Investigating the bottom free surface nappe (ogee profile) across a sharp crested weir caused by the flow in an asymmetrical approach channel
|
|
|
- Rhoda Manning
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Investigating the bottom free surface nappe (ogee profile) across a sharp crested weir caused by the flow in an asymmetrical approach channel S J van Vuuren, G L Coetzee, C P R Roberts The shape of an ogee spillway is based on the shape of the lower nappe of water flowing over an aerated sharp-crested weir. At the design discharge, this shape minimises the possibility of sub-atmospheric pressure occurring on the spillway and maximises the discharge across the spillway. The formulae that are currently in use to approximate the ogee profile consider only two-dimensional flow parameters, being the depth of flow over the spillway crest, the inclination of the upstream wall face, and the pool depth upstream of the spillway. The current formulae for the ogee shape, does not consider the influence of three-dimensional flow. The most significant three-dimensional flow parameters that could affect the shape of the lower nappe are the flow velocity distribution upstream of the spillway, the orientation or angle of the water approaching the spillway, the asymmetrical cross-section of the approach channel, and the curvature of the dam wall. This paper reflects the influence of asymmetrical flow in the approach channel. The investigation was based on a physical model constructed at the Department of Water and Sanitation (DWS). The inclination of the model s sidewalls of the upstream approach channel was varied to cause a change in the symmetricity, while the lower nappe profile was routinely measured. It was found that the flow in the asymmetrical approach channel caused a variation from the theoretical estimated ogee profile. A comparison between the measured nappe profile and the currently used formulae was investigated. It can be concluded that the symmetricity of the approach channel influences the shape of the bottom nappe, which differs from the shape as proposed by the current ogee formulae. It is recommended that three-dimensional flow should be examined when designing an ogee spillway. List of SYMbols A l approach channel cross-sectional area measured from the centreline of the spillway s crest to the left bank (m 2 ) A t total approach channel cross-sectional area (m 2 ) C vertical displacement of the turning point measured at the lower nappe of the ogee profile (m) f horizontal displacement of the turning point measured on the lower nappe of the ogee profile (m) H a velocity head (m) H d measured water depth upstream from the crest of the sharp-crested weir, relative to the crest (m) H e total head (sum of H d and H a ) (m) H o design head of ogee spillway (He - C ) (m) P upstream wall depth of the weir (m) T p turning point (apex position) on lower nappe of the ogee profile S f symmetricity factor of the approach channel v o mean velocity in the approach channel (m/s) INTRODUCTION The ogee spillway relationship (USBR 1987; Hager 1987) is used to define the geometric profile of the spillway section of a dam or hydraulic structure. The ogee relationship describes the bottom nappe associated with the flow over a sharp-crested weir. The current relationship accommodates the influence of the unit discharge, the angle of inclination of the upstream wall face, as well as the relationship of upstream pool depth to the total upstream energy at the apex of the structure. In cases where the discharge flow rate exceeds the design flow rate, the nappe TECHNICAL PAPER Journal of the South African Institution of Civil Engineering Vol 57 No 3, September 215, Pages 57 63, Paper 98 PROF FANIE VAN VUUREN Pr Eng is a professor in the Department of Civil Engineering at the University of Pretoria, and a project leader for a number of Water Research Commission projects. He has 39 years of experience in water resources engineering and holds BSc Eng, BSc Hons Eng, MEng, PhD (Eng) and MBA degrees, all from the University of Pretoria. He has worked as a specialist consultant for various consulting engineering companies, has written numerous technical reports, journal publications and chapters in books, and has presented lectures in many countries. Contact details: Department of Civil Engineering University of Pretoria Pretoria, 1 South Africa T: +27 () E: fanie.vanvuuren@up.ac.za LOUIS COETZEE obtained his BEng (Civil), BEng (Hons) and MEng (cum laude) in Water Resources Engineering at the University of Pretoria, and is currently studying towards a PhD. He joined the academic setting of the University of Pretoria as a junior lecturer in 211 after completing his undergraduate studies. He obtained his early professional experience working for Sinotech CC and is currently employed as an Engineer at SMEC South Africa (Pty) Ltd. He has presented various courses on flood determination, flood lines, drainage structures, stormwater modelling, pipelines, pump stations and drainage systems in conjunction with Prof SJ van Vuuren. He has a special interest in numerical and physical modelling of hydraulic structures and water distribution networks. Contact details: Department of Civil Engineering University of Pretoria Pretoria, 1 South Africa T: +27 () E: glouis.coetzee@up.ac.za DR PAUL ROBERTS Pr Eng, a civil engineer, retired at the end of March 23 from the then South African Department of Water Affairs and Forestry after a career of some 42 years in water resources management. Since retirement he has been active in consulting work in South Africa and Africa. He has also served as the SANCOLD (South African National Committee on Large Dams) secretary since 28. Contact details: SANCOLD PO Box 344 Pretoria, 1 South Africa T: +27 () E: paul.roberts@worldonline.co.za Keywords: asymmetrical, cavitation, nappe, ogee profile, physical model, sharp-crested weir Van Vuuren S J, Coetzee G L, Roberts C P R. Investigating the bottom free surface nappe (ogee profile) across a sharp-crested weir caused by the flow in an asymmetrical approach channel. J. S. Afr. Inst. Civ. Eng. 215;57(3), Art. #98, 7 pages. 57
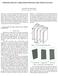
2 H a Table 1 Methods for approximation of the ogee curve Approximation of the ogee curve based on: H d H e T p C The principles of projectile movement Ven te Chow (1 st principles) (Chow 1959) Experimental methods United States Bureau of Reclamation (USBR 1987) P f Brink Velocity (Wahl et al 28) Ven te Chow (modified) (Chow 1959) United States Army Corps of Engineers (USACE 197) United States Army Corps of Engineers (USACE (b) 1987) Creeger (Chanson 24) Figure 1 Position of the turning point of the curvature at the maximum elevation of the ogee profile detaches from the surface of the spillway and a sub-atmospheric pressure region is generated that may lead to cavitation (Savage & Johnson 21; Momber 2). Cavitation usually occurs during a unit discharge, in excess of the design head, where the surface pressure can be reduced at positions along the spillway to sub-atmospheric pressure. This may cause the formation of vapour cavities. Vapour cavities may also be formed on the spillway where an irregularity in the surface exists. The vapour cavities (also referred to as miniscule air bubbles) will progress along the flow path due to the high flow velocity on the spillway to a region downstream where sufficient pressure is available that will lead to the collapse of the air vacuum. This generates localised high pressures. Should these vapour cavities collapse near the spillway structure, there will be some superficial damage to the spillway s surface where the vapour bubble has collapsed. This cavitation damage can ultimately result in substantial erosion and, if ignored, will subsequently cause failures of the spillway chute. Minute cracks, offsets and increased surface roughness intensify this cavitation process. The extent of cavitation damage is a function of the cavitation indices at key locations on the spillway chute and the duration of flow over the spillway. This emphasises the need for a geometric, accurate and precise spillway profile to reduce the possibility of sub-atmospheric pressure formation (USACE 29). It is hypothesised that the geometric profile of the ogee spillway will be influenced by the following factors: a. The asymmetrical cross-sectional approach channel upstream from the spillway b. The relative orientation of the spillway with regard to the approaching flow c. The curvature of the spillway in relation to the depth of the structure. This study evaluated the existing ogee relationship, considering in particular the threedimensional flow parameters resembling an asymmetrical approach channel. The physical model was set up in accordance with ASTM Designation: D (Standard Test Method for Open-Channel Flow Measurement of Water with Thin- Plate Weirs (ASTM International 21) and ISO 1438: Hydrometry Open channel flow measurement using thin-plate weirs (ISO 28). Froude similarity was selected with an undistorted scale of 1:1 for the physical model. THEORETICAL CONSIderATION Research on the projectile movement of a free-falling jet of water revealed that the shape of the lower nappe of a jet of water flowing over a ventilated sharp-crested weir resembled the shape of an ogee spillway (Chow 1959; Hager 1987; Knapp et al 197; Melsheimer & Murphy 197; Ministry of Science and Technology 27; Murphy 1973; USACE (a) 1987; USACE (b) 1987; USBR 1987; Wahl et al 28). However, both the numerical relationships for the flow over a sharp-crested weir and the principle for the projectile movement of a free-falling jet of water describing this shape only consider the two-dimensional characteristics of the flow, namely the available energy (i.e. depth and velocity of water flowing over the spillway crest), the angle of inclination of the upstream wall face, and the height of the spillway above the natural ground level (USBR 1987; USCE 197; Vischer & Hager 1999). This approximation of coplanar (two-dimensional) flow neglects the three-dimensional flow parameters which are occurring upstream of the spillway. Research indicated that the vertical displacement of a flow particle at the crest s origin is equal to the vertical distance between the highest point of the nappe and the elevation of the ogee crest (Chow 1959). Figure 1 depicts this position, which is recognised as the turning point of the curvature (T p ). Rajaratnam et al (1968) (referenced by Vischer & Hager, Dam Hydraulics 1999) indicated that the vertical value of C can be empirically estimated by Equation 1 and the horizontal distance (f) to this coordinate measured from the crest can be estimated by Equation 2. The experiments done by Rajaratnam et al (1968) were actually for a confined weir. C =.112 H d.4v o 2 2g f =.25 H d.4v o 2 Scimeni (Chanson 24) Knapp (Chanson 24) Montes (Chanson 24) CE-516 (Ministry of Science and Technology 27) Note: The reader is referred to the associated reference for more detail about each approximation of the ogee profile 2g (1) (2) A wealth of literature sources are available on the approximation of the ogee profile for spillway design, and several endeavours have been made in developing a two-dimensional relationship that would be able to mathematically describe the most desirable shape of the ogee curve. These relationships exclude the asymmetricity of valleys and the asymmetricity of the topographical approach channels that influence the flow pattern and velocity distribution upstream of the spillway, leading to an insufficient design of the ogee spillway (Van Vuuren et al 211). Methods defining the geometry of the ogee spillway s crest are governed by the relative 58 Journal of the South African Institution of Civil Engineering Volume 57 Number 3 September 215
3 Table 2 Various scenarios executed with allocated notation Notation Description of approach channel Total discharge (l/s) Unit discharge (l/s/m) Head (H d ) (mm) Equivalent ogee head (H o ) (mm) Symmetricity factor (S f ) Scenario A Symmetrical (baseline) Scenario B Scenario C Asymmetrical, sidewall inclined at 45 Asymmetrical, sidewall inclined at Crest of weir: 2 mm thick stainless steel plate, laser cut to a 9 angle Plywood sheet fixed to square hollow section frame Sliding circular hollow section for adjusting the inclination of the sidewall height of the structure, the available design head and upstream face slope of the spillway. Other factors that should also be considered are the approach channel symmetricity, approach channel depth, orientation of the spillway relative to the flow path and the curvature (if applicable) of the hydraulic structure (Van Vuuren et al 211). Literature reflects that in 1888 some of the first research was conducted to investigate the shape of the ogee profile. Ever since then the ogee spillway has been the most studied spillway geometry (Savage & Johnson 21; Thandaveswara 26). The nappe-shaped profile is an ideal profile because at the design discharge, water flowing over the crest of the spillway always remains in contact with the surface of the spillway as it glides over it. Additionally, for the ogee shape, there will be no sub-atmospheric pressure regions that may develop on the spillway surface at the design discharge. Some of the well-regarded approximations of the ogee profile are grouped according to the two categories shown in Table 1. EXPerIMENTAL SetuP AND Procedure A physical model of a sharp-crested weir was constructed at the Department of Water Affairs and Sanitation s Hydraulic Laboratory, South Africa. The model provided the opportunity to: Figure 2 Generic upstream cross-sectional view of the asymmetrical approach channel with sidewall inclined at various angles Varying inclination of the sidewall provide the model with the correct dimensions and specifications in order to ensure that equations provided by the current literature are valid and that international credibility is achieved (ASTM International 21; ISO 28) provide an undisturbed, uniform approach flow pattern across the weir, and vary the flow rate to enable the investigation of different stages versus flow rate scenarios, as well as measuring the stage of the approach flow accurately measure the profile of the underlying nappe of water flowing over the sharpcrested weir. Three configurations of the physical model were investigated as reflected in Table 2, the first being the symmetrical layout with vertical sidewall, used as baseline reference for the other configuration. The other layouts comprised one having an inclined sidewall of 45 and the other an inclined sidewall of 6. Six sheets of plywood were attached to steel frames and these were lowered into the approach channel of the physical model. The plywood sidewalls could vary between angles that ranged from 45 to 9. This allowed the symmetricity of the approach channel to be changed to an asymmetrical approach channel with one sidewall either being sloped at 45 or 6. The total length of the sidewall measured 7.2 m. The cross-sectional view of the variable approach channel is depicted in Figure 2. The symmetrical approach channel, used as baseline scenario, was compared with the asymmetrical approach layouts that were conducted at various sidewall inclinations. The various scenarios executed were labelled as indicated in Table 2. For each of the scenarios conducted a separate datasheet was set up in which the XYZ-coordinates of the lower nappe profile were populated. The stage depth measured in stilling columns by two OTT-point gauges was averaged and converted to the design head of an equivalent ogee structure. Equation 1 as defined by Rajaratnam et al (1968) was applied to calculate the equivalent ogee design head. The measured ogee profile for each of the scenarios was plotted in a three-dimensional XYZ surface plot against the theoretical ogee profile (USACE 197). RESultS AND DISCUSSION The experimental results produced by the asymmetrical approach channel generated seven ogee curves for each channel configuration, representing the three-dimensional shape of the asymmetrical bottom nappe. In the case of the symmetrical base line recordings, the ogee curve was measured at five increments along the crest of the sharp-crested weir, representing the three-dimensional shape of the symmetrical bottom nappe. These measured curves were representing the shape of the nappe that extends from the left boundary, centre and up to the right boundary of the nappe. The positions of the curves were chosen to ensure that all the scenarios could be analysed individually and later compared with the other scenarios. Each point measured was recorded as a three-dimensional XYZ coordinate. These measurements were depicted in a two-dimensional XZ-plot in Figure 4, and were compared with the theoretical ogee profile by the USBR (1987), USACE (197), and Ministry of Science and Technology (CE-516) (27). The measured ogee profile was plotted as a red surface in a three-dimensional XYZ-plot in Figure 5. Overlapping the measured ogee surface plot in Figure 5 is the theoretical ogee profile by the USACE (197) depicted by the green surface. Journal of the South African Institution of Civil Engineering Volume 57 Number 3 September
4 Figure 3 High flow velocities observed at the boundary of the sharp-crested weir s crest as caused by the steep inclination of the 6 sidewall Scenario A: Symmetrical approach channel (baseline) It can be seen in the two-dimensional plot of scenario A that the ogee profile in the centre of the nappe was greater than those measured at the outer boundaries. This trend can be visualised in more detail in the final results in which the surface plot of the measured nappe was depicted in an XYZ plot. The reason for this outcome can be explained due to the fact that the ogee profile was measured for a symmetrical approach channel, and that an increased flow rate exists in the centre of the structure, resulting in minimal contraction and flow resistance at this location. The result was that the theoretical approximations of the ogee profile tend to underestimate the measured ogee profile at the centre of the weir and overestimate the ogee profile at the boundaries where flow contraction and resistance was a maximum. Overestimation of the ogee profile is not as critical as underestimation. The overestimation of the ogee profile at the boundaries will simply imply that a positive hydrostatic pressure is present in these regions on the spillway. However, underestimating the ogee profile may cause a more detrimental effect, which may lead to cavitation of the surface of the spillway if significant sub-atmospheric pressures are experienced. Long-term exposure to extensive sub-atmospheric conditions may cause failure of the spillway structure. Scenario B: Asymmetrical approach channel with sidewall inclined at 45 In the two-dimensional plot of scenario B it was noticed that the ogee profile was greater toward the side of the inclined sidewall, unlike in scenario A where the greatest ogee profile occurred in the centre of the flow, due to the symmetricity of the approach channel. The greatest ogee profile tends to lie between the 6 mm and 8 mm measuring location. The inclined sidewall was installed to the right of the approach channel. The centreline tends to be moved off-centre in the direction where the inclined sidewall had been installed. The result was that the theoretical approximations of the ogee profile tend to underestimate the measured ogee profile between the 6 mm and 8 mm mark measured along the crest, and again overestimate the ogee profile at the boundaries similar to the symmetrical approach channel layout. Scenario C: Asymmetrical approach channel with sidewall inclined at 6 Similar to scenario B the two-dimensional plot of scenario C reflected that the ogee profile was greater towards the side of the inclined sidewall. The greatest ogee profile tends to lie at the 8 mm measuring location. This indicated that the ogee nappe was moved offcentre even more than in the case when the inclination of the sidewall was 45. This 6 angle sidewall was steep and extended closely to the boundary of the 1 2 mm mark of the sharp-crested weir so that this could have caused the sharp-crested weir not to function as a fully-contracted weir anymore. This may be the reason for the higher velocities present in this region (less flow resistance), thus resulting in the ogee profile to be the greatest at this location. The result was that the theoretical approximations of the ogee profile tended to underestimate the measured ogee profile between the 4 mm and 1 mm mark as measured along the crest, and again overestimated the ogee profile at the boundaries similar to the symmetrical approach channel layout. High flow velocities present in this region can be observed in Figure 3 where the flow pattern can be clearly visualised. This confirms the hypothesis that an asymmetrical approach channel influences not only the geometric shape of the ogee profile, but also the symmetricity of flow across the hydraulic structure. The centreline tends to be moved off-centre in the direction where the inclined sidewall had been installed. It is therefore proposed that a symmetricity factor (S f ) be used to estimate the severity of the asymmetricity of the approach channel. This will allow for future classification of the approach channels into different categories depending on the severity of the asymmetricity. The proposed relationship for the symmetricity factor is given in Equation 3. The symmetricity factors for scenarios A to C are given in Table 2. S f = A l A t (3) In the case of a symmetrical approach channel, the symmetricity factor (S f ) would therefore be equal to.5, and values less than.5 would indicate that an asymmetrical approach channel is perceptible. The classification of the symmetricity factor needs further investigation and will be published in a forthcoming paper. CONCLUSIONS AND recommendations The change in the symmetricity of the approach channel has unambiguously proved to alter the shape of the ogee profile. This alteration is appreciated in the following ways: The profile of the nappe differs along the length of the weir. From the experiments conducted it was also revealed that the side of the weir with the inclined sidewall caused the profile of the nappe to be higher than at the opposite side. When comparing the asymmetrical approach channel s ogee profile with the baseline/symmetrical nappe profile, the profile of the asymmetrical approach channel configuration was increased at the vicinity of the inclined wall. If an ogee spillway were to be designed considering only the two-dimensional flow parameters, problems would arise if the cross-section is asymmetrical. The profile would tend to be higher than expected towards the inclined sidewall 6 Journal of the South African Institution of Civil Engineering Volume 57 Number 3 September 215
5 15 Horizontal x-scale (mm) Scenario A: 1 mm Scenario A: 2 mm 5 Scenario A: 4 mm Scenario A: 6 mm Scenario A Vertical y-scale (mm) 5 15 Scenario A: 1 mm Scenario A: 1 1 mm USBR (1987) USACE compound curve (197) USBR (insignificant approach velocity, 1987) CE-516 (27) 2 1 Horizontal x-scale (mm) Scenario B: 1 mm Scenario B: 2 mm Scenario B: 4 mm Scenario B: 6 mm Scenario B Vertical z-scale (mm) Scenario B: 8 mm Scenario B: 1 mm Scenario B: 1 1 mm USBR (1987) USACE compound curve (197) 5 6 USBR (insignificant approach velocity, 1987) 7 CE-516 (27) 2 1 Horizontal x-scale (mm) Scenario C: 1 mm Scenario C: 2 mm Scenario C: 4 mm Scenario C: 6 mm Scenario C Vertical z-scale (mm) Scenario C: 8 mm Scenario C: 1 mm Scenario C: 1 1 mm USBR (1987) USACE compound curve (197) 5 6 USBR (insignificant approach velocity, 1987) 7 CE-516 (27) Figure 4 Measured ogee profile for different scenarios and compared with various other approximations Journal of the South African Institution of Civil Engineering Volume 57 Number 3 September
6 2 2 Scenario A Scenario B Scenario C Figure 5 Measured ogee profile (red profile) for different scenarios and compared with the USACE (197) approximation (green profile) 62 Journal of the South African Institution of Civil Engineering Volume 57 Number 3 September 215
7 of the structure, yet lower than expected on the opposite side. This may cause the dual problem of potential separation from the spillway structure causing cavitation damage due to sub-atmospheric pressure, and sub-optimal discharge on the opposite side, respectively. The deduction of the comparison of measured profiles with the theoretically calculated ogee profiles produced diverse results: i. The USBR (1987), USACE (197), Hager (1987) and Ministry of Science and Technology (CE-516) (27) ogee approximations corresponded well with the geometry of the measured ogee profiles, although these curves had a tendency to underestimate the actual ogee profile at the position on the crest where the effective resistance to flow is a minimum. ii. The downstream approximation made by of the ogee curve appeared to overestimate the projection of the nappe profile in the downstream region of the ogee. This demonstrated that the formula was conservative and that the probability of sub-atmospheric pressure occurring in this region is minimised. It is recommended that further studies be carried out (by making use of physical modelling) to assess the effect of the angle of the approach channel relative to the ogee spillway, as well as the curvature of the crest on the geometric shape of the ogee profile. Results obtained from this study, as well as the studies proposed above, should be compared with a numerical simulation using a CFD analysis. It is absolutely imperative and critical to include the effect of threedimensional flow when designing an ogee spillway. This is also indicative of the necessity of physical modelling during the design process, as theoretical curves do not necessarily provide optimal and safe solutions. A design guideline should be developed that would assist design engineers to design suitable, efficient and safe ogee spillways by considering parameters such as the asymmetricity of the approach channel. AckNowledGEMENTS We would like to thank the Water Research Commission for their valued contribution to this study, as well as the Department of Water and Sanitation for the use of their hydraulic laboratory. REFERENceS ASTM International 21. Standard Test Method for Open-channel Flow Measurement of Water with Thinplate Weirs. US Patent No. Designation: D Chanson, H 24. The Hydraulics of Open Channel Flow: An Introduction, 2nd ed. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann. Chow, V T Open-channel Hydraulics, reprint. Illinois, US: The Blackburn Press. Hager, W H Continuous crest profile for standard spillway. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 113(11): ISO (International Organization for Standardization) 28. Hydrometry Open-channel flow measurment using thin-plate weirs. Switzerland, Patent No. ISO Knapp, R, Daily, W & Hammitt, F 197. Cavitation. New York: McGraw-Hill. Melsheimer, E S & Murphy, T E 197. Hydraulic Design Criteria, Sheets to 11-16/2. U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Ministry of Science and Technology (Myanmar) 27. CE-516. Design of Hydraulic Structures, Myanmar: Department of Technical and Vocational Education. Momber, A W 2. Short-time cavitation erosion of concrete. Wear, 241: Murphy, T E Spillway Crest Design. Vicksburg, MS: U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Waterways Experiment Station. Rajaratnam, N, Subramanya, K & Muralidhar, D Flow profiles over sharp-crested weirs. Journal of the Hydraulics Division, ASCE, 94(HY3): Savage, B & Johnson, M 21. Flow over Ogee Spillway: Physical and numerical model case study. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 127(8): Thandaveswara, B 26. National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning (NPTEL). Adras, India: Indian Institute of Technology. USACE (U.S. Army Corps of Engineers) 197. Hydraulic Design Criteria. Vicksburg, MI: USACE Waterways Experiment Station. USACE (U.S. Army Corps of Engineers) 1987a. Hydraulic Design Criteria: Overflow Spillway Crest. Vicksburg, MI: USACE Waterways Experiment Station. USACE (U.S. Army Corps of Engineers) 1987b. Hydraulic Design Criteria: Elliptical Crest Spillway Co-ordinates, Vicksburg, MI: USACE Waterways Experiment Station. USACE (U.S. Army Corps of Engineers) 29. Dam Safety Risk Analysis Best Practices Training Manual. Version 2.2 April 211 ed. Denver, CO: U.S. Department of Interior Bureau of Reclamation. USBR (U.S. Department of Interior Bureau of Reclamation) Spillways, Chapter 9. In: Design of Small Dams, 3rd ed. Washington: U.S. Government Printing Office, pp Van Vuuren, S, Steyn, G, Pilz, N & Koch, H 211. Influence of 3D approaching flow on a Curved Ogee Spillway Section Neckartal Dam Namibia. Stellenbosch: UP Printers. Vischer, D & Hager, W (Eds.) Dam Hydraulics. New York: Wiley, pp Wahl, T L, Frizell, K H & Cohen, E A 28. Computing the trajectory of free jets. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, ASCE, 1.161(2): Journal of the South African Institution of Civil Engineering Volume 57 Number 3 September
LABORATORY STUDY ON THE CONSOLIDATION SETTLEMENT OF CLAY-FILLED GEOTEXTILE TUBE AND BAGS
 Journal of GeoEngineering, Vol. 6, No. 1, pp. Chew 41-45, et al.: April Laboratory 2011 Study on the Consolidation Settlement of Clay-Filled Geotextile Tube and Bags 41 LABORATORY STUDY ON THE CONSOLIDATION
Journal of GeoEngineering, Vol. 6, No. 1, pp. Chew 41-45, et al.: April Laboratory 2011 Study on the Consolidation Settlement of Clay-Filled Geotextile Tube and Bags 41 LABORATORY STUDY ON THE CONSOLIDATION
CEE:3371 Principles of Hydraulics and Hydrology Project #2 Flow Measurement with a Weir
 CEE:3371 Principles of Hydraulics and Hydrology Project #2 Flow Measurement with a Weir Problem Statement The Iowa DNR plans to monitor a proposed prairie restoration project in eastern Iowa as an experiment.
CEE:3371 Principles of Hydraulics and Hydrology Project #2 Flow Measurement with a Weir Problem Statement The Iowa DNR plans to monitor a proposed prairie restoration project in eastern Iowa as an experiment.
2nd International Workshop. Labyrinth and Piano Key Weirs Paris - Chatou, France November 2013
 2nd International Workshop on Labyrinth and Piano Key Weirs Paris - Chatou, France 20-22 November 2013 Improvement of the form of labyrinth weirs Ahmed OUAMANE François LEMPERIERE Laboratory of hydraulic
2nd International Workshop on Labyrinth and Piano Key Weirs Paris - Chatou, France 20-22 November 2013 Improvement of the form of labyrinth weirs Ahmed OUAMANE François LEMPERIERE Laboratory of hydraulic
THREE DIMENSIONAL SLOPE STABILITY
 THREE DIMENSIONAL SLOPE STABILITY Timothy D. Stark, Ph.D, PE Associate Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 205 N. Mathews Ave. Urbana, IL 61801 (217)
THREE DIMENSIONAL SLOPE STABILITY Timothy D. Stark, Ph.D, PE Associate Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 205 N. Mathews Ave. Urbana, IL 61801 (217)
RESPONSE OF ANCHOR IN TWO-PHASE MATERIAL UNDER UPLIFT
 IGC 29, Guntur, INDIA RESPONSE OF ANCHOR IN TWO-PHASE MATERIAL UNDER UPLIFT K. Ilamparuthi Professor and Head, Division of Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Anna University, Chennai 25, India.
IGC 29, Guntur, INDIA RESPONSE OF ANCHOR IN TWO-PHASE MATERIAL UNDER UPLIFT K. Ilamparuthi Professor and Head, Division of Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Anna University, Chennai 25, India.
INFLUENCE OF SOLAR RADIATION AND VENTILATION CONDITIONS ON HEAT BALANCE AND THERMAL COMFORT CONDITIONS IN LIVING-ROOMS
 INFLUENCE OF SOLAR RADIATION AND VENTILATION CONDITIONS ON HEAT BALANCE AND THERMAL COMFORT CONDITIONS IN LIVING-ROOMS Staņislavs GENDELIS, Andris JAKOVIČS Laboratory for mathematical modelling of environmental
INFLUENCE OF SOLAR RADIATION AND VENTILATION CONDITIONS ON HEAT BALANCE AND THERMAL COMFORT CONDITIONS IN LIVING-ROOMS Staņislavs GENDELIS, Andris JAKOVIČS Laboratory for mathematical modelling of environmental
Performance of Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger under Varied Operating Conditions
 Performance of Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger under Varied Operating Conditions N. Prabhu Kishore 1, N. Alekhya 2, J. Ugandhar 3 Asst. Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, MLR Institute of Technology,
Performance of Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger under Varied Operating Conditions N. Prabhu Kishore 1, N. Alekhya 2, J. Ugandhar 3 Asst. Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, MLR Institute of Technology,
Stability of Inclined Strip Anchors in Purely Cohesive Soil
 Stability of Inclined Strip Anchors in Purely Cohesive Soil R. S. Merifield 1 ; A. V. Lyamin 2 ; and S. W. Sloan 3 Abstract: Soil anchors are commonly used as foundation systems for structures requiring
Stability of Inclined Strip Anchors in Purely Cohesive Soil R. S. Merifield 1 ; A. V. Lyamin 2 ; and S. W. Sloan 3 Abstract: Soil anchors are commonly used as foundation systems for structures requiring
Heat Transfer Enhancement using Herringbone wavy & Smooth Wavy fin Heat Exchanger for Hydraulic Oil Cooling
 Enhancement using Herringbone wavy & Smooth Wavy fin Exchanger for Hydraulic Oil Cooling 1 Mr. Ketan C. Prasadi, 2 Prof. A.M. Patil 1 M.E. Student, P.V.P.I.T.,Budhagaon,Sangli AP-India 2 Associate Professor,
Enhancement using Herringbone wavy & Smooth Wavy fin Exchanger for Hydraulic Oil Cooling 1 Mr. Ketan C. Prasadi, 2 Prof. A.M. Patil 1 M.E. Student, P.V.P.I.T.,Budhagaon,Sangli AP-India 2 Associate Professor,
Numerical Analysis of the Bearing Capacity of Strip Footing Adjacent to Slope
 International Journal of Science and Engineering Investigations vol. 4, issue 46, November 25 ISSN: 225-8843 Numerical Analysis of the Bearing Capacity of Strip Footing Adjacent to Slope Mohammadreza Hamzehpour
International Journal of Science and Engineering Investigations vol. 4, issue 46, November 25 ISSN: 225-8843 Numerical Analysis of the Bearing Capacity of Strip Footing Adjacent to Slope Mohammadreza Hamzehpour
Numerical Analysis of Leakage through Geomembrane Lining Systems for Dams
 The First Pan American Geosynthetics Conference & Exhibition 25 March 2008, Cancun, Mexico Numerical Analysis of Leakage through Geomembrane Lining Systems for Dams C.T. Weber, University of Texas at Austin,
The First Pan American Geosynthetics Conference & Exhibition 25 March 2008, Cancun, Mexico Numerical Analysis of Leakage through Geomembrane Lining Systems for Dams C.T. Weber, University of Texas at Austin,
Modeling and Simulation of Axial Fan Using CFD Hemant Kumawat
 Modeling and Simulation of Axial Fan Using CFD Hemant Kumawat Abstract Axial flow fans, while incapable of developing high pressures, they are well suitable for handling large volumes of air at relatively
Modeling and Simulation of Axial Fan Using CFD Hemant Kumawat Abstract Axial flow fans, while incapable of developing high pressures, they are well suitable for handling large volumes of air at relatively
Analysis of Pullout Resistance of Soil-Nailing in Lateritic Soil
 Analysis of Pullout Resistance of Soil-Nailing in Lateritic Soil B,L.A. Isaka 1, B.C. Madushanka 1 and N.H. Priyankara 1 1 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Faculty of Engineering University
Analysis of Pullout Resistance of Soil-Nailing in Lateritic Soil B,L.A. Isaka 1, B.C. Madushanka 1 and N.H. Priyankara 1 1 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Faculty of Engineering University
3D-Evaluation Method for Descaling Capability of Hot Strip Mill
 82 China Steel Technical Report, No. 24, 3D-Evaluation pp. 83-87, (2011) Method for Descaling Capability of Hot Strip Mill 3D-Evaluation Method for Descaling Capability of Hot Strip Mill CHUN-CHAO SHIH*,
82 China Steel Technical Report, No. 24, 3D-Evaluation pp. 83-87, (2011) Method for Descaling Capability of Hot Strip Mill 3D-Evaluation Method for Descaling Capability of Hot Strip Mill CHUN-CHAO SHIH*,
Effect of Placement of Footing on Stability of Slope
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF) : 3.134 ISSN (Print) : 2348-6406 ISSN (Online): 2348-4470 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Effect of Placement of Footing
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF) : 3.134 ISSN (Print) : 2348-6406 ISSN (Online): 2348-4470 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Effect of Placement of Footing
Simulation Of Pneumatic Drying: Influence Of Particle Diameter And Solid Loading Ratio
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol.4, No.4, pp 1633-1641, Oct-Dec 2012 Simulation Of Pneumatic Drying: Influence Of Particle Diameter And Solid Loading
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol.4, No.4, pp 1633-1641, Oct-Dec 2012 Simulation Of Pneumatic Drying: Influence Of Particle Diameter And Solid Loading
The effect of embedment on a foundation subjected to vertical vibration a field study
 TECHNICAL PAPER Journal of the South African Institution of Civil Engineering ISSN 121-219 Vol 59 No 4, December 217, Pages 26 33, Paper 1377 DR SILIPIUS MBAWALA is a lecturer in the Department of Civil
TECHNICAL PAPER Journal of the South African Institution of Civil Engineering ISSN 121-219 Vol 59 No 4, December 217, Pages 26 33, Paper 1377 DR SILIPIUS MBAWALA is a lecturer in the Department of Civil
Experimental Investigation of Elliptical Tube Bank Cross Flow Heat Exchanger with Inline Arrangement & 45 Angle of Attack
 Experimental Investigation of Elliptical Tube Bank Cross Flow Heat Exchanger with Inline Arrangement & 45 Angle of Attack #1 Digvijay A. Shelar, #2 N.S. Gohel, #3 R. S. Jha #1 Mechanical Engineering Department,
Experimental Investigation of Elliptical Tube Bank Cross Flow Heat Exchanger with Inline Arrangement & 45 Angle of Attack #1 Digvijay A. Shelar, #2 N.S. Gohel, #3 R. S. Jha #1 Mechanical Engineering Department,
CFD Analysis of a 24 Hour Operating Solar Refrigeration Absorption Technology
 IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 11 April 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 CFD Analysis of a 24 Hour Operating Solar Refrigeration Absorption Technology
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 11 April 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 CFD Analysis of a 24 Hour Operating Solar Refrigeration Absorption Technology
POTENTIAL OF NON - AZEOTROPIC REFRIGERANT MIXTURE AS WORKING REFRIGERANT IN HOT WATER HEAT PUMPS. FJ Smit and JP Meyer
 POTENTIAL OF NON - AZEOTROPIC REFRIGERANT MIXTURE AS WORKING REFRIGERANT IN HOT WATER HEAT PUMPS FJ Smit and JP Meyer Research Group for Heating and Cooling Technology, Laboratory for Energy, PO Box 524,
POTENTIAL OF NON - AZEOTROPIC REFRIGERANT MIXTURE AS WORKING REFRIGERANT IN HOT WATER HEAT PUMPS FJ Smit and JP Meyer Research Group for Heating and Cooling Technology, Laboratory for Energy, PO Box 524,
STAFFORD TRACT NORTH OF US90A 1.0 INTRODUCTION 1.1 OBJECTIVE
 1.0 INTRODUCTION 1.1 OBJECTIVE This report, prepared for submittal to TxDOT, analyzes existing and proposed detention facilities draining into the TxDOT US90A storm sewer system. The results of the detailed
1.0 INTRODUCTION 1.1 OBJECTIVE This report, prepared for submittal to TxDOT, analyzes existing and proposed detention facilities draining into the TxDOT US90A storm sewer system. The results of the detailed
Experimental Study of Direct Contact Condensation of Steam on Water Droplets
 , July 1-3, 2015, London, U.K. Experimental Study of Direct Contact Condensation of Steam on Water Droplets Semra GUMRUK, Murat K. AKTAS Abstract Air or water cooled condensers are used to reduce the moisture
, July 1-3, 2015, London, U.K. Experimental Study of Direct Contact Condensation of Steam on Water Droplets Semra GUMRUK, Murat K. AKTAS Abstract Air or water cooled condensers are used to reduce the moisture
Thermal Design of Condenser Using Ecofriendly Refrigerants R404A-R508B for Cascade Refrigeration System
 Thermal Design of Condenser Using Ecofriendly Refrigerants R404A-R508B for Cascade Refrigeration System A D Parekh, and P R Tailor Abstract Because of damaging effect of CFC refrigerants on stratospheric
Thermal Design of Condenser Using Ecofriendly Refrigerants R404A-R508B for Cascade Refrigeration System A D Parekh, and P R Tailor Abstract Because of damaging effect of CFC refrigerants on stratospheric
A DETAILED ANALYSIS OF SLOPE STABILITY USING FINITE ELEMENT METHOD (FEM)
 A DETAILED ANALYSIS OF SLOPE STABILITY USING FINITE ELEMENT METHOD (FEM) S. Halder 1*, M. O. Imam 2 & M. S. Basir 1 1 Department of Civil & Water Resources Engineering, Chittagong University of Engineering
A DETAILED ANALYSIS OF SLOPE STABILITY USING FINITE ELEMENT METHOD (FEM) S. Halder 1*, M. O. Imam 2 & M. S. Basir 1 1 Department of Civil & Water Resources Engineering, Chittagong University of Engineering
PULLOUT CAPACITY OF HORIZONTAL AND INCLINED PLATE ANCHORS IN CLAYEY SOILS
 PULLOUT CAPACITY OF HORIZONTAL AND INCLINED PLATE ANCHORS IN CLAYEY SOILS BALESHWAR SINGH Associate Professor Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Guwahati 78139, India
PULLOUT CAPACITY OF HORIZONTAL AND INCLINED PLATE ANCHORS IN CLAYEY SOILS BALESHWAR SINGH Associate Professor Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Guwahati 78139, India
Finned Heat Sinks for Cooling Outdoor Electronics under Natural Convection
 Finned s for Cooling Outdoor Electronics under Natural Convection Lian-Tuu Yeh, Ph D & PE Thermal Consultant, Dallas, TX, 75252 USA Abstract For tower or poled mounted electronics, the heat sink weight
Finned s for Cooling Outdoor Electronics under Natural Convection Lian-Tuu Yeh, Ph D & PE Thermal Consultant, Dallas, TX, 75252 USA Abstract For tower or poled mounted electronics, the heat sink weight
Modeling of Ceiling Fan Based on Velocity Measurement for CFD Simulation of Airflow in Large Room
 Modeling of Ceiling Fan Based on Velocity Measurement for CFD Simulation of Airflow in Large Room Y. Momoi 1, K. Sagara 1, T. Yamanaka 1 and H. Kotani 1 1 Osaka University, Graduate School of Eng., Dept.
Modeling of Ceiling Fan Based on Velocity Measurement for CFD Simulation of Airflow in Large Room Y. Momoi 1, K. Sagara 1, T. Yamanaka 1 and H. Kotani 1 1 Osaka University, Graduate School of Eng., Dept.
Design And Analysis Of Centrifugal Pump
 Design And Analysis Of Centrifugal Pump GUIDED BY: Assistant Professor Jayendra B. Patel PRESENTED BY: Makwana Hardik Modh Hiren Patel Gaurang Patel Dhaval 1 Introduction It Convert the mechanical energy
Design And Analysis Of Centrifugal Pump GUIDED BY: Assistant Professor Jayendra B. Patel PRESENTED BY: Makwana Hardik Modh Hiren Patel Gaurang Patel Dhaval 1 Introduction It Convert the mechanical energy
Chih Ted Yang. Education. Professional Experiences
 Chih Ted Yang Engineering Research Center, A207 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Colorado State University Fort Collins, Colorado 80523-1372 Office Phone (970) 491-8160, Fax (970) 491-8032
Chih Ted Yang Engineering Research Center, A207 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Colorado State University Fort Collins, Colorado 80523-1372 Office Phone (970) 491-8160, Fax (970) 491-8032
Chapter 4 - Preparation of Stormwater Site Plans
 Chapter 4 - Preparation of Stormwater Site Plans The Stormwater Site Plan is the comprehensive report containing all of the technical information and analysis necessary for the City to evaluate a proposed
Chapter 4 - Preparation of Stormwater Site Plans The Stormwater Site Plan is the comprehensive report containing all of the technical information and analysis necessary for the City to evaluate a proposed
The Performance of Diffuse Ceiling Inlet and other Room Air Distribution Systems Nielsen, Peter Vilhelm; Jakubowska, Ewa
 Aalborg Universitet The Performance of Diffuse Ceiling Inlet and other Room Air Distribution Systems Nielsen, Peter Vilhelm; Jakubowska, Ewa Published in: COLD CLIMATE HVAC 2009 Publication date: 2009
Aalborg Universitet The Performance of Diffuse Ceiling Inlet and other Room Air Distribution Systems Nielsen, Peter Vilhelm; Jakubowska, Ewa Published in: COLD CLIMATE HVAC 2009 Publication date: 2009
Fire Resistance - Implications for regulations and standards of the September 11th terrorist attacks on the world trade centre Tom Lennon, FRS, BRE
 Fire Resistance - Implications for regulations and standards of the September 11th terrorist attacks on the world trade centre Tom Lennon, FRS, BRE Malaysia May 2003 Questions What is fire resistance?
Fire Resistance - Implications for regulations and standards of the September 11th terrorist attacks on the world trade centre Tom Lennon, FRS, BRE Malaysia May 2003 Questions What is fire resistance?
COMPARISON OF SHEAR STRENGTH PARAMETERS OF BLACK COTTON SOIL WITH EFFECT OF RELATIVE COMPACTION
 Vol-2 Issue-4 16 COMPARISON OF SHEAR STRENGTH PARAMETERS OF BLACK COTTON SOIL WITH EFFECT OF RELATIVE COMPACTION Prof. Usha k. Patel Assistant Professor, LDCE Prof. M. G. Vanza Associate Professor, LDCE
Vol-2 Issue-4 16 COMPARISON OF SHEAR STRENGTH PARAMETERS OF BLACK COTTON SOIL WITH EFFECT OF RELATIVE COMPACTION Prof. Usha k. Patel Assistant Professor, LDCE Prof. M. G. Vanza Associate Professor, LDCE
Effect of Flow Distortion in Inlet Duct on the Performance of Centrifugal Blower
 Effect of Flow Distortion in Inlet Duct on the Performance of Centrifugal Blower Kalpesh W. Shirsath 1, S.R. Patil 2, Sumit M. Naik 3 PG Student 1,3, Assistant Professor 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering
Effect of Flow Distortion in Inlet Duct on the Performance of Centrifugal Blower Kalpesh W. Shirsath 1, S.R. Patil 2, Sumit M. Naik 3 PG Student 1,3, Assistant Professor 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering
Effect of characteristics of unsaturated soils on the stability of slopes subject to rainfall
 Japanese Geotechnical Society Special Publication The 15th Asian Regional Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering Effect of characteristics of unsaturated soils on the stability of slopes
Japanese Geotechnical Society Special Publication The 15th Asian Regional Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering Effect of characteristics of unsaturated soils on the stability of slopes
Optimized Finned Heat Sinks for Natural Convection Cooling of Outdoor Electronics
 Journal of Electronics and Information Science (2018) 3: 22-33 Clausius Scientific Press, Canada Optimized Finned Heat Sinks for Natural Convection Cooling of Outdoor Electronics Lian-Tuu Yeh, ASME Fellow
Journal of Electronics and Information Science (2018) 3: 22-33 Clausius Scientific Press, Canada Optimized Finned Heat Sinks for Natural Convection Cooling of Outdoor Electronics Lian-Tuu Yeh, ASME Fellow
Thermal Analysis of Concentric Tube Heat Exchanger Using Louvered Strip Inserts
 Thermal Analysis of Concentric Tube Heat Exchanger Using Louvered Strip Inserts Anoop P S 1, N. Sreenivasalu Reddy 2 1 PG scholar, Raja Rajarajeswari College of Engineering, Bangalore-560074, Karnataka,
Thermal Analysis of Concentric Tube Heat Exchanger Using Louvered Strip Inserts Anoop P S 1, N. Sreenivasalu Reddy 2 1 PG scholar, Raja Rajarajeswari College of Engineering, Bangalore-560074, Karnataka,
HEFAT th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics Sun City, South Africa Paper number:pp1
 HEFAT27 5 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics Sun City, South Africa Paper number:pp PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF AIR-COOLED CONDENSER USING MICRO-FIN TUBES P.A.Patil
HEFAT27 5 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics Sun City, South Africa Paper number:pp PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF AIR-COOLED CONDENSER USING MICRO-FIN TUBES P.A.Patil
MEMORANDUM. September 10, 2018
 September 10, 2018 MEMORANDUM TO: Chad Bird, City of Decorah FROM: Larry Weber and Dan Gilles, Iowa Flood Center, IIHR Hydroscience & Engineering COPY TO: Dana Werner, St. Paul District Corps of Engineers,
September 10, 2018 MEMORANDUM TO: Chad Bird, City of Decorah FROM: Larry Weber and Dan Gilles, Iowa Flood Center, IIHR Hydroscience & Engineering COPY TO: Dana Werner, St. Paul District Corps of Engineers,
Low Gradient Velocity Control Short Term Steep Gradient [1] Channel Lining Medium-Long Term Outlet Control Soil Treatment Permanent
![Low Gradient Velocity Control Short Term Steep Gradient [1] Channel Lining Medium-Long Term Outlet Control Soil Treatment Permanent Low Gradient Velocity Control Short Term Steep Gradient [1] Channel Lining Medium-Long Term Outlet Control Soil Treatment Permanent](/thumbs/77/74849271.jpg) Grass Linings DRAINAGE CONTROL TECHNIQUE Low Gradient Velocity Control Short Term Steep Gradient [1] Channel Lining Medium-Long Term Outlet Control Soil Treatment Permanent [1] May be used on short, steep
Grass Linings DRAINAGE CONTROL TECHNIQUE Low Gradient Velocity Control Short Term Steep Gradient [1] Channel Lining Medium-Long Term Outlet Control Soil Treatment Permanent [1] May be used on short, steep
Analysis of Triangle Heating Technique using High Frequency Induction Heating in Forming Process of Steel Plate
 Analysis of Triangle Heating Technique using High Frequency Induction Heating in Forming Process of Steel Plate KEYWORDS: Steel-plate forming, Induction heating, Triangle heating, Transverse shrinkage,
Analysis of Triangle Heating Technique using High Frequency Induction Heating in Forming Process of Steel Plate KEYWORDS: Steel-plate forming, Induction heating, Triangle heating, Transverse shrinkage,
EFFECT OF RELICT JOINTS IN RAIN INDUCED SLOPE FAILURES IN RESIDUAL SOIL
 EFFECT OF RELICT JOINTS IN RAIN INDUCED SLOPE FAILURES IN RESIDUAL SOIL Neethimappiriya Tharmalingam, Student (Email: neethi_26@yahoo.com) N.W.H. Lakshamana, Student (Email: hansaka8888@yahoo.com) R.D.T.B.
EFFECT OF RELICT JOINTS IN RAIN INDUCED SLOPE FAILURES IN RESIDUAL SOIL Neethimappiriya Tharmalingam, Student (Email: neethi_26@yahoo.com) N.W.H. Lakshamana, Student (Email: hansaka8888@yahoo.com) R.D.T.B.
Prediction of Soil Infiltration Rate Based on Sand Content of Soil
 Agricultural Engineering Research Journal 3 (): 0-4, 013 ISSN 18-3906 IDOSI Publications, 013 DOI: 10.589/idosi.aerj.013.3..1109 Prediction of Soil Infiltration Rate Based on Sand Content of Soil 1 1 Majid
Agricultural Engineering Research Journal 3 (): 0-4, 013 ISSN 18-3906 IDOSI Publications, 013 DOI: 10.589/idosi.aerj.013.3..1109 Prediction of Soil Infiltration Rate Based on Sand Content of Soil 1 1 Majid
MANUAL OF DESIGN, INSTALLATION, AND MAINTENANCE REQUIREMENTS FOR STORMWATER MANAGEMENT PLANS
 MANUAL OF DESIGN, INSTALLATION, AND MAINTENANCE REQUIREMENTS FOR STORMWATER MANAGEMENT PLANS May 2007 SECTION 1 Responsibility of Applicant TABLE OF CONTENTS A. Stormwater Management Plan Required Information
MANUAL OF DESIGN, INSTALLATION, AND MAINTENANCE REQUIREMENTS FOR STORMWATER MANAGEMENT PLANS May 2007 SECTION 1 Responsibility of Applicant TABLE OF CONTENTS A. Stormwater Management Plan Required Information
THE ROLE OF SUCTION IN THE PERFORMANCE OF CLAY FILL RONALD F. REED, P.E. 1 KUNDAN K. PANDEY, P.E. 2
 THE ROLE OF SUCTION IN THE PERFORMANCE OF CLAY FILL RONALD F. REED, P.E. 1 KUNDAN K. PANDEY, P.E. 2 Abstract Plastic clay is commonly used as fill. Proper placement is the key to the performance of the
THE ROLE OF SUCTION IN THE PERFORMANCE OF CLAY FILL RONALD F. REED, P.E. 1 KUNDAN K. PANDEY, P.E. 2 Abstract Plastic clay is commonly used as fill. Proper placement is the key to the performance of the
Study on the Effect of Blade Angle on the Performance of a Small Cooling Tower
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 42 : 378-384 (2008) Study on the Effect of Blade Angle on the Performance of a Small Cooling Tower Montri Pirunkaset* and Santi Laksitanonta ABSTRACT This paper presents the effect
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 42 : 378-384 (2008) Study on the Effect of Blade Angle on the Performance of a Small Cooling Tower Montri Pirunkaset* and Santi Laksitanonta ABSTRACT This paper presents the effect
EFFECT OF DIVERSE STREAM PATTERNS ON THE PERFORMANCE OF SOLAR AIR HEATER
 Int. J. Mech. Eng. & Rob. Res. 2013 P Velmurugan and R Kalaivanan, 2013 Research Paper ISSN 2278 0149 www.ijmerr.com Vol. 2, No. 1, January 2013 2013 IJMERR. All Rights Reserved EFFECT OF DIVERSE STREAM
Int. J. Mech. Eng. & Rob. Res. 2013 P Velmurugan and R Kalaivanan, 2013 Research Paper ISSN 2278 0149 www.ijmerr.com Vol. 2, No. 1, January 2013 2013 IJMERR. All Rights Reserved EFFECT OF DIVERSE STREAM
Effect of Foundation Embedment of PWR Structures in SSI Analysis considering Spatial Incoherence of Ground Motions
 The th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering October -7,, Beijing, China Effect of Foundation Embedment of PWR Structures in SSI Analysis considering Spatial of Ground Motions Joo-Hyung Kang and Sang-Hoon
The th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering October -7,, Beijing, China Effect of Foundation Embedment of PWR Structures in SSI Analysis considering Spatial of Ground Motions Joo-Hyung Kang and Sang-Hoon
FIRE RESISTANCE LEVEL ASSESSMENTS AND DEVELOPMENT OF APPROPRIATE INPUT DATA
 FIRE RESISTANCE LEVEL ASSESSMENTS AND DEVELOPMENT OF APPROPRIATE INPUT DATA Andrew Barnett Fire Safety Engineer Scientific Fire Services Pty Ltd INTRODUCTION Co-authors: Mahmut Horasan, Scientific Fire
FIRE RESISTANCE LEVEL ASSESSMENTS AND DEVELOPMENT OF APPROPRIATE INPUT DATA Andrew Barnett Fire Safety Engineer Scientific Fire Services Pty Ltd INTRODUCTION Co-authors: Mahmut Horasan, Scientific Fire
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fire Modelling
 Advantages and Disadvantages of Fire Modelling Dr Guillermo Rein School of Engineering University of Edinburgh & Imperial College London Dr Guillermo Rein 9 May 2012 Chief Fire Officers Association Annual
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fire Modelling Dr Guillermo Rein School of Engineering University of Edinburgh & Imperial College London Dr Guillermo Rein 9 May 2012 Chief Fire Officers Association Annual
Heat transfer and heating rate of food stuffs in commercial shop ovens
 Sādhanā Vol. 32, Part 5, October 2007, pp. 535 544. Printed in India Heat transfer and heating rate of food stuffs in commercial shop ovens P NAVANEETHAKRISHNAN,PSSSRINIVASAN and S DHANDAPANI Department
Sādhanā Vol. 32, Part 5, October 2007, pp. 535 544. Printed in India Heat transfer and heating rate of food stuffs in commercial shop ovens P NAVANEETHAKRISHNAN,PSSSRINIVASAN and S DHANDAPANI Department
Engineering Simulation in Built Environment and Civil Engineering Projects
 Engineering Simulation in Built Environment and Civil Engineering Projects Fluid Dynamics Simulation Mark Owens ANSYS UK Ltd 2010 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary Fires and Smoke
Engineering Simulation in Built Environment and Civil Engineering Projects Fluid Dynamics Simulation Mark Owens ANSYS UK Ltd 2010 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary Fires and Smoke
CENTRIFUGAL PUMPS. STATE the purposes of the following centrifugal pump components:
 Pumps DOE-HDBK-1018/1-93 CENTRIFUGAL PUMPS CENTRIFUGAL PUMPS Centrifugal pumps are the most common type of pumps found in DOE facilities. Centrifugal pumps enjoy widespread application partly due to their
Pumps DOE-HDBK-1018/1-93 CENTRIFUGAL PUMPS CENTRIFUGAL PUMPS Centrifugal pumps are the most common type of pumps found in DOE facilities. Centrifugal pumps enjoy widespread application partly due to their
Pollutant Removal Benefits
 Bioswales Bioswales Similar to biocells, but have a slight, but positive grade toward an outlet Designed to convey the WQv event at very low velocities Promote filtration through native vegetation, infiltration
Bioswales Bioswales Similar to biocells, but have a slight, but positive grade toward an outlet Designed to convey the WQv event at very low velocities Promote filtration through native vegetation, infiltration
2. HEAT EXCHANGERS MESA
 1. INTRODUCTION Multiport minichannel and microchannel aluminium tubes are becoming more popular as components in heat exchangers. These heat exchangers are used in various industrial applications and
1. INTRODUCTION Multiport minichannel and microchannel aluminium tubes are becoming more popular as components in heat exchangers. These heat exchangers are used in various industrial applications and
EFFECT OF COMPACTION ON THE UNSATURATED SHEAR STRENGTH OF A COMPACTED TILL
 EFFECT OF COMPACTION ON THE UNSATURATED SHEAR STRENGTH OF A COMPACTED TILL Vanapalli, S.K., Pufahl, D.E., and Fredlund, D.G. (University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK., Canada, S7N 5A9) Abstract An experimental
EFFECT OF COMPACTION ON THE UNSATURATED SHEAR STRENGTH OF A COMPACTED TILL Vanapalli, S.K., Pufahl, D.E., and Fredlund, D.G. (University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK., Canada, S7N 5A9) Abstract An experimental
ENGG*4360 Soil-Water Conservation Systems Design. Course Description & Outlines - Fall 2010
 Calendar Description School of Engineering University of Guelph ENGG*4360 Soil-Water Conservation Systems Design Course Description & Outlines - Fall 2010 Properties of soil and land use governing the
Calendar Description School of Engineering University of Guelph ENGG*4360 Soil-Water Conservation Systems Design Course Description & Outlines - Fall 2010 Properties of soil and land use governing the
Manhardt Lindel / ERHARD-Armaturen VALVE & PIPELINE CAVITATION
 Manhardt Lindel / ERHARD-Armaturen VALVE & PIPELINE CAVITATION What is cavitation? Cavitation is a physical process, which can arise in liquids. It describes the phase transition between the liquid and
Manhardt Lindel / ERHARD-Armaturen VALVE & PIPELINE CAVITATION What is cavitation? Cavitation is a physical process, which can arise in liquids. It describes the phase transition between the liquid and
Hydraulic analysis marks start of rebuilding after bridge collapse
 Hydraulic analysis marks start of rebuilding after bridge collapse By Tawny Quast The remains of the I-35W Bridge shortly after the collapse. On August 1, 2007, the I-35W bridge over the Mississippi River
Hydraulic analysis marks start of rebuilding after bridge collapse By Tawny Quast The remains of the I-35W Bridge shortly after the collapse. On August 1, 2007, the I-35W bridge over the Mississippi River
Experimental study on heat transfer characteristics of horizontal concentric tube using twisted wire brush inserts
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 416, P-ISSN 2347 5161 216 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Experimental
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 416, P-ISSN 2347 5161 216 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Experimental
Using FDS Modelling to Establish Performance Criteria for Water Mist Systems on Very Large Fires in Tunnels
 Using FDS Modelling to Establish Performance Criteria for Water Mist Systems on Very Large Fires in Tunnels Jack R. Mawhinney, P. Eng., FSFPE Javier J. Trelles, Ph.D. Authors & acknowledgement J. R. Mawhinney
Using FDS Modelling to Establish Performance Criteria for Water Mist Systems on Very Large Fires in Tunnels Jack R. Mawhinney, P. Eng., FSFPE Javier J. Trelles, Ph.D. Authors & acknowledgement J. R. Mawhinney
Load-Carrying Capacity of Stone Column Encased with Geotextile. Anil Kumar Sahu 1 and Ishan Shankar 2
 Load-Carrying Capacity of Stone Column Encased with Geotextile Anil Kumar Sahu 1 and Ishan Shankar 2 1 Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Delhi Technological University, Delhi, India (sahuanilkr@yahoo.co.in)
Load-Carrying Capacity of Stone Column Encased with Geotextile Anil Kumar Sahu 1 and Ishan Shankar 2 1 Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Delhi Technological University, Delhi, India (sahuanilkr@yahoo.co.in)
Developing a Fire Test Strategy for Storage Protection Under Sloped Ceilings
 Developing a Fire Test Strategy for Storage Protection Under Sloped Ceilings Justin A. Geiman, Noah L. Ryder Fire & Risk Alliance, Rockville, MD, USA André W. Marshall Custom Spray Solutions, Silver Spring,
Developing a Fire Test Strategy for Storage Protection Under Sloped Ceilings Justin A. Geiman, Noah L. Ryder Fire & Risk Alliance, Rockville, MD, USA André W. Marshall Custom Spray Solutions, Silver Spring,
Study of Hot-air Recirculation around Off-road Tier-4 Diesel Engine Unit Using CFD Abbreviations Keywords Abstract Introduction and Background
 Study of Hot-air Recirculation around Off-road Tier-4 Diesel Engine Unit Using CFD Siddharth Jain, Yogesh Deshpande, Atul Bokane, Arun Kumar Santharam, and Deepak Babar, Halliburton Abbreviations: Computational
Study of Hot-air Recirculation around Off-road Tier-4 Diesel Engine Unit Using CFD Siddharth Jain, Yogesh Deshpande, Atul Bokane, Arun Kumar Santharam, and Deepak Babar, Halliburton Abbreviations: Computational
DRAFT ONONDAGA LAKE CAPPING AND DREDGE AREA AND DEPTH INITIAL DESIGN SUBMITTAL H.3 STATIC SLOPE STABILITY ANALYSES
 DRAFT ONONDAGA LAKE CAPPING AND DREDGE AREA AND DEPTH INITIAL DESIGN SUBMITTAL H.3 STATIC SLOPE STABILITY ANALYSES Parsons P:\Honeywell -SYR\444576 2008 Capping\09 Reports\9.3 December 2009_Capping and
DRAFT ONONDAGA LAKE CAPPING AND DREDGE AREA AND DEPTH INITIAL DESIGN SUBMITTAL H.3 STATIC SLOPE STABILITY ANALYSES Parsons P:\Honeywell -SYR\444576 2008 Capping\09 Reports\9.3 December 2009_Capping and
Thermal Performance Enhancement of Inclined Rib Roughness Solar Air Heater
 Thermal Performance Enhancement of Inclined Rib Roughness Solar Air Heater Gurpreet Singh and Satwant Singh Lala Lajpat Rai Institute of Engineering and Technology, Moga (Punjab) 142001 Abstract : Artificial
Thermal Performance Enhancement of Inclined Rib Roughness Solar Air Heater Gurpreet Singh and Satwant Singh Lala Lajpat Rai Institute of Engineering and Technology, Moga (Punjab) 142001 Abstract : Artificial
American International Journal of Research in Science, Technology, Engineering & Mathematics
 American International Journal of Research in Science, Technology, Engineering & Mathematics Available online at http://www.iasir.net ISSN (Print): 2328-3491, ISSN (Online): 2328-358, ISSN (CD-ROM): 2328-3629
American International Journal of Research in Science, Technology, Engineering & Mathematics Available online at http://www.iasir.net ISSN (Print): 2328-3491, ISSN (Online): 2328-358, ISSN (CD-ROM): 2328-3629
Identification of key parameters on Soil Water Characteristic Curve
 Identification of key parameters on Soil Water Characteristic Curve A.A. Heshmati 1, M.R. Motahari 2,* 1, 2 School of Civil Engineering, Iran University of Science and Technology P.O. Box 16765-163, Narmak,
Identification of key parameters on Soil Water Characteristic Curve A.A. Heshmati 1, M.R. Motahari 2,* 1, 2 School of Civil Engineering, Iran University of Science and Technology P.O. Box 16765-163, Narmak,
Transition of soil strength during suction pile retrieval
 Maritime Heritage and Modern Ports 415 Transition of soil strength during suction pile retrieval S. Bang 1, Y. Cho 2 & K. Jones 1 1 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, South Dakota School
Maritime Heritage and Modern Ports 415 Transition of soil strength during suction pile retrieval S. Bang 1, Y. Cho 2 & K. Jones 1 1 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, South Dakota School
Estimation of Spray Lubrication and Die Temperature for Die Wear Life Prediction in Hot Forging
 0 Research Report Estimation of Spray Lubrication and Die Temperature for Die Wear Life Prediction in Hot Forging Masatoshi Sawamura, Yasuhiro Yogo, Sayuri Kondo, Toshiaki Tanaka, Koukichi Nakanishi, Toshiyuki
0 Research Report Estimation of Spray Lubrication and Die Temperature for Die Wear Life Prediction in Hot Forging Masatoshi Sawamura, Yasuhiro Yogo, Sayuri Kondo, Toshiaki Tanaka, Koukichi Nakanishi, Toshiyuki
EFFECTS OF VARIABLES ON NATURAL CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER THROUGH V-CORRUGATED VERTICAL PLATES
 International Journal of Mechanical and Materials Engineering (IJMME), Vol. 2 (2007), No. 2, 109--117. EFFECTS OF VARIABLES ON NATURAL CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER THROUGH V-CORRUGATED VERTICAL PLATES M. Hasanuzzaman
International Journal of Mechanical and Materials Engineering (IJMME), Vol. 2 (2007), No. 2, 109--117. EFFECTS OF VARIABLES ON NATURAL CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER THROUGH V-CORRUGATED VERTICAL PLATES M. Hasanuzzaman
CHAPTER 8 SLOPE STABILITY ANALYSIS
 TM 5-818-1 / AFM 88-3. Chap. 7 CHAPTER 8 SLOPE STABILITY ANALYSIS 8-1. General. This chapter is concerned with characteristics and critical aspects of the stability of excavation slopes; methods of designing
TM 5-818-1 / AFM 88-3. Chap. 7 CHAPTER 8 SLOPE STABILITY ANALYSIS 8-1. General. This chapter is concerned with characteristics and critical aspects of the stability of excavation slopes; methods of designing
GAS DETECTOR LOCATION. Ø.Strøm and J.R. Bakke, GexCon AS, Norway
 AUTHOR BIOGRAPHICAL NOTES GAS DETECTOR LOCATION Ø.Strøm and J.R. Bakke, GexCon AS, Norway Øyvind Strøm graduated in 1996 from Stavanger University College with a M.Sc. degree in Offshore Safety Technology.
AUTHOR BIOGRAPHICAL NOTES GAS DETECTOR LOCATION Ø.Strøm and J.R. Bakke, GexCon AS, Norway Øyvind Strøm graduated in 1996 from Stavanger University College with a M.Sc. degree in Offshore Safety Technology.
CFD-AIDED TENABILITY ASSESSMENT OF RAILWAY TUNNEL TRAIN FIRE SCENARIOS
 CFD-AIDED TENABILITY ASSESSMENT OF RAILWAY TUNNEL TRAIN FIRE SCENARIOS Yunlong Liu*, Xijuan Liu and Bradley Paroz Fire Science and Technology Laboratory CSIRO Manufacturing and Infrastructure Technology
CFD-AIDED TENABILITY ASSESSMENT OF RAILWAY TUNNEL TRAIN FIRE SCENARIOS Yunlong Liu*, Xijuan Liu and Bradley Paroz Fire Science and Technology Laboratory CSIRO Manufacturing and Infrastructure Technology
FROSTING BEHAVIOR OF FIN-TUBE HEAT EXCHANGER ACCORDING TO REFRIGERANT FLOW TYPE
 HEFAT2012 9 th International nference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 16 18 July 2012 Malta FROSTING BEHAVIOR OF FIN-TUBE HEAT EXCHANGER ACCORDING TO REFRIGERANT FLOW TYPE Kim K.,
HEFAT2012 9 th International nference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 16 18 July 2012 Malta FROSTING BEHAVIOR OF FIN-TUBE HEAT EXCHANGER ACCORDING TO REFRIGERANT FLOW TYPE Kim K.,
INDOOR CLIMATE IN HEATING CONDITION OF A LARGE GYMNASIUM WITH UNDER-FLOOR SUPPLY/RETURN SYSTEM
 INDOOR CLIMATE IN HEATING CONDITION OF A LARGE GYMNASIUM WITH UNDER-FLOOR SUPPLY/RETURN SYSTEM Mingjie Zheng Research Laboratory, SANKO AIR CONDITIONING CO., LTD. Nagoya, 450-0003, JAPAN ABSTRACT In large
INDOOR CLIMATE IN HEATING CONDITION OF A LARGE GYMNASIUM WITH UNDER-FLOOR SUPPLY/RETURN SYSTEM Mingjie Zheng Research Laboratory, SANKO AIR CONDITIONING CO., LTD. Nagoya, 450-0003, JAPAN ABSTRACT In large
Recent BRANZFIRE enhancements and validation
 Recent BRANZFIRE enhancements and validation Michael Spearpoint University of Canterbury Summary BRANZFIRE is a multi-compartment fire zone model that has been under development since 1996 predominately
Recent BRANZFIRE enhancements and validation Michael Spearpoint University of Canterbury Summary BRANZFIRE is a multi-compartment fire zone model that has been under development since 1996 predominately
Experimental Comparison of Natural Convection Heat Transfer from a Blackened V-Fin Array
 International Journal of Modern Studies in Mechanical Engineering (IJMSME) Volume 4, Issue 1, 2018, PP 11-16 ISSN 2454-9711 (Online) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2454-9711.0401002 www.arcjournals.org
International Journal of Modern Studies in Mechanical Engineering (IJMSME) Volume 4, Issue 1, 2018, PP 11-16 ISSN 2454-9711 (Online) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2454-9711.0401002 www.arcjournals.org
Optimized fan system design for the one-year cycle of a Heat Pump. Ziehl-Abegg SE Frieder Lörcher
 Optimized fan system design for the one-year cycle of a Heat Pump Ziehl-Abegg SE Frieder Lörcher Outline Targets for the energetical optimization of fan unit Numerical optimization procedure Results with
Optimized fan system design for the one-year cycle of a Heat Pump Ziehl-Abegg SE Frieder Lörcher Outline Targets for the energetical optimization of fan unit Numerical optimization procedure Results with
Real Time Pipeline Leak Detection on Shell s North Western Ethylene Pipeline
 Real Time Pipeline Leak Detection on Shell s North Western Ethylene Pipeline Dr Jun Zhang & Dr Ling Xu* REL Instrumentation Limited ABSTRACT In the past ten years, a number of pipeline leak detection systems
Real Time Pipeline Leak Detection on Shell s North Western Ethylene Pipeline Dr Jun Zhang & Dr Ling Xu* REL Instrumentation Limited ABSTRACT In the past ten years, a number of pipeline leak detection systems
Effects of Non-Uniform Refrigerant and Air Flow Distributions on Finned- Tube Evaporator Performance
 Effects of Non-Uniform Refrigerant and Air Flow Distributions on Finned- Tube Evaporator Performance Jong Min Choi, W. Vance Payne and Piotr A. Domanski National Institute of Standards and Technology Building
Effects of Non-Uniform Refrigerant and Air Flow Distributions on Finned- Tube Evaporator Performance Jong Min Choi, W. Vance Payne and Piotr A. Domanski National Institute of Standards and Technology Building
Design and Development of Water Cooled Condenser for Domestic Refrigerator
 Design and Development of Water Cooled Condenser for Domestic Refrigerator Anil S. Patil Research PG Student, GF s Godavari College of Engineering, Jalgaon Dr. Atul A Patil Assot. Prof. GF s Godavari College
Design and Development of Water Cooled Condenser for Domestic Refrigerator Anil S. Patil Research PG Student, GF s Godavari College of Engineering, Jalgaon Dr. Atul A Patil Assot. Prof. GF s Godavari College
Evaluating Low Impact Development Practices for Stormwater Management on an Industrial Site in Mississippi
 Evaluating Low Impact Development Practices for Stormwater Management on an Industrial Site in Mississippi Dennis S. Painter, Tennessee Valley Authority, Nashville, Tennessee Donald Becker, Tennessee Valley
Evaluating Low Impact Development Practices for Stormwater Management on an Industrial Site in Mississippi Dennis S. Painter, Tennessee Valley Authority, Nashville, Tennessee Donald Becker, Tennessee Valley
Numerical Studies On The Performance Of Methanol Based Air To Air Heat Pipe Heat Exchanger
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA) IJCRGG ISSN 0974-4290 Vol.5, No.2, pp 925-934, April-June 2013 ICGSEE-2013[14th 16th March 2013] International Conference on Global Scenario in Environment
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA) IJCRGG ISSN 0974-4290 Vol.5, No.2, pp 925-934, April-June 2013 ICGSEE-2013[14th 16th March 2013] International Conference on Global Scenario in Environment
Smoke Alarm Response Time:
 Smoke Alarm Response Time: Examining the Relationship Between Working Smoke Alarms, Fire Service Response Times and Fire Outcomes Joseph Clare, Charles Jennings, Len Garis November 2018 Executive Summary
Smoke Alarm Response Time: Examining the Relationship Between Working Smoke Alarms, Fire Service Response Times and Fire Outcomes Joseph Clare, Charles Jennings, Len Garis November 2018 Executive Summary
Numerical Stability Analysis of a Natural Circulation Steam Generator with a Non-uniform Heating Profile over the tube length
 Numerical Stability Analysis of a Natural Circulation Steam Generator with a Non-uniform Heating Profile over the tube length HEIMO WALTER Institute for Thermodynamics and Energy Conversion Vienna University
Numerical Stability Analysis of a Natural Circulation Steam Generator with a Non-uniform Heating Profile over the tube length HEIMO WALTER Institute for Thermodynamics and Energy Conversion Vienna University
Effect of pile sleeve opening and length below seabed on the bearing capacity of offshore jacket mudmats
 NGM 2016 Reykjavik Proceedings of the 17 th Nordic Geotechnical Meeting Challenges in Nordic Geotechnic 25 th 28 th of May Effect of pile sleeve opening and length below seabed on the bearing capacity
NGM 2016 Reykjavik Proceedings of the 17 th Nordic Geotechnical Meeting Challenges in Nordic Geotechnic 25 th 28 th of May Effect of pile sleeve opening and length below seabed on the bearing capacity
Adsorption refrigeration system using waste heat
 Adsorption refrigeration system using waste heat 1 RISHI SREEKUMAR, 2 SANJEEV SINGH, 3 HIMANSHU SHEKHAR, 4 RAUSHAN KUMAR, 5 Dr. R. S. BINDU 1,2,3,4 BE Students, 5 Professor Mechanical Engineering Department
Adsorption refrigeration system using waste heat 1 RISHI SREEKUMAR, 2 SANJEEV SINGH, 3 HIMANSHU SHEKHAR, 4 RAUSHAN KUMAR, 5 Dr. R. S. BINDU 1,2,3,4 BE Students, 5 Professor Mechanical Engineering Department
CHOOSING A FIRE VENTILATION STRATEGY FOR AN UNDERGROUND METRO STATION
 - 165 - CHOOSING A FIRE VENTILATION STRATEGY FOR AN UNDERGROUND METRO STATION Wojciech Węgrzyński, Grzegorz Krajewski, Paweł Sulik Fire Research Department, Building Research Institute (ITB), Poland ABSTRACT
- 165 - CHOOSING A FIRE VENTILATION STRATEGY FOR AN UNDERGROUND METRO STATION Wojciech Węgrzyński, Grzegorz Krajewski, Paweł Sulik Fire Research Department, Building Research Institute (ITB), Poland ABSTRACT
Design Optimization of Variable Geometry Microchannel Heat Exchangers
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2014 Design Optimization of Variable Geometry Microchannel Heat Exchangers Long
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2014 Design Optimization of Variable Geometry Microchannel Heat Exchangers Long
Experimental Investigation of Tube Configuration for a Surface Condenser
 Experimental Investigation of Tube Configuration for a Surface Condenser Shrikant Subhash Chaudhari 1, T Mahender 2, Subramanyam Pavuluri 3 PG Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, MLR Institute
Experimental Investigation of Tube Configuration for a Surface Condenser Shrikant Subhash Chaudhari 1, T Mahender 2, Subramanyam Pavuluri 3 PG Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, MLR Institute
WASHINGTON COUNTY OREGON
 WASHINGTON COUNTY OREGON LONG RANGE PLANNING DIVISION North Bethany Subarea Stream Corridors: Existing Regulations In Oregon, there is a distinct difference between the land use rules that apply in rural
WASHINGTON COUNTY OREGON LONG RANGE PLANNING DIVISION North Bethany Subarea Stream Corridors: Existing Regulations In Oregon, there is a distinct difference between the land use rules that apply in rural
Fire and smoke management in a uni-directional road tunnel for a congested traffic condition
 Fire and smoke management in a uni-directional road tunnel for a congested traffic condition Y Liu, J Munro Parsons Brinckerhoff Australia B Dandie Thiess Pty Ltd., Australia ABSTRACT Emergency smoke ventilation
Fire and smoke management in a uni-directional road tunnel for a congested traffic condition Y Liu, J Munro Parsons Brinckerhoff Australia B Dandie Thiess Pty Ltd., Australia ABSTRACT Emergency smoke ventilation
PRESSURE-ENTHALPY CHARTS AND THEIR USE By: Dr. Ralph C. Downing E.I. du Pont de Nemours & Co., Inc. Freon Products Division
 INTRODUCTION PRESSURE-ENTHALPY CHARTS AND THEIR USE The refrigerant in a refrigeration system, regardless of type, is present in two different states. It is present as liquid and as vapor (or gas). During
INTRODUCTION PRESSURE-ENTHALPY CHARTS AND THEIR USE The refrigerant in a refrigeration system, regardless of type, is present in two different states. It is present as liquid and as vapor (or gas). During
INDOOR HUMAN THERMAL COMFORT OPTIMAL CONTROL WITH DESICCANT WHEEL COOLING SYSTEM
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 61 (2014 ) 882 886 The 6 th International Conference on Applied Energy ICAE2014 INDOOR HUMAN THERMAL COMFORT OPTIMAL CONTROL WITH
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 61 (2014 ) 882 886 The 6 th International Conference on Applied Energy ICAE2014 INDOOR HUMAN THERMAL COMFORT OPTIMAL CONTROL WITH
Andrzej Kesy Kazimierz Pulaski University of Technology and Humanities, Radom, Poland, and
 Fabrication of hydrodynamic torque converter impellers by using the selective laser sintering method Jaroslaw Kotlinski, Marcin Migus and Zbigniew Kesy Technical University of Radom, Radom, Poland Andrzej
Fabrication of hydrodynamic torque converter impellers by using the selective laser sintering method Jaroslaw Kotlinski, Marcin Migus and Zbigniew Kesy Technical University of Radom, Radom, Poland Andrzej
EFFECT OF CENTRAL PILE IN INCREASING THE BEARING CAPACITY OF BORED PILE GROUPS
 EFFECT OF CENTRAL PILE IN INCREASING THE BEARING CAPACITY OF BORED PILE GROUPS Mohamed M. Shahin Department of Civil Engineering, 7 th October University, Misurata,, Libya, E-mail: Mohamed_zubi@yahoo.com
EFFECT OF CENTRAL PILE IN INCREASING THE BEARING CAPACITY OF BORED PILE GROUPS Mohamed M. Shahin Department of Civil Engineering, 7 th October University, Misurata,, Libya, E-mail: Mohamed_zubi@yahoo.com
APPLICATION OF CFD SIMULATIONS FOR LOCATING OUTDOOR UNITS ON HIGH RISE TOWER Basant Kumar Gupta 1, Anand Patil 2
 APPLICATION OF CFD SIMULATIONS FOR LOCATING OUTDOOR UNITS ON HIGH RISE TOWER Basant Kumar Gupta 1, Anand Patil 2 1 Zeus Numerix Private Limited, Pune, India 2 Pankaj Dharkar & Associates, Mumbai, India
APPLICATION OF CFD SIMULATIONS FOR LOCATING OUTDOOR UNITS ON HIGH RISE TOWER Basant Kumar Gupta 1, Anand Patil 2 1 Zeus Numerix Private Limited, Pune, India 2 Pankaj Dharkar & Associates, Mumbai, India
GUIDE FOR SELECTING AN APPROPRIATE METHOD TO ANALYZE THE STABILITY OF SLOPES ON RECLAIMED SURFACE MINES 1
 GUIDE FOR SELECTING AN APPROPRIATE METHOD TO ANALYZE THE STABILITY OF SLOPES ON RECLAIMED SURFACE MINES 1 John J. Bowders, Jr. and Sun Chai Lee 2 Abstract: Geotechnical engineers have long Recognized the
GUIDE FOR SELECTING AN APPROPRIATE METHOD TO ANALYZE THE STABILITY OF SLOPES ON RECLAIMED SURFACE MINES 1 John J. Bowders, Jr. and Sun Chai Lee 2 Abstract: Geotechnical engineers have long Recognized the
Piles subject to excavation-induced soil movement in clay
 Piles subject to -induced soil movement in clay Des foundations soumis au mouvement du sol du a l' dans l'argile D.E.L. Ong, C.F. Leung & Y.K. Chow Centre for Soft Ground Engineering, National University
Piles subject to -induced soil movement in clay Des foundations soumis au mouvement du sol du a l' dans l'argile D.E.L. Ong, C.F. Leung & Y.K. Chow Centre for Soft Ground Engineering, National University
