstroom Campus) INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND With the approval of the Spatial Planning and Land Use Management Act (SPLUMA) (Act 16 of 2013) and its Regulations on 23 March 2015, the last bastion of spatial and statutory planning legislation reform (dating back to previous political dispensations) within municipalities were removed. Although the transitional arrangements of this process is still in process within Provincial and Municipal Spheres of Government by formulating its own new transformation structures and procedures (migration to a new land development system), the question remains if the historic disjointedness in municipalities and lack of integration will be addressed efficiently and effectively on all strategic, functional and operational levels? This project is an endeavour to address and resolve the implications of the historical lack of integration between spatial planning and the role of municipal engineer in planning activities. The improvement of the relationship between professions in an effort to promote sustainable urban and territorial planning will enhance the quality of planning documents to support delivery and normalization within all spatial systems.
2 The availing of a capacity building guideline will address the need for closer co-operation between the two core professions directing planning and infrastructure development. The need for an improved understanding between the two professions result from the goals and objectives as included in the National Transport Master Plan (NATMAP) (2011); National Development Plan (NDP) (2012); Draft Integrated Urban Development Framework (DIUDF) (2014) and the Draft National Transport Strategic Framework (NLTSF) (2014). The complexities of the South African policy and legislative framework in the light of division of powers, functions and duties of the various spheres of government can clearly be depicted in Figure 1. Figure 1: Complexities of integration between Spheres of Government in South Africa. Source: Own synthesis, ORIENTATION AND CONTEXT The cooperation and integration between activities within professions depend on the nature of the profession, its definition, competencies, training and eventually the professional service rendered to clients and the
3 public. It is within this context that the research project endeavours to improve the understanding of the roles of Urban and Regional Planners and Municipal Engineers. Definitions for Urban and Regional Planning as a profession The planning profession is being controlled by the Planning Profession Act (2002) (Act 36) through a Professional Body called the South African Council for Planners (SACPLAN). SACPLAN (2015) includes the flowing definition for urban and regional planning: The core of Urban and Regional Planning is concerned with people and how they use space: Where and under what conditions people live; How people make their livelihoods; How people move between their homes and other destinations; How and under what conditions land is used. These concerns are manifested as spatial systems and networks. Planning is a strategic, rather than a comprehensive activity, which implies selectivity and a focus on what really makes a difference to the fortunes of an area over time. It is a field of expertise which involves initiating and managing change in the built and natural environment, across a spectrum of contexts, ranging from urban to rural; and delineated at different geographic scales (national, regional, sub-regional, city, town, village, neighbourhood), in order to further human development and environmental sustainability. Planning operates specifically in the fields of: Delimiting, regulating and managing land uses; Organisation of service infrastructure, utilities, facilities and housing for sustainable human settlements; Co-ordination and integration of social, cultural, economic and physical components of settlements through synthesis and integration of information, for preparation of strategic, policy, statutory and other development plans. The term planning' also implies a mode of governance driven by policies through a deliberative process and judgment of collective action in relation to these policies. Therefore, planning is not a neutral technical exercise: it is shaped by values which must be made explicit. Planning itself is fundamentally concerned with making ethical judgements. The Planning Profession is also directed by the South African Planning Institute (SAPI) and the South African Association of Consulting Professional Planners (SAACPP). These voluntary organizations supports SACPLAN in fulfilling its function and role. In 2013, SACPLAN appointed service providers to formulate a comprehensive Report of Competencies and Standards (Phase 1) inter alia inclusive of the following outputs: Consolidated Report on Competencies and Standards; Guidelines for Competencies and Standards for Curricula Development; Job Profiling Guidelines; Registration Guidelines. SACPLAN (2015) is at present in the process of formulating the following reports (Phase 2) of the Competencies and Standards Project) (2015) in order to enhance professionalization: Accreditation Criteria; Continued Professional Development (CPD) Policy; Formulation of an Examination System; Development of Qualifications in SAQA format; Policy for Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL). Abovementioned should be interpreted in terms of the Draft Rules and Code of Conduct for Registered Persons (Notice 445 of 2013) as published in the Government Gazette. In essence the outcome of the
4 Competencies and Standards Project (Phase 1 and Phase 2) will result in completing professionalization of the Planning Profession and eventually Work Reservation for Planners. Context of spatial planning Spatial planning (inclusive of land use planning) functions within a specific interface with transportation planning and environmental management. This relationship is determined by the policy and legislative frameworks guiding such disciplines (Refer to Table 1 and Table 2) Table 3 shows the focus, interface and planning instruments as provided in Spatial Planning, Transportation Planning and Environmental Management. However, for the purposes of this presentation, the need to promote improved cooperation between Urban and Regional Planning and Municipal Engineers does not only stem from SPLUMA (2013). It also relates to the need for engineering input into Spatial Development Frameworks (SDF s) and land development in general. In this the identification of policy levers as identified in the Draft Integrated Urban Development Framework (DIUDF) (2014) is of importance: Integrated Spatial Planning; Integrated Transport and Mobility; Integrated and Sustainable Human Settlements; Integrated Urban Infrastructure; Efficient Land Governance and Management; Inclusive Economic Development; Empowered and Active Communities; Effective Urban Governance. Alignment of roles, functions and focuses between Urban and Regional Planning (URP s) and Municipal Engineering (ME s) The need for alignment in roles, functions and focuses between the two professions and other disciplines (as described above) should also be considered from the perspectives as provided in documents such as: Municipal Infrastructure: Roles and Responsibilities of National Sector Departments, Provincial Counterparts and Municipalities (DPLG and CoGTA) (DPLG, 2006) and the policies as contained in the Municipal Infrastructure Grant (MIG) (CoGTA, ). The IMESA President in his Presidential Address in 2014 referred to the importance to resolving certain crucial issues in the achieving of the goals of the NDP. This in itself is indicative of the need for the Research Project as Reported on in Part 2 of this presentation to build capacity between URP and Municipal Engineering. SPLUMA (2013) and the DIUDF (2014) makes this integration essential. Figure 2 demonstrates the need for alignment to ensure system wide sustainability in planning, infrastructure development and service delivery. Figure 2: Enhancement of sustainability through alignment and integration. Source: Own synthesis, 2015.
5 Table 1: Core policies guiding the interface between spatial planning, transportation planning and environmental management Urban and regional planning Transportation planning Environmental management Reconstruction and Development Plan (1994) Growth, Economic and Redistribution Strategy (1996) White Paper on South African Land Policy (1997) Urban Development Framework (1997) Rural Development Framework (1997) White Paper on Water and Sanitation (1997) White Paper on Local Government (1998) Green Paper on Development and Planning (1999) National Integrated Rural Development Strategy (2000) King Report II on Corporate Governance for South Africa (2002) White Paper on Spatial Planning and Land Use Management (2001) National Spatial Development Perspective (2003) Mining Charter (2003) Construction Charter (2005) ASGISA, 2006 National Spatial Development Perspective (2006) Housing Atlas (2006) Sustainable Human Settlement Planning: Resource Book (2008) (NDoH) Area Based Planning. Department of Rural Development and Land Reform (2008/2009) NPC: A Guide to the National Planning Framework (2009) NPC: Green Paper. National Strategic Planning (2009) Comprehensive Rural Development Programme. Department of Rural Development and Land Reform (2009) National Planning Commission Diagnostic Overview (2011)* National Development Plan (2012)* Draft Integrated Urban Development Framework (2015) *Cross cutting policies Source: Own synthesis, 2015 White Paper on National Transport Policy (1996) Moving South Africa (1996) Rural Transport Strategy for South Africa (2003) Draft minimum requirements for the preparation of integrated transport plans (ITP) (2007) NDOT: Public Transport Strategy (2007) NDOT: Public Transport Action Plan ( ) National Land Transport Strategic Framework ( ) (2002) (Draft) NDOT: Road Infrastructure Strategic Framework for South Africa (2006) NDOT: Rural Transport Strategy for South Africa (2007) NDOT: Implementation Strategy to Guide the Provision of Accessible Transport in South Africa. (2009) NDOT: Final Draft National Scholar Transport Policy (2009) NDOT: Transport Action Plan (2010) NDOT: National Transport Master Plan 2050 (NATMAP) (2010) NDOT: Road Freight Strategy for South Africa (2011) NDOT: Non-Motorized Transport (NMT) Policy (2012) NDOT: Department of Transport Strategic Plan ( ) TRANSNET: Long Term Planning Framework (2012) PRASA: PRASA National Strategic Plan (2012) NDOT: Draft National Land Transport Strategic Framework (NLSF) (2014) NDOT: NATMAP Synopsis Report (Draft) 2015* Global Biodiversity Strategy: Guidelines for action to save, study and use earth s biotic wealth sustainably and equitably (Published by the WRI; IUCN and UNEP in 1992) Balancing the Scales: Guidelines for increasing Biodiversity s Chances through Bioregional Management, (Published by the World Resources Institute in 1996). Minimum requirements for the Classification, Handling and Disposal of Hazardous Waste (Second Edition (1998) (DWAF) Integrated Environmental Management Guidelines Series (1992) DEAT: An Environmental Policy for South Africa (Green Paper) (1996) White Paper on Integrated Pollution and Waste Management for South Africa (2000) Strategic Environmental Assessment in South Africa (2000) DEAT (2002a) Screening, Information Series 1, Department of Environmental Affairs and Tourism (DEAT), Pretoria. DEAT (2002b) Scoping, Integrated Environmental Management, Information Series 2, Department of Environmental Affairs and Tourism (DEAT), Pretoria. DEAT (2002c) Specialist Studies, Information Series 4, Department of Environmental Affairs and Tourism (DEAT), Pretoria. DEAT (2002d) Impact Significance, Integrated Environmental Management, Information Series 5, Department of Environmental Affairs and Tourism (DEAT), Pretoria. DEAT (2004a) Overview of Integrated Environmental Management, Integrated Environmental Management, Information Series 0, Department of Environmental Affairs and Tourism (DEAT), Pretoria. DEAT (2004b) Criteria for determining Alternatives in EIA, Integrated Environmental Management, Information Series 11, Department of Environmental Affairs and Tourism (DEAT), Pretoria. DEAT (2004c) Environmental Impact Reporting, Integrated Environmental Management, Information Series 15, Department of Environmental Affairs and Tourism (DEAT), Pretoria. Strengthening Sustainability in the Integrated Development Planning Process (2001) State of the Environment Reporting: Draft Guidelines for Local Municipalities (2005) DEAT Information Series ( ) National Framework for Sustainable Development (2008)
6 Table 2: Core legislative Framework guiding interface between spatial planning, transportation planning and environmental management Urban and regional planning Transportation planning Environmental management National Building Regulations and Building Standards Act (103 of 1977) Town Planning and Township Ordinance, Ordinance 15 of 1986 Land Use Ordinance (Cape of Good Hope), Ordinance 15 of 1985 Removal of Restrictions Act 84 of 1967 The Less Formal Township Establishment Act, Act 113 of 1991 The Physical Planning Act, 88 of 1967 (Sec 6, 8 and 11) Development Facilitation Act, Act No. 67 of 1995 (DFA) Constitution of the Republic of South Africa (108 of 1996) Bill of Human Rights (1996) Physical Planning Act (88 of 1967) Municipal Structures Act (117 of 1998) Restitution of Land Rights Act (22 of 1993) Interim Protection of Informal Rights Act (76 of 1995) Prevention of Illegal Eviction from Unlawful Occupation of Land Act (19 of 1998) Reconstruction and Development Programme Act (79 of 1998) Municipal Systems Act 32 of 2000 Development Facilitation Act 67 of 1995 (DFA) Physical Planning Act 125 of 1991 Less Formal Township Establishment Act 113 of 1991 (LEFTEA) Subdivision of Agricultural Land Act 70 of 1970 (SALA) Removal of Restrictions Act 84 of 1967 Community Land Reform Act 28 of 1996 (CLARA) Housing Act (107 of 1997) National Land Use Management Bill (Draft 2008) Local Government: Municipal Integrated Development Planning Regulations, Spatial Planning and Land Use Management Act (SPLUMA) (Act 16 of 2013)* R. 239 SPLUMA Regulations (23 March 2015)* * Cross cutting legislation Source: Own synthesis, Advertising on Roads and Ribbon Development Act (21 of 1940) Fencing Act (31 of 1963) National Land Transport Transition Act (Act 22 of 2000)* Urban Transport Act (Act 78 of 1977) National Transport Interim Arrangements Act (Act 45 of 1998) Transport Appeal Tribunal Act (At 39 of 1998) Cross Border road Transport Act (Act 4 of 1998) Road Traffic Act (Act 29 of 1989) National Road Traffic Act (Act 93 of 1996) The South African National Roads Agency Limited and National Roads Act (7 of 1998) National Land Transport Act, 2009 (Act 5 of 2009) and Regulations (R.1208, 2009) R. 877 National Land Transport Act (5/2009): National Land Transport Regulations on Contracting for Public Transport Services. Health Act (63 of 1977) Water Act (54 of 1956) National Water Act (36 of 1991) Water Services Act (108 of 1997) National Environmental Management Act 107 of 1998 (NEMA) National Environmental Management: Air Quality Act (39 of 2004) National Environmental Management: Waste Act 59 of 2009 National Environmental Management: Biodiversity Act 10 of 2004 (NEMBA) National Environmental Management: Protected Areas Act 57 of 2003 (NEMPAA) National Heritage Resources Act 25 of 1999 (NHRA) Mineral and Petroleum Resources Development Act 28 of 2002 (MPRDA) World Heritage Convention Act 49 of 1999 Biodiversity Act 10 of 2004 R.543: National Environmental Management Act (107/1998): Environmental Impact Assessment Regulations, 2010 (33306) R.544: Listing Notice 1: List of activities and competent authorities identified in terms of sections 24 (2) and 24D (33306) R.545: Listing Notice 2: List of activities and competent authorities identified in terms of sections 24 (2) and 24D (33306) R.546: Listing Notice 3: List of activities and competent authorities identified in terms of sections 24 (2) and 24D (33306) R.547: Environmental Management Framework Regulations, 2010
7 Table 3: Interface in focus and instruments as provided for in Spatial Planning, Transportation Planning and Environmental Management. SPLUMA (2013) NLTTA (2000)/NTA (2009) NEMA (1998) Development principles and norms and standards Intergovernmental support Spatial Development Frameworks (SDF s) National Spatial Development Framework (NSDF) Provincial Spatial Development Framework (PSDF) Regional Development Framework (RSDF) Municipal Development Framework (MSDF) Land Use Management (LUM) Land Development Management (LDM) Municipal Land Use Plans (MLUP) Statutory Planning (SP) General principles for transportation planning Types of transportation plans Provisions on transportation planning National Land Transport Strategic Framework (NLTSF) Provincial Land Transport Frameworks (PLTF) Integrated Transport Plans (ITPs) Freight Transport Plans (FTP) Transportation plans and changes in land use and public transport infrastructure and services Rationalization of public transport services (RATPLANS) Public Transport Plans (PTP s) Commuter rail plans (CRP) Transport Impact Studies (TIS s) Traffic Impact Assessments (TIA s) General objectives Environmental Implementation Plans (EIP s) Environmental Management Plans (EMP s) Integrated Environmental Management (IEM) Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA s) Environmental Authorizations (EA s) Strategic Environmental Assessments (SEA s) Environmental Management Programme (EMP s) Monitoring and Performance Assessment (M&PA s) Mine Closure Plans (MCP s) Source: Own synthesis from SPLUMA (2013), NLTTA (2000), NLTA (2009) and NEMA (1998). Part 2: The need for capacity building Ms. I. Jansen van Rensburg Masters Student in Urban and Regional Planning North West University (Potchefstroom Campus) PROJECT BACKGROUND Urban and Regional Planning is included as one of the main role players in the vast multi-disciplinary sector that is the built environment. The role of Urban and Regional planning is unavoidable and integral in the success of, among others, sustainable and efficient development (Schoeman, 2010). Along with the democratisation of South Africa in 1994, the new government inherited the long list of spatial planning and development problems that was the result of failed attempts to address possible spatial planning problems and development regulations in the past. These problems included segregation, fragmented and spatial system and other problems with regards to, not only spatial problems but also economic implications (Drewes, 2013; Schoeman, 2010; van Wyk, 2012:25 & 25). As a result of the implementation of wall-to-wall municipalities after the 1994 elections in South Africa, a large amount of new municipalities were developed, such as local, district and local municipalities (Drewes, 2013; van Wyk, 2012: ). This development resulted in Urban and Regional Planning responsibilities being assumed by newly established and existing local municipalities. Of these municipalities, many do not have the financial means to employ full-time Urban and Regional Planners to manage these responsibilities (IMESA, 2009). Recognizing the need for capacity building in physical development planning at all levels, IMESA (Institute of Municipal Engineers of Southern Africa) identified the need in all municipalities, including all local-,
8 district- and national authorities, for equipping them with a user-friendly and comprehensive user guideline, the project will assist in carrying out their Urban and Regional Planning duties and associated responsibilities. The project is proposed to serve in this need (IMESA, 2009). Further need assessment was conducted in order to confirm the presumed need and to establish whether or not the project will be adequate and sufficient. The project is further described by Schoeman (2014) as: The project consists of capacity building guidelines to empower municipal engineers and engineering staff to have a basic understanding of the theory, concepts, definitions, practices and procedures underpinning the Profession of Planning. The point of departure is not to train engineering staff to become Urban and Regional Planners but to enable such members of staff to engage with planning specialists and related applications such as spatial plans, land development applications etc. Urban and regional planning in the built environment The domain of Urban and Regional Planning can be viewed from an interface perspective with the inclusion of other disciplines (Schoeman, 2013) such as engineering, architecture, environmental management, etc. It is stated that the planning education and, the interfaces within the academic and research environment, are used to form the basis for developments such as residential development (Schoeman 2013). Urban and Regional Planning and its associated policy and legislative framework, serves as the foundation and integration between other disciplines (see Part 1). There are several challenges that the current Urban and Regional Planning Domain should address, in order to promote the interfaces between professions in human settlement development (Schoeman, 2013). The micro and macro context, in which Urban and Regional planning is included within a multi-disciplinary system, will also illustrate the close proximity of engineering and in particular Engineering Planning. Through Figure 1 it is clearly indicated that engineering is a fundamental and vital aspect to Urban and Regional Planning ( URP ). It is also clear that engineering will not be able to stand on its own, with no support from other disciplines. This results in an interdependent relationship between not only the two fields in question, but also within the fields indicated as Fields fundamental to URP (Schoeman, 2010). Figure 3: Micro and macro interface relationships between Urban and Regional Planning and other dicsiplines. Source: Adapted from (Schoeman, 2010; Schoeman, 2013).
9 In view of the above mentioned, it is clear that Engineering plays an integral and vital role in Urban and Regional Planning and its associated practices. It is thus important that an understanding of this profession is generated in the endeavours of those persons in Engineering and associated professions, have an understanding of what the implications of Urban and Regional Planning procedures entails as well as their impacts thereon. AIMS AND OBJECTIVES The primary aim of the project is to provide capacity building guidelines in Urban and Regional Planning practices in order to enhance effectiveness and efficiency of municipal engineers and engineering staff in their engagement, participation and contribution in statutory land development applications, policy compilations, spatial planning and related development processes within municipalities. The secondary aims will: Explore the interface and relevance of Urban and Regional Planning in the built environment; Explore the interaction of Urban and Regional Planning within a multi-disciplinary environment; Determine, explain and provide an understanding of Urban and Regional Planning practices and the working thereof in the built environment; Provide an overview of the policy and legislative frameworks relevant to the goal of this document; Establish a framework in order to determine which information should be included in the document, thus deemed as important information regarding capacity building; Provide and illustrate understandable information serving as summarisations of the information determined as important and relevant to the aim of the capacity building guidelines; Ensure that the information provided is easily understandable and will enhance capacity building as determined by the aim of the guidelines. The following objectives will be addressed in accordance with the aim and sub-aims of this document, the reader will: When facing a problem in the practitioners field, be able to refer to policies, legislation, regulations, principles, guidelines, and/or knowledge from urban and regional planning to help solve a problem in a multi-disciplinary manner; Be able to participate in conversation regarding Urban and Regional Planning; Be able to better understand the information relevant to urban and regional planning regarding statutory land development applications; Be able to provide adequate and accurate comments on statutory land use planning applications; Be able to participate in the compilation and implementation of developmental policies; Be able to better assist in processes regarding spatial planning and related development processes; Be able to refer to the document, when having questions and concerns regarding the content, related to Urban and Regional Planning problems; Have the capacity to substantiate their decisions regarding Urban and Regional Planning practices relevant to their specialised fields. THE PURPOSE & CONTENT OF THE PROJECT The purpose of this project is to provide an understanding of Urban and Regional Planning and associated practices (IMESA, 2009), the policy and legislative framework, that it accompanies and the implications it has for spatial development, transportation, environment, land development and layout planning, the provision of engineering services and housing, sustainable development, etc. A basic knowledge of this will build capacity with staff working in related disciplines (see Part 1). The project will also enable an understanding of the processes supporting statutory planning and the content of processes documents required for the development of various categories of land applications to be submitted to all municipalities and tribunals, along with an understanding of the engineers responsibility regarding the scope and extent of their planning related responsibilities.
10 Figure 2 illustrates the proposed contents of the project, this however was adapted through the course of the project to obtain the proposed and existing content layout indicated later in this paper. Definitions & Terminology Environmental interface Transportation Sustainable development Introduction & Background Legal practices Engineering services Assisting Software Policy & Legislative framework Existing spatial development Housing Provision Building & construction management control Regulatory Framework Land use management Township development & layout planning Planning administration Figure 4: Project contents. Source: Own Synthesis. The changes, as a result of the imminent Spatial Planning and Land Use Management Act (SPLUMA) No. 16 of 2013, is included in the project. This will enable the relevant parties to make a transition from the old legislation towards an integrated approach as proposed by the Act. As a result the Act will also form an important focus of the project, as it will have a large influence in the town planning applications and its associated processes. SPLUMA commenced on 01 July 2015, with implications on various municipalities. The municipalities however, are granted with a transitioning period. Up until the new policies for each municipality or province have been developed, the existing processes will be used, if it is not in contradiction with SPLUMA, or has been repealed. The interaction between Urban and Regional Planning and Engineering forms an integral part of this project, as it will be attempted to not only guide the engineer needing to deal with town planning applications, but also the town planner to understand the role of the engineer in the applications they present. The project includes a summarisation of what the role of the engineer will be regarding the particular topic, as well as whom he/she can contact for assistance, what resources (documents) and practitioner can be consulted, the processes that need to be followed, etc. It will typically be presented in a table similar to the following, with accompanying explanations where processes should be explained. Concept Process to follow Table 1: Example of a table of Important knowledge to take note of. Township Related Issues Town Planning Applications The following processes can be seen as the general processes in all land development applications (SPLUMA, 2013): 1. Submission of application 2. Fees and documents to accompany application 3. Simultaneous submission of applications 4. Screening of application 5. Registration of application 6. Notice of category 1 land development application 7. Notice of a category 2 land development or land use application 8. Objections 9. Comments pursuant to circulation 10. Amendments to application prior to referral 11. Referral of application by administrator 12. Decision and determination by land development officer
11 The role of the Engineer What is important to know How it should be implemented Consultants to contact for assistance Resources to consult Source: Own synthesis. 13. Procedure of tribunal 14. Consolidation and separation of applications 15. Continuation of application by new applicant 16. Power of tribunal to conduct site inspection 17. Decisions of tribunal 18. Conditions determined by tribunal 19. Non-compliance with conditions determined by tribunal 20. Approval of land development application that requires amendment of land use scheme 21. Approval of land development application on land where no town planning or land use scheme applies 22. Notification by administrator of decision of tribunal 23. Amendment of approval 24. Withdrawal of application 25. Effective date of decision by tribunal or land development officer It is the responsibility of the municipal engineer to provide comments on all town planning applications. These comments should include aspects such as; Roads (maintenance and provision thereof); Stormwater (possible impact); Water & sanitation and electricity (sufficiency of capacity for proposed development); etc. Consideration should be made to aspects including inter alia bulk- and internal services, cost effectiveness, development contributions. Not all town planning applications are the same; circumstances and applicable legislation differ; SDF s, LUMS and other policies should be consulted for each application and should not be seen as blue prints as some are adaptable and can be changed; illegal developments may warrant the proposed development even though the municipal documentation does not necessarily support the application completely. The aspect of urban fragmentation should be considered for each application as it influences its validity. It is good to provide consequent and rigid comments on applications, it prevents the establishment of presidents, however if the proposed development does not necessarily comply with the policy documents, it should be considered with greater diligence. Engineering comments should be provided in the required timeframe, the delay in the provision thereof, causes a ripple effect in the delay regarding the completion of the applications, resulting in a bottle-neck effect in all municipal departments. Engineering contributions should be explained in greater detail as the developers and owners are not educated in understanding the difference in green- and brown field developments and the difference in contributions. Town Planner; Land Surveyor; Attorney; Consulting Engineers; Environmentalists; Government Departments; etc. these consultants, and others, can make significant contributions and should be consulted. Policy and legislative documentation including inter alia Town Planning Scheme, SDF, IDP, LUMS, ITP, environmental guidelines. SUPPORTING RESEARCH As previously mentioned quantitative and qualitative data have been collected in order to support the evaluation of the proposed programme developed for capacity building in Municipal Engineers. Firstly a need assessment is conducted by means of survey distribution. This was used to determine the current level of skills in Urban and Regional Planning and related fields and the expectations and experience from the related professions towards each other. Secondly, an evaluability assessment will be conducted on the proposed programme after the evaluation of the qualitative and quantitative data collected through the
12 questionnaires has been completed. A summary for the programme monitoring regarding the current and future use of the programme is included. Questionnaires were handed out during the IMESA Conference 2014 on the basis of group-administered and hand-delivered practices. A total of 817 delegates were registered to attend the conference of which 175 feedbacks were received during the conference time frame from October The questionnaires contained three (3) sections, including quantitative and qualitative questions. An incentive was provided to encourage feedback from the conference delegates. A brochure was circulated along with the questionnaires in which the purpose, goal, background and competition details were explained, a description of the topics included in Section B of the survey was also provided. The following sections will illustrate the data collected during this survey. Need assessment Figure 5 illustrates that 71 (55.9%) of the participants indicated that they are of the opinion the Municipal Engineers of South Africa do not have sufficient working knowledge of the domain of Urban and Regional Planning. Furthermore, 118 (93.7%) of the participants are of the opinion that it is necessary to broaden the understanding of Urban and Regional Planning under Municipal Engineers. This is then substantiated with the low levels of average knowledge provided in Figure 6. Number of resposes Open ended questions - Section B (a) Opinion on existing knowledge of Engineers on Urban & Regional Planning (b) Opinion on whether or not the project is needed Yes No Figure 5: Open ended questions - Section B. Source: Own synthesis from IMESA Conference 2014 Questionnaires.
13 Total level of knowledge per topic Level of knowledge Topics Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 Figure 7: Total level of knowledge per topic. Source: Own synthesis from IMESA Conference 2014 Questionnaires. Generally the data is extremely reliable, receiving a.944 through the use of Cronbach s Alpha, subsequently a factor analysis the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin Measure of sampling adequacy was determined as.916 with a Bartlett s test resulted in a 0 factor score. Two (2) factors were extracted through factor analysis. These factors are known as the Baseline knowledge and Output driven knowledge. Though a Varimax- and Oblimin rotation, the knowledge areas were linked to these two (2) factors. These factors are known as the Baseline knowledge and Output driven knowledge. Baseline knowledge Definitions & Terminology Policy & Legislative Framework SPLUMA (Act No. 16 of 2013) Development Principles; Norms & Standards Intergovernmental Support Spatial Development Frameworks Land Use Management Related Land Development Matters Output driven knowledge Environmental & Developmental Procedures Transportation Provision Engineering Services Provision Housing Provision Township Related Issues Building Management Control Sustainable Development Figure 6: Two (2) knowledge groups. Source: Own synthesis from IMESA Conference 2014 Questionnaires. Figure 8 illustrates the level of knowledge relating to the private and public sectors as indicated during the IMESA Conference 2014 survey. Although it is expected that the average level of knowledge for Baseline
14 knowledge should generally be much higher for the public sector than for the private sector, it is evident that it is not the case. Engineers in the private sector do not generally deal directly with Urban and Regional Planning, thus it is expected that their average Output driven knowledge is higher than that of Baseline knowledge. In contrast the engineers in the public sectors are required to provide opinions and comments on most of the Town planning applications received by the municipalities, as well as policies and legislation rolled out by the municipalities and governmental departments. As a result they are expected to have a much higher average level of Baseline knowledge with a very small difference between the averages of that of Output driven knowledge, resulting in the confirmation of the need for a project such as the Capacity Building Guidelines. Average level of knowledge for private vs public sectors on a scale of 1-5 Level of knowledge 3,7 3,6 3,5 3,4 3,3 3,2 3,1 3 2,9 2,8 2,7 Public Sector Private Sector Baseline knowledge Output driven knowledge Figure 8: Average level of knowledge for private vs public sectors. Source: Own synthesis from IMESA Conference 2014 Questionnaires. Figure 9 illustrates the average level of knowledge per group of years experience by participants. Included in this figure is the amount of responses received for each group, ensuring better interpretation of the results obtained. Even though several of the participants indicated that they are of the opinion. That engineers with more experience will have a greater knowledge regarding Urban and Regional Planning, the results of the survey indicated that the engineers with less experience do indeed have the greatest average level of knowledge followed by those with the most amount of experience, this however can be attributed to the amount of responses received per years experience group. The cause of this can be either the result of Level of knowledge for years' experience on a scale 1-5 Level of knowledge 4 3,5 3 2,5 2 1,5 1 0,5 0 < > 31 Missing Years' experience Number of responses Baseline knowledge Output driven knowledge Quantity Figure 9: Level of knowledge for years experience. Source: Own synthesis from IMESA Conference 2014 Questionnaires.
15 engineers having to conduct Urban and Regional Planning related responsibilities or that they have received a more comprehensive tertiary education. Again the need for the programme is stressed. Further research regarding the origin of the lack of capacity was done through the determination of modules included in qualification provided at tertiary institution accredited by ECSA and supported by SAICE. This shortfall was confirmed through the questionnaires circulated and feedbacks received. Evaluability assessment The problem statement and substantiation provides the pre-conditions for evaluability assessment. These preconditions are in line with the need assessment done regarding the project. As a result this exemplifies the evaluability of the project and establishes that the project can be evaluated on grounds of the content thereof, in light of the need that has been established. Included in the project is several main topics/themes with several sub-themes provided with detailed explanations and descriptions included under each. Figure 10 provides a short description of what is included in the project: Programme monitoring 1. Introduction & background Purpose of the project, aims & objectives, etc. 2. Policy framework SDF, LED, IDP, LUMS, NEPAD, etc. 3. Legislative framework RDP, NDP, NSDP, SPLUMA, etc. 4. Spatial development Regulations, land use management, etc. 5. Environmental & developmental interface NEMA, geographical-, climate considerations, etc. 6. Transportation & Provision of Engineering services 7. Provision of Housing 8. Township related issues 9. Planning & development administration NATMAP, service design, guidelines, formalization, etc. Integrates settlement, housing development, housing in S.A., etc. Applications, township establishment, layout planning & design, etc. Sector plans, public participation, asset management, etc. 10. Sustainable development Sustainable cities, challenges, settlements, etc. 11. Supporting software GIS, CAD, etc. Figure 10: Project contents. Source: Own synthesis.
16 Programme monitoring was done in several forms and will continue to be done beyond the completion of the research project. The manner in which programme monitoring took place included: The review and adaptation from the original proposed Table of Content provided by IMESA, in order to obtain the contents provided in Figure 10. The original contents was deemed as inadequate by the practitioners in the field of Urban and Regional Planning; Correspondence took place between the Research Team and the project initiators (IMESA) regarding the amendment and improvement of the project; IMESA Executive Committee members, received feedback during the IMESA Conference 2014, as provided by the researchers; Limited responses and feedback was provided to the researcher, thus it is possible that the project could not reach its full potential, resulting in the possible provision of a revised version in order to enable the project in reaching its full and expected potential. The programme is proposed to be implemented on a national bases with distribution of a summary done by IMESA. It is hoped that the project will then be provided in numerous ways including the publication thereof on the IMESA website, provision of short courses, etc. Figures 11 & 12 illustrates the responses received during the IMESA Conference 2014 regarding the participants preference receiving to such a project. Preference was given to receiving a short course with the submission of an assignment (69.5%), subsequent preference was given to receiving a soft- (46.8%) or digital copy (31.9%) of the project. Verbal presentation of guidelines 30,5% 69,5% Seminar with submission of assignment Short course with submission of assignment Figure 11: Verbal presentation of guidelines. Source: Own synthesis from IMESA Conference 2014 Questionnaires.
17 Physical presentation of the guidelines 21,3% 31,9% Hard copy Soft copy (digital and interactive copy) Online (possible to update at least every 2 years) CONCLUSION 46,8% Figure 12: Physical presentation of the guidelines. Source: Own synthesis from IMESA Conference 2014 Questionnaires. To conclude, the purpose of this paper was to provide an overview and report back on the description of the Capacity Building guidelines, including the substantiation and the evaluation thereof. The inclusion of comprehensive descriptions of all Urban and Regional Planning related topics, and information for specifically the engineers, will contribute in enabling engineers to not only improve their comprehension of Urban and Regional Planning, but will enable them to make more meaningful contributions in their related fields of expertise. The process of the project is evaluated in order to ensure its sufficiency and effectiveness. Through further research the need for a project of this magnitude was again reiterated along with the specific areas to which the need relates. This resulted in the provision of a suitable Capacity Building Guideline for Engineers and Engineering staff within Municipalities. It is recommended that the project be implemented on a national basis with the use of short courses in order to provide orientation and much needed information to those engineers in need. At a later stage the project can be distributed to the majority of local-, provincial- and district municipalities with the inclusion of knowledge assessment prior to receiving the information and a re-evaluation after the course has been completed. Proposals have been made regarding possible negotiations with Skills Education Training Authorities (SETA) for the accreditation of the project in order for it to be included regarding education and training of engineers and engineering staff in municipalities and other professions that may require information in Urban and Regional Planning. These SETA s may include the Construction Education & Training Authority (CETA); Education, Training & Development Practices SETA (ETDP); Local Government, Education and Training Authority (LGSETA); Manufacturing, Engineering & related Services Education and Training Authority (MERSETA); etc. (Serviceseta, 2012). Other proposals include the inclusion of the programme for Continued Professional Development (CPD) provided by IMESA and its branches. Further research can be done at each municipality in order to determine where the least amount of average knowledge is located, this can result in the better implementation of the project. The specific role of the engineer in Urban and Regional Planning can also be evaluated and determined. For future reference, a more specific determination can be made on what the specific sub-themes is in which capacity building is needed. This will ensure a more precise provision of information as it is possible that not all the included information for this study is required.
18 Part 3: Strategy and Way Forward Prof. C.B. Schoeman Unit for Environmental Sciences and Management North West University (Potchefstroom Campus) From the Research Project the following conclusions can be deduced: Professional capacity: From the research it is evident that both the professions of Urban and Regional Planning and Municipal Engineers can be classified as scarce skills in all municipalities. Need for Capacity Building: The implementation of the SPLUMA (2013) will give rise to a more important responsibility for URP s and ME s staff to improve alignment in planning, infrastructure development and services provision. Planning Instruments and Processes: Municipal Engineers need to be involved in all cycles of spatial planning inclusive of IDP s, SDF formulation, Strategic Planning, and urban regeneration in terms of the policies and considerations as included in the DIUDF (2014). Complexities within Governance: In the longer term the debate relating to the positioning of Municipal Engineering within Municipalities should be considered. The importance of infrastructure and service delivery to the public necessitates considerations such as depoliticising such services and to locate it in new structures such as Infrastructure Agencies on a regional basis. Planning is political sensitive and should remain within Municipalities. Training and Education of Professionals: Planning Schools and Engineering Departments within the tertiary sector should consider to improve the knowledge and exposure of students to both planning and engineering skills and practices. Presentation of the Research Project to IMESA Branches: Capacity building on SPLUMA (2013) and the body of the research to be presented at all IMESA Branch Meetings. REFERENCES Cooperative Governance and Traditional Affairs.2014: Municipal Infrastructure Grant Policy. Pretoria. Government Printer. Department of Development Planning and Local Government. 2006: Municipal Infrastructure: Roles and Responsibilities of National Sector Departments, Provincial Counterparts and Municipalities. Pretoria. Government Printer. Department of Provincial and Local Government. 2004: Municipal Infrastructure: Roles and Responsibilities of National Sector Departments, Provincial Counterparts and Municipalities. Drewes. J.E Regional analysis and application. Potchefstroom: NWU, Potchefstroom Campus. (Study guide SBRS 411). Government Gazette.2013: South African Council for Planners: Rules and Draft Code of Conduct for Registered Persons. Pretoria. Government Printer. Government of South Africa. 2013: Spatial Planning and Land Use Management Act (16 of 2013). Pretoria. Government Printer. Government of South Africa. 2015: Regulations in Terms of the Spatial Planning and Land Use Management Act (16 of 2013)/ (R.239) 23 March, Pretoria. Government Printer. IMESA Manual on Town and Regional Planning Practices: Volume 1. (Unpublished). IMESA (2014) Presidential Address. Durban. National Department of Transport. 2011: National Transport Master Plan. Pretoria. National Department of Transport. 2014: Draft National Transport Strategic Framework. Pretoria. National Department of Transport. 2015: Draft NATMAP 2050 Synopsis Report. Pretoria. National Planning Commission.2012: National Development Plan. Pretoria. SACPLAN. 2014: Competencies and Standards Project (Phase 1). Midrand. SACPLAN (2015): Competencies and Standards Project (Phase 2) (in process). Midrand. Schoeman. C.B Urban and regional planning and the interface with environmental management and transportation planning. Inaugural address (238).
An analysis of the transportation planning for the 2010 Soccer World Cup in South Africa
 Urban Transport XV 105 An analysis of the transportation planning for the 2010 Soccer World Cup in South Africa C. B. Schoeman School for Environmental Sciences and Development, North West University (Potchefstroom
Urban Transport XV 105 An analysis of the transportation planning for the 2010 Soccer World Cup in South Africa C. B. Schoeman School for Environmental Sciences and Development, North West University (Potchefstroom
Application of traffic impact studies as part of the EIA process: a case study as applied to the extension of a mineral processing plant
 Urban Transport XIX 519 Application of traffic impact studies as part of the EIA process: a case study as applied to the extension of a mineral processing plant I. M. Schoeman School for Computer, Statistical
Urban Transport XIX 519 Application of traffic impact studies as part of the EIA process: a case study as applied to the extension of a mineral processing plant I. M. Schoeman School for Computer, Statistical
The Jigsaw: Legal Instruments for Biodiversity Planning in South Africa
 The Jigsaw: Legal Instruments for Biodiversity Planning in South Africa Annual Conference, Environmental Law Association AUGUST 2012 Dr. Marie Parramon-Gurney Head of Programmes: Sustainability and Development
The Jigsaw: Legal Instruments for Biodiversity Planning in South Africa Annual Conference, Environmental Law Association AUGUST 2012 Dr. Marie Parramon-Gurney Head of Programmes: Sustainability and Development
Town of Cobourg Heritage Master Plan. Statutory Public Meeting
 Town of Cobourg Heritage Master Plan Statutory Public Meeting April 25 th 2016 Presentation Overview 1. Introduction 2. Project background and schedule overview 3. Review of strategic direction content
Town of Cobourg Heritage Master Plan Statutory Public Meeting April 25 th 2016 Presentation Overview 1. Introduction 2. Project background and schedule overview 3. Review of strategic direction content
AILA CPD TREE OF KNOWLEDGE DESIGNING AND CONSTRUCTING
 AILA CPD TREE OF KNOWLEDGE This Tree of Knowledge provides a list of core competencies on which the CPD framework will evolve, and is designed to provide a filing repository for future CPD resources. DESIGNING
AILA CPD TREE OF KNOWLEDGE This Tree of Knowledge provides a list of core competencies on which the CPD framework will evolve, and is designed to provide a filing repository for future CPD resources. DESIGNING
Published in March 2005 by the. Ministry for the Environment. PO Box , Wellington, New Zealand ISBN: X.
 Action Pack Published in March 2005 by the Ministry for the Environment Manatū Mō Te Taiao PO Box 10-362, Wellington, New Zealand ISBN: 0-478-18994-X ME number: 580 This document is available on the Ministry
Action Pack Published in March 2005 by the Ministry for the Environment Manatū Mō Te Taiao PO Box 10-362, Wellington, New Zealand ISBN: 0-478-18994-X ME number: 580 This document is available on the Ministry
Our Constitutional imperative
 PARLIAMENT: PUBLIC HEARINGS EFFICACY OF SOUTH AFRICA'S ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT (EIA) REGIME Henri Fortuin Cape Town 29July 2013 Our Constitutional imperative Section 24 of our Constitution gives
PARLIAMENT: PUBLIC HEARINGS EFFICACY OF SOUTH AFRICA'S ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT (EIA) REGIME Henri Fortuin Cape Town 29July 2013 Our Constitutional imperative Section 24 of our Constitution gives
Stephen Berrisford Planning law and policy consultant Concise CV
 Stephen Berrisford Planning law and policy consultant Concise CV Areas of expertise Qualified lawyer & urban planner Law & policy reform Strategic advice and planning Project management Sectoral experience
Stephen Berrisford Planning law and policy consultant Concise CV Areas of expertise Qualified lawyer & urban planner Law & policy reform Strategic advice and planning Project management Sectoral experience
THE ARCHITECTURAL POLICY OF ESTONIA. Passed at the Parliamentary sitting , protocol no. 43, item no. 5
 THE ARCHITECTURAL POLICY OF ESTONIA Passed at the Parliamentary sitting 22.10.2002, protocol no. 43, item no. 5 THE ARCHITECTURAL POLICY OF ESTONIA With the development of a market economy the responsibility
THE ARCHITECTURAL POLICY OF ESTONIA Passed at the Parliamentary sitting 22.10.2002, protocol no. 43, item no. 5 THE ARCHITECTURAL POLICY OF ESTONIA With the development of a market economy the responsibility
Heritage Resources Management
 CPD Course School of Architecture, Planning and Geomatics Heritage Resources Management 6-8 August 2018 Course Objectives This three-day course is aimed at guiding professionals and lay people who need
CPD Course School of Architecture, Planning and Geomatics Heritage Resources Management 6-8 August 2018 Course Objectives This three-day course is aimed at guiding professionals and lay people who need
Bachelor of City Planning [BCP] (Hons)
![Bachelor of City Planning [BCP] (Hons) Bachelor of City Planning [BCP] (Hons)](/thumbs/96/128460542.jpg) November 2015 A/Prof Simon Pinnegar Discipline Director, Planning Bachelor of City Planning [BCP] (Hons) What s new? https://www.be.unsw.edu.au/undergraduate-degrees/city-planning/sydney-changing-were-also-changing
November 2015 A/Prof Simon Pinnegar Discipline Director, Planning Bachelor of City Planning [BCP] (Hons) What s new? https://www.be.unsw.edu.au/undergraduate-degrees/city-planning/sydney-changing-were-also-changing
CONSULTANT VACANCY ANNOUNCEMENT
 United Nations Human Settlements Programme Future Saudi Cities Programme United Nations, Diplomatic Quarters, Riyadh Telephone: +966 (11) 488 5301 Fax: +966 (11) 488 5309, www.unhabitat.org CONSULTANT
United Nations Human Settlements Programme Future Saudi Cities Programme United Nations, Diplomatic Quarters, Riyadh Telephone: +966 (11) 488 5301 Fax: +966 (11) 488 5309, www.unhabitat.org CONSULTANT
VILLAGE OF BOLTON HERITAGE CONSERVATION DISTRICT PLAN
 Page 1 1. INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND 1.1 THE PROJECT VILLAGE OF BOLTON HERITAGE CONSERVATION DISTRICT PLAN TERMS OF REFERENCE The Town of Caledon (Town) is a large, predominantly rural municipality with
Page 1 1. INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND 1.1 THE PROJECT VILLAGE OF BOLTON HERITAGE CONSERVATION DISTRICT PLAN TERMS OF REFERENCE The Town of Caledon (Town) is a large, predominantly rural municipality with
UDF PLANS AND GUIDELINES
 UDF PLANS AND GUIDELINES 5 Land Use Land Use Development Plan Plan no. 3 Land Use Development Mixed Use Retail / Leisure Residential Civic and Institutional Proposed Zoning Table Development Edges Plan
UDF PLANS AND GUIDELINES 5 Land Use Land Use Development Plan Plan no. 3 Land Use Development Mixed Use Retail / Leisure Residential Civic and Institutional Proposed Zoning Table Development Edges Plan
Required total credit : 43 All graduate students must register one of RES 501, RES 502 or RES 503, RES 504 or RES 505, RES 506 or RES 509, RES 510.
 İZMİR INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY GRADUATE SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF ARCHITECTURAL RESTORATION CURRICULUM OF THE M.S. PROGRAM IN ARCHITECTURAL RESTORATION (NON-THESIS) Fall Semester
İZMİR INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY GRADUATE SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF ARCHITECTURAL RESTORATION CURRICULUM OF THE M.S. PROGRAM IN ARCHITECTURAL RESTORATION (NON-THESIS) Fall Semester
LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTURE
 Landscape Architecture 1 LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTURE Dexter Bldg.(34), Room 251 Phone: 805.756.1319 https://landscape.calpoly.edu Department Chair: Omar Faruque Academic Program Program name Landscape Architecture
Landscape Architecture 1 LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTURE Dexter Bldg.(34), Room 251 Phone: 805.756.1319 https://landscape.calpoly.edu Department Chair: Omar Faruque Academic Program Program name Landscape Architecture
Living with World Heritage in Africa
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE Living with World Heritage in Africa [26 26-29 September 2012] South Africa BACKGROUND DOCUMENT The Government of the Republic of South Africa, in collaboration with the African
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE Living with World Heritage in Africa [26 26-29 September 2012] South Africa BACKGROUND DOCUMENT The Government of the Republic of South Africa, in collaboration with the African
A study on the regional landscape planning framework on the relationships between urban and rural areas: case study of Tokachi region, Hokkaido, Japan
 A study on the regional landscape planning framework on the relationships between urban and rural areas: case study of Tokachi region, Hokkaido, Japan K. Yamagishi & H. Kobayashi Laboratory of Urban Planning
A study on the regional landscape planning framework on the relationships between urban and rural areas: case study of Tokachi region, Hokkaido, Japan K. Yamagishi & H. Kobayashi Laboratory of Urban Planning
HERITAGE WESTERN CAPE GUIDELINES FOR PUBLIC MONUMENTS AND MEMORIALS
 HERITAGE WESTERN CAPE GUIDELINES FOR PUBLIC MONUMENTS AND MEMORIALS Adapted from the Public Monuments and Memorials Project by SAHRA for DAC (2003) and amended following the public consultation meeting
HERITAGE WESTERN CAPE GUIDELINES FOR PUBLIC MONUMENTS AND MEMORIALS Adapted from the Public Monuments and Memorials Project by SAHRA for DAC (2003) and amended following the public consultation meeting
ONTARIO MUNICIPAL BOARD
 PL 120483 ONTARIO MUNICIPAL BOARD Applicant/Appellant: 2124123 Ontario Limited Subject: OPA, Rezoning and Draft Plan of Subdivision Municipal Address: 3940 Highway 7 East Municipality: City of Markham
PL 120483 ONTARIO MUNICIPAL BOARD Applicant/Appellant: 2124123 Ontario Limited Subject: OPA, Rezoning and Draft Plan of Subdivision Municipal Address: 3940 Highway 7 East Municipality: City of Markham
Urban and regional planning and the interface with environmental management and transportation planning
 Urban and regional planning and the interface with environmental management and transportation planning Prof. C.B. Schoeman School for Environmental Sciences and Development North West University (Potchefstroom
Urban and regional planning and the interface with environmental management and transportation planning Prof. C.B. Schoeman School for Environmental Sciences and Development North West University (Potchefstroom
Cotswolds AONB Landscape Strategy and Guidelines. June 2016
 Cotswolds AONB Landscape Strategy and Guidelines June 2016 Cotswolds AONB Landscape Strategy and Guidelines Introduction The evolution of the landscape of the Cotswolds AONB is a result of the interaction
Cotswolds AONB Landscape Strategy and Guidelines June 2016 Cotswolds AONB Landscape Strategy and Guidelines Introduction The evolution of the landscape of the Cotswolds AONB is a result of the interaction
THAT the attached Terms of Reference for the Thornhill Centre Street Study be approved.
 COMMITTEE OF THE WHOLE AUGUST 18, 2003 THORNHILL CENTRE STREET STUDY PLANNING FILE: 15.92 Recommendation The Commissioner of Planning recommends: THAT the attached Terms of Reference for the Thornhill
COMMITTEE OF THE WHOLE AUGUST 18, 2003 THORNHILL CENTRE STREET STUDY PLANNING FILE: 15.92 Recommendation The Commissioner of Planning recommends: THAT the attached Terms of Reference for the Thornhill
VCA Guidance Note. Contents
 Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Who can register a VCA?... 2 3. VCAs and sustainable development... 3 4. Verifying conservation performance... 4 4.1 Transparent, voluntary commitments... 4 4.2 Independent
Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Who can register a VCA?... 2 3. VCAs and sustainable development... 3 4. Verifying conservation performance... 4 4.1 Transparent, voluntary commitments... 4 4.2 Independent
9 CITY OF VAUGHAN OFFICIAL PLAN AMENDMENT NO BOCA EAST INVESTMENTS LIMITED
 9 CITY OF VAUGHAN OFFICIAL PLAN AMENDMENT NO. 631 - BOCA EAST INVESTMENTS LIMITED The Planning and Economic Development Committee recommends the adoption of the recommendations contained in the following
9 CITY OF VAUGHAN OFFICIAL PLAN AMENDMENT NO. 631 - BOCA EAST INVESTMENTS LIMITED The Planning and Economic Development Committee recommends the adoption of the recommendations contained in the following
AUCKLAND DESIGN OFFICE. Terms of Reference: Auckland Urban Design Panel 2017
 AUCKLAND DESIGN OFFICE Terms of Reference: Auckland Urban Design Panel 2017 Auckland Design Office 3 Contents 4 Introduction Benefits of the Panel 6 Terms of Reference The Purpose of the Auckland Urban
AUCKLAND DESIGN OFFICE Terms of Reference: Auckland Urban Design Panel 2017 Auckland Design Office 3 Contents 4 Introduction Benefits of the Panel 6 Terms of Reference The Purpose of the Auckland Urban
ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT
 ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT NOTICE OF ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT PROCESS FOR THE SARATOGA VEGETATION CLEARING SECTION 24G ON PORTION 4 OF THE FARM KLAAS VOOGDS RIVIER NO. 40, ROBERTSON, WESTERN
ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT NOTICE OF ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT PROCESS FOR THE SARATOGA VEGETATION CLEARING SECTION 24G ON PORTION 4 OF THE FARM KLAAS VOOGDS RIVIER NO. 40, ROBERTSON, WESTERN
Strategic Environmental Assessment Screening Report. Dublin Port Masterplan Review 2017
 Strategic Environmental Assessment Screening Report Dublin Port Masterplan Review 2017 Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Purpose of the Masterplan... 2 3 Task 1.1 Pre-Screening Check... 5 4 Task
Strategic Environmental Assessment Screening Report Dublin Port Masterplan Review 2017 Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Purpose of the Masterplan... 2 3 Task 1.1 Pre-Screening Check... 5 4 Task
Awarding body monitoring report for: Institute of Legal Executives (ILEX) February 2008 QCA/08/3734
 Awarding body monitoring report for: Institute of Legal Executives (ILEX) February 2008 QCA/08/3734 2008 Qualifications and Curriculum Authority 2 Contents Introduction...4 Regulating external qualifications...4
Awarding body monitoring report for: Institute of Legal Executives (ILEX) February 2008 QCA/08/3734 2008 Qualifications and Curriculum Authority 2 Contents Introduction...4 Regulating external qualifications...4
Resolution XII NOTING also that with the increasingly rapid urbanization, wetlands are being threatened in two principle ways:
 12 th Meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Wetlands (Ramsar, Iran, 1971) Punta del Este, Uruguay, 1-9 June 2015 Resolution XII.10 Wetland City 1 Accreditation of the Ramsar Convention
12 th Meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Wetlands (Ramsar, Iran, 1971) Punta del Este, Uruguay, 1-9 June 2015 Resolution XII.10 Wetland City 1 Accreditation of the Ramsar Convention
UNIVERSITY OF MUMBAI
 AC 6/6/2012 Item No. 4.80 UNIVERSITY OF MUMBAI Syllabus for the Master of Architecture Programme : M.Arch. Course :Urban Design (As per Credit Based Semester and Grading System with effect from the academic
AC 6/6/2012 Item No. 4.80 UNIVERSITY OF MUMBAI Syllabus for the Master of Architecture Programme : M.Arch. Course :Urban Design (As per Credit Based Semester and Grading System with effect from the academic
The Charter of European Planning BARCELONA 2013
 The Charter of European Planning BARCELONA 2013 The Vision for Cities and Regions Territoires of Europe in the 21st Century ECTP-CEU (The European Council of Spatial Planners Le Conseil Européen des Urbanistes)
The Charter of European Planning BARCELONA 2013 The Vision for Cities and Regions Territoires of Europe in the 21st Century ECTP-CEU (The European Council of Spatial Planners Le Conseil Européen des Urbanistes)
AUCKLAND DESIGN OFFICE. Terms of Reference: Auckland Urban Design Panel
 AUCKLAND DESIGN OFFICE Terms of Reference: Auckland Urban Design Panel Auckland Design Office 3 Contents 4 Introduction Benefits of the Panel 6 Terms of Reference The Purpose of the Auckland Urban Design
AUCKLAND DESIGN OFFICE Terms of Reference: Auckland Urban Design Panel Auckland Design Office 3 Contents 4 Introduction Benefits of the Panel 6 Terms of Reference The Purpose of the Auckland Urban Design
!"#"$%&'"()*%+*,*-.%/"0.%(,$*&$,(*+%/*)1"* 2"314314("*!.2)/.5)* 0/%-$"/2!,$*+./"*2),).%(*-%,/!/%%'6*78*',/51*9:7;*
 !"#"$%&'"()*%+*,*-.%/"0.%(,$*&$,(*+%/*)1"* 2"314314("*!.2)/.5)* 0/%-$"/2!,$*+./"*2),).%(*-%,/!/%%'6*78*',/51*9:7;* Meeting Agenda Item Discussion Item Presenter 1. Opening and Welcome 2. Introductions
!"#"$%&'"()*%+*,*-.%/"0.%(,$*&$,(*+%/*)1"* 2"314314("*!.2)/.5)* 0/%-$"/2!,$*+./"*2),).%(*-%,/!/%%'6*78*',/51*9:7;* Meeting Agenda Item Discussion Item Presenter 1. Opening and Welcome 2. Introductions
Appendix A. Planning Processes. Introduction
 1 Planning Processes Introduction This appendix outlines a number of planning processes which are used in the Auckland Region to support the effective management of development in the region s rural and
1 Planning Processes Introduction This appendix outlines a number of planning processes which are used in the Auckland Region to support the effective management of development in the region s rural and
Fire Sprinklers Working Group Final Report
 Introduction The Building Act received Royal Assent on March 25, 2015. The Act aims to establish more consistent building requirements across British Columbia and create a more robust and modern building
Introduction The Building Act received Royal Assent on March 25, 2015. The Act aims to establish more consistent building requirements across British Columbia and create a more robust and modern building
Draft Resolution XII.10
 12 th Meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Wetlands (Ramsar, Iran, 1971) Punta del Este, Uruguay, 1-9 June 2015 Ramsar COP12 DR10, Rev. 2 21:45, 8 June Draft Resolution XII.10
12 th Meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Wetlands (Ramsar, Iran, 1971) Punta del Este, Uruguay, 1-9 June 2015 Ramsar COP12 DR10, Rev. 2 21:45, 8 June Draft Resolution XII.10
TEXAS CHAPTER AMERICAN SOCIETY OF LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTS 2019 PROFESSIONAL AWARDS GUIDELINES
 TEXAS CHAPTER AMERICAN SOCIETY OF LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTS 2019 PROFESSIONAL AWARDS GUIDELINES The Texas Chapter of the American Society of Landscape Architects invites, from the Chapter membership, submission
TEXAS CHAPTER AMERICAN SOCIETY OF LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTS 2019 PROFESSIONAL AWARDS GUIDELINES The Texas Chapter of the American Society of Landscape Architects invites, from the Chapter membership, submission
BASIC ASSESSMENT PROCESS
 BASIC ASSESSMENT PROCESS NOTICE OF A BASIC ASSESSMENT PROCESS FOR THE PROPOSED MIXED USE DEVELOPMENT ON THE REMAINDER OF PORTION 2, REMAINDER OF PORTION 7, PORTION 7, REMAINDER OF PORTION 9, REMAINDER
BASIC ASSESSMENT PROCESS NOTICE OF A BASIC ASSESSMENT PROCESS FOR THE PROPOSED MIXED USE DEVELOPMENT ON THE REMAINDER OF PORTION 2, REMAINDER OF PORTION 7, PORTION 7, REMAINDER OF PORTION 9, REMAINDER
Connecting rural dwellings with rural development
 Connecting rural dwellings with rural development Dr Mark Scott Department of Planning and Environmental Policy University College Dublin Mark.Scott@ucd.ie Introduction Growing emphasis in the EU is being
Connecting rural dwellings with rural development Dr Mark Scott Department of Planning and Environmental Policy University College Dublin Mark.Scott@ucd.ie Introduction Growing emphasis in the EU is being
Cranfield University Masterplan
 Central Bedfordshire Council EXECUTIVE Tuesday, 5 December 2017 Cranfield University Masterplan Report of: Cllr Nigel Young, Executive Member for Regeneration, (nigel.young@centralbedfordshire.gov.uk )
Central Bedfordshire Council EXECUTIVE Tuesday, 5 December 2017 Cranfield University Masterplan Report of: Cllr Nigel Young, Executive Member for Regeneration, (nigel.young@centralbedfordshire.gov.uk )
Managing our Landscapes Conversations for Change
 Managing our Landscapes Conversations for Change Frequently Asked Questions The new State Government is committed to a significant reform program that will change the way natural resources are managed.
Managing our Landscapes Conversations for Change Frequently Asked Questions The new State Government is committed to a significant reform program that will change the way natural resources are managed.
Planning Department. Director of Planning. Manager of Planning. Planning Technician/ Sustainability Coordinator. Planner II/ Heritage Coordinator
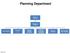 Department Director of Manager of Policy Planner Planner II (2) Planner II/ Heritage Coordinator Technician/ Sustainability Coordinator Technician Administrative Clerk March 2017 Department 2018 Business
Department Director of Manager of Policy Planner Planner II (2) Planner II/ Heritage Coordinator Technician/ Sustainability Coordinator Technician Administrative Clerk March 2017 Department 2018 Business
Welcome. /The Design Companion 4. /Planning London 7. /Getting Homes Built 8. /Transport & Streets 10. /Tech & The City 12
 Welcome With the draft publication of the London Plan and the Mayor s Transport Strategy (MTS) this year s events programme will examine both documents in detail with a wide range of seminars, debates
Welcome With the draft publication of the London Plan and the Mayor s Transport Strategy (MTS) this year s events programme will examine both documents in detail with a wide range of seminars, debates
BASIC ASSESSMENT PROCESS THE PROPOSED CANELANDS EXTENSION, KWAZULU-NATAL KZN DAEA REF NO: DM/0031/2012 BACKGROUND INFORMATION DOCUMENT AUGUST 2012
 BASIC ASSESSMENT PROCESS THE PROPOSED CANELANDS EXTENSION, KWAZULU-NATAL KZN DAEA REF NO: DM/0031/2012 BACKGROUND INFORMATION DOCUMENT AUGUST 2012 WHAT DOES THIS DOCUMENT TELL YOU? This document aims to
BASIC ASSESSMENT PROCESS THE PROPOSED CANELANDS EXTENSION, KWAZULU-NATAL KZN DAEA REF NO: DM/0031/2012 BACKGROUND INFORMATION DOCUMENT AUGUST 2012 WHAT DOES THIS DOCUMENT TELL YOU? This document aims to
PhD in URBAN PLANNING, DESIGN, AND POLICY - 32nd cycle
 PhD in URBAN PLANNING, DESIGN, AND POLICY - 32nd cycle Research Field: NOVEL APPROACHES FOR THE CO-DESIGN OF URBAN SERVICES TOWARDS THE SHARING SOCIETY Monthly net income of PhDscholarship (max 36 months)
PhD in URBAN PLANNING, DESIGN, AND POLICY - 32nd cycle Research Field: NOVEL APPROACHES FOR THE CO-DESIGN OF URBAN SERVICES TOWARDS THE SHARING SOCIETY Monthly net income of PhDscholarship (max 36 months)
BACKGROUND INFORMATION DOCUMENT (BID) AND INVITATION TO PARTICIPATE
 To: Interested and Affected Parties 2 October 2017 NOTIFICATION OF ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT PROCESS FOR THE PROPOSED DEVELOPMENT OF RESIDENTIAL HOUSING ON PORTION 56 OF THE FARM CHELSEA NO. 25,
To: Interested and Affected Parties 2 October 2017 NOTIFICATION OF ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT PROCESS FOR THE PROPOSED DEVELOPMENT OF RESIDENTIAL HOUSING ON PORTION 56 OF THE FARM CHELSEA NO. 25,
CIDA Curriculum Matrix - Miami University First Year
 - rimary evidence. Limit: 3 ''s per expectation. 1 '' per expectation is mandatory unless the Standard 2. Global Context for Design - Entry-level interior designers have a global view and weigh design
- rimary evidence. Limit: 3 ''s per expectation. 1 '' per expectation is mandatory unless the Standard 2. Global Context for Design - Entry-level interior designers have a global view and weigh design
CITY CLERK. Parkland Acquisition Strategic Directions Report (All Wards)
 CITY CLERK Clause embodied in Report No. 10 of the, as adopted by the Council of the City of Toronto at its meeting held on November 6, 7 and 8, 2001. 10 Parkland Acquisition Strategic Directions Report
CITY CLERK Clause embodied in Report No. 10 of the, as adopted by the Council of the City of Toronto at its meeting held on November 6, 7 and 8, 2001. 10 Parkland Acquisition Strategic Directions Report
Planning Primer Legislative Background, Policy Documents and Development Review Processes. Presented by: Planning Services Date: April 6, 2017
 Planning Primer Legislative Background, Policy Documents and Development Review Processes Presented by: Planning Services Date: April 6, 2017 Agenda Legislative Background 7:30 to 8:00 pm Questions 8:00
Planning Primer Legislative Background, Policy Documents and Development Review Processes Presented by: Planning Services Date: April 6, 2017 Agenda Legislative Background 7:30 to 8:00 pm Questions 8:00
K. SMART ASSOCIATES LIMITED
 Planning Justification Report Zoning By-Law Amendment 185 King Street North Waterloo, Ontario April 7th, 2017 Project Reference Number 16-245 K. SMART ASSOCIATES LIMITED CONSULTING ENGINEERS AND PLANNERS
Planning Justification Report Zoning By-Law Amendment 185 King Street North Waterloo, Ontario April 7th, 2017 Project Reference Number 16-245 K. SMART ASSOCIATES LIMITED CONSULTING ENGINEERS AND PLANNERS
Describing the Integrated Land Management Approach
 Describing the Integrated Land Management Approach ISBN No. 978-0-7785-8902-0 (Online Edition) Pub No. I/422 What is Integrated Land Management? Integrated land management (ILM) is the strategic, planned
Describing the Integrated Land Management Approach ISBN No. 978-0-7785-8902-0 (Online Edition) Pub No. I/422 What is Integrated Land Management? Integrated land management (ILM) is the strategic, planned
ROAD ACCESS MANAGEMENT IN PRACTICE: THE PORT ELIZABETH CASE
 ROAD ACCESS MANAGEMENT IN PRACTICE: THE PORT ELIZABETH CASE C. J. HOLDERNESS and H. J. STANDER* Khuthele Projects (Pty) Ltd, F02, Rostra, The Forum, Century City, 7441 *BKS (Pty) Ltd, P O Box 112, Bellville,
ROAD ACCESS MANAGEMENT IN PRACTICE: THE PORT ELIZABETH CASE C. J. HOLDERNESS and H. J. STANDER* Khuthele Projects (Pty) Ltd, F02, Rostra, The Forum, Century City, 7441 *BKS (Pty) Ltd, P O Box 112, Bellville,
BUSINESS PLAN CEN/TC 250 STRUCTURAL EUROCODES EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
 Page: 1 BUSINESS PLAN CEN/TC 250 STRUCTURAL EUROCODES EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Scope CEN/TC 250 covers the standardization of structural and geotechnical design rules for building and civil engineering works
Page: 1 BUSINESS PLAN CEN/TC 250 STRUCTURAL EUROCODES EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Scope CEN/TC 250 covers the standardization of structural and geotechnical design rules for building and civil engineering works
2013 season ticket for CPD events
 2013 season ticket for CPD events Sponsored by: RTPI West Midlands 2013 season ticket for CPD events To help members plan their CPD and book places at a discount RTPI West Midlands has a season ticket
2013 season ticket for CPD events Sponsored by: RTPI West Midlands 2013 season ticket for CPD events To help members plan their CPD and book places at a discount RTPI West Midlands has a season ticket
CITY OF HELSINKI ACCESSIBILITY GUIDELINES
 CITY OF HELSINKI ACCESSIBILITY GUIDELINES 2011 HELSINKI FOR ALL 2(13) Contents 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 Drafting of the accessibility guidelines... 3 1.2 Aim and content of the accessibility guidelines...
CITY OF HELSINKI ACCESSIBILITY GUIDELINES 2011 HELSINKI FOR ALL 2(13) Contents 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 Drafting of the accessibility guidelines... 3 1.2 Aim and content of the accessibility guidelines...
SUSTAINABLE CONSERVATION SYSTEMS FOR PRESERVATION OF MONUMENTS, SITES IN THEIR SETTINGS
 SUSTAINABLE CONSERVATION SYSTEMS FOR PRESERVATION OF MONUMENTS, SITES IN THEIR SETTINGS Staneva Hristina / Bulgarian National Correspondent of the HEREIN Project Associated member of the ICVA This paper
SUSTAINABLE CONSERVATION SYSTEMS FOR PRESERVATION OF MONUMENTS, SITES IN THEIR SETTINGS Staneva Hristina / Bulgarian National Correspondent of the HEREIN Project Associated member of the ICVA This paper
We then summarise our aspirations for public policy governing the relationship between the land and the people of Scotland.
 Scottish Environment LINK submission of evidence to the House of Commons Scottish Affairs Committee consultation on comprehensive land reform in Scotland Land, sea and air Land, sea and air are the spaces
Scottish Environment LINK submission of evidence to the House of Commons Scottish Affairs Committee consultation on comprehensive land reform in Scotland Land, sea and air Land, sea and air are the spaces
NEW REGIONAL OFFICIAL PLAN HIGH LEVEL PROCESS & FRAMEWORK
 NEW REGIONAL OFFICIAL PLAN HIGH LEVEL PROCESS & FRAMEWORK Why A New Official Plan Originally the role of Regionally Planning and content of Regional Official Plan (1970s) primarily focused on protecting
NEW REGIONAL OFFICIAL PLAN HIGH LEVEL PROCESS & FRAMEWORK Why A New Official Plan Originally the role of Regionally Planning and content of Regional Official Plan (1970s) primarily focused on protecting
Spatial / Land Use Planning System in Slovakia
 SEA and spatial planning in Slovakia: Current practices and lessons for practical application of the EC Directive Szentendre, April 14-16, 2004 Spatial / Land Use Planning System in Slovakia Spatial planning
SEA and spatial planning in Slovakia: Current practices and lessons for practical application of the EC Directive Szentendre, April 14-16, 2004 Spatial / Land Use Planning System in Slovakia Spatial planning
For the Quality of Limburg draft PEL2014
 For the Quality of Limburg draft PEL2014 Executive of the Province of Limburg, 6 May 2014 Contents 0. For the Quality of Limburg 7 1. Essen ce and most important changes 9 2. Limbu rg's ambitions and challenges
For the Quality of Limburg draft PEL2014 Executive of the Province of Limburg, 6 May 2014 Contents 0. For the Quality of Limburg 7 1. Essen ce and most important changes 9 2. Limbu rg's ambitions and challenges
Coordinadion and Cooperation. The Czech Republic Experience
 18th Council of Europe Meeting of the Workshops for the Implementation of the European Landscape Convention National policies for the implementation of the European Landscape Convention: challenges and
18th Council of Europe Meeting of the Workshops for the Implementation of the European Landscape Convention National policies for the implementation of the European Landscape Convention: challenges and
TSHWANE STRENGTHENING PROJECT PHASE 1, GAUTENG PROVINCE: Draft Scoping Report: Apollo - Verwoerdburg July 2009
 APPROACH TO UNDERTAKING THE ENVIRONMENTAL SCOPING STUDY CHAPTER 3 An Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) process refers to that process (as per the EIA Regulations) which involves the identification
APPROACH TO UNDERTAKING THE ENVIRONMENTAL SCOPING STUDY CHAPTER 3 An Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) process refers to that process (as per the EIA Regulations) which involves the identification
Design Guidance. Introduction, Approach and Design Principles. Mauritius. November Ministry of Housing and Lands. .. a
 sig evelo r D Mauritius s. Utilities.. Individu a s. er itects.to ls chpers.po e Public. T. h rban D Sc U e me Promot e h ners. A Design Guidance o.h Planne rs n w iticians r l useholde National Development
sig evelo r D Mauritius s. Utilities.. Individu a s. er itects.to ls chpers.po e Public. T. h rban D Sc U e me Promot e h ners. A Design Guidance o.h Planne rs n w iticians r l useholde National Development
LANDSCAPE INSTITUTE CORPORATE STRATEGY ISSUED 3RD APRIL Landscape Institute 107 Grays Inn Road London WC1X 8TZ United Kingdom
 LANDSCAPE INSTITUTE CORPORATE STRATEGY ISSUED 3RD APRIL 2018 Landscape Institute 107 Grays Inn Road London WC1X 8TZ United Kingdom MISSION The Landscape Institute (LI) aims to lead and inspire the landscape
LANDSCAPE INSTITUTE CORPORATE STRATEGY ISSUED 3RD APRIL 2018 Landscape Institute 107 Grays Inn Road London WC1X 8TZ United Kingdom MISSION The Landscape Institute (LI) aims to lead and inspire the landscape
BETTER URBAN PLANNING
 BETTER URBAN PLANNING SUBMISSION TO THE PRODUCTIVITY COMMISSION 3 OCTOBER 2016 BACKGROUND TO IPENZ The Institution of Professional Engineers New Zealand (IPENZ) is the lead national professional body representing
BETTER URBAN PLANNING SUBMISSION TO THE PRODUCTIVITY COMMISSION 3 OCTOBER 2016 BACKGROUND TO IPENZ The Institution of Professional Engineers New Zealand (IPENZ) is the lead national professional body representing
Implemented by. Integrated Resource Management in Asian Cities: the Urban NEXUS
 Implemented by Integrated Resource Management in Asian Cities: the Urban NEXUS 10/12/2013 Page 1 The Governance Dimension of the Urban Nexus: Integrated Spatial Planning as Essential Condition for Sound
Implemented by Integrated Resource Management in Asian Cities: the Urban NEXUS 10/12/2013 Page 1 The Governance Dimension of the Urban Nexus: Integrated Spatial Planning as Essential Condition for Sound
SUSTAINABLE URBAN DEVELOPMENT AND COHESION POLICY EUROPEAN COMMISSION. Urban Policy within the framework of EU Cohesion Policy
 Urban Policy within the framework of EU Cohesion Policy 2007-2013 16/09/2007 SUSTAINABLE URBAN DEVELOPMENT AND COHESION POLICY 2007-2013 Marco Orani European Commission Directorate General for 1 SUSTAINABLE
Urban Policy within the framework of EU Cohesion Policy 2007-2013 16/09/2007 SUSTAINABLE URBAN DEVELOPMENT AND COHESION POLICY 2007-2013 Marco Orani European Commission Directorate General for 1 SUSTAINABLE
ENVIRONMENTAL ETHICS AND PROJECT MANAGEMENT OF ARCHITECTURE
 19-004 The 2005 World Sustainable Building Conference, ENVIRONMENTAL ETHICS AND PROJECT MANAGEMENT OF ARCHITECTURE Seiki TAGAWA Ph.D 1 1 Department of Design and ure, Hokkaido Tokai University, 224 Chuwa
19-004 The 2005 World Sustainable Building Conference, ENVIRONMENTAL ETHICS AND PROJECT MANAGEMENT OF ARCHITECTURE Seiki TAGAWA Ph.D 1 1 Department of Design and ure, Hokkaido Tokai University, 224 Chuwa
Strasbourg SUMP Award: Finalist factsheet. Local Transport facts. Urban transport policy objectives of the city:
 Strasbourg 2013 SUMP Award: Finalist factsheet Local Transport facts Name of the authority: Urban Community of Strasbourg, FR Website: www.strasbourg.eu Contact: Maeva Moreau Telephone: +33 388436514 Email:
Strasbourg 2013 SUMP Award: Finalist factsheet Local Transport facts Name of the authority: Urban Community of Strasbourg, FR Website: www.strasbourg.eu Contact: Maeva Moreau Telephone: +33 388436514 Email:
Environmental Hazards and Risk Management
 Terms of Reference for ESPON-INTERACT Thematic Study Environmental Hazards and Risk Management Environmental hazards and risk management/preventions are important elements in the discussion of future Structural
Terms of Reference for ESPON-INTERACT Thematic Study Environmental Hazards and Risk Management Environmental hazards and risk management/preventions are important elements in the discussion of future Structural
Harbour-front Enhancement Committee. Wan Chai Development Phase II. Planning and Engineering Review
 Paper No. 4/2004 For discussion on 6 May 2004 Harbour-front Enhancement Committee Wan Chai Development Phase II Planning and Engineering Review PURPOSE This paper briefs Members on the scope, approach,
Paper No. 4/2004 For discussion on 6 May 2004 Harbour-front Enhancement Committee Wan Chai Development Phase II Planning and Engineering Review PURPOSE This paper briefs Members on the scope, approach,
1.0 Purpose of a Secondary Plan for the Masonville Transit Village
 Report to Planning and Environment Committee To: Chair and Members Planning & Environment Committee From: John M. Fleming Managing Director, Planning and City Planner Subject: Masonville Transit Village
Report to Planning and Environment Committee To: Chair and Members Planning & Environment Committee From: John M. Fleming Managing Director, Planning and City Planner Subject: Masonville Transit Village
SOCIETY OF FIRE PROTECTION ENGINEERS POSITION STATEMENT P THE ENGINEER AND THE TECHNICIAN DESIGNING FIRE PROTECTION SYSTEMS.
 SOCIETY OF FIRE PROTECTION ENGINEERS POSITION STATEMENT P-01-05 THE ENGINEER AND THE TECHNICIAN DESIGNING FIRE PROTECTION SYSTEMS October, 2005 Society of Fire Protection Engineers - 1 - Position Statement
SOCIETY OF FIRE PROTECTION ENGINEERS POSITION STATEMENT P-01-05 THE ENGINEER AND THE TECHNICIAN DESIGNING FIRE PROTECTION SYSTEMS October, 2005 Society of Fire Protection Engineers - 1 - Position Statement
PRESENTATION ON JOHANNESBURG S BIODIVERSITY PROGRAMME
 PRESENTATION ON JOHANNESBURG S BIODIVERSITY PROGRAMME Member of Mayoral Committee: Cllr Prema Naidoo Environmental Management & Johannesburg City Parks PRESENTATION OVERVIEW Jo burg Overview & Context
PRESENTATION ON JOHANNESBURG S BIODIVERSITY PROGRAMME Member of Mayoral Committee: Cllr Prema Naidoo Environmental Management & Johannesburg City Parks PRESENTATION OVERVIEW Jo burg Overview & Context
CHAPTER The title of P.L.1983, c.337 is amended to read as follows:
 CHAPTER 77 AN ACT concerning landscape architects, amending the title and body of, and supplementing, P.L.1983, c.337 and revising various parts of the statutory law. BE IT ENACTED by the Senate and General
CHAPTER 77 AN ACT concerning landscape architects, amending the title and body of, and supplementing, P.L.1983, c.337 and revising various parts of the statutory law. BE IT ENACTED by the Senate and General
CANADIAN SOCIETY OF LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTS DRAFT STRATEGIC PLAN 2018_20. Approved by the CSLA Members at the date AGM
 CANADIAN SOCIETY OF LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTS DRAFT STRATEGIC PLAN 2018_20 Approved by the CSLA Members at the date AGM about the CSLA The Canadian Society of Landscape Architects (CSLA) is a professional organization
CANADIAN SOCIETY OF LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTS DRAFT STRATEGIC PLAN 2018_20 Approved by the CSLA Members at the date AGM about the CSLA The Canadian Society of Landscape Architects (CSLA) is a professional organization
BEDFORD BOROUGH COUNCIL PLAN IMPLEMENTATION MONITORING REPORT
 BEDFORD BOROUGH COUNCIL PLAN IMPLEMENTATION MONITORING REPORT 2017-18 Summary 1 Progress on local development documents 1 Local development documents adopted in the monitoring period 1st April 2017 31st
BEDFORD BOROUGH COUNCIL PLAN IMPLEMENTATION MONITORING REPORT 2017-18 Summary 1 Progress on local development documents 1 Local development documents adopted in the monitoring period 1st April 2017 31st
SOUTH AFRICA S PREPARATIONS FOR HABITAT III COMMON AFRICAN POSITION FOR HABITAT III. Habitat III Urban Breakfast 5 October 2016
 SOUTH AFRICA S PREPARATIONS FOR HABITAT III COMMON AFRICAN POSITION FOR HABITAT III Habitat III Urban Breakfast 5 October 2016 Context and Background 1. Africa intends actively shaping the New Urban Agenda,
SOUTH AFRICA S PREPARATIONS FOR HABITAT III COMMON AFRICAN POSITION FOR HABITAT III Habitat III Urban Breakfast 5 October 2016 Context and Background 1. Africa intends actively shaping the New Urban Agenda,
Transforming Library Services in the digital information environment
 Transforming Library Services in the digital information environment Jennefer Nicholson, IFLA Secretary General Colombo, 29 December 2015 2/11/2016 Major global influences and opportunities United Nations
Transforming Library Services in the digital information environment Jennefer Nicholson, IFLA Secretary General Colombo, 29 December 2015 2/11/2016 Major global influences and opportunities United Nations
Perth and Kinross Council Development Management Committee 8 June Pre-Application Report by Development Quality Manager
 Perth and Kinross Council Development Management Committee 8 June 2016 5(3)(i) 16/259 Pre-Application Report by Development Quality Manager Residential development at St Martins Road, Land 120 metres West
Perth and Kinross Council Development Management Committee 8 June 2016 5(3)(i) 16/259 Pre-Application Report by Development Quality Manager Residential development at St Martins Road, Land 120 metres West
PSRC REVIEW REPORT & CERTIFICATION RECOMMENDATION
 PSRC REVIEW REPORT & CERTIFICATION RECOMMENDATION KITSAP COUNTY COUNTYWIDE PLANNING POLICIES July 2, 2012 BACKGROUND A major emphasis of the Washington State Growth Management Act (GMA) is the need to
PSRC REVIEW REPORT & CERTIFICATION RECOMMENDATION KITSAP COUNTY COUNTYWIDE PLANNING POLICIES July 2, 2012 BACKGROUND A major emphasis of the Washington State Growth Management Act (GMA) is the need to
Great Easton Neighbourhood Plan Statement of Basic Conditions
 Great Easton Neighbourhood Plan 2017-2031 Statement of Basic Conditions OCTOBER 2016 GREAT EASTON PARISH COUNCIL Contents 1.0 Introduction....Page 2 2.0 Summary of Submission Documents and Supporting Evidence..
Great Easton Neighbourhood Plan 2017-2031 Statement of Basic Conditions OCTOBER 2016 GREAT EASTON PARISH COUNCIL Contents 1.0 Introduction....Page 2 2.0 Summary of Submission Documents and Supporting Evidence..
Stock-Taking on Integrated Coastal Zone Management (ICZM) in the Black Sea IMPLEMENTATION AUDIT QUESTIONNAIRE 2010
 Stock-Taking on Integrated Coastal Zone Management (ICZM) in the Black Sea IMPLEMENTATION AUDIT QUESTIONNAIRE 2010 PURPOSE The purposes of this questionnaire are: (a) to perform the policy, legal and institutional
Stock-Taking on Integrated Coastal Zone Management (ICZM) in the Black Sea IMPLEMENTATION AUDIT QUESTIONNAIRE 2010 PURPOSE The purposes of this questionnaire are: (a) to perform the policy, legal and institutional
Cooperative Research in Water Management
 Proceedings of the 8 th International Conference on Applied Informatics Eger, Hungary, January 27 30, 2010. Vol. 1. pp. 273 281. Cooperative Research in Water Management Margit Horosz-Gulyás, Katalin Katonáné
Proceedings of the 8 th International Conference on Applied Informatics Eger, Hungary, January 27 30, 2010. Vol. 1. pp. 273 281. Cooperative Research in Water Management Margit Horosz-Gulyás, Katalin Katonáné
COUNCIL POLICY 19(35) AND 19(35A) RELATING TO THE URBAN DESIGN AWARDS PROGRAM
 COUNCIL POLICY 19(35) AND 19(35A) RELATING TO THE URBAN DESIGN AWARDS PROGRAM 19(35) Urban Design Awards The City of London Urban Design Awards Program is intended to recognize, celebrate and inspire design
COUNCIL POLICY 19(35) AND 19(35A) RELATING TO THE URBAN DESIGN AWARDS PROGRAM 19(35) Urban Design Awards The City of London Urban Design Awards Program is intended to recognize, celebrate and inspire design
Sustainable cities through integrated land use management systems
 The Sustainable City IX, Vol. 1 189 Sustainable cities through integrated land use management systems W. Fourie i@consulting (Pty) Ltd., Registered with the South African Council of Planners, South Africa
The Sustainable City IX, Vol. 1 189 Sustainable cities through integrated land use management systems W. Fourie i@consulting (Pty) Ltd., Registered with the South African Council of Planners, South Africa
Protocol between Local Housing Authorities and Fire and Rescue Authorities to improve fire safety
 Protocol between Local Housing Authorities and Fire and Rescue Authorities to improve fire safety Foreword by Communities and Local Government Ministers It is always a priority to ensure safety from the
Protocol between Local Housing Authorities and Fire and Rescue Authorities to improve fire safety Foreword by Communities and Local Government Ministers It is always a priority to ensure safety from the
Prescription of qualifications. ARB Criteria at Part 2
 Prescription of qualifications ARB Criteria at Part 2 Approved: January 2010 Effective From: 2011/2012 Introduction Under the Architects Act 1997, the Architects Registration Board (ARB) has the responsibility
Prescription of qualifications ARB Criteria at Part 2 Approved: January 2010 Effective From: 2011/2012 Introduction Under the Architects Act 1997, the Architects Registration Board (ARB) has the responsibility
Cape Environmental Assessment Practitioners(Pty)
 BACKGROUND INFORMATION DOCUMENT (BID) Introduction Cape Environmental Assessment Practitioners(Pty) Ltd Reg. No. 2008/004627/07 Telephone: (044) 874 0365 First Floor, Eagles View Building Facsimile: (044)
BACKGROUND INFORMATION DOCUMENT (BID) Introduction Cape Environmental Assessment Practitioners(Pty) Ltd Reg. No. 2008/004627/07 Telephone: (044) 874 0365 First Floor, Eagles View Building Facsimile: (044)
Official Plan Review: Draft Built Form Policies
 PG.30.1 REPORT FOR ACTION Official Plan Review: Draft Built Form Policies Date: May 15, 2018 To: Planning and Growth Management Committee From: Chief Planner and Executive Director, City Planning Division
PG.30.1 REPORT FOR ACTION Official Plan Review: Draft Built Form Policies Date: May 15, 2018 To: Planning and Growth Management Committee From: Chief Planner and Executive Director, City Planning Division
Świętokrzyskie region (PL): Modern water supply and sewerage disposal for more effective utilisation of local assets.
 Świętokrzyskie region (PL): Modern water supply and sewerage disposal for more effective utilisation of local assets. SYNTHESIS The Serwis village project was an infrastructure project in Nowa Słupia commune
Świętokrzyskie region (PL): Modern water supply and sewerage disposal for more effective utilisation of local assets. SYNTHESIS The Serwis village project was an infrastructure project in Nowa Słupia commune
INTERMEDIATE EXAMINATION 2.1 PART (1) URP 401 Land Economics. URP 402 Research methods in Planning. URP 403 History of Town Planning II
 INTERMEDIATE EXAMINATION 2.1 PART (1) URP 401 Land Economics URP 402 Research methods in Planning URP 403 History of Town Planning II URP 404 Population and Urbanization Studies I URP 405 Planning Studio
INTERMEDIATE EXAMINATION 2.1 PART (1) URP 401 Land Economics URP 402 Research methods in Planning URP 403 History of Town Planning II URP 404 Population and Urbanization Studies I URP 405 Planning Studio
BOARD OF EXAMINERS OF LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTS
 STATE OF RHODE ISLAND AND PROVIDENCE PLANTATIONS BOARD OF EXAMINERS OF LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTS RULES AND REGULATIONS Revised RHODE ISLAND STATE BOARD OF EXAMINERS OF LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTS RULES OF THE BOARD
STATE OF RHODE ISLAND AND PROVIDENCE PLANTATIONS BOARD OF EXAMINERS OF LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTS RULES AND REGULATIONS Revised RHODE ISLAND STATE BOARD OF EXAMINERS OF LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTS RULES OF THE BOARD
International Summer School. African Heritage and the Pillars of Sustainability. Call for Papers
 International Summer School African Heritage and the Pillars of Sustainability Call for Papers African Heritage and the Pillars of Sustainability Call for Papers 2016 International Summer School Iringa,
International Summer School African Heritage and the Pillars of Sustainability Call for Papers African Heritage and the Pillars of Sustainability Call for Papers 2016 International Summer School Iringa,
Extension of Registered Gas Installer Scheme to include Non-Domestic Gas Works
 Extension of Registered Gas Installer Scheme to include Non-Domestic Gas Works Information Paper Reference: CER/16373 Date Published: 15/12/2016 Closing Date: NA Executive Summary The CER has decided to
Extension of Registered Gas Installer Scheme to include Non-Domestic Gas Works Information Paper Reference: CER/16373 Date Published: 15/12/2016 Closing Date: NA Executive Summary The CER has decided to
Road Safety Impact Assessment
 Road Safety Impact Assessment October 2016 TRANSPORT INFRASTRUCTURE IRELAND (TII) PUBLICATIONS About TII Transport Infrastructure Ireland (TII) is responsible for managing and improving the country s national
Road Safety Impact Assessment October 2016 TRANSPORT INFRASTRUCTURE IRELAND (TII) PUBLICATIONS About TII Transport Infrastructure Ireland (TII) is responsible for managing and improving the country s national
The Dreispitz in Basel / Switzerland: New economy on old sites
 The Dreispitz in Basel / Switzerland: New economy on old sites 1. Introduction At 50.000m 2 Dreispitz is currently the largest and most ambitious development project in Basel, the second biggest town in
The Dreispitz in Basel / Switzerland: New economy on old sites 1. Introduction At 50.000m 2 Dreispitz is currently the largest and most ambitious development project in Basel, the second biggest town in
Glenborough at Easton Land Use Master Plan
 Implementation 114 9.0 IMPLEMENTATION 9.1 OVERVIEW This chapter summarizes the administrative procedures necessary to implement the proposed land use plan, infrastructure improvements, development standards,
Implementation 114 9.0 IMPLEMENTATION 9.1 OVERVIEW This chapter summarizes the administrative procedures necessary to implement the proposed land use plan, infrastructure improvements, development standards,
ROLE OF EIA PRACTITIONERS IN IMPROVING EIA REPORTING QUALITY - CHALLENGES AND SOLUTIONS: A CASE STUDY OF EIA SYSTEM IN PUNJAB PAKISTAN
 ROLE OF EIA PRACTITIONERS IN IMPROVING EIA REPORTING QUALITY - CHALLENGES AND SOLUTIONS: A CASE STUDY OF EIA SYSTEM IN PUNJAB PAKISTAN ABSTRACT Nasim-ur-Rehman Shah Environmental impact assessment is an
ROLE OF EIA PRACTITIONERS IN IMPROVING EIA REPORTING QUALITY - CHALLENGES AND SOLUTIONS: A CASE STUDY OF EIA SYSTEM IN PUNJAB PAKISTAN ABSTRACT Nasim-ur-Rehman Shah Environmental impact assessment is an
